当前位置:网站首页>Deep dive kotlin synergy (19): flow overview
Deep dive kotlin synergy (19): flow overview
2022-07-03 03:59:00 【RikkaTheWorld】
Series eBook : Portal
Flow It means A data flow for asynchronous computing .Flow The interface itself allows only those flowing elements to be collected , This means that each element only reaches the end of the flow , We'll deal with them (Flow Of collect Similar to a collection forEach).
interface Flow<out T> {
suspend fun collect(collector: FlowCollector<T>)
}
You can see , collect yes Flow The only member function in . Other functions are defined as extension functions . This is related to Iterable or Sequence similar , They all have iterator As a member function .
interface Iterable<out T> {
operator fun iterator(): Iterator<T>
}
interface Sequence<out T> {
operator fun iterator(): Iterator<T>
}
flow vs Other ways of representing data
For the use of RxJava or Reactor For people who , The concept of flow should be their most familiar , But for other unfamiliar people , A better explanation may be needed .
Suppose you need a function to return multiple values , If these values are provided at the same time , We will use things like List and Set Such a collection .
fun allUsers(): List<User> =
api.getAllUsers().map {
it.toUser() }
The essence here is List and Set Represents a fully computed set . Processing these values takes time , So we need to wait for all the values to be processed , Then you can get them .
fun getList(): List<Int> = List(3) {
Thread.sleep(1000)
"User$it"
}
fun main() {
val list = getList()
println("Function started")
list.forEach {
println(it) }
}
// (3 sec)
// Function started
// User0
// User1
// User2
If the elements appear one after another , One method we will use is Sequence.
fun getSequence(): Sequence<String> = sequence {
repeat(3) {
Thread.sleep(1000)
yield("User$it")
}
}
fun main() {
val list = getSequence()
println("Function started")
list.forEach {
println(it) }
}
// Function started
// (1 sec)
// User0
// (1 sec)
// User1
// (1 sec)
// User2
When the calculation may be CPU intensive ( For example, calculate complex results ) Or blocked ( Such as reading files ) When , Sequence is a suitable data flow for on-demand calculation . however , You have to know Terminal operation of the sequence ( Such as forEach) It won't hang , So any Hang in the sequence builder means blocking the waiting thread to process this value . Is that why sequence In the scope of the builder , In addition to the SequenceScope Functions called on the receiver (yield and yieldAll) Outside , You cannot use any pending functions .
fun getSequence(): Sequence<String> = sequence {
repeat(3) {
delay(1000) // There is a compilation error
yield("User$it")
}
}
This mechanism is introduced to prevent the sequence from being misused . for example , Someone may want to use paging from Http Port to get a list of all users , Until you receive blank data .
Even if the above example can be compiled , It won't be right , Because of terminal operation ( Such as forEach) The thread will be blocked instead of suspended , This may cause unexpected thread blocking .
// Don't do this , We should use Flow Instead of Sequence
fun allUsersSequence(
api: UserApi
): Sequence<User> = sequence {
var page = 0
do {
val users = api.takePage(page++) // Hang up , So compilation error
yieldAll(users)
} while (!users.isNullOrEmpty())
}
I hope you've learned that thread blocking can be dangerous , Will lead to unexpected situations , To make this clearer , Take a look at the following example , We use Sequence, So it's forEach It's a blocking operation . That's why a coroutine started on the same thread waits , The execution of one process will block the execution of another process :
fun getSequence(): Sequence<String> = sequence {
repeat(3) {
Thread.sleep(1000)
// Even if it can be used here delay(1000) , The result is the same
yield("User$it")
}
}
suspend fun main() {
withContext(newSingleThreadContext("main")) {
launch {
repeat(3) {
delay(100)
println("Processing on coroutine")
}
}
val list = getSequence()
list.forEach {
println(it) }
}
}
// (1 sec)
// User0
// (1 sec)
// User1
// (1 sec)
// User2
// Processing on coroutine
// (0.1 sec)
// Processing on coroutine
// (0.1 sec)
// Processing on coroutine
under these circumstances , We should use Flow instead of Sequence. It fully supports synergy . Its builder and operation can be suspended , And support structured concurrency and appropriate exception handling . We will explain these in the next chapter . But now let's see how it helps this case .
