当前位置:网站首页>50个常用的Numpy函数解释,参数和使用示例
50个常用的Numpy函数解释,参数和使用示例
2022-07-06 13:10:00 【deephub】
Numpy是python中最有用的工具之一。它可以有效地处理大容量数据。使用NumPy的最大原因之一是它有很多处理数组的函数。在本文中,将介绍NumPy在数据科学中最重要和最有用的一些函数。
创建数组
1、Array
它用于创建一维或多维数组
Dtype:生成数组所需的数据类型。
ndim:指定生成数组的最小维度数。
import numpy as np
np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
----------------
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
还可以使用此函数将pandas的df和series转为NumPy数组。
sex = pd.Series(['Male','Male','Female'])
np.array(sex)
------------------------
array(['Male', 'Male', 'Female'], dtype=object)
2、Linspace
创建一个具有指定间隔的浮点数的数组。
start:起始数字
end:结束
Num:要生成的样本数,默认为50。
np.linspace(10,100,10)
--------------------------------
array([ 10., 20., 30., 40., 50., 60., 70., 80., 90., 100.])
3、Arange
在给定的间隔内返回具有一定步长的整数。
step:数值步长。
np.arange(5,10,2)
-----------------------
array([5, 7, 9])
4、Uniform
在上下限之间的均匀分布中生成随机样本。
np.random.uniform(5,10,size = 4)
------------
array([6.47445571, 5.60725873, 8.82192327, 7.47674099])
np.random.uniform(size = 5)
------------
array([0.83358092, 0.41776134, 0.72349553])
np.random.uniform(size = (2,3))
------------
array([[0.7032511 , 0.63212039, 0.6779683 ],
[0.81150812, 0.26845613, 0.99535264]])
5、Random.randint
在一个范围内生成n个随机整数样本。
np.random.randint(5,10,10)
------------------------------
array([6, 8, 9, 9, 7, 6, 9, 8, 5, 9])
6、Random.random
生成n个随机浮点数样本。
np.random.random(3)
---------------------------
array([0.87656396, 0.24706716, 0.98950278])
7、Logspace
在对数尺度上生成间隔均匀的数字。
Start:序列的起始值。
End:序列的最后一个值。
endpoint:如果为True,最后一个样本将包含在序列中。
base:底数。默认是10。
np.logspace(0,10,5,base=2)
------------------
array([1.00000000e+00, 5.65685425e+00, 3.20000000e+01, 1.81019336e+02,1.02400000e+03])
8、zeroes
np.zeroes会创建一个全部为0的数组。
shape:阵列的形状。
Dtype:生成数组所需的数据类型。’ int ‘或默认’ float ’
np.zeros((2,3),dtype='int')
---------------
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
np.zeros(5)
-----------------
array([0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
9、ones
np.ones函数创建一个全部为1的数组。
np.ones((3,4))
------------------
array([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
10、full
创建一个单独值的n维数组。
fill_value:填充值。
np.full((2,4),fill_value=2)
--------------
array([[2, 2, 2, 2],
[2, 2, 2, 2]])(2,4) : ꜱʜᴀᴘᴇ
11、Identity
创建具有指定维度的单位矩阵。
np.identity(4)
----------
array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])#ᴅᴇꜰᴀᴜʟᴛ ᴅᴀᴛᴀ ᴛʏᴘᴇ ɪꜱ `ꜰʟᴏᴀᴛ`
数组操作
12、min
返回数组中的最小值。
axis:用于操作的轴。
out:用于存储输出的数组。
arr = np.array([1,1,2,3,3,4,5,6,6,2])
np.min(arr)
----------------
1
13、max
返回数组中的最大值。
np.max(arr)
------------------
6
14、unique
返回一个所有唯一元素排序的数组。
return_index:如果为True,返回数组的索引。
return_inverse:如果为True,返回唯一数组的下标。
return_counts:如果为True,返回数组中每个唯一元素出现的次数。
axis:要操作的轴。默认情况下,数组被认为是扁平的。
np.unique(arr,return_counts=True)
---------------------
(
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]), ## Unique elements
array([2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2], dtype=int64) ## Count
)
15、mean
返回数组的平均数
np.mean(arr,dtype='int')
-------------------------------
3
16、medain
返回数组的中位数。
arr = np.array([[1,2,3],[5,8,4]])
np.median(arr)
-----------------------------
3.5
17、digitize
返回输入数组中每个值所属的容器的索引。
bin:容器的数组。
right:表示该间隔是否包括右边或左边的bin。
a = np.array([-0.9, 0.5, 0.9, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 3.6, 4.7, 5.3])
bins = np.array([0,1,2,3])
np.digitize(a,bins)
-------------------------------
array([0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 4, 4, 4], dtype=int64)
Exp Value
x < 0 : 0
0 <= x <1 : 1
1 <= x <2 : 2
2 <= x <3 : 3
3 <=x : 4
Compares -0.9 to 0, here x < 0 so Put 0 in resulting array.
