当前位置:网站首页>【MagNet】《Progressive Semantic Segmentation》
【MagNet】《Progressive Semantic Segmentation》
2022-07-02 07:48:00 【bryant_ meng】

CVPR-2021
List of articles
1 Background and Motivation
When doing high-resolution image segmentation tasks , because GPU Resource constraints , You can't train the original picture directly
The solution is often downsample the big image or divide the image into local patches for separate processing
However downsample Many details will be lost ,patches The method lacks a holistic view ( Global information )
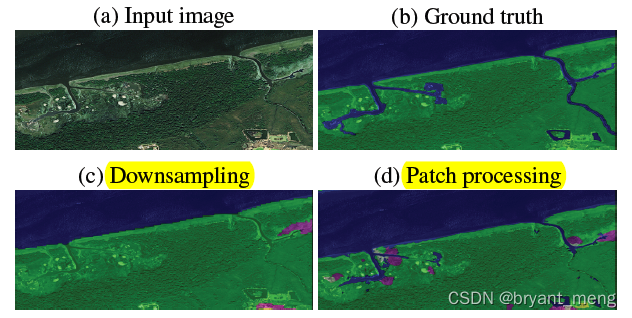
The author combines the advantages of the above two methods , Put forward a multi-scale segmentation framework for high-resolution images——MagNet
stay Cityscapes / DeepGlobe / Gleason Its effectiveness is verified on three high-resolution image datasets
2 Related Work
Multi-scale, eg:FPN / ASPP / HRNet
multi-stage, eg:Auto-ZoomNet
context aggregation,eg:BiseNet
Segmentation refinement
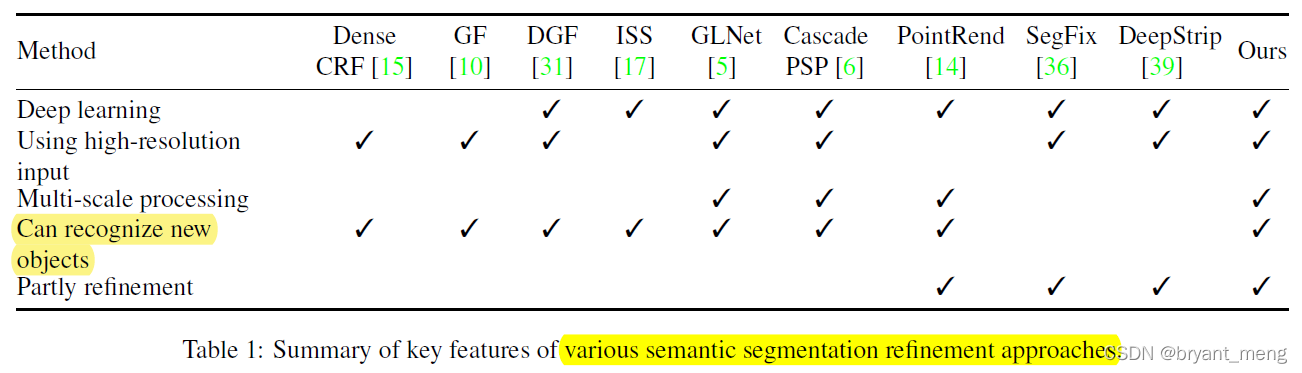
3 Advantages / Contributions
Aiming at the problem of high-resolution image segmentation , Design MagNet The Internet ,Experiments on three high-resolution datasets of urban views, aerial scenes, and medical images show that MagNet consistently outperforms the state-of-theart methods by a significant margin
4 Method
There are two core modules
segmentation network(module, Ordinary partition network )
refinement module( Proposed by the author )
4.1 Multistage processing pipeline

- s Express scale
- p Express patch
- X Represents the input picture
- Y Indicates the output picture
