当前位置:网站首页>Exploring shared representations for personalized federated learning paper notes + code interpretation
Exploring shared representations for personalized federated learning paper notes + code interpretation
2022-06-12 07:18:00 【Programmer long】
The address of the paper is here
One . Introduce
In federated learning, due to the heterogeneous data on each client , As a result, the global training model cannot meet the requirements of each client . The author solves this problem by using the common representatives between clients . say concretely , The Federative learning problem with heterogeneous data is regarded as a parallel learning task , There may be some common structure between these tasks , The author's goal is to learn and utilize this common representation to improve the model quality of each client , Based on this, this paper puts forward FedRep( Federation represents learning ).
FedRep: Federation means learning to leverage all data stored across clients , Use gradient based updates to learn global low dimensional representations . Besides , Enables each client to compute a personalized 、 Low dimensional classifier , Responsible for the unique identification of local data for each client .
Two . Problem definition
Traditional federalism learns from n Optimize the following targets on clients :
min ( q 1 , . . . , q n ) ∈ Q n 1 n ∑ i = 1 n f i ( q i ) \min_{(q_1,...,q_n)\in\mathcal{Q_n}}\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^nf_i(q_i) (q1,...,qn)∈Qnminn1i=1∑nfi(qi)
among f i f_i fi It means the first one i Loss functions on clients , q i q_i qi It means the first one i Models on clients . However, there is less data on the client , At the same time, the number of clients is huge , The client cannot learn a model with a small loss , Therefore, federated learning allows parameter interaction between clients . The traditional way is to let the client learn a common model , That is to say q 1 = q 2 = . . . = q n q_1=q_2=...=q_n q1=q2=...=qn, But when the client data is obviously heterogeneous , The client model should be closer to the local data . So we need to learn a group { q i } \{q_i\} { qi} Make it satisfied with its own data .
Learn a common expression (Learning a Common Representation). We consider a global representation ϕ : R d → R k \phi:\mathbb{R}^d \to \mathbb{R}^k ϕ:Rd→Rk, Map data to a lower dimension k; Special presentation header of the client : R k → Y \mathbb{R}^k \to \mathcal{Y} Rk→Y. According to this , The first i A model on a client is a combination of local parameters and global representations on the client : q i ( x ) = ( h i ∘ ϕ ) ( x ) q_i(x)=(h_i \circ\phi)(x) qi(x)=(hi∘ϕ)(x). It is worth noting that ,k Far less than d, That is to say, the number of parameters that each client must learn locally is very small . We rewrite our global optimization objectives according to the new content :
min ϕ ∈ Φ 1 n ∑ i = 1 n min h i ∈ H f i ( h i ∘ ϕ ) \min_{\phi \in \Phi}\frac{1}{n}\sum_{i=1}^n\min_{h_i\in\mathcal{H}}f_i({h_i} \circ\phi) ϕ∈Φminn1i=1∑nhi∈Hminfi(hi∘ϕ)
among Φ \Phi Φ Is a feasible representation class , and H \mathcal{H} H Is a feasible header . The client uses the data of all customers to learn the global model , At the same time, use your own local information to learn personalized headers .
3、 ... and . FedRep Algorithm
The algorithm idea is shown in the figure :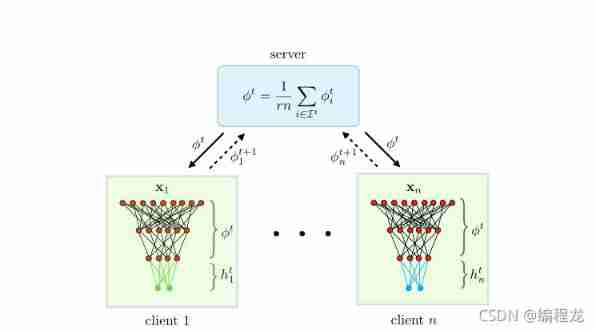
Server and client learn together ϕ \phi ϕ, The client learns its own parameter headers h h h.
Client update : In every round , The selected client is trained . These clients come from the server ϕ i \phi_i ϕi Update your own h i h_i hi, as follows :
h i t , s = G R D ( f i ( h i t , s − 1 , ϕ t ) , h i t , s − 1 , α ) h_i^{t,s} = GRD(f_i(h_i^{t,s-1},\phi^t),h_i^{t,s-1},\alpha) hit,s=GRD(fi(hit,s−1,ϕt),hit,s−1,α)
GRD Is an optimal representation of gradient descent , It means that we have a set of parameters h stay f Use a gradient descent to α \alpha α Update for step size . After training τ h \tau_h τh Step update h after , We are the same ϕ \phi ϕ Conduct τ ϕ \tau_\phi τϕ Secondary update , as follows :
ϕ i t , s = G R D ( f i ( h i t , τ h , ϕ i t , s − 1 ) , ϕ i t , s − 1 , α ) \phi_i^{t,s}=GRD(f_i(h_i^{t,\tau_h},\phi_i^{t,s-1}),\phi_i^{t,s-1},\alpha) ϕit,s=GRD(fi(hit,τh,ϕit,s−1),ϕit,s−1,α)
Server update : After the client completes the update, it returns to the server ϕ i t , τ ϕ \phi_i^{t,\tau_\phi} ϕit,τϕ, After the service end is aggregated, it is averaged .
The algorithm is shown in the figure below :
Four . Code details
The author's code points here
I believe that this article should not be difficult to understand , That is, it can be processed once in layers .
First , The main concern is how to layer . According to the idea , We need to divide into rep Layer and the head layer ,head For your own parameters .rep Is to participate in sharing , Before layering , Let's take a look at the Internet :
class CNNCifar100(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, args):
super(CNNCifar100, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.6)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(128 * 5 * 5, 256)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, args.num_classes)
self.cls = args.num_classes
self.weight_keys = [['fc1.weight', 'fc1.bias'],
['fc2.weight', 'fc2.bias'],
['fc3.weight', 'fc3.bias'],
['conv2.weight', 'conv2.bias'],
['conv1.weight', 'conv1.bias'],
]
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 128 * 5 * 5)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.drop((F.relu(self.fc2(x))))
x = self.fc3(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
A very simple one CNN The Internet , We store the names of each layer , Facilitate layering .
if args.alg == 'fedrep' or args.alg == 'fedper':
if 'cifar' in args.dataset:
w_glob_keys = [net_glob.weight_keys[i] for i in [0,1,3,4]]
elif 'mnist' in args.dataset:
w_glob_keys = [net_glob.weight_keys[i] for i in [0,1,2]]
elif 'sent140' in args.dataset:
w_glob_keys = [net_keys[i] for i in [0,1,2,3,4,5]]
else:
w_glob_keys = net_keys[:-2]
Here is a brief hierarchical operation , You can see that for us to deal with cifar100 Words ,rep Layer get yes 0 1 3 4, The corresponding is except fc3 The last floor of . So the last layer is head, Others are rep.
Then start training , Training is to obtain the parameters of the server for the client rep Add your own parameters head, The code is :
if args.alg != 'fedavg' and args.alg != 'prox':
for k in w_locals[idx].keys():
if k not in w_glob_keys:
w_local[k] = w_locals[idx][k]
among w_glob_keys Namely rep Parameters of ,w_local For all parameters .
The last is training :
for iter in range(local_eps):
done = False
# for FedRep, First we train head Fix rep, A few rounds of training
if (iter < head_eps and self.args.alg == 'fedrep') or last:
for name, param in net.named_parameters():
if name in w_glob_keys:
param.requires_grad = False
else:
param.requires_grad = True
# Then train rep Fix head
elif iter == head_eps and self.args.alg == 'fedrep' and not last:
for name, param in net.named_parameters():
if name in w_glob_keys:
param.requires_grad = True
else:
param.requires_grad = False
边栏推荐
- libprint2
- 基于eNSP加防火墙的千人中型校园/企业网络规划与设计(附所有配置命令)
- 初中学历,从不到3K,到月薪30K+,不设限的人生有多精彩
- Learning to continuously learn paper notes + code interpretation
- Day 5 of pyhon
- 8 IO Library
- esp32 hosted
- The most understandable explanation of coordinate transformation (push to + diagram)
- Vscode outline preview cannot find file symbol
- [image detection] SAR image change detection based on depth difference and pcanet with matlab code
猜你喜欢