Compares 0.5 to 0, here 0 <= x <1 so Put 1.
Compares 5.4 to 4, here 3<=x so Put 4
18、reshape
它是NumPy中最常用的函数之一。它返回一个数组,其中包含具有新形状的相同数据。
A = np.random.randint(15,size=(4,3))
A
----------------------
array([[ 8, 14, 1],
[ 8, 11, 4],
[ 9, 4, 1],
[13, 13, 11]])
A.reshape(3,4)
-----------------
array([[ 8, 14, 1, 8],
[11, 4, 9, 4],
[ 1, 13, 13, 11]])
A.reshape(-1)
-------------------
array([ 8, 14, 1, 8, 11, 4, 9, 4, 1, 13, 13, 11])
19、expand_dims
它用于扩展数组的维度。
arr = np.array([ 8, 14, 1, 8, 11, 4, 9, 4, 1, 13, 13, 11])
np.expand_dims(A,axis=0)
-------------------------
array([[ 8, 14, 1, 8, 11, 4, 9, 4, 1, 13, 13, 11]])
np.expand_dims(A,axis=1)
---------------------------
array([[ 8],
[14],
[ 1],
[ 8],
[11],
[ 4],
[ 9],
[ 4],
[ 1],
[13],
[13],
[11]])
20、squeeze
通过移除一个单一维度来降低数组的维度。
arr = np.array([[ 8],[14],[ 1],[ 8],[11],[ 4],[ 9],[ 4],[ 1],[13],[13],[11]])
np.squeeze(arr)
---------------------------
array([ 8, 14, 1, 8, 11, 4, 9, 4, 1, 13, 13, 11])
21、count_nonzero
计算所有非零元素并返回它们的计数。
a = np.array([0,0,1,1,1,0])
np.count_nonzero(a)
--------------------------
3
22、argwhere
查找并返回非零元素的所有下标。
a = np.array([0,0,1,1,1,0])
np.argwhere(a)
---------------------
array([[2],[3],[4]], dtype=int64)
23、argmax & argmin
argmax返回数组中Max元素的索引。它可以用于多类图像分类问题中获得高概率预测标签的指标。
arr = np.array([[0.12,0.64,0.19,0.05]])
np.argmax(arr)
---------
1
argmin将返回数组中min元素的索引。
np.argmin(min)
------
3
24、sort
对数组排序。
kind:要使用的排序算法。{‘quicksort’, ‘mergesort’, ‘heapsort’, ‘stable’}
arr = np.array([2,3,1,7,4,5])
np.sort(arr)
----------------
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7])
25、abs
返回数组中元素的绝对值。当数组中包含负数时,它很有用。
A = np.array([[1,-3,4],[-2,-4,3]])np.abs(A)
---------------
array([[1, 3, 4],
[2, 4, 3]])
26、round
将浮点值四舍五入到指定数目的小数点。
decimals:要保留的小数点的个数。
a = np.random.random(size=(3,4))
a
-----
array([[0.81695699, 0.42564822, 0.65951417, 0.2731807 ],
[0.7017702 , 0.12535894, 0.06747666, 0.55733467],
[0.91464488, 0.26259026, 0.88966237, 0.59253923]])
np.round(a,decimals=0)
------------
array([[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[0., 1., 0., 1.]])
