当前位置:网站首页>Data analysis course notes (III) array shape and calculation, numpy storage / reading data, indexing, slicing and splicing
Data analysis course notes (III) array shape and calculation, numpy storage / reading data, indexing, slicing and splicing
2022-07-07 00:21:00 【M Walker x】
Data analysis course notes
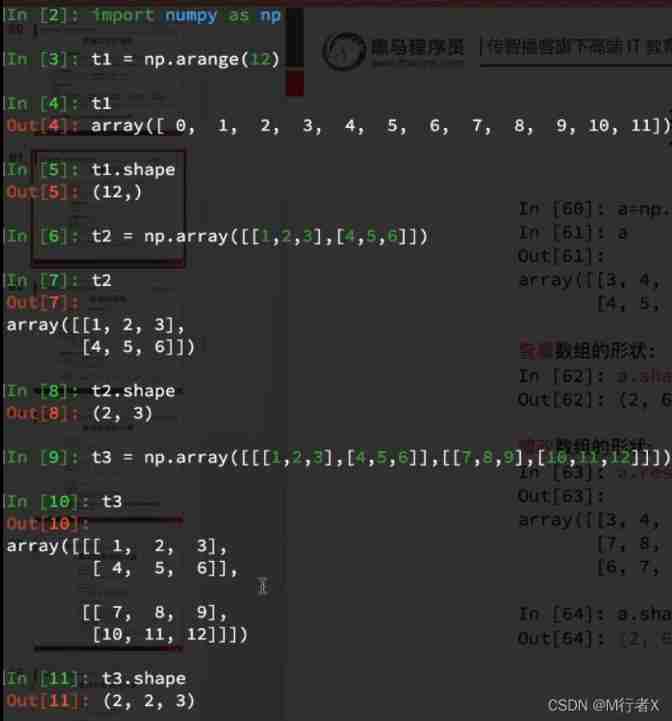
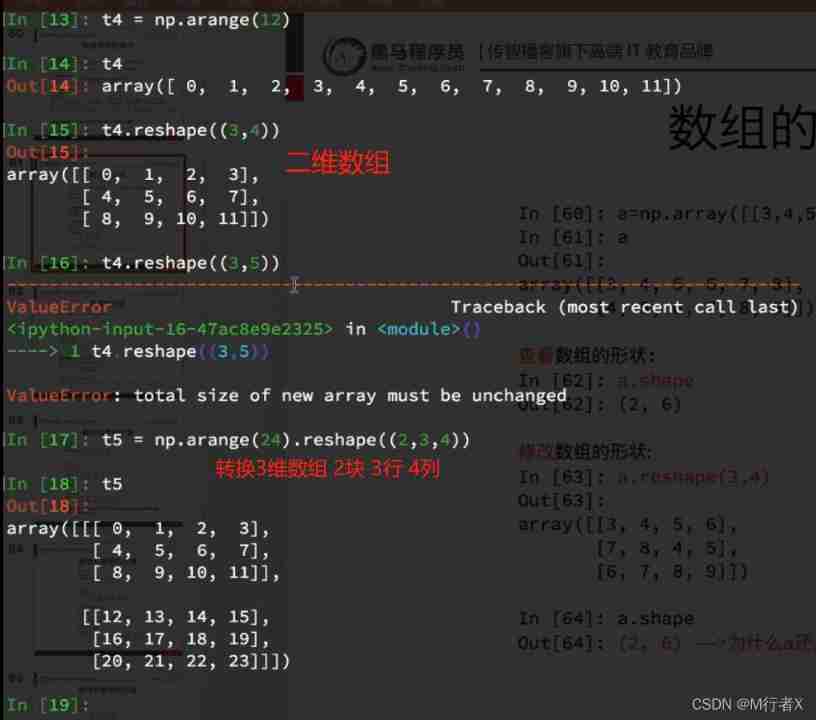
The shape of the array


