当前位置:网站首页>Typescript release 4.8 beta
Typescript release 4.8 beta
2022-07-07 15:08:00 【Alibaba Amoy technology team official website blog】

TypeScript Has been in 2022.06.21 Release 4.8 beta edition , You can 4.8 Iteration Plan View all included Issue And PR. If you want to experience new features first , perform :
$ npm install [email protected]To install beta Version of TypeScript, Or in the VS Code Install in JavaScript and TypeScript Nightly To update the built-in TypeScript Support .
This is the fourth article of the author TypeScript Update log , The last one is 「TypeScript 4.7 beta Release 」, You can find in the creation of this account , Next, the author will continue to update TypeScript Of DevBlog relevant , Thanks for reading .
in addition , because beta There is usually no significant difference between the version and the official version , This series will only introduce beta Version and informal version .
About 4.8 A detailed analysis of the official version , And the use of the new decorator , I will be in TypeScript Comprehensive advanced guide In the update .
Decorators on the road
stay 4 In the TC39 At the bimonthly meeting , Decorator proposal successfully entered Stage 3, This is also the reason why the decorator proposal has gone through several versions Stage 4 Last time .TypeScript Decorator related syntax is also heavily used in , But actually TS Decorator in (experimental)、Babel Decorator in (legacy) Are based on the first version of the decorator proposal , Now, TC39 The decorator proposal in has been iterated to the Third Edition .
If you are interested in learning more about the history of decorators , You can read the author's approach MidwayJS: First time to know TS Ornaments and IoC Mechanism In the introduction , Or Mr. heshijun is Should it be in production Use in typescript Of decorator? Answer .
With the update of the new decorator proposal ,TypeScript It must be supported accordingly , However, due to its large workload , at present 4.8 beta The version does not include the introduction of the new decorator ( So it's on the way ), But its specific function must be related to the decorator proposal proposal-decorators The descriptions in are basically the same .
Although we have a new version of the decorator , However, there is no need to worry about the old version of the decorator being swept into the dust of history , Support for older decorators will certainly be retained for a long time , Language support 、 Framework improvements 、 Users accept , Every step is too slow . We may arrive at TypeScript 20.0 beta The official announcement that the support for experimental decorators will be abandoned will be seen in the version , I hope I am still updating this column .
For users , Don't worry about the extra cost of learning , The new decorator can completely cover the ability of the old decorator in most cases . But for developers of framework base Libraries , The difference between the two versions of decorators is really quite large , Such as the operation sequence of decorators and metadata correlation .
Cross type and union type are narrowed and enhanced
TypeScript 4.8 Version pair --strictNullChecks Further enhancements have been made , Mainly reflected in the joint type and cross type , And the type narrows the performance .
for instance , As TypeScript In the type system Top Type ,unknown Type contains all other types , actually unknown and {} | null | undefined The effect is consistent : Of unique significance null、undefined type , Plus the origin of all things {}.
Why do you say {} Is the origin of all things ? be based on TypeScript Structured type comparison of , The compatibility between two types is compared by whether their internal attribute types are consistent :
class Cat {
eat() { }
}
class Dog {
eat() { }
}
function feedCat(cat: Cat) { }
feedCat(new Dog())In this case feedCat The function can accept Dog Parameters of type , The reason is that Dog The type and Cat Types are considered consistent under the comparison of structured type systems .
Further more , If at this time Dog Add a new method :
class Cat {
eat() { }
}
class Dog {
eat() { }
bark() { }
}
function feedCat(cat: Cat) { }
feedCat(new Dog())At this point, the example still holds , The reason is that at this time Dog Type comparison Cat Type has one more attribute , Under the judgment of structured type system, it can be considered that Dog The type is Cat Subtypes of types , Just like this. :
class Dog extends Cat {
bark() { }
} Back to the point , because {} It's an empty object , therefore except null、undefined All foundation types except , Can be regarded as inherited from {} Later derived from .
