当前位置:网站首页>Mysql30 transaction Basics
Mysql30 transaction Basics
2022-07-06 10:29:00 【Protect our party a Yao】
One . Overview of database transactions
1.1. Storage engine support
SHOW ENGINES Command to view the current MySQL What are the supported storage engines , And whether these storage engines support transactions .
show engines;
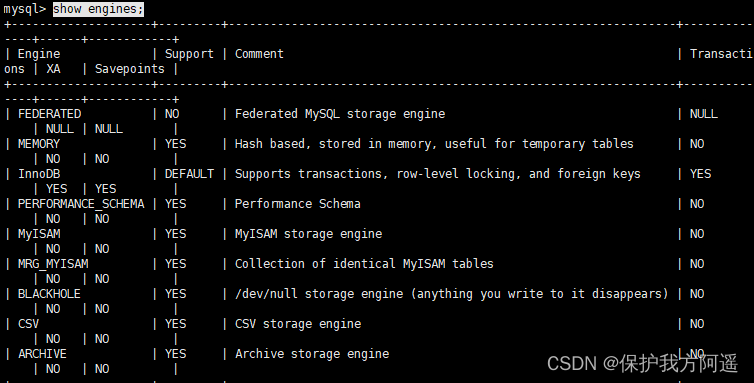
Can see in MySQL in , Only InnoDB It's transactional .
1.2. Basic concepts
Business : A set of logical operating units , To change data from one state to another .
Principles of transaction processing : Ensure that everything is done as A unit of work To execute , Even if something goes wrong , Can't change this way of execution . When multiple operations are performed in a transaction , Either all transactions are committed ( commit ), So these changes are permanent It's preserved ; Or the database management system will give up All done modify , The whole transaction is rolled back ( rollback ) To the initial state .
1.3. The transaction ACID characteristic
- Atomicity (atomicity): Atomicity means that a transaction is an indivisible unit of work , Or submit it all , Either all failures roll back .
- Uniformity (consistency): According to the definition , Consistency refers to before and after transaction execution , Data from a Legitimacy status Change to another Legitimacy status . This state is Semantically Not grammatical , Related to specific business . What is the legal data state ? Satisfy Predetermined constraints The state of is called legal state . More popular , This state is defined by you ( For example, meet the constraints in the real world ). Satisfy this state , The data is consistent , Not satisfied with this state , The data is inconsistent ! If an operation in a transaction fails , The system will automatically undo the currently executing transaction , Return to the state before the transaction operation .
- Isolated type (isolation): Transaction isolation refers to the execution of a transaction Can't be disturbed by other affairs , That is, the operation within a transaction and the data pair used Concurrent Other transactions are isolated , Transactions that execute concurrently cannot interfere with each other .
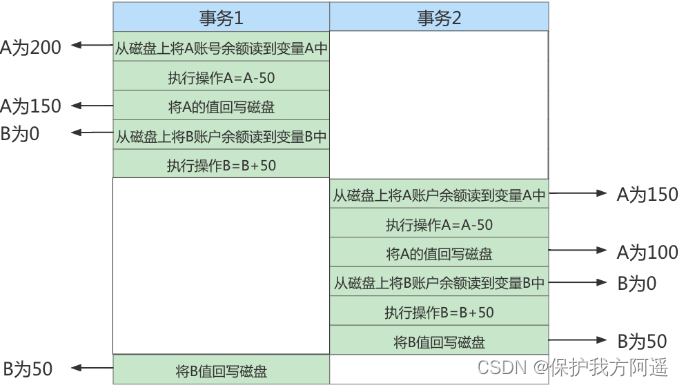
What if there's no guarantee of isolation ? hypothesis A The account has 200 element ,B Account 0 element .A Account to B Account transfer twice , The amount of each time is 50 element , Execute in two transactions . If isolation cannot be guaranteed , The following will happen :
UPDATE accounts SET money = money - 50 WHERE NAME = 'AA';
UPDATE accounts SET money = money + 50 WHERE NAME = 'BB';
- persistence (durability): Persistence means that once a transaction is committed , The change it makes to the data in the database is Permanent , Other subsequent operations and database failures should not have any impact on it . Persistence is through Transaction log To ensure that the . Including the log Redo log and Rollback log . When we modify data through transactions , First, the change information of the database will be recorded in the redo log , Then modify the corresponding row in the database . The advantage of this is , Even if the database system crashes , After the database is restarted, you can also find the redo log that has not been updated to the database system , Re execution , This makes the transaction persistent .