The calculation of array


Calculate in different dimensions
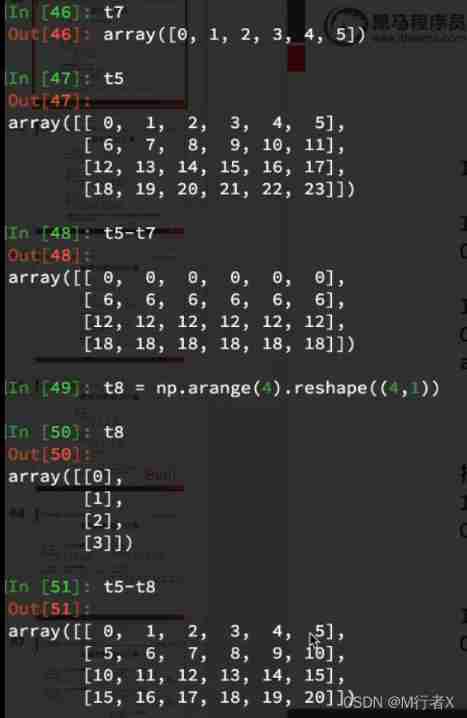
Broadcasting principles


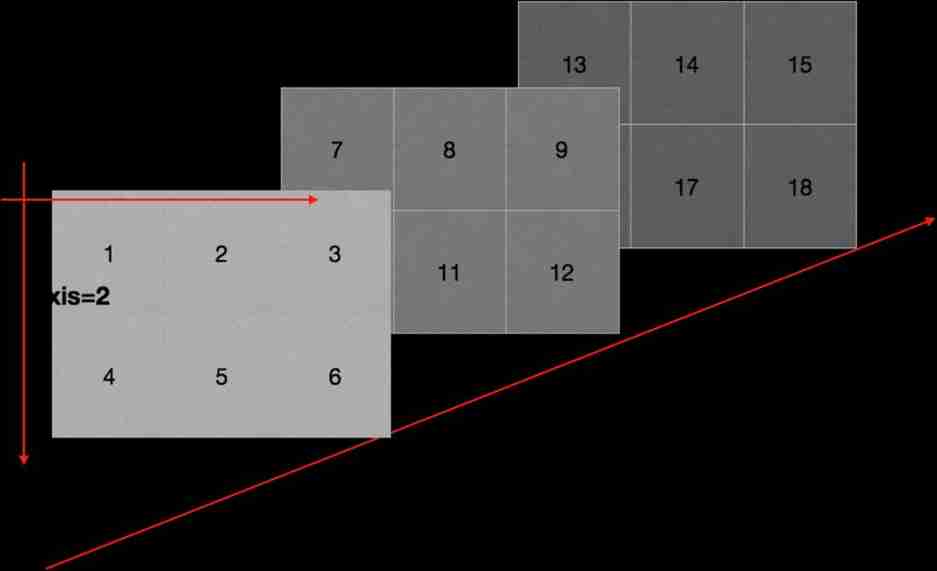
Axis (axis)


numpy Reading data

np.loadtxt(fname,dtype=np.float,delimiter=None,skiprows=0,usecols=None,unpack=False)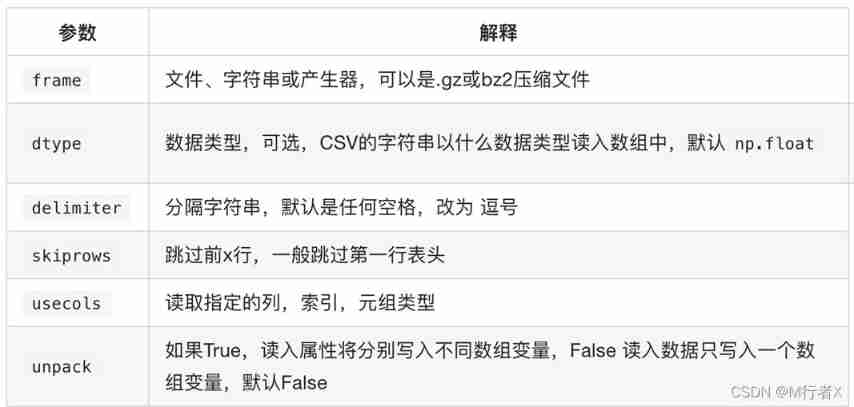