- X ˉ \bar{X} Xˉ Indicates input to segmentation network Medium tensor, Fixed size
- Y ˉ \bar{Y} Yˉ From refinement module The output of the tensor, Fixed size
- O ˉ \bar{O} Oˉ From segmentation network The output of the tensor, Fixed size
With 4 scale As an example
If you input a picture h and w by 1024x2048
each scale Under the patch The size is :
1024x2048
512x1024
256x512
128x256
segmentation and refinement The input and output of the module are 128x256
4.2 Refinement module
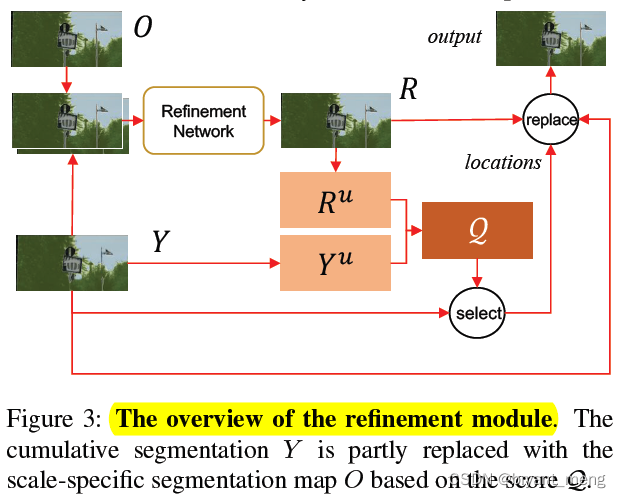
1)refinement module There are two inputs to
- the cumulative result from the previous stages, Y ˉ \bar{Y} Yˉ
- the result obtained by running the segmentation module at and only at the current scale, O ˉ \bar{O} Oˉ
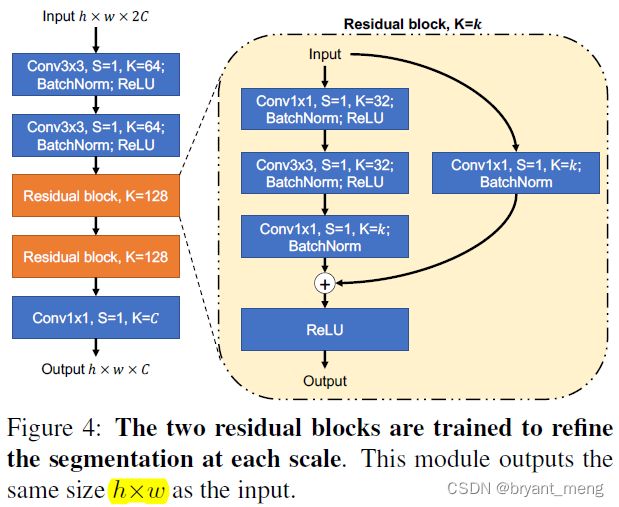
2)refinement network The structure is as follows
O+Y=R
3) history scale Results and current scale result set

Let Y u Y_u Yu and R u R_u Ru denote the prediction uncertainty maps for Y Y Y and R R R respectively.
4)uncertainty maps For the definition of
for each pixel of Y , the prediction confidence at this location is defined as the absolute difference between the highest probability value and the second-highest value (among the C probability values for C classes).
5) Use two prediction uncertainty maps Choose Y Y Y ( Cumulative segmentation graph ) Of k k k Refine at four locations .
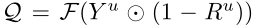
- k k k It means Y Y Y The inaccuracy of prediction , and R R R Where the prediction is more accurate
- ⨀ \bigodot ⨀ yes element-wise multiplication
- F F F Means median filtering , To smooth out the score map
