当前位置:网站首页>Just remember Balabala
Just remember Balabala
2022-07-06 10:30:00 【Don't understand anything】
const References to
Usually : The type of reference must strictly match the object type it is bound to
int a = 100;
int &val = a;
But constant references don't need .
double i = 14.42;
const int& i0 = i;
cout << i0;The final output is 14;
in other words , The constant reference will carry out type conversion on the referenced object whose type does not match .
Here i0 Quoted a int Object of type , however i It's a double floating point number . So to ensure that i0 Bound to an integer , The compiler changes the above code into the following form :
const int temp = i; // Use variables to realize type conversion
const int &i0 = temp; // Reuse i0 For temporary quantity ( At this time, the type is matched ) Binding It's nice .
in addition , At this time, constant references , In fact, it seems not to be a constant in the strict sense , Although but , We still can't directly deal with const References to objects , Assign a value , Or other operations that try to change constants . however , You can change the value of constants in other ways
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int val = 100;
const int &cval = val;
cout << cval << endl;
int& ival = val;
++ival;
cout << cval;
}
The output is
100
101Or directly to the original object val Assign a value , It will change too. const The value of the reference of the object .
Add : Usually , References cannot be assigned with literal values , But constant references are ok
const int &val = 42;
cout << val;The result is 42
in other words , Objects cannot be changed by constant references , It doesn't matter whether it's bound to a literal or an object , Anyway, we can't make changes, so there is no meaningless change .
Pointers and const
const double pi = 3.14;// Initialize double constant pi
const double* cptr = π// You can only use a pointer to a constant to store the address of a constant object
double a = 100;
cptr = &a;
cout << *cptr; // Output 100;
++ *cptr;// Constant cannot be assigned
The type of the pointer must be consistent with the type of the object it refers to . But there are two exceptions , The first exception is Allow a pointer to a constant to point to a non constant object .
Look at the code above , We found that , pointer to const , It only requires that the value of the object cannot be changed through this pointer , We can even change the pointer directly , Point to a very large number of objects , There is no binding relationship between the two .
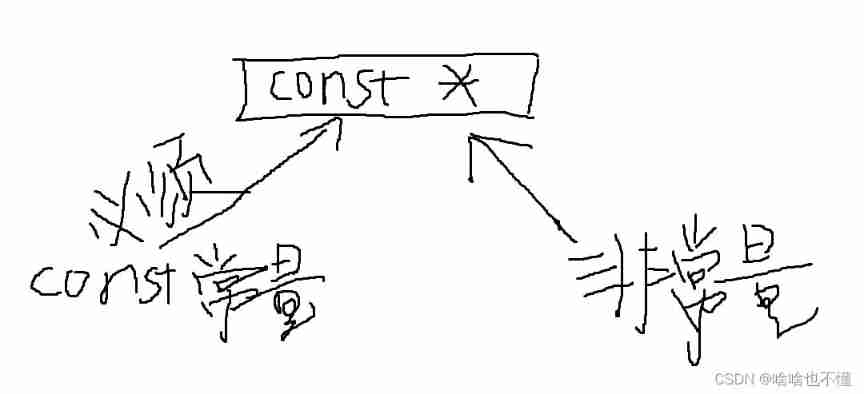
This is the picture I drew myself , My own understanding , I don't know if there are any mistakes ,const The address of the constant must be stored in const * Type in the , however const * You can also store a very large number of addresses . But no matter whose address it is stored , Can't pass the dereference character “*”, Yes Object . and const Same reference , Although it can't be directly through the pointer pair Object , But there are other ways to change the object , It doesn't matter .
there const Just saying : This pointer points to a constant , This constant cannot be arbitrarily changed through this pointer . And what to say next const Pointers are very different .
In the book : A pointer or reference to a constant , Just pointers or references “ Be opinionated ” only , They feel that they point to constants , So consciously do not change the value of the object .
const The pointer
Actually, the above , Our focus is on the type . So we can change the direction of the pointer . What to say next const The pointer , Is to set the pointer itself as a constant . Constant pointers are the same as constants , Must be initialized , And after initialization , The address stored in the pointer can no longer be changed .
