当前位置:网站首页>Using GPU to train network model
Using GPU to train network model
2022-07-08 01:02:00 【booze-J】
The network model architecture used in this article :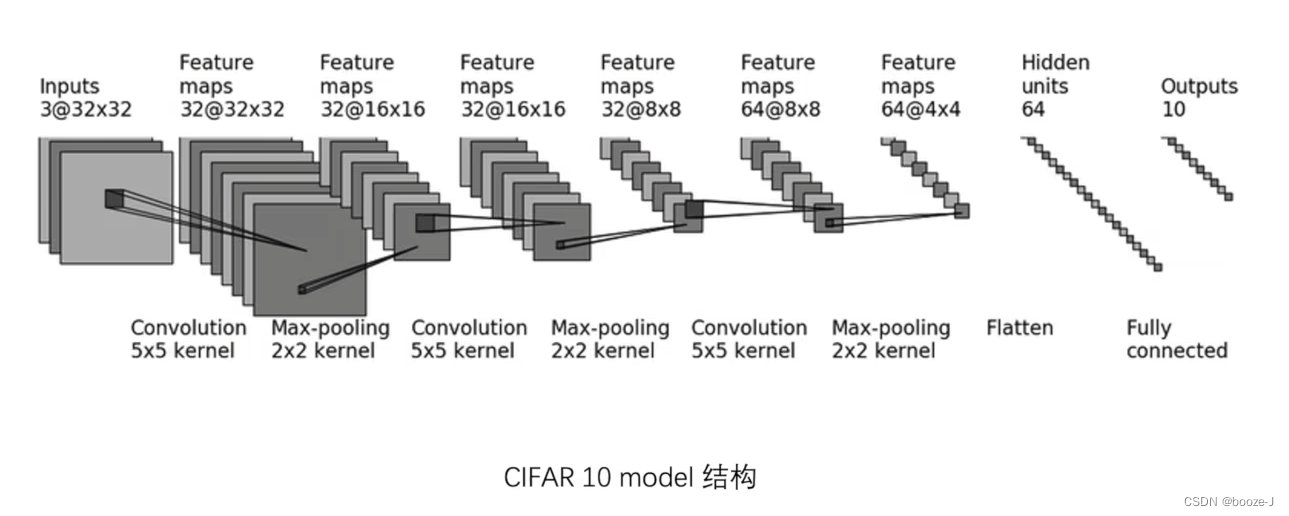
GPU There are two ways to train :
Mode one
Use gpu Training as long as you find : A network model 、 data ( Enter and label )、 The loss function is called again .cuda() that will do .
CPU Training code :
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import time
# Prepare the dataset
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10',train=True,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10',train=False,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
# length length
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print(" The length of the training data set is :{}".format(train_data_size))
print(" The length of the test data set is :{}".format(test_data_size))
# utilize dataloader To load the dataset
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data,batch_size=64)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=64)
# Create a network model
# Building neural networks ( Open a separate file to store the network model )
class Booze(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Booze, self).__init__()
self.model = Sequential(
Conv2d(3, 32, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 32, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024, 64),
Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
obj = Booze()
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Define optimizer
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(obj.parameters(),lr = learning_rate)
# Set some parameters of the training network
# Record the number of workouts
total_train_step=0
# Record the number of tests
total_test_step=0
# Number of training rounds
epoch = 10
# add to tensorboard
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(epoch):
print("------------- The first {} Round of training begins ------------".format(i+1))
# The training steps begin [train()](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html#torch.nn.Module.train)
obj.train()
for data in train_dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
outputs = obj(imgs)
# Calculate the loss between the output value and the target value
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
# Optimizer optimization model :
# Use the optimizer to clear the gradient
optimizer.zero_grad()
# A gradient of each parameter node is obtained by back propagation
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_train_step += 1
if total_train_step%100==0:
end_time = time.time()
print(end_time-start_time)
print(" Training times :{},Loss:{}".format(total_train_step,loss.item()))
writer.add_scalar("train_loss",loss.item(),total_train_step)
# The test step begins :
# Note that there is no need to tune the model in the process of testing
obj.eval() # [eval()](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html#torch.nn.Module.eval)
total_test_loss = 0
total_accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
outputs = obj(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
total_test_loss+=loss
accurcay = (outputs.argmax(1)==targets).sum()
total_accuracy+=accurcay
print(" On the overall test set Loss:{}".format(total_test_loss))
print(" Accuracy on the overall test set :{}".format(total_accuracy/test_data_size))
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy",total_accuracy/test_data_size,total_test_step)
writer.add_scalar('test_loss',total_test_loss,total_test_step)
total_test_step+=1
torch.save(obj,"./model/obj_{}.pth".format(i))
print(" Model saved ")
writer.close()
Code run results :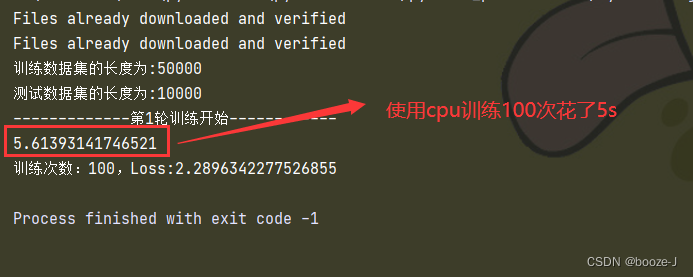
GPU Training code :
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Sequential, Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import time
# Prepare the dataset
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10',train=True,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='./CIFAR10',train=False,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
# length length
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print(" The length of the training data set is :{}".format(train_data_size))
print(" The length of the test data set is :{}".format(test_data_size))
# utilize dataloader To load the dataset
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data,batch_size=64)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=64)
