当前位置:网站首页>Su embedded training - Day8
Su embedded training - Day8
2022-07-08 00:58:00 【Light chasing rain】
data structure
- One curriculum structure
- Two Why learn data structures
- 3、 ... and The concept of data structure
- Four The order sheet ( Sequential storage of linear tables )
- 4.1 Concept
- 4.2 Operation of sequence table
- 4.2.1 Create an empty order table
- 4.2.2 Judge whether the sequence table is full
- 4.2.3 insert data
- 4.2.4 Traversal order table
- 4.2.5 Judge whether the sequence table is empty
- 4.2.6 Delete the data and return the deleted data
- 4.2.6 Insert data by location
- 4.2.7 Delete data by location , And return the deleted data
- 4.2.8 Modify the data according to the data
- 4.2.9 Modify the data according to the position
- 4.2.10 Find location by data
- 4.2.11 Find data by location
- practice :
- 4.3 The overall code
One curriculum structure
Concept
The order sheet , Single chain list , One way circular list , Bidirectional circular linked list , queue , Stack ,
Trees
chart
Algorithm :
Search algorithm , Sorting algorithm
Two Why learn data structures
- Program = data structure + Algorithm
Data structures are very important for writing code , It is also a basic course
2. Any programming language , Data structure is a very important part
such as c++ Inside STL( Standard template library )
The essence of database is to write the content of data structure
The traversal algorithm of data graph is the foundation of artificial intelligence
Red and black trees will be reflected in the drive
3. We have finished learning before c Language foundation , Difficult places : The pointer , Array , Structure , function , The course of data structure will use these things every day , It is an in-depth understanding of these knowledge points .
3、 ... and The concept of data structure
3.1 Basic concepts
data structure :
data : Subjects of study
structure : The relationship between the data
Data structure is mainly to study the relationship between data
In actual development , The data structure is mainly used to temporarily store data in memory after understanding the relationship between data
3.2 Definition of data structure
Data structure mainly studies the logical relationship, storage relationship and operation of data
3.3 logical relationship
Logical relationship mainly refers to the logical relationship between data , It mainly refers to the collar connection
Logical relationship involves the concepts of direct predecessor and direct successor when considering the relationship between data
linear relationship : One-to-one relationship , Any data can only have one direct precursor and one direct successor
for example : The linear table , Stack , queue
Tree relationship : One to many relationship , Any data can only have one direct precursor , But there can be many direct successors
for example : Trees , Binary tree
Graphical relationships :( reticulation relationships ): many-to-many , Any data has multiple direct precursors and multiple direct successors .
for example : chart
3.4 Storage relationship
Storage relation refers to how data is stored in memory
Sequential storage :
Data in memory will open up a continuous memory space for storage , Generally, arrays are used to store data
Chain store :
When data is stored in memory, there is no need to open up a continuous space .
Index storage ( Generally do not use )
Hash store ( Generally do not use )
Be careful : Theoretically, any logical structure can be realized by two storage methods .
3.5 operation
increase Delete Change check
Four The order sheet ( Sequential storage of linear tables )
4.1 Concept
The linear table : One to one relationship between data
Sequential storage : Need to open up a continuous memory space in memory to store data , Generally, data is used to store data , To facilitate the operation of data , A variable is usually defined to hold the subscript of the last element
4.2 Operation of sequence table
4.2.1 Create an empty order table
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// In order to improve the expansibility of the code , Alias the data type , It is convenient to modify the data types in the table
typedef int DataType;
#define N 32
// Define a structure
typedef struct
{
DataType data[N];
int pos; // The array subscript
}seqlist;
// Creation of sequence table
seqlist * SeqlistCreate();
// Judge whether the sequence table is full
int SeqlistIsFull(seqlist *st);
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
seqlist *st = SeqlistCreate();
return 0;
}