- 1 − R 1-R 1−R Equivalent to attention mechanism , Used to correct Y Y Y Weighted
5) Y u Y_u Yu and R u R_u Ru The combination mode of is 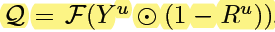
among F denotes median blurring to smooth the score map( median filtering )
⨀ \bigodot ⨀ yes element-wise multiplication
Is equivalent to R Focus on updating the uncertainties of , The specific understanding is as follows
R R R map Some location The better the classification ,softmax Pull more open , that prediction confidence The bigger it is ,1-R The smaller it is , It means you don't have to go refine The area
R R R map Some location The worse the classification ,softmax cannot pull open , that prediction confidence The smaller it is ,1-R The bigger it is , It means to focus on refine The area
ps: Follow up select and replace It seems that I can't analyze too many details , It needs to be combined with the code
4.3 MagNetFast
stay MagNet On the basis of
- Reduce scale Number
- Reduce each scale Up refine Of patch Number (only selects the patches with the highest prediction uncertainty Y u Y^u Yu for refinement)
5 Experiments
When training, each scale On randomly extract image patches
When it comes to testing ,extract non-overlapping patches for processing
5.1 Datasets
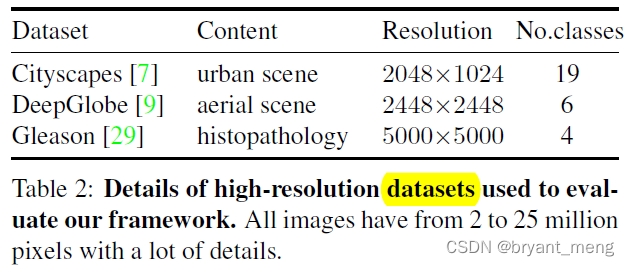
5.2 Experiments on the Cityscapes dataset
1)Benefits of multiple scale levels

scale Set to 4 The best effect
Notice here ,patch size The smaller it is ,refine The higher the accuracy of
patch size In turn (hxw)
1024x2048->512x1024->256x512->128x256
Network size is patch resize The size is 128x256
