当前位置:网站首页>Class constant pool and runtime constant pool
Class constant pool and runtime constant pool
2022-07-07 03:58:00 【The season when the monsoon dies】
class Constant pool
java The file is being compiled into class After the document , stay class A constant pool will be generated in the file , The literal amount used to store code 、 Symbol reference , Such as static、void、public wait . This constant pool is called class Constant pool . use javap The command generates a readable JVM Bytecode instruction file :
javap -v ScheduledBlockChainTask.class
The red box indicates class Constant pool information , There are two main types of constants in the constant pool : Literal and symbolic references .
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = "abcdefg";
int d = "abcdefg- Fully qualified names of classes and interfaces
- Name and descriptor of the field
- The name and descriptor of the method
- Create a string constant pool for Strings , Similar to the cache
- When creating a string constant , First, query whether the string constant pool exists
- The string exists , Return reference instance , non-existent , Instantiate the string and put it in the pool
- Jdk1.6 And before : There is a permanent generation , The runtime constant pool is in the permanent generation , Runtime constant pool contains string constant pool
- Jdk1.7: There is a permanent generation , But gradually “ To the eternal generation ”, The string constant pool is separated from the runtime constant pool in the permanent generation into the heap
- Jdk1.8 And after : There is no permanent generation , Runtime constant pool in meta space , The string constant pool is still in the heap
Three string operations
- Assign strings directly
String s = "lamu"; // s Point to references in the constant pool - new String();
String s1 = new String("zhuge"); // s1 Point to an object reference in memory - intern Method
String s1 = new String("zhuge");
String s2 = s1.intern();
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //falseintern Method returns the reference of the object in the string constant pool . stay jdk6 And below , If the object exists in the string constant pool , Returns the reference of the object in the string constant pool . without , Then add the object to the string constant pool , Returns the reference of this object in the string constant pool . stay jdk6 In the previous version , If the object exists in the string constant pool , Returns the reference of the object in the string constant pool . without , Then check whether the object exists in the heap , If there is , Put the reference of this object in the heap into the string constant pool and return .
String Splicer “+” What will the bottom do
If at compile time , It can determine the value of objects before and after splicing , Then it will be spliced directly in the compilation stage , Put the final value into the string constant pool . If you can't know the value of the object before and after splicing at the compilation stage , Then an object will be created in the heap and string constant pool by splicing the front and rear field values at run time .
String s1 = new String("he") + new String("llo");
String s2 = s1.intern();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
// stay JDK 1.6 Lower output yes false, Created 6 Objects
// stay JDK 1.7 And above version output is true, Created 5 Objects
// Of course, we didn't consider GC, But these objects do exist or exist
// Be careful : Whether the constant pool has a corresponding object depends on the literal , Objects with non-existent literals will not appear in the constant pool
String s0="hello";
String s1="hello";
String s2="he" + "llo";
System.out.println( s0==s1 ); //true
System.out.println( s0==s2 ); //true s2 It will be optimized to "hello".
String s0="hello";
String s1=new String("hello");
String s2="he" + new String("llo");
System.out.println( s0==s1 ); // false s0 In the constant pool ,s1 In the heap
System.out.println( s0==s2 ); // false new String("llo") Cannot optimize at compile time , therefore s2 Finally, it is generated in the heap
System.out.println( s1==s2 ); // false s1 and s2 It's all in the pile , But they are new Two different objects come out
String a = "ab";
String bb = "b";
String b = "a" + bb;
System.out.println(a == b); // false Variable bb Unknown at compile time , Can't optimize
String a = "ab";
final String bb = "b";
String b = "a" + bb;
System.out.println(a == b); // true bb use final modification , The compile time is known ,b It can be optimized to "ab"
String a = "ab";
final String bb = getBB();
String b = "a" + bb;
System.out.println(a == b); // false Method is used final modification , It also needs to generate dynamic link execution code at runtime , Therefore, the compilation time is unknown , Can't optimize
private static String getBB() {
return "b";
}
String str2 = new StringBuilder(" Computer ").append(" technology ").toString();
System.out.println(str2 == str2.intern()); //true
// str2 Equal to the objects in the heap " Computer technology ", Because there is no literal " Computer technology ", So this object does not exist in the constant pool .
// str2.intern() The reference to the heap object in the returned string constant pool , So it's the same object
String str1 = new StringBuilder("ja").append("va").toString();
System.out.println(str1 == str1.intern()); //false
// java Is the key word , stay JVM The initialized related classes are put into the string constant pool .
String s1=new String("test");
System.out.println(s1==s1.intern()); //false
// new The object that comes out already exists in the constant pool ,s1.intern() Returns an object from a constant pool .
//5 Plastic packaging Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Character The object of ,
// When the value is less than 127 You can use the object pool
Integer i1 = 127; // The underlying layer of this call is actually executed Integer.valueOf(127), It uses IntegerCache Object pool
Integer i2 = 127;
System.out.println(i1 == i2);// Output true
// Greater than 127 when , No objects are taken from the object pool
Integer i3 = 128;
Integer i4 = 128;
System.out.println(i3 == i4);// Output false
// use new Keywords newly generated objects do not use object pools
Integer i5 = new Integer(127);
Integer i6 = new Integer(127);
Integer i7 = 127;
System.out.println(i5 == i6);// Output false
System.out.println(i5 == i7);// Output false
//Boolean Class also implements object pooling Technology
Boolean bool1 = true;
Boolean bool2 = true;
System.out.println(bool1 == bool2);// Output true
// Floating point wrapper classes don't implement object pooling
Double d1 = 1.0;
Double d2 = 1.0;
System.out.println(d1 == d2);// Output false边栏推荐
- Mobile measurement and depth link platform - Branch
- PIP download only, not install
- 维护万星开源向量数据库是什么体验
- Preprocessing - interpolation
- 太方便了,钉钉上就可完成代码发布审批啦!
- 复杂因子计算优化案例:深度不平衡、买卖压力指标、波动率计算
- HW-小记(二)
- tflite模型转换和量化
- QT opens a file and uses QFileDialog to obtain the file name, content, etc
- Confirm the future development route! Digital economy, digital transformation, data This meeting is very important
猜你喜欢