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int val = 100;
int* const cptr = &val; // hold * Put it before the keyword to indicate that the pointer is a constant
// This writing form implies a layer of meaning
// That is, the constant is the value of the pointer itself ( The address of the object pointed to )
// Instead of pointing to the object
// The object pointed to can be modified by the dereference character .
const double pi = 3.14;
// The first one here const This ensures that this constant cannot be modified by a pointer
// the second const To ensure the , The address of this pointer , Already bound to this pointer , Can't change .
const double* const pip = π
//pip = &val; illegal , because pip Is a constant pointer , After being initialized , You cannot change the value
//*pip = 1111; illegal , It points to a double constant , Cannot be modified by this pointer , The value of the object he points to .
int* const cptr1 = &val;
*cptr1 = 100;
cout << *cptr1;// Output 100, The type here int
// Means that after dereferencing, you get a int Variable of type , You can change the value
// If it is const int , Then the value cannot be modified
}
I feel this kind of definition statement , Look from right to left , It's a good choice .
top floor const
As mentioned earlier , The pointer itself is an object , It can point to another object . So the pointer itself is a constant , And whether the pointer refers to a constant is two independent problems .
Bottom const: Indicates that the object pointed to is a constant , Related to composite types such as pointers and references .
top floor const: Indicates that the pointer itself is a constant , top floor const Any object can be represented as a constant , For any data type .
What's more special is : The pointer can be either the bottom layer const, It can also be the top floor const
int const a = 100;
cout << a;