stay 4.8 edition , Now? unknown and {} | null | undefined Can be compatible with each other :
declare let v1: unknown;
declare let v2: {} | null | undefined;
v1 = v2;
// An error will be reported before , Because I think unknown Contains more type information
v2 = v1; meanwhile , about {},4.8 Version will use {} The cross type of , Such as obj & {} Directly simplify to obj type , Premise is obj Not from generics , And not null / undefined. This is because the cross type requires that both types be satisfied at the same time , And as long as obj No null / undefined type , It can be considered that it must also conform to {} type , So you can directly put {} Remove... From the cross type :
type T1 = {} & string; // string
type T2 = {} & 'linbudu'; // 'linbudu'
type T3 = {} & object; // object
type T4 = {} & { x: number }; // { x: number }
type T5 = {} & null; // never
type T6 = {} & undefined; // never And based on this change , You can use it now {} To eliminate the null And undefined, That is, the original built-in tool type NonNullable The implementation will be changed to the following :
type _NonNullable<T> = T extends null | undefined ? never : T;
type NonNullable<T> = T & {}; The implementation principle is null & {}、undefined & {} Will be judged directly as never , Thus disappear in the union type result .
from NonNullable We can know the implementation changes of , Now if a value is not null Neither undefined , So its value is actually equal to it and {} The value to cross , In other words, we can write the following code :
function throwIfNullable<T>(value: T): NonNullable<T> {
if (value === undefined || value === null) {
throw Error("Nullable value!");
}
return value;
} in the past , This example will throw an error : type T Cannot assign a value to NonNullable<T> The type of , Now we know that if we eliminate null And undefined , that T In fact, it's equivalent to T & {}, That is to say NonNullable<T> .
Last , Because of these changes , Now? TypeScript The analysis of type control flow has also been further enhanced , Now? unknown Variables of type will be treated as {} | null | undefined, So it will if else Of truthy The branch is narrowed down to {}:
function narrowUnknown(x: unknown) {
if (x) {
x; // {}
}
else {
x; // unknown
}
} In the template string type infer extract
stay 4.7 In the version TypeScript Support infer extends grammar , So that we can take one step directly infer To the value of the expected type , There is no need to judge the conditional statement again :
type FirstString<T> =
T extends [infer S, ...unknown[]]
? S extends string ? S : never
: never;
// be based on infer extends
type FirstString<T> =
T extends [infer S extends string, ...unknown[]]
? S
: never;4.8 The version has been further enhanced on this basis , When infer Constrained to a primitive type , Then it will now try to infer The type information of is derived to the level of literal type :
// Previously number, For now '100'
type SomeNum = "100" extends `${infer U extends number}` ? U : never;
// Previously boolean, For now 'true'
type SomeBool = "true" extends `${infer U extends boolean}` ? U : never; meanwhile ,TypeScript It checks whether the extracted value can be remapped back to the original string , Such as SomeNum I'll check String(Number("100")) Is it equal to "100", In the following example, it is because it cannot be remapped back , It can only be deduced to number type :
// String(Number("1.0")) → "1",≠ "1.0"
type JustNumber = "1.0" extends `${infer T extends number}` ? T : never; Type derivation in binding types
TypeScript Generic populations in are also affected by their callers , As the following example :
declare function chooseRandomly<T>(x: T,): T;
const res1 = chooseRandomly(["linbudu", 599, false]); here res1 The types of and the generics of functions T It will be deduced as Array<string | number | boolean>, But if we take a different approach :
declare function chooseRandomly<T>(x: T,): T;
const [a, b, c] = chooseRandomly(["linbudu", 599, false]); here a、b、c Derived as string、number、boolean type , That is to say, the generic type of the function is filled with [string, number, boolean] Such a tuple type .
This generic padding is called a binding pattern (Binding Pattern), And in the 4.8 In the version , Type derivation based on binding mode is disabled , Because its impact on generics is not always correct :
declare function f<T>(x?: T): T;
const [x, y, z] = f(); In this case ,[x, y, z] The binding pattern of forces generic parameters to be filled with [any, any, any], And this is very unreasonable —— How can you be sure that I am an array structure ?
Prompt for congruent comparison of object literal value and numeric literal value
We know that JavaScript in {} === {} It's not true , Because objects use reference addresses to store , This is actually comparing two different reference addresses . In order to better avoid the wrong use of === To compare object and array types ,TypeScript An error message will now appear :
const obj = {};
// This sentence will always return to false, because JavaScript Compare objects using reference addresses in , Not the actual value
if(obj === {}){
}Allied , Before that, if you were if The function... Is incorrectly used in the statement ,TypeScript It will also give you a hint :
const func = () => {};
// This expression will always return true, Do you want to call func ?
if(func) { }Compiler Optimize
4.8 The version is also correct tsc Some performance optimization work has been done , Including listening mode --watch, Incremental build --incremental as well as Project References Under the --build Pattern . For example, in the current monitoring mode , Files that are not changed due to user actions will be skipped .