fun getFlow(): Flow<String> = flow {
repeat(3) {
delay(1000)
emit("User$it")
}
}
suspend fun main() {
withContext(newSingleThreadContext("main")) {
launch {
repeat(3) {
delay(100)
println("Processing on coroutine")
}
}
val list = getFlow()
list.collect {
println(it) }
}
}
// (0.1 sec)
// Processing on coroutine
// (0.1 sec)
// Processing on coroutine
// (0.1 sec)
// Processing on coroutine
// (1 - 3 * 0.1 = 0.7 sec)
// User0
// (1 sec)
// User1
// (1 sec)
// User2
Flow It should be used for data flows that need to use coroutines . for example , It can be used to generate a from API Page by page user flow . for example , If we call allUserFlow(api).first(), We will get to the first page ; If we call allUserFlow(api).toList() , We will get all the data ; If we call allUserFlow(api).find { it.id == id }, We will always pull the page data , Until we find the page we want to find .
fun allUsersFlow(
api: UserApi
): Flow<User> = flow {
var page = 0
do {
val users = api.takePage(page++) // Hang up
emitAll(users)
} while (!users.isNullOrEmpty())
}
Flow Characteristics of
Flow Terminal operation of ( Such as collect) A collaboration will be suspended , Instead of blocking threads . They also support other coroutine functions , For example, exception handling .Flow Processing can be cancelled , And it can support structured concurrency externally . flow The builder will not hang , No scope is required .
The following example shows CoroutineName How context is passed from the collection to flow In the builder . It also shows that ,launch The cancellation of will also lead to flow The processing of is cancelled .
// Be careful , This function will not hang , And you don't need any CoroutineScope
fun usersFlow(): Flow<String> = flow {
repeat(3) {
delay(1000)
val ctx = currentCoroutineContext()
val name = ctx[CoroutineName]?.name
emit("User$it in $name")
}
}
suspend fun main() {
val users = usersFlow()
withContext(CoroutineName("Name")) {
val job = launch {
// collect It's suspended
users.collect {
println(it) }
}
launch {
delay(2100)
println("I got enough")
job.cancel()
}
}
}
// (1 sec)
// User0 in Name
// (1 sec)
// User1 in Name
// (0.1 sec)
// I got enough
Flow Nomenclature
- Flow Need to start somewhere , It usually starts with a flow builder , From different objects or from some helper Function to , The most important options are explained in the next chapter
- Flow The last operation on is called terminal operation , This is very important , Because it is usually the only suspended function , Or you need the operation of the scope of the collaboration . A typical terminal operation is
collect. However , There are other terminal operations , I will explain in the following chapters - Between start operation and terminal operation , We may have intermediate operations , Each operation modifies the flow in some way , We will be in Flow Life cycle of and Handle Flow Learn different intermediate operations in the chapter of

The actual cases
Practice shows , What we need more often is flow, instead of channel. If request data flow , We usually want to request on demand . If you need to observe something , For example, changes in the database or from UI Perception of components , You may want every observer to receive these events . When no one wants to observe , You should also stop listening . This is why in all these cases , Use flow It's better than using channel Better ( Although in some cases , We mix the two ).
flow The most typical uses include :
- Receive from Server Messages sent in the connectivity channel , Such as WebSocket、 Notice, etc
- Observe the user's actions , Such as text change or click
- Receive updates of other information from sensors or devices , Such as position or direction
- Observe the changes in the database
Here's how we use Room Library to observe SQL Database changes :
@Dao
interface MyDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM somedata_table")
fun getData(): Flow<List<SomeData>>
}
Let's look at some examples , See how to use it flow To deal with from API Response flow for . First , Suppose you implement the chat function , The message passes Server Channel and notification sending . Treat two data sources as a stream , Combine them together , Then use this flow to update the view , It's very convenient . Another example might be to use it to provide better and better response results . for example , When we're in SkyScanner When searching for the best flight on , Some quotations will arrive soon , But over time , There will be more and better quotations to reach , therefore , You will see better and better results . This is also used flow A good example of .