amount to refine The accuracy of is
Original picture x(128/1024) -> Original picture x(128/512)-> Original picture x(128/256)-> Original picture x(128/128)
That is to say
256->512->1024->2048
Now feel the effect
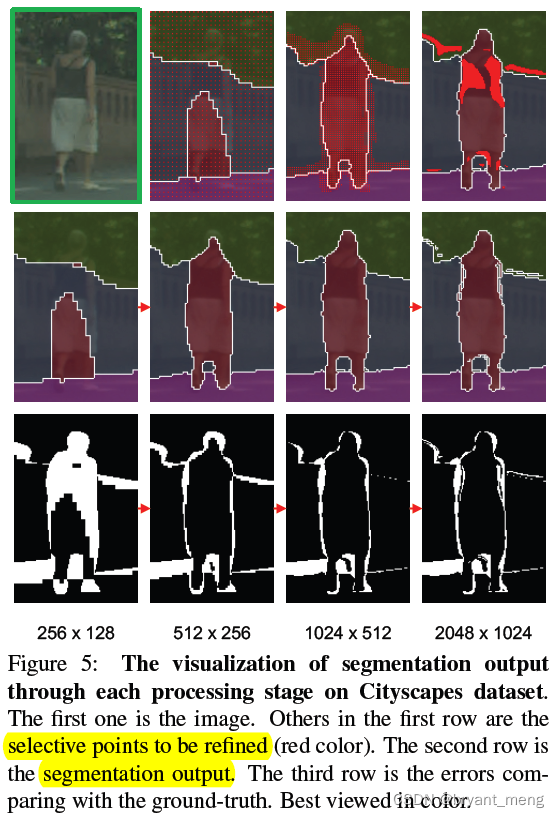
The second line should be refine Later results
Zoom in on the first line , The second picture is all red dots
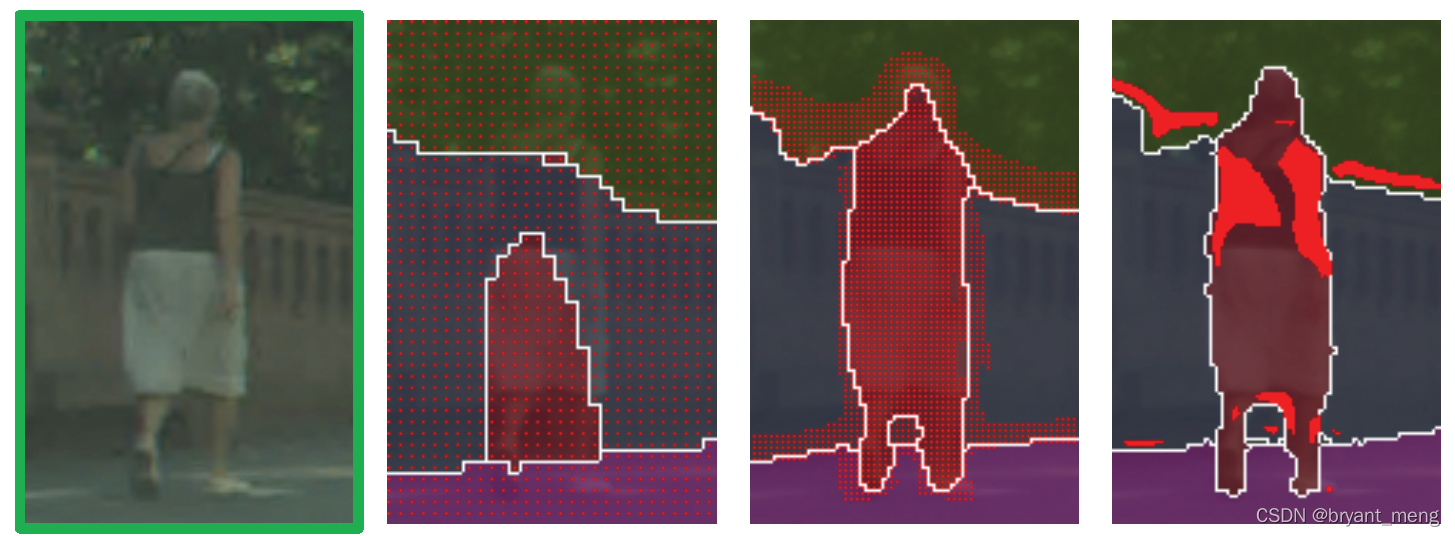
2)Comparing segmentation approaches

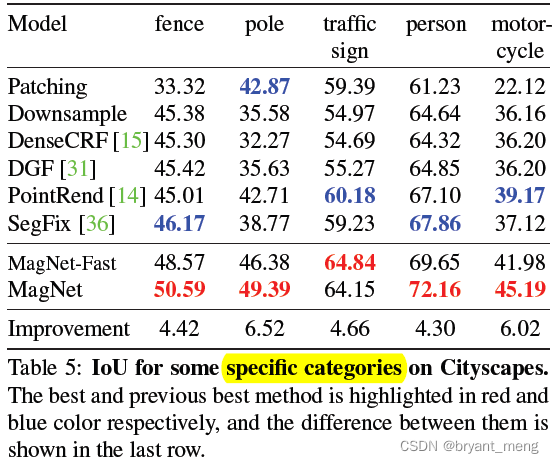
There are many analogy poles ( More delicate ), The segmentation is better than before
3)Ablation study: point selection
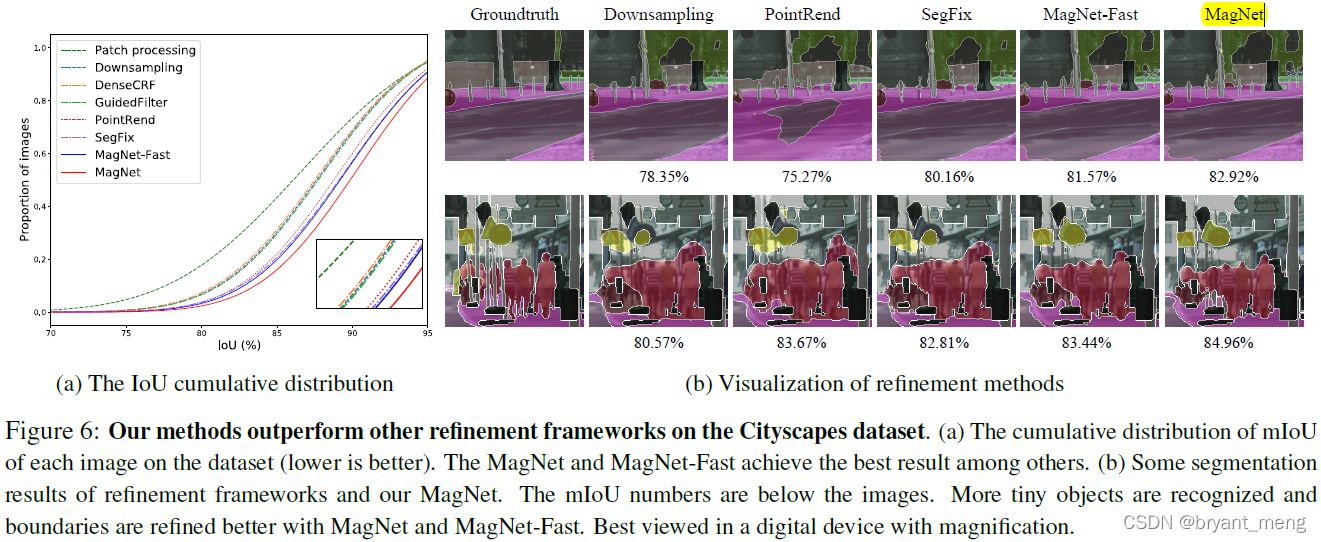
chart (a) It can be seen that ,MagNet Of IoU Bigger than other methods
4)Ablation study: point selection
Here we explore some Y u Y^u Yu and R u R^u Ru Combination of , 2 16 = 65536 2^{16} = 65536 216=65536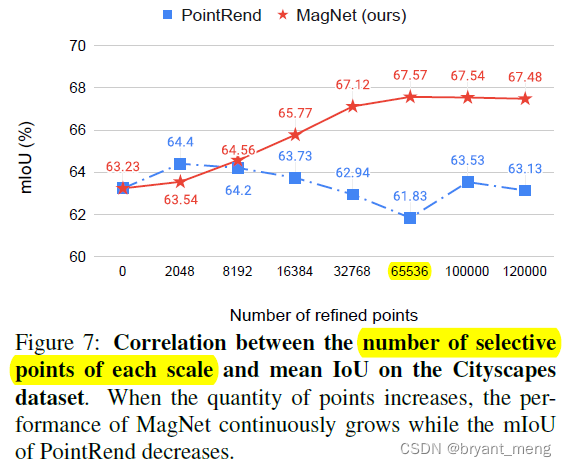
Here we explore each scale need refine Of point Number
5)Ablation study: segmentation backbones
5.3 DeepGlobe
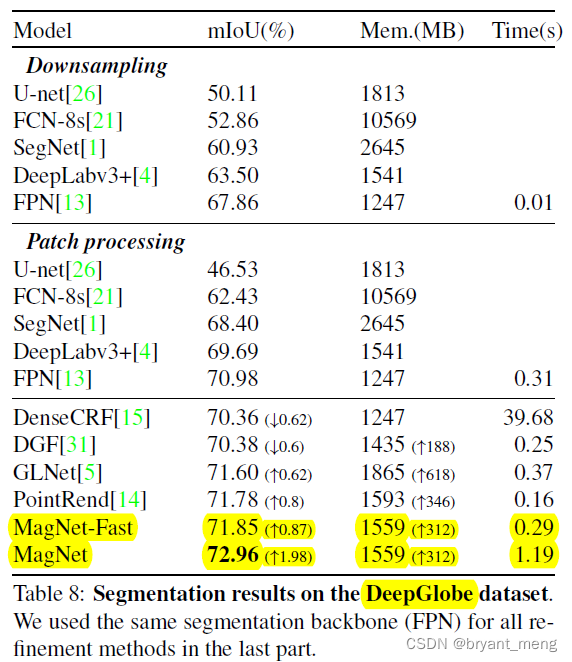
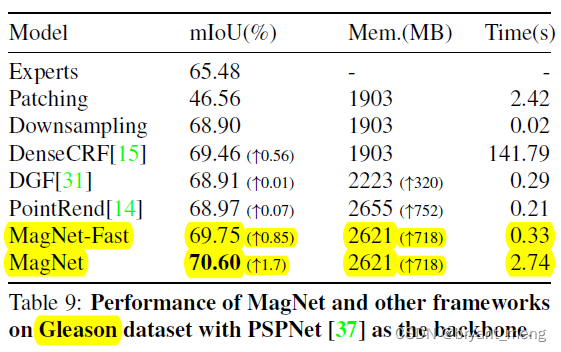
5.4 Gleason
6 Conclusion(own)
accumulated Good idea
stage Too much speed should be much slower
Granularity and resolution
边栏推荐
- Execution of procedures
- Tencent machine test questions
- 【FastDepth】《FastDepth:Fast Monocular Depth Estimation on Embedded Systems》
- Using MATLAB to realize: power method, inverse power method (origin displacement)
- MoCO ——Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning
- CONDA common commands
- [introduction to information retrieval] Chapter 7 scoring calculation in search system