// Creation of sequence table
seqlist *SeqlistCreate()
{
// Apply for space on the heap
seqlist *st = (seqlist *)malloc(sizeof(seqlist));
// initialization , Identify that there are no elements in the current sequence table
st->pos = -1;
// Return the first address of the sequence table
return st;
}
4.2.2 Judge whether the sequence table is full
// Judge whether the sequence table is full
int SeqlistIsFull(seqlist *st)
{
#if 0
if(st->pos == N -1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
#endif
return st->pos == N -1 ? 1 : 0;
}
4.2.3 insert data
// insert data
void SeqlistInsert(seqlist *st,DataType value)
{
if(SeqlistIsFull(st) == 1)
{
printf(" Insert the failure , The sequence table is full !\n");
return;
}
// Save the variables of the last element pos Self increasing
st->pos++;
// Insert data into pos The location of
st->data[st->pos] = value;
printf(" Insert the success !\n");
}
4.2.4 Traversal order table
// Traversal order table
void SeqlistPrint(seqlist *st)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ;i <= st->pos;i++)
{
printf("%d ",st->data[i]);
}
putchar(10);
}
4.2.5 Judge whether the sequence table is empty
// Judge whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqlistIsEmpty(seqlist *st)
{
return st->pos == -1 ? 1 : 0;
}
4.2.6 Delete the data and return the deleted data
// Delete the data and return the data to be deleted
DataType SeqlistDelete(seqlist *st)
{
if(SeqlistIsEmpty(st) == 1)
{
printf(" Delete failed , Sequence table is empty !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
DataType value = st->data[st->pos];
st->pos--;
printf(" Delete successful !\n");
return value;
}
4.2.6 Insert data by location
// Insert data by location
void SeqlistInsertByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value)
{
if(SeqlistIsFull(st))
{
printf(" Insert the failure , The sequence table is full !\n");
return;
}
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos + 1)
{
printf(" Insert the failure , Wrong insertion position !\n");
return;
}
int i;
if(p == st->pos + 1)
{
st->data[p] = value;
st->pos++;
}
else
{
for(i = st->pos;i >= p;i--)
{
st->data[i + 1] = st->data[i];
}
// Put the inserted data in P The location of
st->data[p] = value;
st->pos++;
}
printf(" Inserting data by location succeeded !\n");
return;
}
4.2.7 Delete data by location , And return the deleted data
// Delete data by location , Return deleted data
DataType SeqlistDeleteByPos(seqlist *st,int p)
{
if(SeqlistIsEmpty(st))
{
printf(" Sequence table is empty , Delete by location failed !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Delete failed , Wrong input position !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
// Save the data to be deleted in value in
DataType value = st->data[p];
// take p Upward data moves downward
int i;
for(i = p;i < st->pos;i++)
{
st->data[i] = st->data[i + 1];
}
st->pos--;
printf(" Data deletion by location succeeded \n");
return value;
}
4.2.8 Modify the data according to the data
// Modify the data according to the data
void SeqlistUpdateByData(seqlist *st,DataType OldValue,DataType NewValue)
{
int i,flags = 0;
for(i = 0 ; i <= st->pos;i++)
{
if(st->data[i] == OldValue)
{
st->data[i] = NewValue;
flags = 1;
}
}
if(flags == 0)
{
printf(" Failed to modify data ,%d non-existent \n",OldValue);
}
}
4.2.9 Modify the data according to the position
// Modify the data according to the position
void SeqlistUpdateByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value)
{
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Modification failed , The position is wrong !\n");
return;
}
st->data[p] = value;
printf(" Successfully modify the data according to the location !\n");
}
4.2.10 Find location by data
// Find location by data
int SeqlistSearchPos(seqlist *st,DataType value)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i <= st->pos;i++)
{
if(st->data[i] == value)
{
printf(" Find the location according to the data successfully !\n");
return i;
}
}
printf(" To find the failure , data %d non-existent \n",value);
return -1;
}
4.2.11 Find data by location
// Find data by location
DataType SeqlistSearchData(seqlist *st,int p)
{
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Failed to find data by location , The position is wrong !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
printf(" Data search by location succeeded !\n");
return st->data[p];
}
practice :
1. Delete duplicate data
( Compare the first data with the following data , If there are duplicates, delete the following data )
s1: 1 2 2 2 1 1 3 4 2 4 5 4 1
.....
