当前位置:网站首页>C Primer Plus Chapter 15 (bit operation)
C Primer Plus Chapter 15 (bit operation)
2022-07-05 06:15:00 【His Last Bow】
Catalog
1. Binary system 、 Bits and bytes
- With 2 The number represented by the base is called Binary number (binary number)
1 1 0 1
1 * 2^3 + 1 * 2^2 + 0 * 2^1 + 1 * 2^0 = 13
1.1 Binary integer
C Language use byte (byte) Represents the required size of the storage system character set
- 1 byte = 8 position
Yes 1 byte (8 position ) In different ways Bit combination (bit pattern)
unsigned char: 0000 0000 ~ 1111 1111 = 0 ~ 255
signed char : 1000 0000 ~ 0111 1111 = -128 ~ 127
1.2 Signed integers
Sign quantity (sign-magnitude) notation :1 position ** Higher order potential (high-order bit)** Store symbols , be left over 7 Bits represent the number itself
- 1111 1111 ~ 0111 1111 = -127 ~ 127
- There are two 0 :
- 0000 0000 = +0
- 1000 0000 = -0
Binary complement (two’s-complement) Method : Take the opposite , Add 1
- 1111 1111 ~ 0111 1111 = -128 ~ 127
Binary inverse (one’s-complement) Method : Take the opposite
- 1000 0000 ~ 0111 1111 = -127 ~ 127
- There are two 0 :
- 0000 0000 = +0
- 1111 1111 = -0
1.3 Binary floating point numbers
- Floating point numbers are stored in two parts
- Binary decimals
- Binary index
1.3.1 Binary decimals
- With 2 Power of as denominator
1 0 1
1/2 + 0/4 + 1/8 = 0.625
- Many fractions cannot be accurately represented by binary decimals
- It can only accurately represent multiple 1/2 The sum of the powers of
1.3.2 floating-point number
- Several bits store binary fractions , Other bits store index
2. Other hexadecimal numbers
- Octal and hexadecimal numeration systems are usually used
2.1 octal
- octal (octal) It refers to octal numeration system
- With 8 Represent numbers for the base
4 5 1
4 * 8^2 + 5 * 8^1 + 1 * 8^0 = 297
Each octal digit corresponds to 3 Binary bits
Binary equivalent to octal
Octal digit Equivalent binary 0 000 1 001 2 010 3 011 4 100 5 101 6 110 7 111
2.2 Hexadecimal
- Hexadecimal (hexadecimal or hex) It refers to the hexadecimal numeration system
- With 16 Represent numbers for the base
A 3 F
10 * 16^2 + 3 * 16^1 + 15 * 16^0 = 2623
Each hexadecimal digit corresponds to 4 Binary bits
Decimal system 、 Hexadecimal and equivalent binary digits
Decimal system Hexadecimal Equivalent binary 0 0 0000 1 1 0001 2 2 0010 3 3 0011 4 4 0100 5 5 0101 6 6 0110 7 7 0111 8 8 1000 9 9 1001 10 A 1010 11 B 1011 12 C 1100 13 D 1101 14 E 1110 15 F 1111
3. C Bitwise operators
3.1 Bitwise logical operators
- Bitwise (bitwise) operation : Operations are carried out for each bit , It doesn't affect the left and right bits
3.1.1 Binary inversion or bitwise inversion :~
- hold 1 Turn into 0 , hold 0 Turn into 1
- The operator does not change the original value
char c = 0b10011010;
~c;
printf("%d\n%d\n", c, ~c);
// ~(1001 1010) = -102
// 0110 0101 = 101
3.1.2 Bitwise AND :&
- A fellow 1 Only then 1
char c1 = 0b10010011;
char c2 = 0b00111101;
printf("%d\n", c1 & c2);
// 1001 0011
// 0011 1101
// &
// 0001 0001
3.1.3 Press bit or :|
- Yes 1 Then for 1
char c1 = 0b10010011;
char c2 = 0b00111101;
printf("%d\n", c1 | c2);
// 1001 0011
// 0011 1101
// |
// 1011 1111
3.1.4 Bitwise XOR :^
- The difference is 1
char c1 = 0b10010011;
char c2 = 0b00111101;
printf("%d\n", c1 ^ c2);
// 1001 0011
// 0011 1101
// ^
// 1010 1110
3.7 Shift Operators
3.7.1 Move left :<<
- Move the object to the left of the operator to the left , The number of bits specified by the right object
- The operator does not change the original value
char c = 0b10001010;
c << 2;
printf("%d\n%d\n", c, c << 2);
// 00 1000 1010
// 10 0010 1000
// High truncation
// 0010 1000
3.7.2 Move right :>>
- Move the object to the left of the operator to the right , The number of bits specified by the right object
- The operator does not change the original value
char c = 0b10001010;
c >> 2;
printf("%d\n%d\n", c, c >> 2);
// 1000 1010
// 1110 0010 10
// Low truncation
// 1110 0010
3.7.3 usage : Shift Operators
- in the light of 2 The power of provides fast multiplication and division
- number << n :number multiply 2 Of n The next power
- number >> n : If number non-negative , Then use number Divide 2 Of n The next power
4. Bit fields
- Bit fields (bit field) It's a signed int or unsigned int A set of adjacent bits in a type variable
- Build through a structure declaration
struct {
int a : 1;
int b : 2;
int c : 3;
} abc;
// abc Include for 3 individual 1 Bit field
abc.a = 0;
abc.c = 1;
// Because the number of digits in the field is 1 , So it can only be assigned 0 or 1
If the total number of digits declared exceeds int (unsigned int Empathy ) Number of digits , Will use the next one int Storage location
- When this happens , first int Will leave an unnamed “ hole ”
- You can use unnamed field widths “ fill ” Unnamed “ hole ”
- Use a width of 0 The unnamed field of causes the next field to be stored in the next int in
struct { int a : 1; int : 2; int b : 2; int : 0; int c : 3; } abc; // a and b There is a 2 Bit gap // c Will be stored in the next int z
边栏推荐
- Traversal of leetcode tree
- Currently clicked button and current mouse coordinates in QT judgment interface
- [cloud native] record of feign custom configuration of microservices
- wordpress切换页面,域名变回了IP地址
- Full Permutation Code (recursive writing)
- 1040 Longest Symmetric String
- leetcode-1200:最小绝对差
- leetcode-31:下一个排列
- Daily question 1189 Maximum number of "balloons"
- 7. Processing the input of multidimensional features
猜你喜欢
Erreur de connexion Navicat à la base de données Oracle Ora - 28547 ou Ora - 03135
![[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?](/img/a3/7a1564cd9eb564abfd716fef08a9e7.jpg)
[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?
