当前位置:网站首页>DRF JWT authentication module and self customization
DRF JWT authentication module and self customization
2020-11-06 01:29:00 【itread01】
JWT Module
stay djangorestframework in , There is an extension kit module that can be used for JWT Certification , Use the following command to install :
pip install djangorestframework-jwt
Now , Let's start using it .
JWT To configure
All configuration of the module will be from settings.py Read from , And drf The same thing , It will first read from the project global folder settings.py, And then read your own settings.py, So if we're going to do something about JWT Configure , In the project global folder settings.py You can configure it in :
import datetime
JWT_AUTH = {
# Configure expiration time
'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=7),
# The configuration request header carries token At the beginning of
'JWT_AUTH_HEADER_PREFIX': 'JWT',
}
If you want to know more about the configuration , You can view the default configuration file read by the module .
from rest_framework_jwt import settings
In the default configuration file , You can see the following code , It will go to the global first to find the configuration , Then go to the region to find the configuration :
USER_SETTINGS = getattr(settings, 'JWT_AUTH', None)
auth Components
Here's how to use auth Components and JWT Matching use of , It's very convenient of course ,auth Components can be said to be Django At the heart of .
I'm going to do this , For built-in user Table as extension kit , Add avatar field , Only after login can the user modify the avatar , Otherwise, the default avatar will be used .
Preparation work
First of all, we need to build in auth_user Table as extension kit , As shown below :
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser
class User(AbstractUser):
avatar = models.FileField(upload_to="avatar",default="avatar/default.png")
Secondly, configure the path to upload files , Declare media Where it is , And announcing our built-in auth_user The table has an extension kit :
MEDIA_ROOT = BASE_DIR / "media"
AUTH_USER_MODEL = "app01.User"
# python manage.py makemigrations
# python manage.py migrate
Finally, open the resource exposure interface :
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path,re_path
from django.views.static import serve
from django.conf import settings
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
re_path(r"^media/(?P<path>.*)", serve, {"document_root": settings.MEDIA_ROOT}),
]
Register API
Now , We need to do a registered API Interface , As shown below :
class Register(ViewSet):
def register(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
serializer = UserModelSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
serializer.save()
return Response(data=serializer.data,status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED)
return Response(data=serializer.errors,status=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED)
We can stipulate that register This method has to be POST Request access to , stay url Configuration in (ViewSet yes ViewSetMixin Subclasses of , So there is actions Arguments ):
path('register/', views.Register.as_view(actions={"post":"register"})),
Because of auth_user Your password needs ciphertext , So we rewrite the model serializer's create Method .
from rest_framework import serializers
from rest_framework.exceptions import ValidationError
from app01 import models
class UserModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
re_password = serializers.CharField(required=True, write_only=True)
# This field does not exist in the table , Let's write one ourselves
class Meta:
model = models.User
fields = ("username","password","re_password","email")
extra_kwargs = {
"password":{"write_only":True}
}
def create(self, validated_data):
password = validated_data.get("password")
re_password = validated_data.get("re_password")
email = validated_data.get("email")
if re_password != password:
raise ValidationError(" The two passwords are not the same ")
if models.User.objects.filter(email=email):
raise ValidationError(" Email has been registered ")
validated_data.pop("re_password") # Delete it , Then write
user_obj = models.User.objects.create_user(**validated_data) # Encryption establishment
return user_obj
Sign off token
The next step is to implement the login interface , If you use auth As an extension kit, the login interface will be very simple .
JWT The module has been completed for you , You just need to do this down here :
from rest_framework_jwt.views import obtain_jwt_token # Import view , It's all written , And will do verification
from rest_framework_jwt.views import ObtainJSONWebToken # It's a variable , The inside is actually obtain_jwt_token=ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', obtain_jwt_token),
# path('login/', ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()),
]
Now , When we send the POST On request , If all the checks pass , Will send us a JWT
eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyX2lkIjozLCJ1c2VybmFtZSI6Inl1bnlhIiwiZXhwIjoxNjA0NTYyMzcyLCJlbWFpbCI6IjIzMjNAcXEuY29tIn0._SmZ0e0mj5QVOKUftAwI3xBX4_BOw1ZNjAi94_U3mXg
JWT Certification
Now let's modify the avatar , The avatar must be logged in before it can be modified , So we need to add JWT Certification .
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated # Import license
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication # Import Authentication
class SetAvatar(ViewSet):
authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication] # Store in request.user, If you only configure this , You can't log in
permission_classes = [IsAuthenticated] # It has to be logged in , namely request.user Can't be anonymous
def set_avatar(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
serializer = UserSetAvatar(instance=request.user,data=request.FILES)
if serializer.is_valid():
serializer.save()
return Response(data=" Modification successful ",status=status.HTTP_205_RESET_CONTENT)
return Response(data=" Modification failed ",status=status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED)
The sequence classes are as follows :
class UserSetAvatar(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.User
fields = ("avatar",)
extra_kwargs = {
"avatar":{"write_only":True},
}
url To configure :
path('setavatar/', views.SetAvatar.as_view(actions={"post":"set_avatar"})),
Now , We use POSTMAN To send a request , First log in first , Get JWT:

