当前位置:网站首页>Broadcast variables and accumulators in spark
Broadcast variables and accumulators in spark
2022-07-06 21:44:00 【Big data Xiaochen】
Broadcast variables
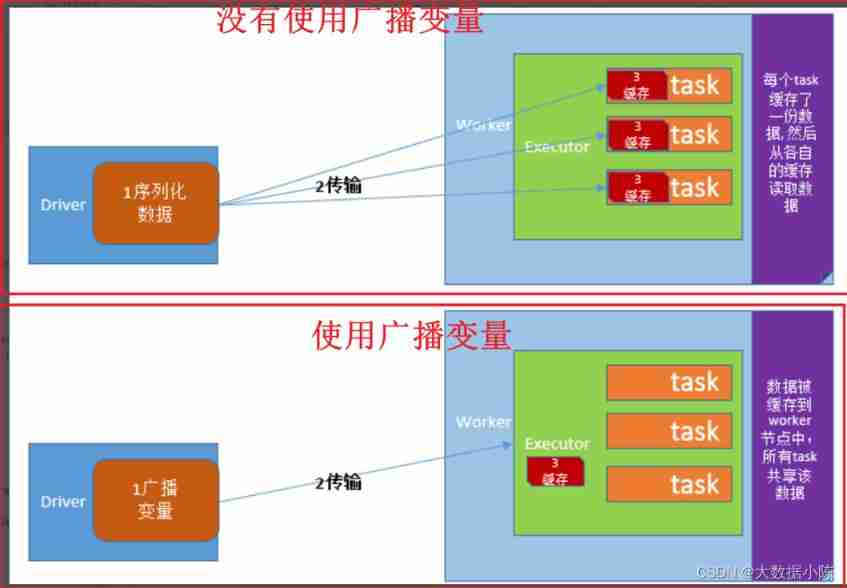
take Driver The shared data of the process is sent to all child nodes Executor In each task of the process .
If you don't use broadcast variable technology , that Driver The client will distribute the shared data to each by default 【Task】 in , Causing great pressure on network distribution .
If broadcast variable technology is used , be Driver The client will only send the shared data to each 【Executor】 One copy .Executor All in 【Task】 Reuse this object .
Ensure that the shared object is available 【 serialize 】 Of . Because the data transmitted across nodes should be serializable .
stay Driver The client broadcasts the shared objects to each Executor:
val bc = sc.broadcast( Shared objects )stay Executor In order to get :
bc.valueaccumulator
All in the cluster Executor Accumulate the same variable .
Spark Currently only support tired 【 Add 】 operation .
Yes 3 A built-in accumulator :【LongAccumulator】、【DoubleAccumulator】、【CollectionAccumulator】.
How to use the integer accumulator
stay Driver End define integer accumulator , Initial value of Fu .
acc=sc.accumulator(0)stay Executor The end accumulates each time 1
acc+=1 perhaps acc.add(1)
eg:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Desc:This is Code Desc
import os
import json
import re
import time
from pyspark import SparkConf, SparkContext, StorageLevel
os.environ['SPARK_HOME'] = '/export/server/spark'
PYSPARK_PYTHON = "/root/anaconda3/bin/python3.8"
# When multiple versions exist , Failure to specify is likely to result in an error
os.environ["PYSPARK_PYTHON"] = PYSPARK_PYTHON
os.environ["PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON"] = PYSPARK_PYTHON
if __name__ == '__main__':
#1- establish SparkContext Context object
conf=SparkConf().setAppName("8_sharevalue").setMaster("local[*]")
sc=SparkContext(conf=conf)
#2- Load data files to form RDD
file_rdd=sc.textFile("file:///export/pyworkspace/pyspark_sz26/pyspark-sparkcore-3.1.2/data/accumulator_broadcast_data.txt")
#3- Define accumulator , Later, when you encounter special symbols, add 1 operation
acc=sc.accumulator(0)
#4- Put special symbols in the list
list_v=[",", ".", "!", "#", "$", "%"]
#5- Broadcast the list to each Executor in
bc=sc.broadcast(list_v)
#6- Data cleaning , Filter blank line
filtered_rdd=file_rdd.filter(lambda line:len(line.strip())>0)
#7- Yes RDD Split according to generalized white space characters
str_rdd=filtered_rdd.flatMap(lambda line:re.split('\\s+',line))
#8- Encounter special symbols , Just add the accumulator 1 operation , And eliminate special symbols , Form new RDD, There are only words in it
def filter_func(str):
# To use global variables acc
global acc
list_m=bc.value
if str in list_m:
acc+=1
return False
else:
return True
word_rdd=str_rdd.filter(filter_func)
# Cache here , effect 1 yes RDD Reuse of , effect 2 It is to prevent the accumulator from accumulating repeatedly
word_rdd.cache()
print(''' Be careful 1- Because the accumulation operation is delayed loading , need Action Operation trigger ,
Now, word_rdd Not yet Action operation , The count is still zero :''', acc.value)
#9- Right up there RDD Conduct wordcount.
wordcount_10=word_rdd.map(lambda word:(word,1))\
.reduceByKey(lambda x,y:x+y)\
.sortBy(lambda x: x[1], ascending=False) \
.take(10)
#10- Print wordcount Word frequency statistics
print('wordcount Word frequency statistics :',wordcount_10)
#11- Number of times to print symbols
print(' Number of symbols :',acc.value)
print(' The total number of words is :', word_rdd.count())
print(' Number of symbols :',acc.value)
print(''' Be careful 2- because word_rdd Yes 2 individual Action operation ,count and take,
If you don't word_rdd Do cache persistence , So for the first time take After triggering the calculation, the accumulator result is 8,
The second time count It will load and calculate again , It will cause continuous accumulation , The result doubled to 16.
add cache After cache persistence , The second time count The operation gets data directly from the cache , Avoid double counting , The accumulator will not double .
''')
边栏推荐
- Nodejs tutorial expressjs article quick start
- PostgreSQL 修改数据库用户的密码
- 袁小林:安全不只是标准,更是沃尔沃不变的信仰和追求
- Five wars of Chinese Baijiu
- Why do job hopping take more than promotion?
- Yyds dry inventory run kubeedge official example_ Counter demo counter
- Why does MySQL index fail? When do I use indexes?
- Quick access to video links at station B
- The difference between break and continue in the for loop -- break completely end the loop & continue terminate this loop
- 首批入选!腾讯安全天御风控获信通院业务安全能力认证
猜你喜欢