Detailed explanation of memory addressing in 8086 real address mode

Pyhon的第四天
![[data clustering] data set, visualization and precautions are involved in this column](/img/46/0b4918ef9c9301fbc374913fe806de.png)
[data clustering] data set, visualization and precautions are involved in this column
Complete set of typescript Basics
Postman splice replacement parameter loop call interface

Planning and design of 1000 person medium-sized campus / enterprise network based on ENSP and firewall (with all configuration commands)

企业微信官方 加解密库 PHP7版本报错 mcrypt_module_open 未定义方法 并且被PHP抛弃 解决方法使用 openssl解决
![[image denoising] salt and pepper noise image denoising based on Gaussian filter, mean filter, median filter and bilateral filter with matlab code attached](/img/f2/16db0b11d4e69946ec45b67ab41b81.png)
[image denoising] salt and pepper noise image denoising based on Gaussian filter, mean filter, median filter and bilateral filter with matlab code attached

AI狂想|来这场大会,一起盘盘 AI 的新工具!

Principle and application of PWM
随机推荐
2022起重机械指挥考试题模拟考试平台操作
Explain in detail the use of dynamic parameter adjustment and topic communication in ROS (principle + code + example)
1. Foundation of MySQL database (1- installation and basic operation)
D cannot use a non CTFE pointer
右击文件转圈卡住、刷新、白屏、闪退、桌面崩溃的通用解决方法
esp32 hosted
8 IO Library
基于eNSP加防火墙的千人中型校园/企业网络规划与设计(附所有配置命令)
9 Sequence container
Putty installation and use
Explain ADC in stm32
Descscheduler secondary scheduling makes kubernetes load more balanced
D
Kotlin plug-ins kotlin Android extensions
RT thread studio learning (x) mpu9250
[college entrance examination] prospective college students look at it, choose the direction and future, and grasp it by themselves
Demonstrate "topic communication, action communication, service communication and parameter server" with a small turtle case
Set up a remote Jupiter notebook
[wax chain tour] release a free and open source alien worlds script TLM
Android studio uses database to realize login and registration interface function