np.round(a,decimals=1)
-------------
array([[0.8, 0. , 0.6, 0.6],
[0.5, 0.7, 0.7, 0.8],
[0.3, 0.9, 0.5, 0.7]])
27、clip
它可以将数组的裁剪值保持在一个范围内。
arr = np.array([0,1,-3,-4,5,6,7,2,3])
arr.clip(0,5)
-----------------
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 5, 5, 2, 3])
arr.clip(0,3)
------------------
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3])
arr.clip(3,5)
------------------
array([3, 3, 3, 3, 5, 5, 5, 3, 3])
替换数组中的值
28、where
返回满足条件的数组元素。
condition:匹配的条件。如果true则返回x,否则y。
a = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
a
-------
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
np.where(a>5) ## Get The Index
--------------------
(array([2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3], dtype=int64),
array([0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2], dtype=int64))
a[np.where(a>5)] ## Get Values
--------------------------
array([ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])
它还可以用来替换pandas df中的元素。
np.where(data[feature].isnull(), 1, 0)
29、put
用给定的值替换数组中指定的元素。
a:数组
Ind:需要替换的索引。
V:替换值。
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
arr
--------
array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
np.put(arr,[1,2],[6,7])
arr
--------
array([1, 6, 7, 4, 5, 6])
30、copyto
将一个数组的内容复制到另一个数组中。
dst:目标
src:来源
arr1 = np.array([1,2,3])
arr2 = np.array([4,5,6])
print("Before arr1",arr1)
print("Before arr2",arr1)
np.copyto(arr1,arr2)
print("After arr1",arr1)
print("After arr2",arr2)
---------------------------
Before arr1 [1 2 3]
Before arr2 [4 5 6]
After arr1 [4 5 6]
After arr2 [4 5 6]
集合操作
31、查找公共元素
intersect1d函数以排序的方式返回两个数组中所有唯一的值。
Assume_unique:如果为真值,则假设输入数组都是唯一的。
Return_indices:如果为真,则返回公共元素的索引。
ar1 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6])
ar2 = np.array([3,4,5,8,9,1])
np.intersect1d(ar1,ar2)
---------------
array([1, 3, 4, 5])
np.intersect1d(ar1,ar2,return_indices=True)
---------------
(array([1, 3, 4, 5]), ## Common Elements
array([0, 2, 3, 4], dtype=int64),
array([5, 0, 1, 2], dtype=int64))
32、查找不同元素
np.setdiff1d函数返回arr1中在arr2中不存在的所有唯一元素。
a = np.array([1, 7, 3, 2, 4, 1])
b = np.array([9, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8])
np.setdiff1d(a, b)
---------------------
array([1, 3, 4])
33、从两个数组中提取唯一元素
Setxor1d 将按顺序返回两个数组中所有唯一的值。
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 6])
b = np.array([1, 4, 9, 4, 36])
np.setxor1d(a,b)
--------------------
array([ 2, 3, 6, 9, 36])
34、合并
Union1d函数将两个数组合并为一个。
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
b = np.array([1, 3, 5, 4, 36])
np.union1d(a,b)
-------------------
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 36])
数组分割
35、水平分割
Hsplit函数将数据水平分割为n个相等的部分。
A = np.array([[3,4,5,2],[6,7,2,6]])
np.hsplit(A,2) ## splits the data into two equal parts
---------------
[ array([[3, 4],[6, 7]]), array([[5, 2],[2, 6]]) ]
np.hsplit(A,4) ## splits the data into four equal parts