袁小林:安全不只是标准,更是沃尔沃不变的信仰和追求

【滑动窗口】第九届蓝桥杯省赛B组:日志统计

Microsoft technology empowerment position - February course Preview

Digital transformation takes the lead to resume production and work, and online and offline full integration rebuilds business logic
爬虫实战(五):爬豆瓣top250
ViT论文详解
嵌入式开发的7大原罪
Fastjson parses JSON strings (deserialized to list, map)

What can one line of code do?
PostgreSQL modifies the password of the database user
随机推荐
20220211 failure - maximum amount of data supported by mongodb
Vim 基本配置和经常使用的命令
Microsoft technology empowerment position - February course Preview
JS method to stop foreach
Univariate cubic equation - relationship between root and coefficient
3D face reconstruction: from basic knowledge to recognition / reconstruction methods!
Z function (extended KMP)
14 years Bachelor degree, transferred to software testing, salary 13.5k
JS learning notes OO create suspicious objects
Technology sharing | packet capturing analysis TCP protocol
The underlying implementation of string
JS operation DOM element (I) -- six ways to obtain DOM nodes
MySQL - transaction details
MySQL - 事务(Transaction)详解
嵌入式开发的7大原罪
【力扣刷题】一维动态规划记录(53零钱兑换、300最长递增子序列、53最大子数组和)
How do I remove duplicates from the list- How to remove duplicates from a list?
Replace Internet TV set-top box application through digital TV and broadband network
50 commonly used numpy function explanations, parameters and usage examples
Four common ways and performance comparison of ArrayList de duplication (jmh performance analysis)