// I found that more than pointers can be used after types const, Other data types can also .Used to declare references to const It's all at the bottom const, Taking the address of constant object is also const
const int ci =100;
&ci: Bottom const
int const a = 100; int b = a; const int* c = &a;// top floor const You can give it to the bottom const initialization . //int* const d = c;// Bottom const Not to the top const initialization ( Copy ), Because because c Itself is the bottom layer const, It is itself a variable // however d It's the top floor const, A constant . So variables cannot be copied to a constant . // Let's do another example , Examples cited const int& bval = b;// References are all at the bottom const const int* const p = &bval; //int* const p2 = &bval; p2 It's a top floor const, however bval It's a ground floor const, Cannot perform
边栏推荐
- [paper reading notes] - cryptographic analysis of short RSA secret exponents
- The governor of New Jersey signed seven bills to improve gun safety
- 15 medical registration system_ [appointment registration]
- Baidu Encyclopedia data crawling and content classification and recognition
- MySQL实战优化高手04 借着更新语句在InnoDB存储引擎中的执行流程,聊聊binlog是什么?
- 使用OVF Tool工具从Esxi 6.7中导出虚拟机
- Pytoch LSTM implementation process (visual version)
- 如何搭建接口自动化测试框架?
- 【C语言】深度剖析数据存储的底层原理
- ZABBIX introduction and installation
猜你喜欢
Unicode decodeerror: 'UTF-8' codec can't decode byte 0xd0 in position 0 successfully resolved

Introduction tutorial of typescript (dark horse programmer of station B)
C miscellaneous two-way circular linked list
MySQL29-数据库其它调优策略
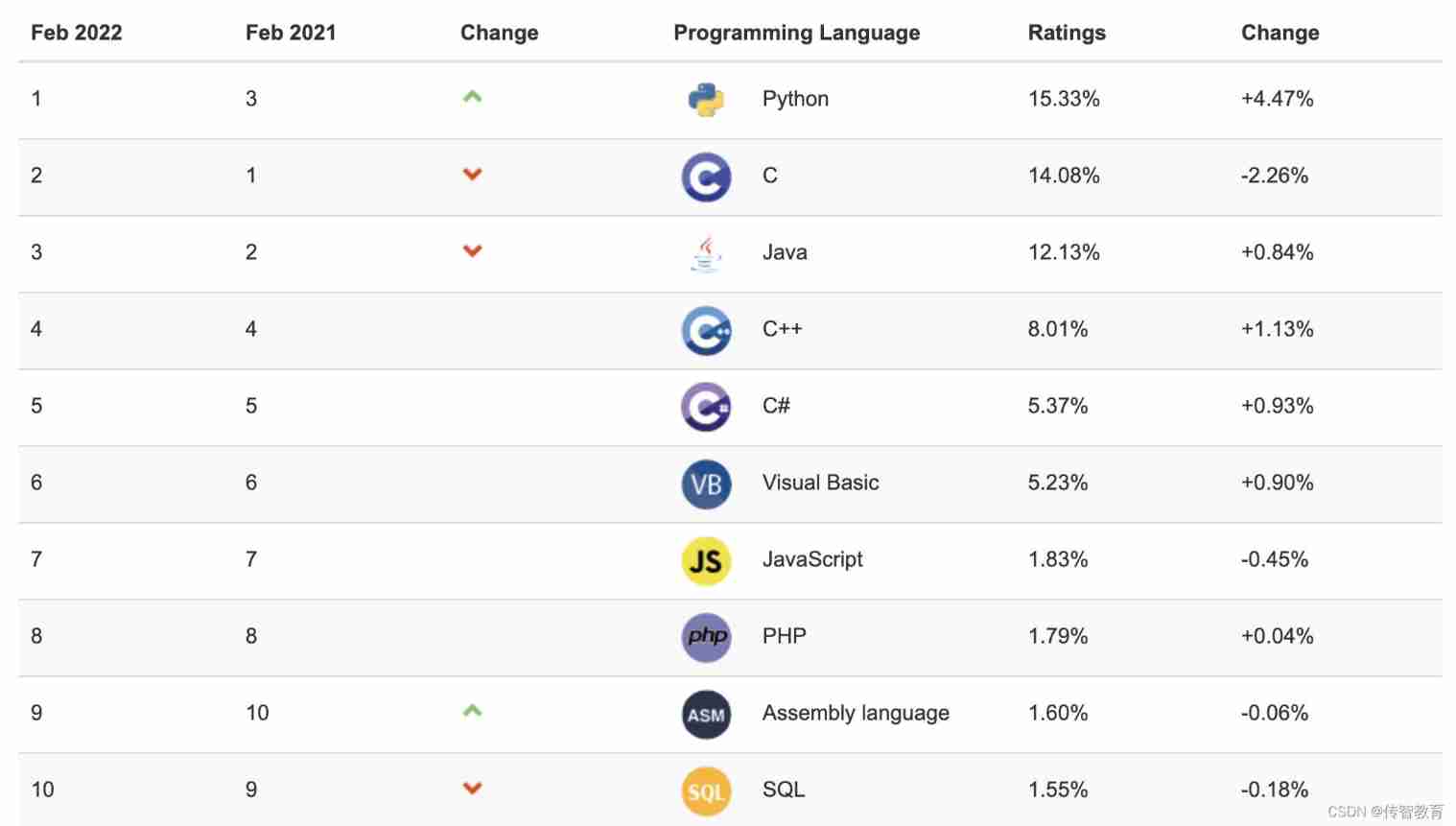
The programming ranking list came out in February. Is the result as you expected?
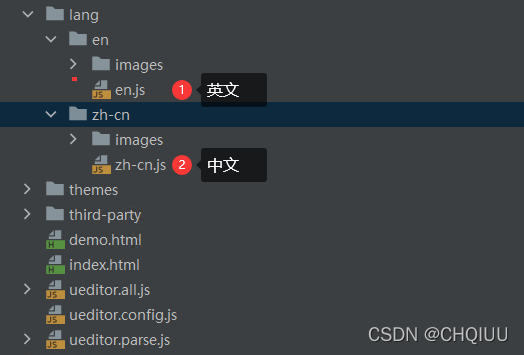
UEditor国际化配置,支持中英文切换
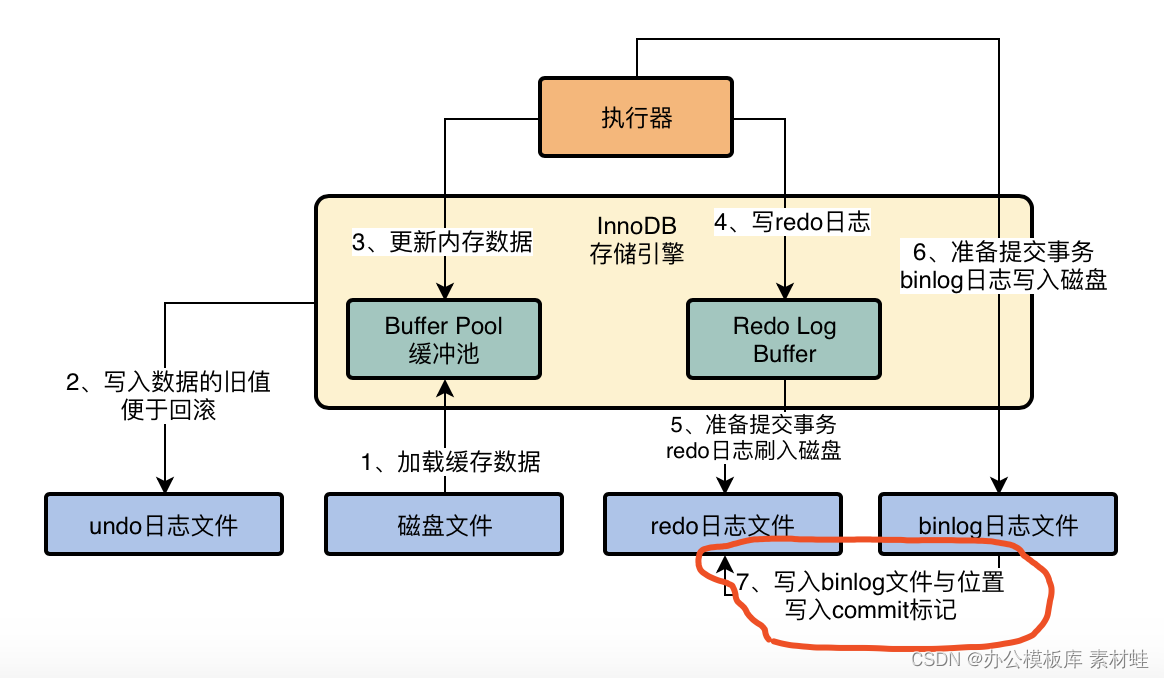
MySQL Real Time Optimization Master 04 discute de ce qu'est binlog en mettant à jour le processus d'exécution des déclarations dans le moteur de stockage InnoDB.