- 【Cascade FPD】《Deep Convolutional Network Cascade for Facial Point Detection》
- 【MobileNet V3】《Searching for MobileNetV3》
- open3d学习笔记二【文件读写】
猜你喜欢
Common CNN network innovations
论文写作tip2
【MnasNet】《MnasNet:Platform-Aware Neural Architecture Search for Mobile》

PointNet原理证明与理解
【MobileNet V3】《Searching for MobileNetV3》
【Cutout】《Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout》

【Sparse-to-Dense】《Sparse-to-Dense:Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image》

Faster-ILOD、maskrcnn_ Benchmark training coco data set and problem summary
A slide with two tables will help you quickly understand the target detection
Play online games with mame32k
随机推荐
【Hide-and-Seek】《Hide-and-Seek: A Data Augmentation Technique for Weakly-Supervised Localization xxx》
What if the laptop can't search the wireless network signal
How to clean up logs on notebook computers to improve the response speed of web pages
聊天中文语料库对比(附上各资源链接)
Handwritten call, apply, bind
yolov3训练自己的数据集(MMDetection)
Implement interface Iterable & lt; T>
Traditional target detection notes 1__ Viola Jones
open3d学习笔记五【RGBD融合】
MMDetection模型微调
【TCDCN】《Facial landmark detection by deep multi-task learning》
ABM论文翻译
Record of problems in the construction process of IOD and detectron2
论文写作tip2
TimeCLR: A self-supervised contrastive learning framework for univariate time series representation
[multimodal] clip model
Calculate the total in the tree structure data in PHP
【FastDepth】《FastDepth:Fast Monocular Depth Estimation on Embedded Systems》
【Cutout】《Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout》
Proof and understanding of pointnet principle