How to adjust bugs in general projects ----- take you through the whole process by hand
MySQL advanced part 1: index

Appium foundation - use the first demo of appium
Leetcode stack related
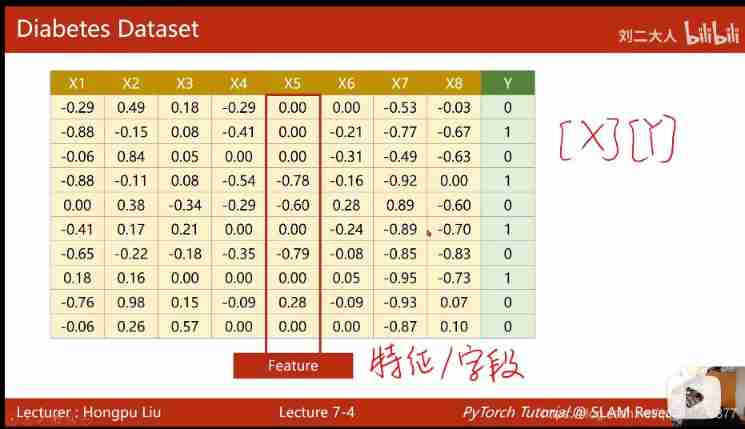
7. Processing the input of multidimensional features
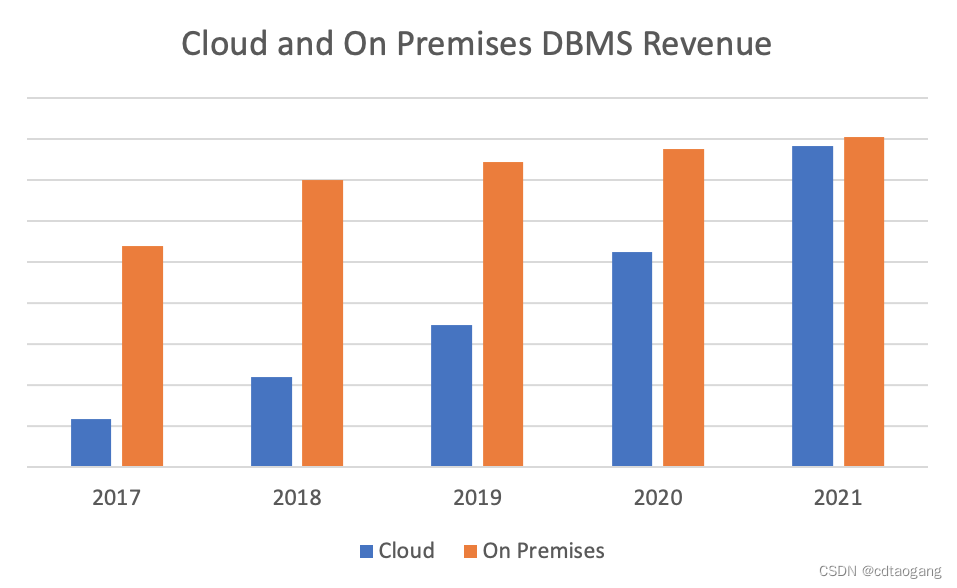
传统数据库逐渐“难适应”,云原生数据库脱颖而出
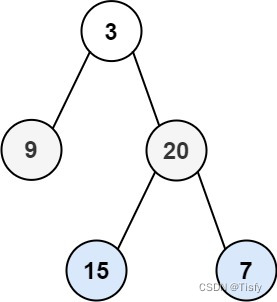
LeetCode 0107.二叉树的层序遍历II - 另一种方法

Appium基础 — 使用Appium的第一个Demo
随机推荐
LeetCode 1200.最小绝对差
Dynamic planning solution ideas and summary (30000 words)
[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?
Multi screen computer screenshots will cut off multiple screens, not only the current screen
Data visualization chart summary (II)
Appium基础 — 使用Appium的第一个Demo
MIT-6874-Deep Learning in the Life Sciences Week 7
The difference between CPU core and logical processor
Network security skills competition in Secondary Vocational Schools -- a tutorial article on middleware penetration testing in Guangxi regional competition
Introduction to LVS [unfinished (semi-finished products)]
QT判断界面当前点击的按钮和当前鼠标坐标
MySQL advanced part 2: MySQL architecture
1039 Course List for Student
Daily question 1342 Number of operations to change the number to 0
How to adjust bugs in general projects ----- take you through the whole process by hand
Leetcode divide and conquer / dichotomy
Leetcode stack related
LeetCode 0107. Sequence traversal of binary tree II - another method
QQ电脑版取消转义符输入表情
Data visualization chart summary (I)