Then you need to add... To the request header JWT Certification , And in body New head portrait added to the body :
It should be noted that there is a new JWT At the time of certification , Need to be in VALUE Add prefix at JWT Random string , Submit in this format , This is because settings.py The prefix is set in .


Finally, click send, It will prompt us that the modification is successful .
Global use
Use it globally JWT Certification , The way is as follows , It will work on all views :
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Authentication module
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication',
),
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES':{
'rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',
}
}
If you want to disable authentication for a view , Then add an empty list :
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
Regional use. See Synonyms at JWT Writing in certification .
JWT Authentication is customized by returning information
In the example above , We can see that after the user logs in , There is only one return message JWT String , Then, can we return the login user name ? It's OK, too .
jwt_response_payload_handler() This function controls the return format , We can override it and then we can do it in settings.py Configuration in .
As shown below :
def jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user=None, request=None):
return {
'status': 0,
'msg': 'ok',
'data': {
'token': token,
'user': UserModelSerializers(user).data
}
}
stay settings.py Configuration in , This configuration is configured in REST_FRAMEWORK in , instead of JWT_AUTH in , Be sure to pay attention to :
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Configure the information returned after successful login
'JWT_RESPONSE_PAYLOAD_HANDLER':"utils.jwt_response_payload_handler",
}
The result of login is as follows :
{
"token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJ1c2VyX2lkIjozLCJ1c2VybmFtZSI6Inl1bnlhIiwiZXhwIjoxNjA0NTY0Njk3LCJlbWFpbCI6IjIzMjNAcXEuY29tIn0.cvmM6LvoVkSQETybss3fVVGZNXT099o8U21tzDvdFe4",
"username": "yunya"
}
JWT Certification process source code reading
It's time to read the source code happily again , So JWT The original code is relatively simple , Let's take a look at .
Issuance process
First , Let's analyze why we only wrote the following login interface , I didn't even write a review , You can sign and issue .
from rest_framework_jwt.views import obtain_jwt_token # Import view , It's all written , And will do verification
from rest_framework_jwt.views import ObtainJSONWebToken # It's a variable , The inside is actually obtain_jwt_token=ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()
urlpatterns = [
path('login/', obtain_jwt_token),
]
First look at obtain_jwt_token, You can find this code :
obtain_jwt_token = ObtainJSONWebToken.as_view()
We found a ObtainJSONWebToken This class , It will execute as_view() Method , I don't care , See who it inherits :