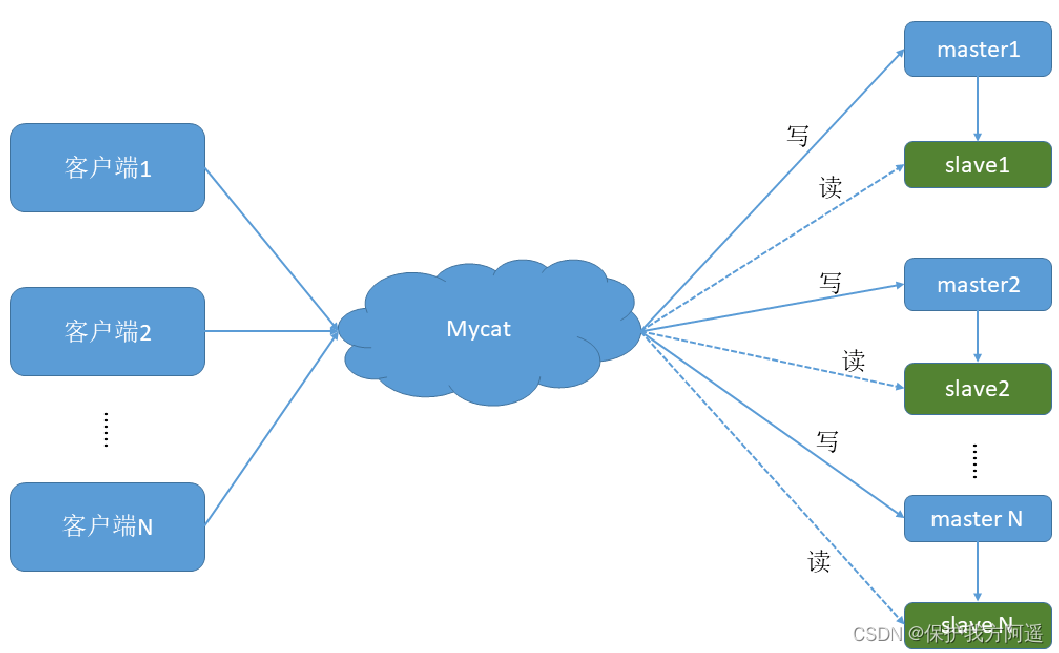
数据库中间件_Mycat总结
![[after reading the series] how to realize app automation without programming (automatically start Kwai APP)](/img/e1/bad9cfa70d3c533cfaddeee40b96f1.jpg)
[after reading the series] how to realize app automation without programming (automatically start Kwai APP)
Cmooc Internet + education
随机推荐
MySQL底层的逻辑架构
MySQL的存储引擎
Security design verification of API interface: ticket, signature, timestamp
Const decorated member function problem
[paper reading notes] - cryptographic analysis of short RSA secret exponents
16 医疗挂号系统_【预约下单】
MySQL 29 other database tuning strategies
How to build an interface automation testing framework?
Super detailed steps for pushing wechat official account H5 messages
MySQL实战优化高手10 生产经验:如何为数据库的监控系统部署可视化报表系统?
MySQL combat optimization expert 12 what does the memory data structure buffer pool look like?
MySQL實戰優化高手08 生產經驗:在數據庫的壓測過程中,如何360度無死角觀察機器性能?
MNIST implementation using pytoch in jupyter notebook
Redis集群方案应该怎么做?都有哪些方案?
Introduction tutorial of typescript (dark horse programmer of station B)
Isn't there anyone who doesn't know how to write mine sweeping games in C language
How to make shell script executable
数据库中间件_Mycat总结
该不会还有人不懂用C语言写扫雷游戏吧
Implement context manager through with