Data sources : https://www.kaggle.com/datasnaek/youtube/data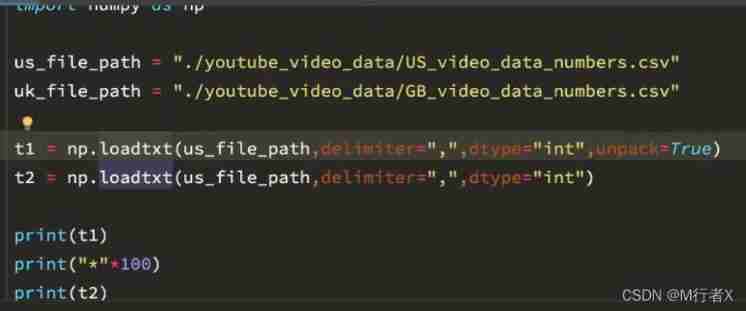



# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int",unpack=True)
t2 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
# print(t1)
print(t2)
print("*"*100)
# Take row
# print(t2[2])
# Take consecutive multiple lines
# print(t2[2:])
# Take discontinuous multiple lines
# print(t2[[2,8,10]])
# print(t2[1,:])
# print(t2[2:,:])
# print(t2[[2,10,3],:])
# Fetch
# print(t2[:,0])
# Take consecutive Columns
# print(t2[:,2:])
# Take discontinuous multiple columns
# print(t2[:,[0,2]])
# Go to rows and columns , Take the first place 3 That's ok , The value of the fourth column
# a = t2[2,3]
# print(a)
# print(type(a))
# Fetching multiple rows and columns , Take the first place 3 Line to line five , The first 2 Column to the first 4 The results of the column
# Go to the intersection of rows and columns
b = t2[2:5,1:4]
# print(b)
# Take multiple non adjacent points
# The result is (0,0) (2,1) (2,3)
c = t2[[0,2,2],[0,1,3]]
print(c)
numpy Index and slice



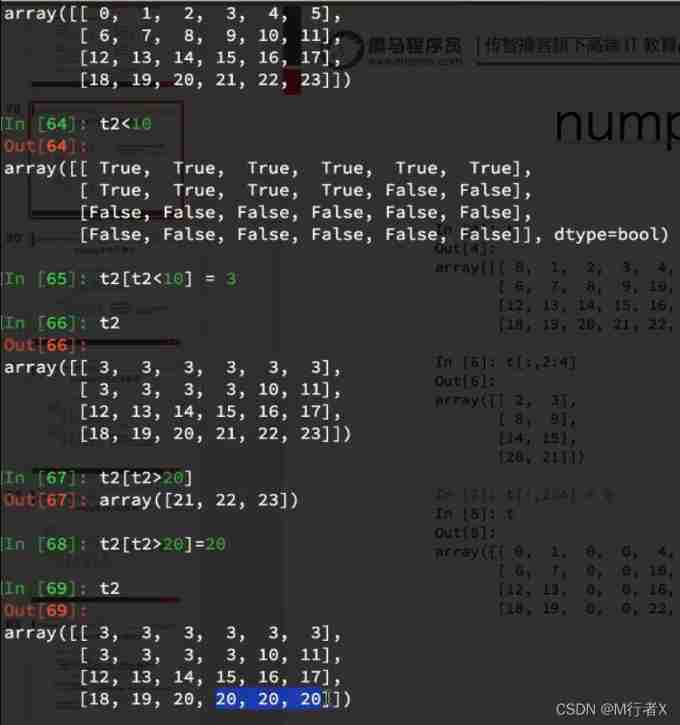
numpy Boolean index in
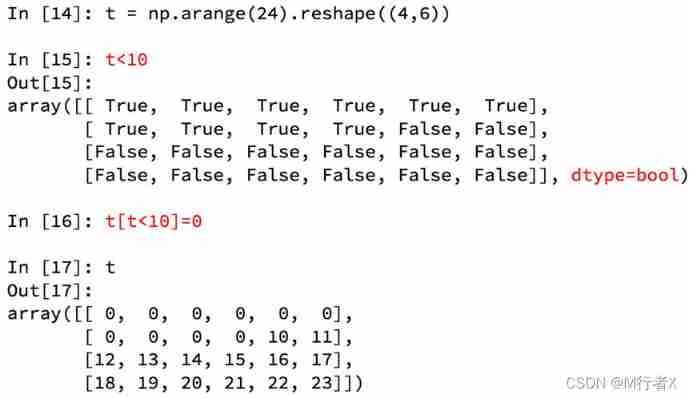