It inherited JSONWebTokenAPIView, And this class inherits APIView, So this APIView We've read the source code of our view more than five times , You can view previous articles . Let's look directly at the authentication of login ,JSONWebTOkenAPIView In the implementation of a post Method :
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data) # You can see that it has a built-in serializer
if serializer.is_valid(): # Direct verification
user = serializer.object.get('user') or request.user
token = serializer.object.get('token')
response_data = jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user, request)
response = Response(response_data)
if api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE:
expiration = (datetime.utcnow() +
api_settings.JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA)
response.set_cookie(api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE,
token,
expires=expiration,
httponly=True)
return response
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
Now you see the serializer, right , The serializer is actually here :
class ObtainJSONWebToken(JSONWebTokenAPIView):
serializer_class = JSONWebTokenSerializer
This is the source code of the serializer , stay __init__ Method to implement the field :
class JSONWebTokenSerializer(Serializer):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(JSONWebTokenSerializer, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.fields[self.username_field] = serializers.CharField() # username Hurdles
self.fields['password'] = PasswordField(write_only=True) # password Hurdles
@property
def username_field(self):
return get_username_field()
def validate(self, attrs):
credentials = {
self.username_field: attrs.get(self.username_field),
'password': attrs.get('password')
}
if all(credentials.values()):
user = authenticate(**credentials) # Here's executing authentication .
if user:
if not user.is_active:
msg = _('User account is disabled.')
raise serializers.ValidationError(msg)
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) # Get load information
return {
'token': jwt_encode_handler(payload), # Load information put in , To generate JWT Of token String
'user': user
}
else:
msg = _('Unable to log in with provided credentials.')
raise serializers.ValidationError(msg)
else:
msg = _('Must include "{username_field}" and "password".')
msg = msg.format(username_field=self.username_field)
raise serializers.ValidationError(msg)
That is to say , In execution JSONWebTOkenAPIView Of post() When the method is used , I'll go through a database query , Get the user object according to the submitted user name and password . And in the serializer , Will generate token() Information . They are all configured functions :
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
jwt_decode_handler = api_settings.JWT_DECODE_HANDLER
jwt_get_username_from_payload = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_GET_USERNAME_HANDLER
( Can we write a validation class to override it , Then it is used for login ? Cell phone number , Email, etc. can be logged in )
Let's continue to see post() Method :
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data) # You can see that it has a built-in serializer
if serializer.is_valid(): # Direct verification
user = serializer.object.get('user') or request.user # request.user It is equivalent to the logged in user
token = serializer.object.get('token') # token Equal to generated jwt Random string
response_data = jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user, request) # Set return information
response = Response(response_data)
if api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE: # Not set , Don't go
expiration = (datetime.utcnow() +
api_settings.JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA)
response.set_cookie(api_settings.JWT_AUTH_COOKIE,
token,
expires=expiration,
httponly=True)
return response # Go straight back to
return Response(serializer.errors, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST) # Failed to verify
OK, The automatic sign off process is over .
Maybe a wisp of , It has its own serializer , And it's done in the serializer JWT String splicing , Finally, go back .
Validation process
Now let's take a look at , When the user logs in , The verification process for revisiting , At the beginning, I must take certification :
authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication]
We all know , stay APIView Medium dispatch() Methods initial() In the method , There will be the following three codes :
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
# Detailed execution steps of these three codes , Especially certification , You can view previous articles
That's authentication first , When you go through authentication, you will execute a authenticators() Methods . Let's go straight to JSONWebTokenAuthentication Medium authenticators() The method can .
This class doesn't have authenticators() This method , So who does it inherit from ?
class JSONWebTokenAuthentication(BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication):
So what we're looking for is actually BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication Medium authenticators() Method .
Finally , eureka :
def authenticate(self, request):
jwt_value = self.get_jwt_value(request) # Get jwt String , To analyze . That is to say [ JWT String ], The content of this string , Exclude prefix , If you are interested, you can have a look at
if jwt_value is None:
return None # If not JWT Validation string , Then return to None
try: # A series of exception catches , All from built-in jwt Module
payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value) # Decode the load part
except jwt.ExpiredSignature:
msg = _('Signature has expired.') # The visa has expired
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
except jwt.DecodeError:
msg = _('Error decoding signature.') # Error decoding visa
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed() # Invalid token
user = self.authenticate_credentials(payload) # If nothing goes wrong , Then execute here
return (user, jwt_value) # return user thing , This will be assigned to reque.user, This meeting jwt The string is assigned to request.auth
=================Request.user About license authentication
for authenticator in self.authenticators:
try:
user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) # There will be a return here user
except exceptions.APIException:
self._not_authenticated()
raise
if user_auth_tuple is not None:
self._authenticator = authenticator
self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple # Assign self.user=user ,self.auth = jwt_value
return
Let's see user How did it come out . It's in BaseJSONWebTokenAuthentication Class :
def authenticate_credentials(self, payload):
User = get_user_model() # Back to the model !! It's not a record object , Through settings.py Medium AUTH_USER_MODEL To acquire
username = jwt_get_username_from_payload(payload) # Get payload User name in