# Create a network model
# Building neural networks ( Open a separate file to store the network model )
class Booze(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Booze, self).__init__()
self.model = Sequential(
Conv2d(3, 32, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 32, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 64, 5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024, 64),
Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
obj = Booze()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# A network model call cuda() Method before returning
obj = obj.cuda()
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Judge first cuda May I use , Then you can move over
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# Loss function call cuda() Method before returning
loss_fn = loss_fn.cuda()
# Define optimizer
learning_rate = 0.01
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(obj.parameters(),lr = learning_rate)
# Set some parameters of the training network
# Record the number of workouts
total_train_step=0
# Record the number of tests
total_test_step=0
# Number of training rounds
epoch = 10
# add to tensorboard
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(epoch):
print("------------- The first {} Round of training begins ------------".format(i+1))
# The training steps begin [train()](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html#torch.nn.Module.train)
obj.train()
for data in train_dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# data call cuda() Method before returning
imgs = imgs.cuda()
# data call cuda() Method before returning
targets = targets.cuda()
outputs = obj(imgs)
# Calculate the loss between the output value and the target value
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
# Optimizer optimization model :
# Use the optimizer to clear the gradient
optimizer.zero_grad()
# A gradient of each parameter node is obtained by back propagation
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_train_step += 1
if total_train_step%100==0:
end_time = time.time()
print(end_time-start_time)
print(" Training times :{},Loss:{}".format(total_train_step,loss.item()))
writer.add_scalar("train_loss",loss.item(),total_train_step)
# The test step begins :
# Note that there is no need to tune the model in the process of testing
obj.eval() # [eval()](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html#torch.nn.Module.eval)
total_test_loss = 0
total_accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_dataloader:
imgs,targets = data
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# data call cuda() Method before returning
imgs = imgs.cuda()
# data call cuda() Method before returning
targets = targets.cuda()
outputs = obj(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
total_test_loss+=loss
accurcay = (outputs.argmax(1)==targets).sum()
total_accuracy+=accurcay
print(" On the overall test set Loss:{}".format(total_test_loss))
print(" Accuracy on the overall test set :{}".format(total_accuracy/test_data_size))
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy",total_accuracy/test_data_size,total_test_step)
writer.add_scalar('test_loss',total_test_loss,total_test_step)
total_test_step+=1
torch.save(obj,"./model/obj_{}.pth".format(i))
print(" Model saved ")
writer.close()
Code run results :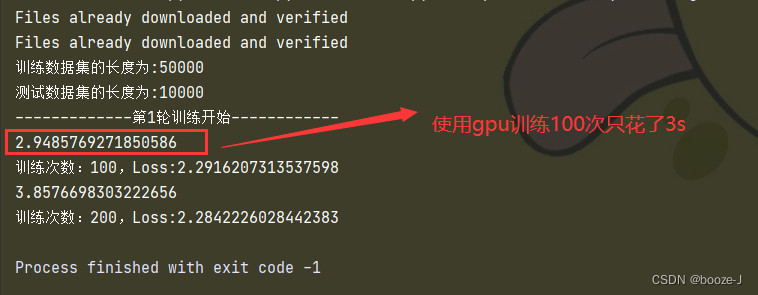
Compared with CPU Training code ,GPU The training code has made the following changes .
CPU Network model in
# Creating neural networks
obj = Booze()
GPU Network model in
obj = Booze()
# Judge first cuda May I use , Then you can move over
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# A network model call cuda() Method before returning
obj = obj.cuda()
CPU Loss function in
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
GPU Loss function in
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Judge first cuda May I use , Then you can move over
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# Loss function call cuda() Method before returning
loss_fn = loss_fn.cuda()
CPU Data in
imgs,targets = data
GPU Data in
imgs,targets = data
if torch.cuda.is_available():
# data call cuda() Method before returning
imgs = imgs.cuda()
# data call cuda() Method before returning
targets = targets.cuda()
in addition , Some notebooks may not have a graphics card , Then I want to experience the pleasure of graphics card , In fact, there are also some online graphics cards that can be used , Like Google's colab You can also use a graphics card online GPU Training .