numpy Ternary operator in


numpy Medium clip( tailoring )
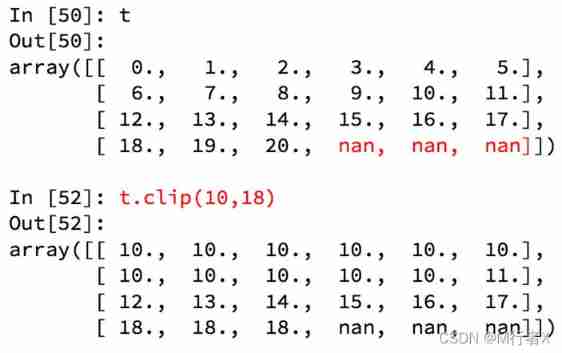

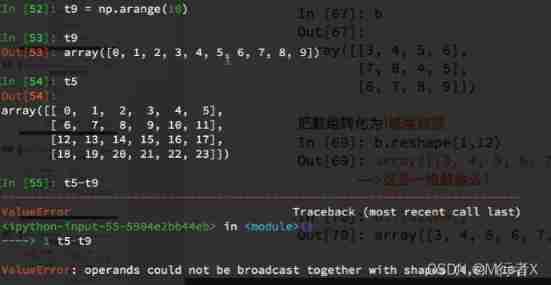
numpy Medium nan and inf
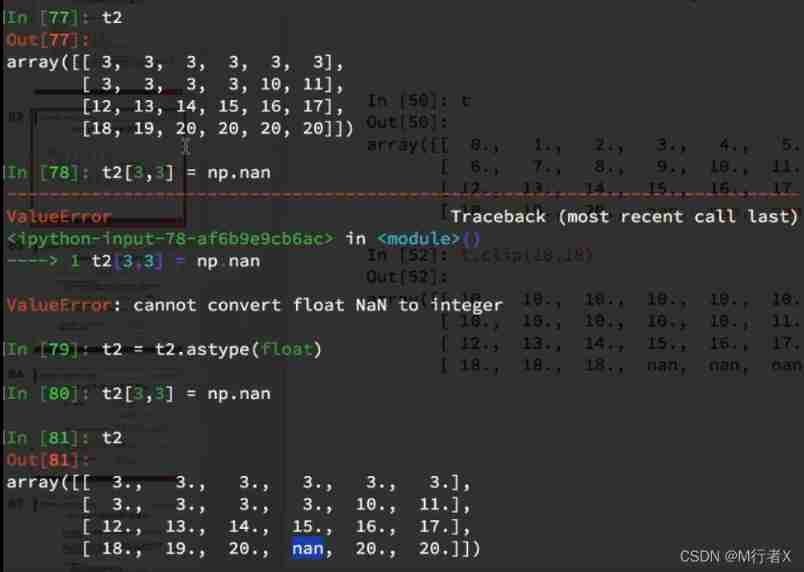