Summer 2022 daily question 1 (1)
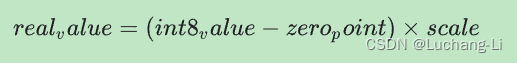
tflite模型转换和量化

map和set的实现

QT 使用QToolTip 鼠标放上去显示文字时会把按钮的图片也显示了、修改提示文字样式
Ubuntu20 installation redisjson record
数据的存储
Baidu map JS development, open a blank, bmapgl is not defined, err_ FILE_ NOT_ FOUND
Do you choose pandas or SQL for the top 1 of data analysis in your mind?
My brave way to line -- elaborate on what happens when the browser enters the URL
![[dpdk] dpdk sample source code analysis III: dpdk-l3fwd_ 001](/img/f6/dced69ea36fc95ef84bb546c56dd91.png)
[dpdk] dpdk sample source code analysis III: dpdk-l3fwd_ 001
随机推荐
海思万能平台搭建:颜色空间转换YUV2RGB
机器学习笔记 - 使用机器学习进行鸟类物种分类
你心目中的数据分析 Top 1 选 Pandas 还是选 SQL?
SSL certificate deployment
On file uploading of network security
MySQL storage engine
25. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS line modification line editing (sketchviewmodel)
When QT uses qtooltip mouse to display text, the picture of the button will also be displayed and the prompt text style will be modified
20. (ArcGIS API for JS) ArcGIS API for JS surface collection (sketchviewmodel)
Confirm the future development route! Digital economy, digital transformation, data This meeting is very important
[hcie TAC] question 3
Ubuntu20 installation redisjson record
Sorting operation partition, argpartition, sort, argsort in numpy
About Confidence Intervals
QT 使用QToolTip 鼠标放上去显示文字时会把按钮的图片也显示了、修改提示文字样式
Arduino droplet detection
Huawei and Xiaomi "copy each other"
Code quality management
Kbone与小程序跨端开发的一些思考
MySQL的存储引擎