s1:1 2 3 4 5
// Delete duplicate data
void SeqlistDeleteRepeat(seqlist *st)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0 ; i < st->pos;i++)
{
for(j = i + 1;j <= st->pos;j++)
{
if(st->data[i] == st->data[j])
{
// Delete by location j The data of
SeqlistDeleteByPos(st,j);
//j-- The purpose is to prevent the data of the deleted position from not being compared
j--;
}
}
}
}
2. Merge tables
( take s2 Inside and outside s1 Different data is saved in s1 Behind )
s1: 1 2 3 4 5
s2: 1 3 5 7 9
…
s1:1 2 3 4 5 7 9
// Merge tables
void SeqlistMerge(seqlist *s1,seqlist *s2)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i <= s2->pos;i++)
{
if(SeqlistSearchPos(s1,s2->data[i]) == -1)
{
SeqlistInsert(s1,s2->data[i]);
}
}
}
4.3 The overall code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// In order to improve the expansibility of the code , Alias the data type , It is convenient to modify the data types in the table
typedef int DataType;
#define N 32
// Define a structure
typedef struct
{
DataType data[N];
int pos; // The array subscript
}seqlist;
// Creation of sequence table
seqlist * SeqlistCreate();
// Judge whether the sequence table is full
int SeqlistIsFull(seqlist *st);
// insert data
void SeqlistInsert(seqlist *st,DataType value);
// Traversal order table
void SeqlistPrint(seqlist *st);
// Judge whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqlistIsEmpty(seqlist *st);
// Delete the data and return the data to be deleted
DataType SeqlistDelete(seqlist *st);
// Insert data by location
void SeqlistInsertByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value);
// Delete data by location , Return deleted data
DataType SeqlistDeleteByPos(seqlist *st,int p);
// Modify the data according to the data
void SeqlistUpdateByData(seqlist *st,DataType OldValue,DataType NewValue);
// Modify the data according to the position
void SeqlistUpdateByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value);
// Find location by data
int SeqlistSearchPos(seqlist *st,DataType value);
// Find data by location
DataType SeqlistSearchData(seqlist *st,int p);
// Delete duplicate data
void SeqlistDeleteRepeat(seqlist *st);
// Merge tables
void SeqlistMerge(seqlist *s1,seqlist *s2);
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
seqlist *st = SeqlistCreate();
if(st == NULL)
{
printf(" Sequence table initialization failed !\n");
return -1;
}
int i;
for(i = 1 ; i <= 32;i++)
{
SeqlistInsert(st,i);
}
SeqlistPrint(st);
for(i = 0 ; i < 10;i++)
{
SeqlistDelete(st);
}
SeqlistPrint(st);
SeqlistInsertByPos(st,7,777);
SeqlistPrint(st);
SeqlistDeleteByPos(st,9);
SeqlistPrint(st);
SeqlistUpdateByData(st,10,999);
SeqlistPrint(st);
SeqlistUpdateByPos(st,17,1001);
SeqlistPrint(st);
printf(" The position is :%d\n",SeqlistSearchPos(st,999));
printf(" The data searched by location is :%d\n",SeqlistSearchData(st,19));
SeqlistInsert(st,1);
SeqlistInsert(st,2);
SeqlistInsert(st,3);
SeqlistInsert(st,1);
SeqlistInsert(st,3);
SeqlistInsert(st,4);
SeqlistInsert(st,5);
SeqlistPrint(st);
SeqlistDeleteRepeat(st);
SeqlistPrint(st);
seqlist *s1 = SeqlistCreate();
seqlist *s2 = SeqlistCreate();
SeqlistInsert(s1,1);
SeqlistInsert(s1,2);
SeqlistInsert(s1,3);
SeqlistInsert(s1,4);
SeqlistInsert(s1,5);
SeqlistInsert(s2,1);
SeqlistInsert(s2,3);
SeqlistInsert(s2,5);
SeqlistInsert(s2,7);
SeqlistInsert(s2,9);
SeqlistMerge(s1,s2);
SeqlistPrint(s1);
return 0;
}
// Creation of sequence table
seqlist *SeqlistCreate()
{
// Apply for space on the heap
seqlist *st = (seqlist *)malloc(sizeof(seqlist));
if(NULL == st)
{
return NULL;
}
// initialization , Identify that there are no elements in the current sequence table
st->pos = -1;
// Return the first address of the sequence table
return st;
}
// Judge whether the sequence table is full
int SeqlistIsFull(seqlist *st)
{
#if 0
if(st->pos == N -1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
#endif
return st->pos == N -1 ? 1 : 0;
}
// insert data
void SeqlistInsert(seqlist *st,DataType value)
{
if(SeqlistIsFull(st) == 1)
{
printf(" Insert the failure , The sequence table is full !\n");
return;