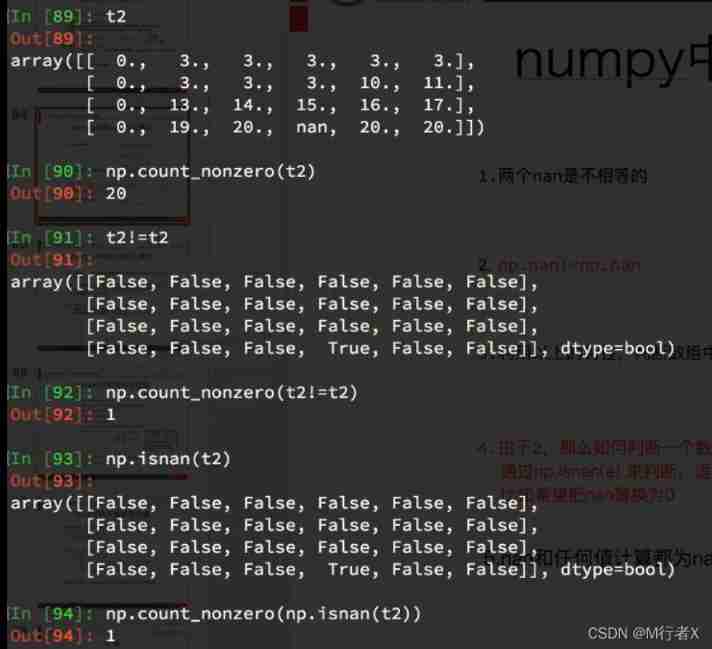
numpy Medium nan Points for attention

numpy Statistical functions commonly used in

All statistical results of multidimensional array are returned by default , If specified axis Returns a result on the current axis 
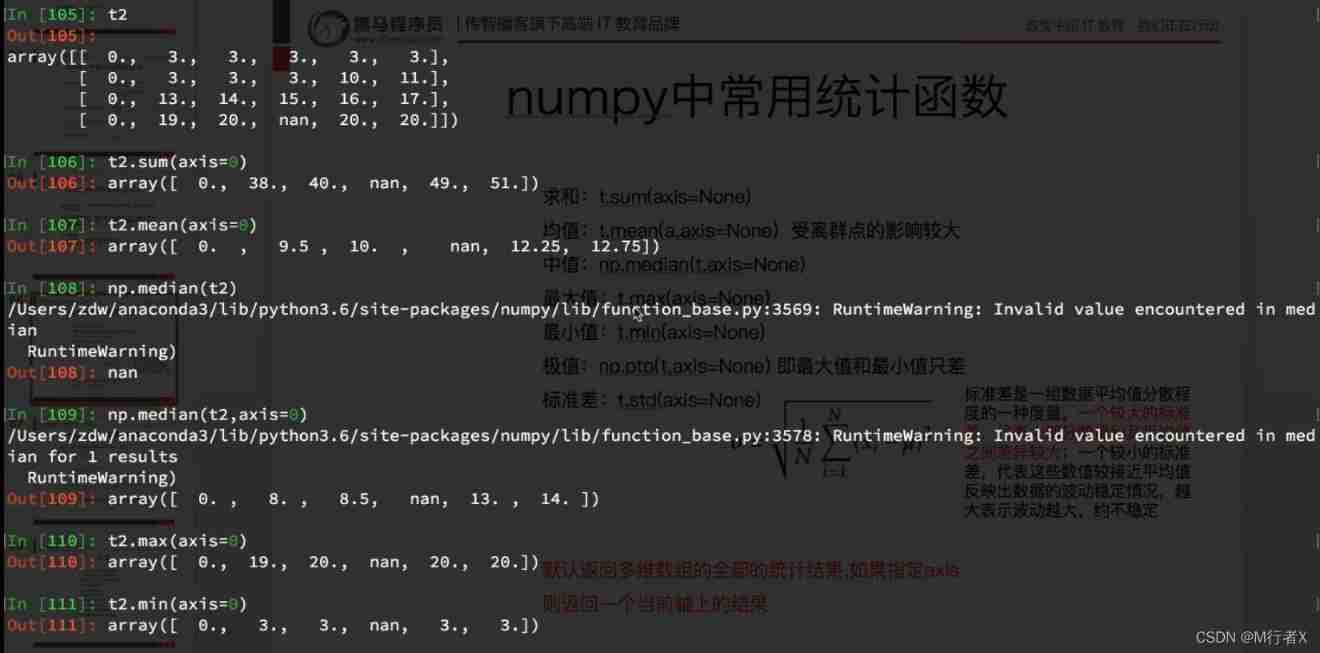
Missing value processing
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
# print(t1)
def fill_ndarray(t1):
for i in range(t1.shape[1]): # Traverse each column
temp_col = t1[:,i] # The current column
nan_num = np.count_nonzero(temp_col!=temp_col)
if nan_num !=0: # Not for 0, Indicates that there are... In the current column nan
temp_not_nan_col = temp_col[temp_col==temp_col] # The current column is not nan Of array
# Check that the current is nan The location of , Assign a value that is not nan The average of
temp_col[np.isnan(temp_col)] = temp_not_nan_col.mean()
return t1
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = np.arange(24).reshape((4, 6)).astype("float")
t1[1, 2:] = np.nan
print(t1)
t1 = fill_ndarray(t1)
print(t1)
- How to select one or more rows of data ( Column )?