-----------------
[ array([[3],[6]]), array([[4],[7]]),
array([[5],[2]]), array([[2],[6]]) ]
36、垂直分割
Vsplit将数据垂直分割为n个相等的部分。
A = np.array([[3,4,5,2],[6,7,2,6]])
np.vsplit(A,2)
----------------
[ array([[3, 4, 5, 2]]), array([[6, 7, 2, 6]]) ]
数组叠加
37、水平叠加
hstack 将在另一个数组的末尾追加一个数组。
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
b = np.array([1,4,9,16,25])
np.hstack((a,b))
---------------------
array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25])
38、垂直叠加
vstack将一个数组堆叠在另一个数组上。
np.vstack((a,b))
----------------------
array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 1, 4, 9, 16, 25]])
数组比较
39、allclose
如果两个数组的形状相同,则Allclose函数根据公差值查找两个数组是否相等或近似相等。
a = np.array([0.25,0.4,0.6,0.32])
b = np.array([0.26,0.3,0.7,0.32])
tolerance = 0.1 ## Total Difference
np.allclose(a,b,tolerance)
---------
False
tolerance = 0.5
np.allclose(a,b,tolerance)
----------
True
40、equal
它比较两个数组的每个元素,如果元素匹配就返回True。
np.equal(arr1,arr2)
-------------
array([ True, True, True, False, True, True])
重复的数组元素
repeat
它用于重复数组中的元素n次。

A:重复的元素
Repeats:重复的次数。
np.repeat('2017',3)
---------------------
array(['2017', '2017', '2017'], dtype='<U4')
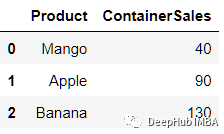
让我们来看一个更实际的示例,我们有一个包含按年数量销售的数据集。
fruits = pd.DataFrame([
['Mango',40],
['Apple',90],
['Banana',130]
],columns=['Product','ContainerSales'])
fruits
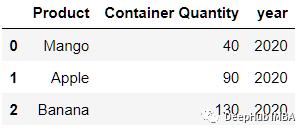
在数据集中,缺少年份列。我们尝试使用numpy添加它。
fruits['year'] = np.repeat(2020,fruits.shape[0])
fruits
41、tile
通过重复A,rep次来构造一个数组。
np.tile("Ram",5)
-------
array(['Ram', 'Ram', 'Ram', 'Ram', 'Ram'], dtype='<U3')
np.tile(3,(2,3))
-------
array([[3, 3, 3],
[3, 3, 3]])
爱因斯坦求和
42、einsum
此函数用于计算数组上的多维和线性代数运算。
a = np.arange(1,10).reshape(3,3)
b = np.arange(21,30).reshape(3,3)
np.einsum('ii->i',a)
------------
array([1, 5, 9])
np.einsum('ji',a)
------------
array([[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[3, 6, 9]])
np.einsum('ij,jk',a,b)
------------
array([[150, 156, 162],
[366, 381, 396],
[582, 606, 630]])
p.einsum('ii',a)
----------
15
统计分析
43、直方图
这是Numpy的重要统计分析函数,可计算一组数据的直方图值。
A = np.array([[3, 4, 5, 2],
[6, 7, 2, 6]])
np.histogram(A)
-------------------
(array([2, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1], dtype=int64),
array([2. , 2.5, 3. , 3.5, 4. , 4.5, 5. , 5.5, 6. , 6.5, 7. ]))
44、百分位数
沿指定轴计算数据的Q-T-T百分位数。
a:输入。
q:要计算的百分位。
overwrite_input:如果为true,则允许输入数组修改中间计算以节省内存。
a = np.array([[2, 4, 6], [4, 8, 12]])
np.percentile(a, 50)
-----------
5.0
np.percentile(a, 10)
------------
3.0
arr = np.array([2,3,4,1,6,7])
np.percentile(a,5)
------------
2.5
45、标准偏差和方差
std和var是NumPy的两个函数,用于计算沿轴的标准偏差和方差。
a = np.array([[2, 4, 6], [4, 8, 12]])
np.std(a,axis=1)
--------
array([1.63299316, 3.26598632])
np.std(a,axis=0) ## Column Wise
--------
array([1., 2., 3.])
np.var(a,axis=1)
-------------------
array([ 2.66666667, 10.66666667])
np.var(a,axis=0)
-------------------
array([1., 4., 9.])