You can read #48784 Learn more about optimization .
Disruptive change
lib.d.ts to update
JavaScript Import of type is no longer allowed in the file , Before that, you can import a type as JSDoc describe :
import { IConfiguration } from 'foo';
/**
* @type {IConfiguration}
*/
export const config = {};This use now throws an error , actually , The more common way is this :
/**
* @type {import("foo").IConfiguration}
*/
export const config = {};
// CommonJs Next :
module.exports = /** @type {import("foo").IConfiguration} */ {} And for JavaScript Type export in file , You can use @typedef To declare a type export :
/**
* @typedef {string | number} MyType
*/
export { MyType }
// Current use
/**
* @typedef {string | number} FooType
*/The full text after , We 4.9 beta Version see :-).
team introduction
Taobao store is the basic link of e-commerce , With 100 million traffic , At the same time, it also faces countless opportunities and challenges . The front-end team of the store carries the Taobao store page serving consumers 、 The backstage of Wangpu management, which serves businesses 、 Serve the outside ISV The developer's module system and other related businesses , It is the closest link between consumers and businesses . in the past 、 Now? 、 future , We are committed to improving the operation experience of businesses and the purchase experience of consumers .
* Expanding reading
do person | Dome Center
edit | Orange King

边栏推荐
- What is data leakage
- CTFshow,信息搜集:web13
- Pandora IOT development board learning (HAL Library) - Experiment 12 RTC real-time clock experiment (learning notes)
- 有一头母牛,它每年年初生一头小母牛。每头小母牛从第四个年头开始,每年年初也生一头小母牛。请编程实现在第n年的时候,共有多少头母牛?
- leetcode:648. Word replacement [dictionary tree board + find the shortest matching prefix among several prefixes]
- 【深度学习】语义分割实验:Unet网络/MSRC2数据集
- ⼀个对象从加载到JVM,再到被GC清除,都经历了什么过程?
- [target detection] yolov5 Runtong voc2007 data set
- 暑期安全很重要!应急安全教育走进幼儿园
- Stm32cubemx, 68 sets of components, following 10 open source protocols
猜你喜欢
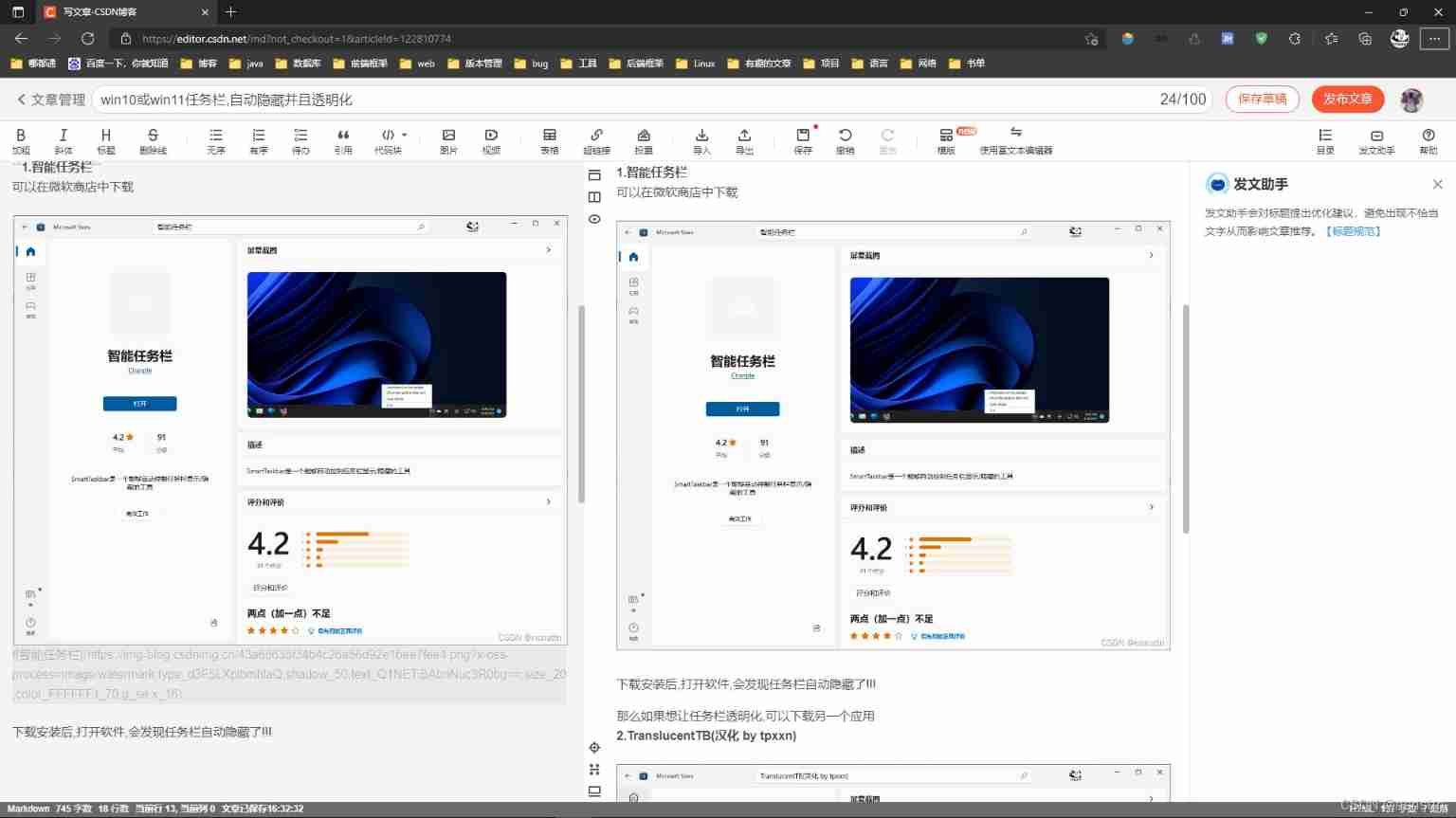
Win10 or win11 taskbar, automatically hidden and transparent
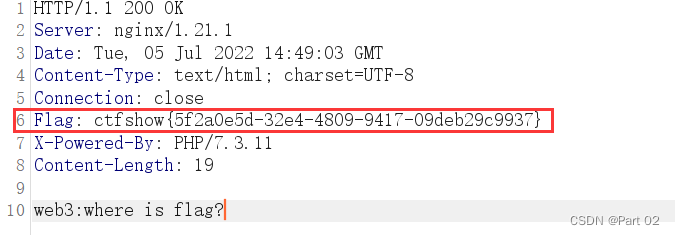
CTFshow,信息搜集:web3

【服务器数据恢复】某品牌StorageWorks服务器raid数据恢复案例

2. 堆排序『较难理解的排序』
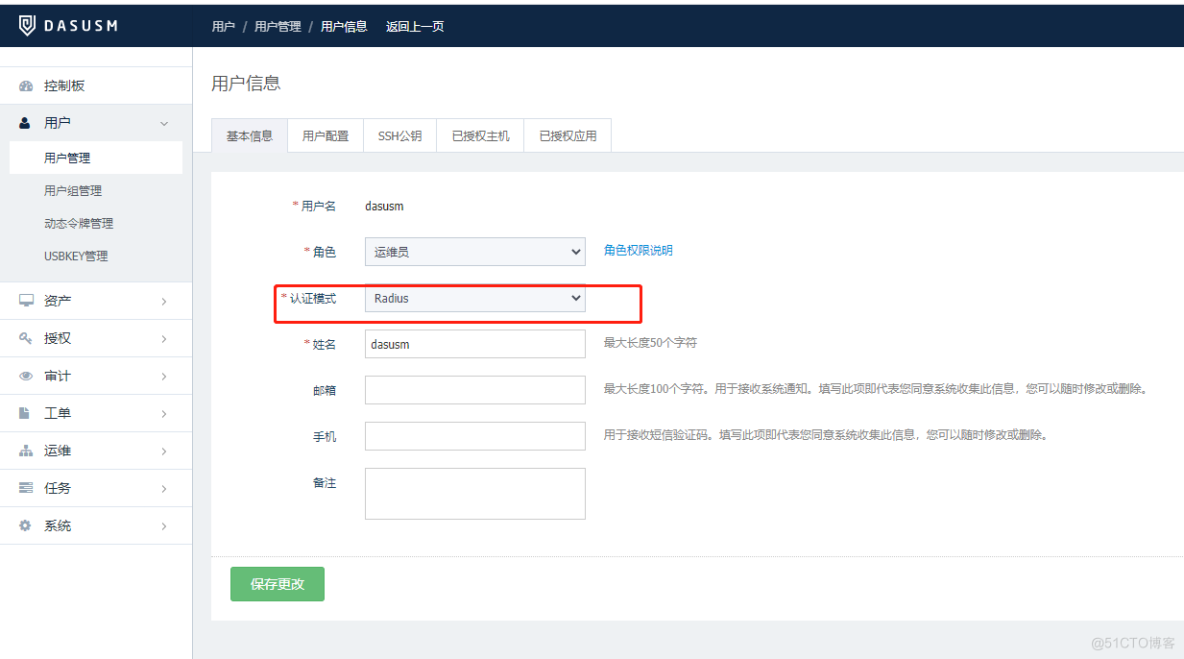
安恒堡垒机如何启用Radius双因素/双因子(2FA)身份认证
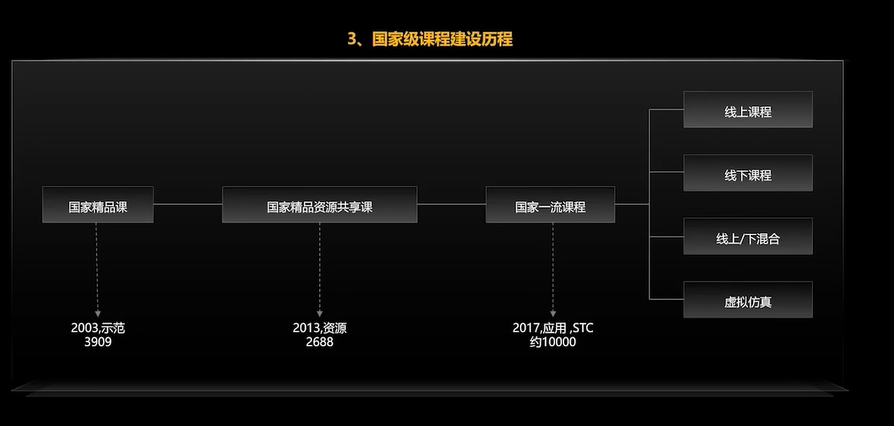
#HPDC智能基座人才发展峰会随笔

Apache多个组件漏洞公开(CVE-2022-32533/CVE-2022-33980/CVE-2021-37839)
【数据挖掘】视觉模式挖掘:Hog特征+余弦相似度/k-means聚类