In addition to these circumstances , For different concurrent processing , flow It is also a useful tool . for example , Suppose you have a list of sellers , You need to get the quotation of each seller . We already know we can use async Implement this in set processing :
suspend fun getOffers(
sellers: List<Seller>
): List<Offer> = coroutineScope {
sellers
.map {
seller ->
async {
api.requestOffers(seller.id) }
}
.flatMap {
it.await() }
}
The above method is correct in many cases , But it has one drawback : When the seller list is large , Sending so many requests at once is not good for us or the server . Of course , This can be done by limiting frequency or current in the server , But we also want to control it on the client , So we can use Flow. under these circumstances , To limit the number of concurrent calls to 20 individual , We can use flaotMapMerge, And set the maximum concurrent number concurrency It is amended as follows 20:
suspend fun getOffers(
sellers: List<Seller>
): List<Offer> = sellers
.asFlow()
.flatMapMerge(concurrency = 20) {
seller ->
suspend {
api.requestOffers(seller.id) }.asFlow()
}
.toList()
Yes Flow Not a collection , Let's talk about concurrency 、 Context 、 Exceptions, etc. for more control . We will explore these features in the next chapter , This is it. ( In my experience ) flow The most useful place . I hope after we introduce all the different functions of it , You can clearly understand this .
Last , Because I prefer the style of responsive programming , Some teams prefer to use response flows rather than suspend functions . This style is in Android It's very popular on TV , among RxJava It's very mainstream , But now Flow Usually considered a better choice .
As you can see ,flow There are quite a few use cases . In some projects , They will be widely used , In other projects , They are only used occasionally . But I hope you know it's useful , It's worth learning .
summary
In this chapter , We introduced Flow The concept of . It expresses support for the process ( Different sequences ) Asynchronous data flow . In quite a few use cases ,flow It is useful to .
边栏推荐
- [Blue Bridge Road -- bug free code] interpretation of some codes of matrix keyboard
- Practical operation of vim
- Read a paper_ ChineseBert
- js/ts底层实现双击事件
- Table structure of Navicat export database
- For instruction, uploading pictures and display effect optimization of simple wechat applet development
- 【学习笔记】seckill-秒杀项目--(11)项目总结