数组打印
46、显示带有两个十进制值的浮点数
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
a = np.array([12.23456,32.34535])
print(a)
------------
array([12.23,32.34])
47、设置打印数组最大值
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
48、增加一行中元素的数量
np.set_printoptions(linewidth=100) ## 默认是 75
保存和加载数据
49、保存
savetxt用于在文本文件中保存数组的内容。
arr = np.linspace(10,100,500).reshape(25,20)
np.savetxt('array.txt',arr)
50、加载
用于从文本文件加载数组,它以文件名作为参数。
np.loadtxt('array.txt')
以上就是50个numpy常用的函数,希望对你有所帮助。
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/f47bb7762ccb41189baff5fe6a10403a
作者:Abhay Parashar
边栏推荐
- Is it profitable to host an Olympic Games?
- 【mysql】游标的基本使用
- 审稿人dis整个研究方向已经不仅仅是在审我的稿子了怎么办?
- R3live notes: image processing section
- 爱可可AI前沿推介(7.6)
- JS学习笔记-OO创建怀疑的对象
- 2022菲尔兹奖揭晓!首位韩裔许埈珥上榜,四位80后得奖,乌克兰女数学家成史上唯二获奖女性
- ICML 2022 | Flowformer: 任务通用的线性复杂度Transformer
- JS according to the Chinese Alphabet (province) or according to the English alphabet - Za sort &az sort
- Pat 1085 perfect sequence (25 points) perfect sequence
猜你喜欢
缓存更新策略概览(Caching Strategies Overview)
![[in depth learning] pytorch 1.12 was released, officially supporting Apple M1 chip GPU acceleration and repairing many bugs](/img/66/4d94ae24e99599891636013ed734c5.png)
[in depth learning] pytorch 1.12 was released, officially supporting Apple M1 chip GPU acceleration and repairing many bugs

Internet News: Geely officially acquired Meizu; Intensive insulin purchase was fully implemented in 31 provinces
Swagger UI tutorial API document artifact

Reference frame generation based on deep learning
![[MySQL] basic use of cursor](/img/cc/39b1e17b48d0de641d3cbffbf2335a.png)
[MySQL] basic use of cursor
![[Li Kou brushing questions] one dimensional dynamic planning record (53 change exchanges, 300 longest increasing subsequence, 53 largest subarray and)](/img/1c/973f824f061d470a4079487d75f0d0.png)
[Li Kou brushing questions] one dimensional dynamic planning record (53 change exchanges, 300 longest increasing subsequence, 53 largest subarray and)

Z function (extended KMP)
039. (2.8) thoughts in the ward
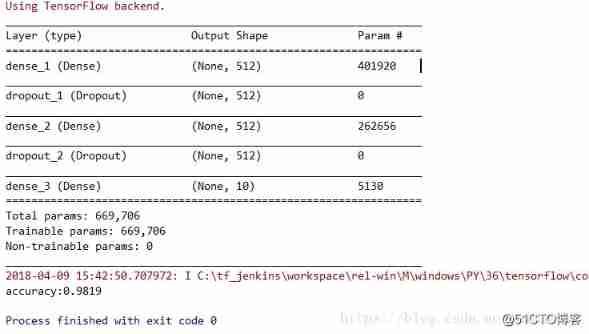
MLP (multilayer perceptron neural network) is a multilayer fully connected neural network model.
随机推荐
基于深度学习的参考帧生成
嵌入式开发的7大原罪
Manifest of SAP ui5 framework json
面试官:Redis中有序集合的内部实现方式是什么?
How do I remove duplicates from the list- How to remove duplicates from a list?
跨分片方案 总结
【Redis设计与实现】第一部分 :Redis数据结构和对象 总结
愛可可AI前沿推介(7.6)
Opencv learning example code 3.2.3 image binarization
PHP saves session data to MySQL database
JS get array subscript through array content
Notes - detailed steps of training, testing and verification of yolo-v4-tiny source code
Proxy and reverse proxy
Quick access to video links at station B
KDD 2022 | 通过知识增强的提示学习实现统一的对话式推荐
JS learning notes OO create suspicious objects
Why does MySQL index fail? When do I use indexes?
3D face reconstruction: from basic knowledge to recognition / reconstruction methods!
MLP (multilayer perceptron neural network) is a multilayer fully connected neural network model.
Set up a time server