![[Data Mining] Visual Pattern Mining: Hog Feature + cosinus Similarity / K - means Clustering](/img/a4/7320f5d266308f6003cc27964e49f3.png)
[Data Mining] Visual Pattern Mining: Hog Feature + cosinus Similarity / K - means Clustering
![[follow Jiangke University STM32] stm32f103c8t6_ PWM controlled DC motor_ code](/img/8d/a6d477a8679ca4f3885b1a7b542437.png)
[follow Jiangke University STM32] stm32f103c8t6_ PWM controlled DC motor_ code
随机推荐
Niuke real problem programming - Day11
Unity之ASE实现卡通火焰
Lidar Knowledge Drop
Bits and Information & integer notes
buffer overflow protection
MySQL bit type resolution
"Baidu Cup" CTF competition 2017 February, web:include
Delete a whole page in word
[Data Mining] Visual Pattern Mining: Hog Feature + cosinus Similarity / K - means Clustering
Xiaomi's path of chip self-development
Andriod --- JetPack :LiveData setValue 和 postValue 的区别
Niuke real problem programming - Day12
What are PV and UV? pv、uv
Used by Jetson AgX Orin canfd
激光雷达lidar知识点滴
Yyds dry goods inventory # solve the real problem of famous enterprises: cross line
Unity之ASE实现全屏风沙效果
众昂矿业:萤石继续引领新能源市场增长
[follow Jiangke University STM32] stm32f103c8t6_ PWM controlled DC motor_ code
[today in history] July 7: release of C; Chrome OS came out; "Legend of swordsman" issued