if not username: # If there is no user name, throw an exception
msg = _('Invalid payload.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
try: # According to the user name in the load , In the model User Trying to retrieve the user's record object in , That is to say, database query will be used here .
user = User.objects.get_by_natural_key(username)
except User.DoesNotExist: # If User If this model doesn't exist, throw the exception , Explain
msg = _('Invalid signature.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
if not user.is_active: # Determine whether the account is disabled
msg = _('User account is disabled.')
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(msg)
return user # return user
no need auth Components
After reading the source code analysis above , Let's think about it again , If not auth What to do with the module ?
It's also very simple , We made our own jwt Then the token This random string will return .
When authenticating, we can rewrite the authentication class , It's all that logic anyway .
Manual sign off
We need to have... In our watch username as well as password Hurdles , Use JWT Module token Several functions of , Make your own token.
# views.py
from rest_framework_jwt.settings import api_settings
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
from users.models import User
class LoginView(APIView): # Sign and sign when you log in token
authentication_classes = []
def post(self,request):
username=request.data.get('username')
password=request.data.get('password')
user=User.objects.filter(username=username,password=password).first()
if user: # We can find out , Login successful , Manual sign off
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user)
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload)
return CommonResponse('100',' Login successful ',data={'token':token})
else:
return CommonResponse('101', ' Login failed ')
If you want to implement multiple login , Cell phones 、 User name 、 Email, etc. can log in , There's also a code here , It's just used with the serializer , It's more complicated :
# Use the user name , Cell phone number , Email , You can log in to #
# The data format that the front end needs to transmit
{
"username":"lqz/1332323223/[email protected]", # User name 、 Or cell phone number 、 Or email
"password":"lqz12345"
}
# Look at
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.viewsets import ViewSetMixin, ViewSet
from app02 import ser
class Login2View(ViewSet): # Exactly the same as above
def login(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 1 need There's a serialized class
login_ser = ser.LoginModelSerializer(data=request.data,context={'request':request}) # context Arguments are similar to pipes , Connect to the serializer
# 2 Generate serialization class objects
# 3 Calling the serial number object is_validad
login_ser.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
token=login_ser.context.get('token') # Take out of the pipe token And return
# 4 return
return Response({'status':100,'msg':' Login successful ','token':token,'username':login_ser.context.get('username')})
# Serialization class
from rest_framework import serializers
from api import models
import re
from rest_framework.exceptions import ValidationError
from rest_framework_jwt.utils import jwt_encode_handler,jwt_payload_handler
class LoginModelSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
username=serializers.CharField() # Re cover username Hurdles , In the data, it is unique,post, Think you store data , I have my own verification
class Meta:
model=models.User
fields=['username','password']
def validate(self, attrs):
print(self.context)
# Write logic here
username=attrs.get('username') # There are three ways to use a user name
password=attrs.get('password')
# By judgment ,username The information is different , The query fields are different
# Regular matching , If it's a cell phone number
if re.match('^1[3-9][0-9]{9}$',username):
user=models.User.objects.filter(mobile=username).first()
elif re.match('^[email protected]+$',username):# Email
user=models.User.objects.filter(email=username).first()
else:
user=models.User.objects.filter(username=username).first()
if user: # There are users
# Verify password , Because it's ciphertext , Use check_password
if user.check_password(password):
# Sign off token
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) # hold user Incoming , obtain payload
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload) # hold payload Incoming , obtain token
self.context['token']=token
self.context['username']=user.username
return attrs
else:
raise ValidationError(' Password error ')
else:
raise ValidationError(' User does not exist ')
JWT Verification
When verifying , Inherit BaseAuthentication Class , Rewrite the validation method :
# app_auth.py
from users.models import User
class MyJSONWebTokenAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
jwt_value = get_authorization_header(request)
if not jwt_value:
raise AuthenticationFailed('Authorization Fields are required ')
try:
payload = jwt_decode_handler(jwt_value)
except jwt.ExpiredSignature:
raise AuthenticationFailed(' Signature expired ')
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
raise AuthenticationFailed(' Illegal users ')
username = jwt_get_username_from_payload(payload)
print(username)
user = User.objects.filter(username=username).first()
print(user)
return user, jwt_value
Then one of your views must be logged in before it can be accessed , Add it to the certification OK 了 .
from users.app_auth import JSONWebTokenAuthentication,MyJSONWebTokenAuthentication
class OrderView(APIView):
# authentication_classes = [JSONWebTokenAuthentication] # You don't have to preset it , With our own
authentication_classes = [MyJSONWebTokenAuthentication] # Because it's not auth_user surface , So there's no need to judge whether it's an anonymous user .
def get(self,request):
print(request.user)
return CommonResponse('100', ' success ',{' Information ':' Test '})
Finally, I want to say
1. Pay attention to the prefix ,JWT The beginning , A space , And then JWT Of token String
2. If you don't have to auth Components , It needs to be generated manually JWT Of token String and manual verification . It's troublesome , Fortunately JWT This module gives us a lot of convenience .
3. Read more source code , Good
版权声明
本文为[itread01]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- Our best practices for writing react components
- Classical dynamic programming: complete knapsack problem
- [actual combat of flutter] pubspec.yaml Configuration file details
- Interface pressure test: installation, use and instruction of siege pressure test
- Music generation through deep neural network
- Face to face Manual Chapter 16: explanation and implementation of fair lock of code peasant association lock and reentrantlock
- A course on word embedding
- How to use parameters in ES6
- Vite + TS quickly build vue3 project and introduce related features
- PN8162 20W PD快充芯片,PD快充充电器方案
猜你喜欢