- How to assign values to selected rows or columns ?
- How to make it bigger than 10 Replace the value of with 10?
- np.where How to use ?
- np.clip How to use ?
- How to transpose ( Exchange axis )?
- Read and save data as csv
- np.nan and np.inf What is it?
- How many common statistical functions do you remember ?
- What information does the standard deviation reflect about the data
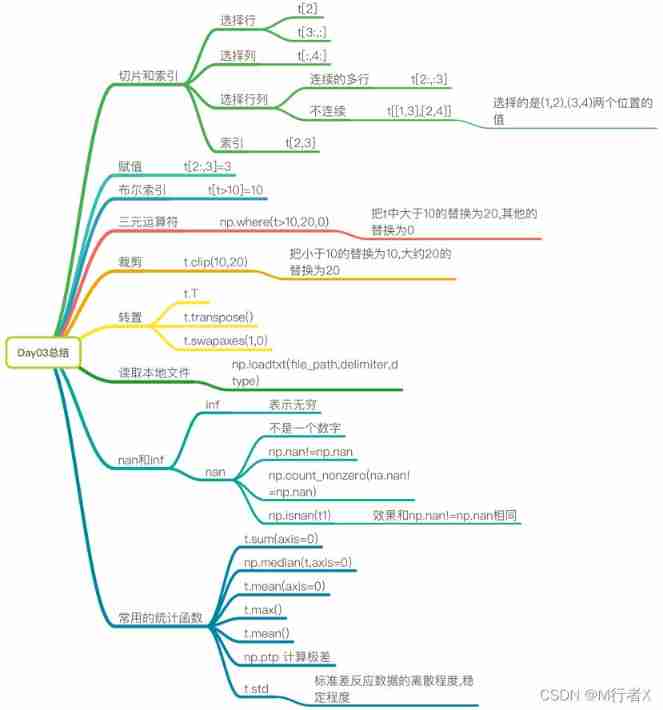
#### numpy Index and slice of
- t[10,20]
- `t[[2,5],[4,8]]`
- t[3:]
- t[[2,5,6]]
- t[:,:4]
- t[:,[2,5,6]]
- t[2:3,5:7]
#### numpy Medium bool Indexes ,where,clip Use
- t[t<30] = 2
- np.where(t<10,20,5)
- t.clip(10,20)
#### Transpose and read local files
- t.T
- t.transpose()
- t.sawpaxes()
- np.loadtxt(file_path,delimiter,dtype)
#### nan and inf What is it?
- nan not a number
- np.nan != np.nan
- Any value sum nan All calculations are nan
- inf infinite
#### Commonly used statistical functions
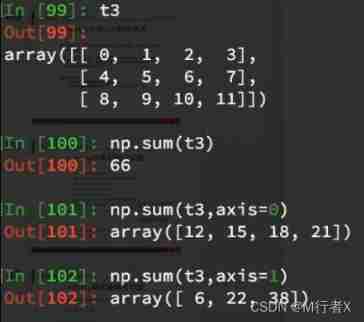
- t.sum()
- t.mean()
- np.meadian()
- t.max()
- t.min()
- np.ptp()
- t.std()