}
// Save the variables of the last element pos Self increasing
st->pos++;
// Insert data into pos The location of
st->data[st->pos] = value;
printf(" Insert the success !\n");
return;
}
// Traversal order table
void SeqlistPrint(seqlist *st)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ;i <= st->pos;i++)
{
printf("%d ",st->data[i]);
}
putchar(10);
}
// Judge whether the sequence table is empty
int SeqlistIsEmpty(seqlist *st)
{
return st->pos == -1 ? 1 : 0;
}
// Delete the data and return the data to be deleted
DataType SeqlistDelete(seqlist *st)
{
if(SeqlistIsEmpty(st) == 1)
{
printf(" Delete failed , Sequence table is empty !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
DataType value = st->data[st->pos];
st->pos--;
printf(" Delete successful !\n");
return value;
}
// Insert data by location
void SeqlistInsertByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value)
{
if(SeqlistIsFull(st))
{
printf(" Insert the failure , The sequence table is full !\n");
return;
}
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos + 1)
{
printf(" Insert the failure , Wrong insertion position !\n");
return;
}
int i;
if(p == st->pos + 1)
{
st->data[p] = value;
st->pos++;
}
else
{
for(i = st->pos;i >= p;i--)
{
st->data[i + 1] = st->data[i];
}
// Put the inserted data in P The location of
st->data[p] = value;
st->pos++;
}
printf(" Inserting data by location succeeded !\n");
return;
}
// Delete data by location , Return deleted data
DataType SeqlistDeleteByPos(seqlist *st,int p)
{
if(SeqlistIsEmpty(st))
{
printf(" Sequence table is empty , Delete by location failed !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Delete failed , Wrong input position !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
// Save the data to be deleted in value in
DataType value = st->data[p];
// take p Upward data moves downward
int i;
for(i = p;i < st->pos;i++)
{
st->data[i] = st->data[i + 1];
}
st->pos--;
printf(" Data deletion by location succeeded \n");
return value;
}
// Modify the data according to the data
void SeqlistUpdateByData(seqlist *st,DataType OldValue,DataType NewValue)
{
int i,flags = 0;
for(i = 0 ; i <= st->pos;i++)
{
if(st->data[i] == OldValue)
{
st->data[i] = NewValue;
flags = 1;
}
}
if(flags == 0)
{
printf(" Failed to modify data ,%d non-existent \n",OldValue);
}
}
// Modify the data according to the position
void SeqlistUpdateByPos(seqlist *st,int p,DataType value)
{
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Modification failed , The position is wrong !\n");
return;
}
st->data[p] = value;
printf(" Successfully modify the data according to the location !\n");
}
// Find location by data
int SeqlistSearchPos(seqlist *st,DataType value)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i <= st->pos;i++)
{
if(st->data[i] == value)
{
printf(" Find the location according to the data successfully !\n");
return i;
}
}
printf(" To find the failure , data %d non-existent \n",value);
return -1;
}
// Find data by location
DataType SeqlistSearchData(seqlist *st,int p)
{
if(p < 0 || p > st->pos)
{
printf(" Failed to find data by location , The position is wrong !\n");
return (DataType)-1;
}
printf(" Data search by location succeeded !\n");
return st->data[p];
}
// Delete duplicate data
void SeqlistDeleteRepeat(seqlist *st)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0 ; i < st->pos;i++)
{
for(j = i + 1;j <= st->pos;j++)
{
if(st->data[i] == st->data[j])
{
// Delete by location j The data of
SeqlistDeleteByPos(st,j);
//j-- The purpose is to prevent the data of the deleted position from not being compared
j--;
}
}
}
}
// Merge tables
void SeqlistMerge(seqlist *s1,seqlist *s2)
{
int i;
for(i = 0 ; i <= s2->pos;i++)
{
if(SeqlistSearchPos(s1,s2->data[i]) == -1)
{
SeqlistInsert(s1,s2->data[i]);
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- Reentrantlock fair lock source code Chapter 0
- 1.线性回归
- The weight of the product page of the second level classification is low. What if it is not included?
- 3 years of experience, can't you get 20K for the interview and test post? Such a hole?
- Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
- Serial port receives a packet of data
- From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
- [OBS] the official configuration is use_ GPU_ Priority effect is true
- 韦东山第三期课程内容概要
- 新库上线 | CnOpenData中国星级酒店数据
猜你喜欢
Prediction of the victory or defeat of the League of heroes -- simple KFC Colonel
【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 006-自动推导类型和输入输出
12. RNN is applied to handwritten digit recognition
New library online | cnopendata China Star Hotel data
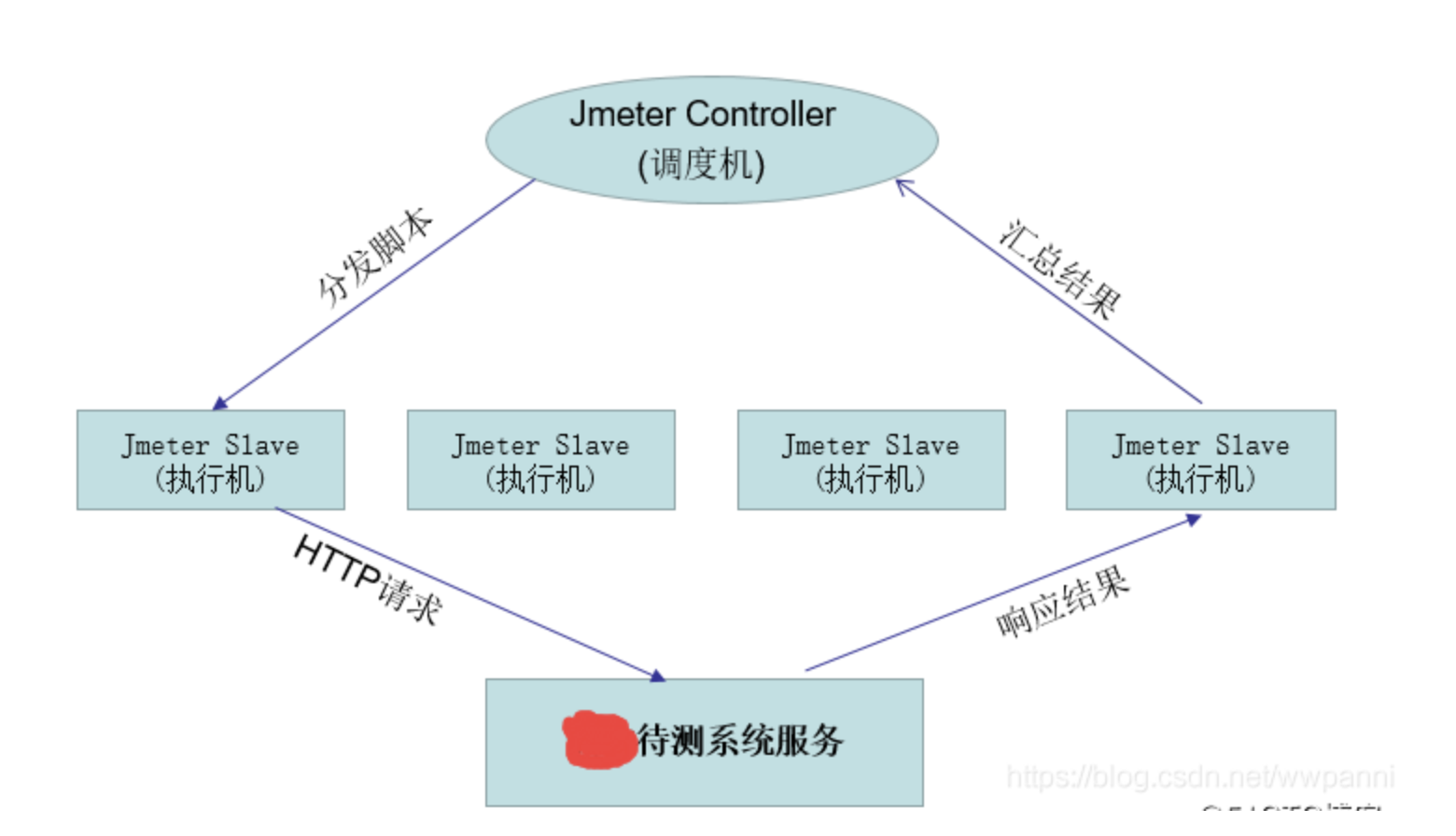
Jemter distributed

Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布
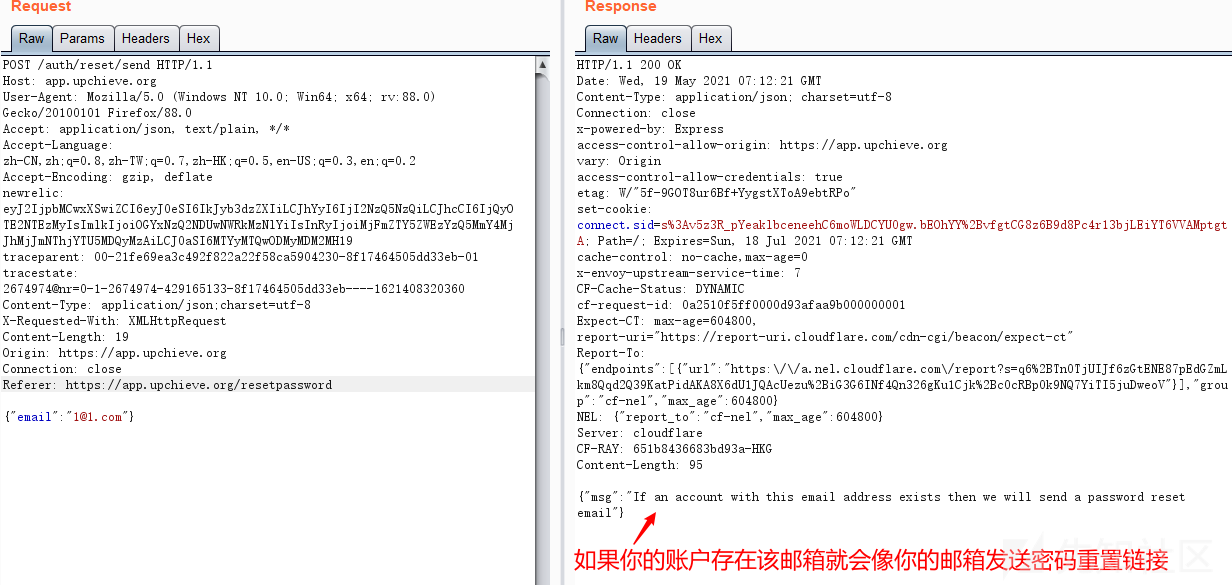
Password recovery vulnerability of foreign public testing
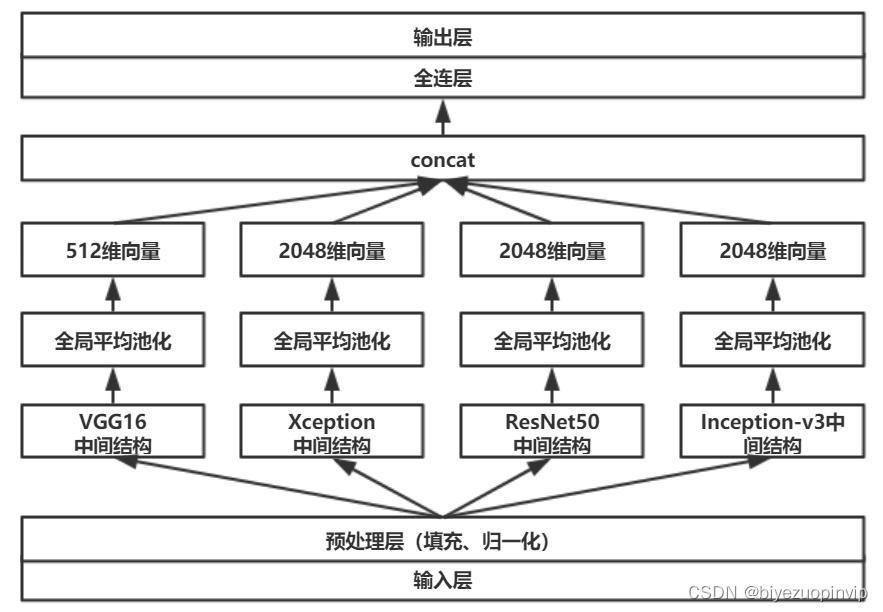
Malware detection method based on convolutional neural network

3 years of experience, can't you get 20K for the interview and test post? Such a hole?

《因果性Causality》教程,哥本哈根大学Jonas Peters讲授
随机推荐
【obs】Impossible to find entrance point CreateDirect3D11DeviceFromDXGIDevice
ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第0篇
Basic types of 100 questions for basic grammar of Niuke
The method of server defense against DDoS, Hangzhou advanced anti DDoS IP section 103.219.39 x
6.Dropout应用
Class head up rate detection based on face recognition
The whole life cycle of commodity design can be included in the scope of industrial Internet
AI遮天传 ML-回归分析入门
jemter分布式
完整的模型训练套路
Fofa attack and defense challenge record
图像数据预处理
【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 006-自动推导类型和输入输出
第四期SFO销毁,Starfish OS如何对SFO价值赋能?
14.绘制网络模型结构
国外众测之密码找回漏洞
[Yugong series] go teaching course 006 in July 2022 - automatic derivation of types and input and output
12. RNN is applied to handwritten digit recognition
22年秋招心得
Service mesh introduction, istio overview