1.4. The state of the transaction
We now know Business It's an abstract concept , It actually corresponds to one or more database operations ,MySQL According to the different stages of these operations Business Roughly divided into several States :
- Activities of the (active): When the database operation corresponding to the transaction is in progress , Let's say the office Activities of the state .
- Partially submitted (partially committed): When the last operation in the transaction is completed , But because the operations are all performed in memory , The impact is not No refresh to disk , Let's say the office Partially submitted state .
- The failure of the (failed): When the affairs office Activities of the perhaps Partially submitted In the state of , You may have encountered some errors ( Error in the database itself 、 Operating system error or direct power failure, etc ) And cannot continue , Or artificially stop the execution of the current transaction , Let's say the office The failure of the state .
- Suspended (aborted): If the transaction is partially executed and becomes The failure of the state , Then you need to restore the operations in the modified transaction to the state before the transaction is executed . let me put it another way , To undo the impact of failed transactions on the current database . We call this revocation process Roll back . When Roll back When the operation is completed , That is, the database is restored to the state before the transaction is executed , Let's say the office Suspended state .
give an example :
UPDATE accounts SET money = money - 50 WHERE NAME = 'AA';
UPDATE accounts SET money = money + 50 WHERE NAME = 'BB';
- The submitted (committed): When one is in Partially submitted The transaction in status will all the modified data Sync to disk After that , We can say that the office The submitted state .
A basic state transition diagram is shown below :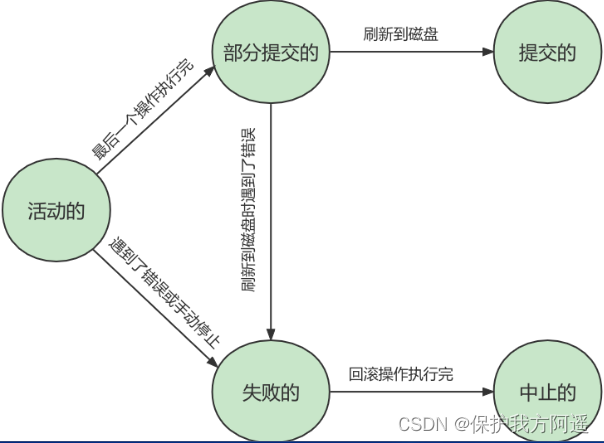
Two . How to use transactions
There are two ways to use transactions , Respectively Explicit transaction and Implicit transaction .
2.1. Explicit transaction
step 1: START TRANSACTION perhaps BEGIN , The function is to explicitly open a transaction .
mysql> BEGIN;
# perhaps
mysql> START TRANSACTION;
START TRANSACTION Sentences are compared with BEGIN What's special is , Can you follow a few Modifier :
① READ ONLY : Identifies that the current transaction is a Read only transactions , That is, the database operation belonging to this transaction can only read data , You can't modify the data .
② READ WRITE : Identifies that the current transaction is a Read write transactions , That is, the database operation belonging to the transaction can read data , You can also modify the data .
③ WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT : Start consistent read .
step 2: Operations in a series of transactions ( Mainly DML, Not included DDL)
step 3: Commit transaction or Suspension of business ( That is, roll back the transaction )
# Commit transaction . When the transaction is committed , Changes to the database are permanent .
mysql> COMMIT;
# Roll back the transaction . That is, undo all ongoing uncommitted modifications
mysql> ROLLBACK;
# Roll back the transaction to a savepoint .
mysql> ROLLBACK TO [SAVEPOINT];
2.2. Implicit transaction
MySQL There's a system variable in autocommit :
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'autocommit';
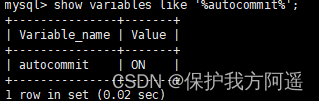
Of course , If we want to close this Automatic submission The function of , You can use one of the following two methods :
- Explicit use START TRANSACTION perhaps BEGIN Statement to open a transaction . In this way, the auto commit function will be temporarily turned off before the transaction is committed or rolled back .
- Put the system variable autocommit Is set to OFF , Just like this. :
SET autocommit = OFF;
# or
SET autocommit = 0;
2.3. Implicit submission of data
- Data definition language (Data definition language, Abbreviation for :DDL).
- To use or modify implicitly mysql Tables in the database .
- Transaction control or statements about locking .
① When a transaction has not been committed or rolled back, we use START TRANSACTION perhaps BEGIN The statement opens
Another transaction , Meeting Implicit submission Last business .