至联云分享:IPFS/Filecoin值不值得投资?

From zero learning artificial intelligence, open the road of career planning!
Python download module to accelerate the implementation of recording
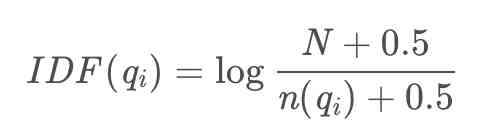
Natural language processing - BM25 commonly used in search

一篇文章带你了解CSS对齐方式

ES6学习笔记(二):教你玩转类的继承和类的对象

Arrangement of basic knowledge points

小程序入门到精通(二):了解小程序开发4个重要文件

vue任意关系组件通信与跨组件监听状态 vue-communication
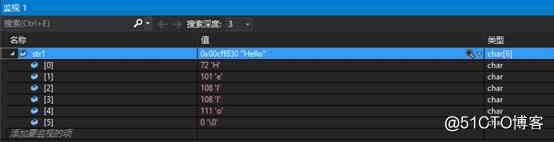
Character string and memory operation function in C language
随机推荐
Python基础变量类型——List浅析
After reading this article, I understand a lot of webpack scaffolding
Named entity recognition in natural language processing: tanford core LP ner (1)
Programmer introspection checklist
Classical dynamic programming: complete knapsack problem
6.2 handleradapter adapter processor (in-depth analysis of SSM and project practice)
6.5 request to view name translator (in-depth analysis of SSM and project practice)
Architecture article collection
Building and visualizing decision tree with Python
每个前端工程师都应该懂的前端性能优化总结:
Windows 10 tensorflow (2) regression analysis of principles, deep learning framework (gradient descent method to solve regression parameters)
一篇文章带你了解CSS对齐方式
Word segmentation, naming subject recognition, part of speech and grammatical analysis in natural language processing
Save the file directly to Google drive and download it back ten times faster
This article will introduce you to jest unit test
Deep understanding of common methods of JS array
Common algorithm interview has been out! Machine learning algorithm interview - KDnuggets
Process analysis of Python authentication mechanism based on JWT
Summary of common algorithms of linked list
一篇文章带你了解HTML表格及其主要属性介绍