Mode two
Use gpu Training as long as you find : A network model 、 data ( Enter and label )、 The loss function is called again .to(device) that will do .
The premise is to define device
for example :
# Use CPU Training
device = torch.device("cpu")
# Use GPU Training
device = torch.device("cuda")
# If there are multiple graphics cards , Use the first graphics card for training
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
# If there are multiple graphics cards , Use the second graphics card for training
device = torch.device("cuda:1")
# if cuda Use if available GPU Training , Otherwise use cpu Train as equipment
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
After defining device After that, as long as the network model 、 data ( Enter and label )、 Loss function call .to(device) that will do
Compared with CPU Training code ,GPU The training code has made the following changes .
CPU Network model in
# Creating neural networks
obj = Booze()
GPU Network model in
obj = Booze()
# call .to(device) Method
obj = obj.to(device)
CPU Loss function in
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
GPU Loss function in
# Create a loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# call .to(device) Method
loss_fn = loss_fn.to(device)
CPU Data in
imgs,targets = data
GPU Data in
imgs,targets = data
# call .to(device) Method
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
边栏推荐
- DNS series (I): why does the updated DNS record not take effect?
- Marubeni official website applet configuration tutorial is coming (with detailed steps)
- 13.模型的保存和載入
- Cascade-LSTM: A Tree-Structured Neural Classifier for Detecting Misinformation Cascades(KDD20)
- The method of server defense against DDoS, Hangzhou advanced anti DDoS IP section 103.219.39 x
- Y59. Chapter III kubernetes from entry to proficiency - continuous integration and deployment (III, II)
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 006 in July 2022 - automatic derivation of types and input and output
- Service mesh introduction, istio overview
- Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
- From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
猜你喜欢
Where is the big data open source project, one-stop fully automated full life cycle operation and maintenance steward Chengying (background)?
QT adds resource files, adds icons for qaction, establishes signal slot functions, and implements
Su embedded training - Day6

第四期SFO销毁,Starfish OS如何对SFO价值赋能?
Get started quickly using the local testing tool postman
Reentrantlock fair lock source code Chapter 0
AI遮天传 ML-回归分析入门
Analysis of 8 classic C language pointer written test questions
接口测试要测试什么?
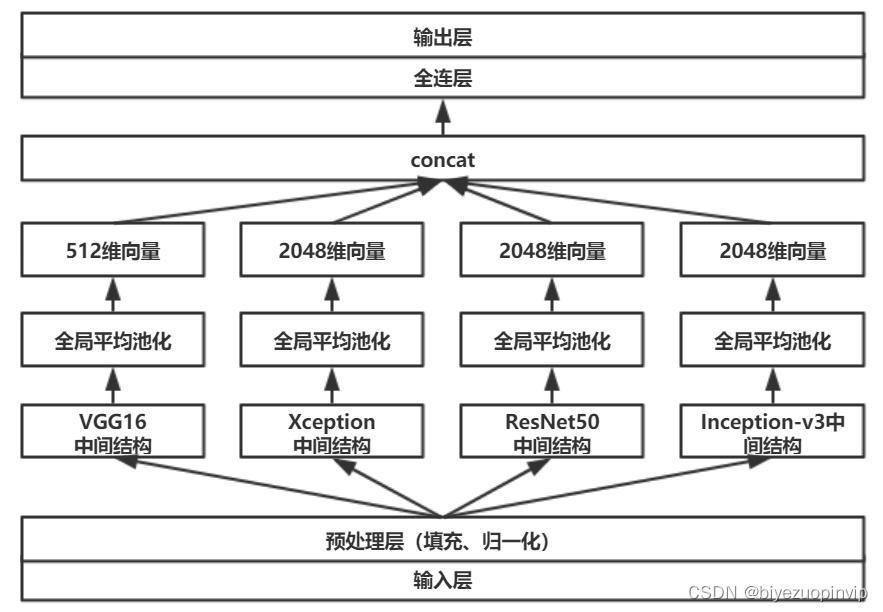
Malware detection method based on convolutional neural network
随机推荐
Kubernetes Static Pod (静态Pod)
3.MNIST数据集分类
【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 006-自动推导类型和输入输出
AI zhetianchuan ml novice decision tree
Reentrantlock fair lock source code Chapter 0
英雄联盟胜负预测--简易肯德基上校
They gathered at the 2022 ecug con just for "China's technological power"
7. Regularization application
Hotel
6.Dropout应用
Fofa attack and defense challenge record
【GO记录】从零开始GO语言——用GO语言做一个示波器(一)GO语言基础
接口测试要测试什么?
Get started quickly using the local testing tool postman
Is it safe to open an account on the official website of Huatai Securities?
Deep dive kotlin collaboration (the end of 23): sharedflow and stateflow
13. Enregistrement et chargement des modèles
5.过拟合,dropout,正则化
Semantic segmentation model base segmentation_ models_ Detailed introduction to pytorch
NTT template for Tourism