import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int",unpack=True)
t_us = np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
# Take the data of the comment
t_us_comments = t_us[:,-1]
# Choose more than 5000 Small data
t_us_comments = t_us_comments[t_us_comments<=5000]
print(t_us_comments.max(),t_us_comments.min())
d = 50
bin_nums = (t_us_comments.max()-t_us_comments.min())//d
# mapping
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.hist(t_us_comments,bin_nums)
plt.show()
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
us_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_file_path = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# t1 = np.loadtxt(us_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int",unpack=True)
t_uk = np.loadtxt(uk_file_path,delimiter=",",dtype="int")
# Choose to like books better than 50 Ten thousand small data
t_uk = t_uk[t_uk[:,1]<=500000]
t_uk_comment = t_uk[:,-1]
t_uk_like = t_uk[:,1]
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8),dpi=80)
plt.scatter(t_uk_like,t_uk_comment)
plt.show()
Data splicing


Data row column exchange

Now I hope to study and analyze the data methods of the two countries in the previous case , So what should I do ?
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
us_data = "./youtube_video_data/US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_data = "./youtube_video_data/GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
# Load country data
us_data = np.loadtxt(us_data,delimiter=",",dtype=int)
uk_data = np.loadtxt(uk_data,delimiter=",",dtype=int)
# Add country information
# The structure is all 0 The data of
zeros_data = np.zeros((us_data.shape[0],1)).astype(int)
ones_data = np.ones((uk_data.shape[0],1)).astype(int)
# Add a column with all 0,1 Array of
us_data = np.hstack((us_data,zeros_data))
uk_data = np.hstack((uk_data,ones_data))
# Splice two sets of data
final_data = np.vstack((us_data,uk_data))
print(final_data)
More easy-to-use methods

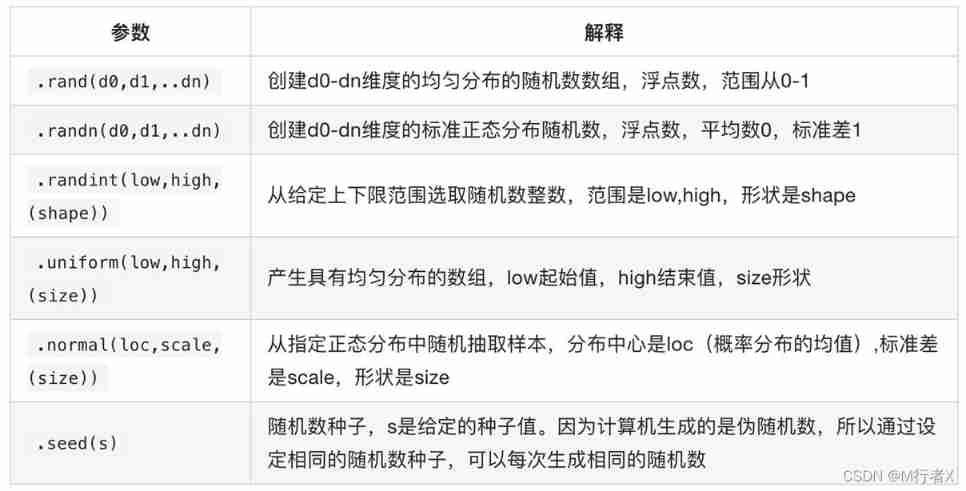
numpy Generate random number
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(10)
t = np.random.randint(0,20,(3,4))
print(t)
numpy Points for attention copy and view


边栏推荐
- Interface joint debugging test script optimization v4.0
- [boutique] Pinia Persistence Based on the plug-in Pinia plugin persist
- Rails 4 asset pipeline vendor asset images are not precompiled
- uniapp实现从本地上传头像并显示,同时将头像转化为base64格式存储在mysql数据库中
- DAY FOUR
- What is AVL tree?
- 48页数字政府智慧政务一网通办解决方案
- 一图看懂对程序员的误解:西方程序员眼中的中国程序员
- Devops can help reduce technology debt in ten ways
- The programmer resigned and was sentenced to 10 months for deleting the code. Jingdong came home and said that it took 30000 to restore the database. Netizen: This is really a revenge
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
微信小程序uploadfile服务器,微信小程序之wx.uploadFile[通俗易懂]
【vulnhub】presidential1
Leecode brushes questions and records interview questions 01.02 Determine whether it is character rearrangement for each other
[2022 the finest in the whole network] how to test the interface test generally? Process and steps of interface test
C语言输入/输出流和文件操作【二】
rancher集成ldap,实现统一账号登录
【CVPR 2022】目标检测SOTA:DINO: DETR with Improved DeNoising Anchor Boxes for End-to-End Object Detection
【2022全网最细】接口测试一般怎么测?接口测试的流程和步骤
MIT 6.824 - Raft学生指南
刘永鑫报告|微生物组数据分析与科学传播(晚7点半)
openresty ngx_ Lua subrequest
2022/2/11 summary
MySQL learning notes (mind map)
Leecode brush question record sword finger offer 58 - ii Rotate string left
Wind chime card issuing network source code latest version - commercially available
okcc呼叫中心的订单管理时怎么样的
Automatic test tool katalon (WEB) test operation instructions
DAY THREE
Interesting wine culture
The difference between redirectto and navigateto in uniapp