- [mathematical logic] predicate logic (predicate logic basic equivalent | eliminate quantifier equivalent | quantifier negative equivalent | quantifier scope contraction expansion equivalent | quantifi
- eth入门之简介
- How to move towards IPv6: IPv6 Transition Technology - Shangwen network quigo
猜你喜欢

What can learning pytorch do?
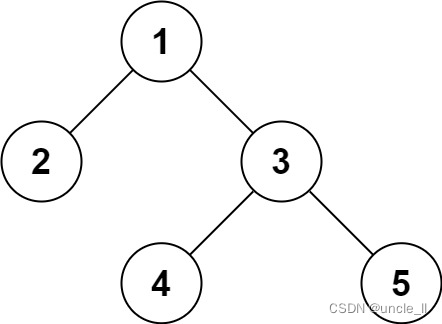
leetcode:297. Serialization and deserialization of binary tree
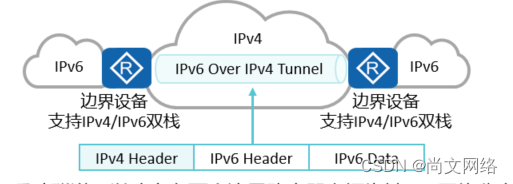
How to move towards IPv6: IPv6 Transition Technology - Shangwen network quigo
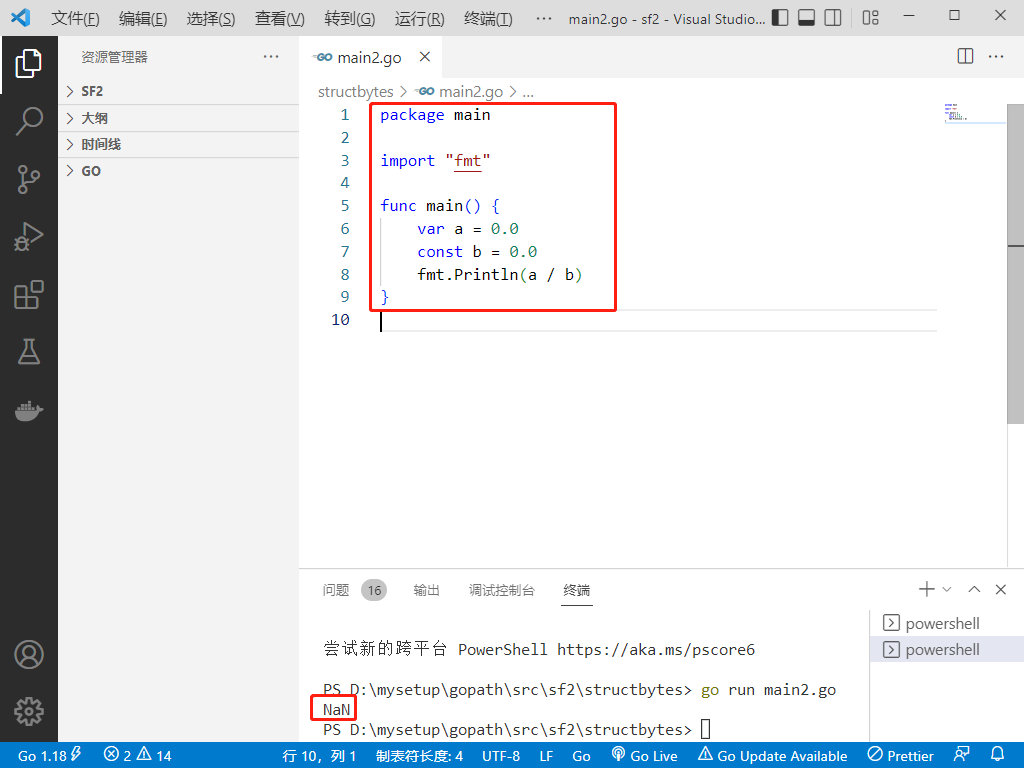
2022-07-02:以下go语言代码输出什么?A:编译错误;B:Panic;C:NaN。 package main import “fmt“ func main() { var a =

Cnopendata China Customs Statistics
Makefile demo
![[brush questions] connected with rainwater (one dimension)](/img/21/318fcb444b17be887562f4a9c1fac2.png)
[brush questions] connected with rainwater (one dimension)
105. SAP UI5 Master-Detail 布局模式的联动效果实现明细介绍

Wechat applet + Alibaba IOT platform + Hezhou air724ug build a serverless IOT system (III) -- wechat applet is directly connected to Alibaba IOT platform aliiot

pytorch项目怎么跑?
随机推荐
MySQL MAC download and installation tutorial
错误 C2694 “void Logger::log(nvinfer1::ILogger::Severity,const char *)”: 重写虚函数的限制性异常规范比基类虚成员函数
In Net 6 project using startup cs
Without sxid, suid & sgid will be in danger- Shangwen network xUP Nange
【学习笔记】seckill-秒杀项目--(11)项目总结
[mathematical logic] predicate logic (first-order predicate logic formula | example)
Recursive use and multi-dimensional array object to one-dimensional array object
eth入门之简介
Dynamic programming: Longest palindrome substring and subsequence
Hutool动态添加定时任务
[brush questions] most elements (super water king problem)
2022 Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination questions and Shandong Province safety officer C certificate simulation examination question bank
How to execute a swift for in loop in one step- How can I do a Swift for-in loop with a step?
[Blue Bridge Road - bug free code] pcf8591 - code analysis of AD conversion
中移物联网OneOS与OneNET入选《2021年物联网示范项目名单》
递归:深度优先搜索
The 10th China Cloud Computing Conference · China Station: looking forward to the trend of science and technology in the next decade
leetcode:297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
"Final review" 16/32-bit microprocessor (8086) basic register
[mathematical logic] predicate logic (judge whether the first-order predicate logic formula is true or false | explain | example | predicate logic formula type | forever true | forever false | satisfi