② Current autocommit The value of the system variable is OFF , We manually set it to ON when , It will be Implicit submission Antecedent
The business to which the sentence belongs .
③ Use LOCK TABLES 、 UNLOCK TABLES And other statements about locking will also Implicit submission What the preceding sentence belongs to
service . - Loading data statements .
- About MySQL Some statements copied .
- Other sentences .
2.4. Use examples 1: Commit and rollback
Let's see MySQL By default , What is the final result of this transaction .
situation 1:
CREATE TABLE USER(NAME VARCHAR(20), PRIMARY KEY (NAME)) ENGINE=INNODB;
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Zhang San ';
COMMIT;
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
ROLLBACK;
SELECT * FROM USER;
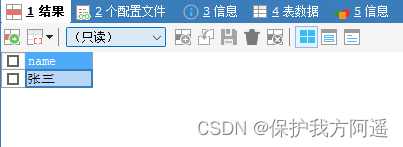
situation 2:
TRUNCATE TABLE `user`;
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Zhang San ';
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
ROLLBACK;
SELECT * FROM USER;
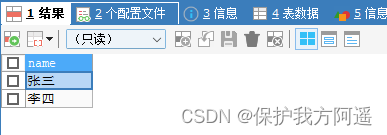
situation 3:
TRUNCATE TABLE `user`;
SET @@completion_type = 1;
BEGIN;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Zhang San ';
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
INSERT INTO USER SELECT ' Li Si ';
ROLLBACK;
SELECT * FROM USER;
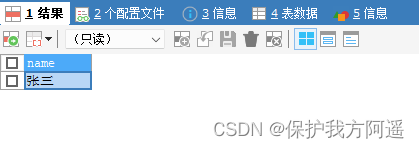
When we set autocommit=0 when , Whether or not START TRANSACTION perhaps BEGIN The way to start things
service , All need to use COMMIT Submit , Make the transaction effective , Use ROLLBACK Roll back the transaction .
When we set autocommit=1 when , Every one of them SQL Statements are automatically submitted . But then , If you take START
TRANSACTION perhaps BEGIN To explicitly open a transaction , Then this transaction can only be COMMIT Will not take effect until ,
stay ROLLBACK Will roll back when .
3、 ... and . Transaction isolation level
MySQL It's a client / The server Architecture software , For the same server , There can be several clients connected to it , After each client connects to the server , It can be called a conversation ( Session ). Each client can issue a request statement to the server in its own session , A request statement may be part of a transaction , That is to say, the server may handle multiple transactions at the same time . Business has Isolation, Characteristics of , In theory, in a certain transaction Access to certain data when , Other things should be done line up , When the transaction is committed , Other transactions can continue to access this data . But it's good for Too much performance impact , We want to keep the transaction isolated , You also want the server to handle multiple transactions accessing the same data The performance should be as high as possible , It depends on how the two trade off .
3.1. Data preparation
We need to create a table :
CREATE TABLE student (
studentno INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
class varchar(20),
PRIMARY KEY (studentno)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARSET=utf8;
Then insert a piece of data into the table :
INSERT INTO student VALUES(1, ' Millet ', '1 class ');
Now the data in the table is like this :
select * from student;
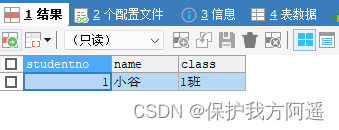
3.2. Data concurrency problem
For transaction isolation and concurrency , How can we make a choice ? Let's first look at the transactions that access the same data in Serial execution is not guaranteed ( That is, after executing one, execute another ) What problems may arise in the case of :
- Dirty write ( Dirty Write ): For two things Session A、Session B, If the transaction Session A Revised the other one Not submitted Business Session B A modified The data of , That means something happened Dirty write .
- Dirty reading ( Dirty Read ): For two things Session A、Session B,Session A Read It has been Session B to update But Not submitted Field of . Later, if Session B Roll back ,Session A Read The content of is Temporary and invalid Of .Session A and Session B Each opens a transaction ,Session B The transaction in will first studentno As a 1 The record of name Update column to ’ Zhang San ’, then Session A To query this studentno by 1 The record of , If you read a column name The value of is ’ Zhang San ’, and Session B The transaction in is rolled back later , that Session A A transaction in is equivalent to reading a nonexistent data , This phenomenon is called Dirty reading .
- It can't be read repeatedly ( Non-Repeatable Read ): For two things Session A、Session B,Session A Read It's a field , then Session B to update This field . after Session A Read again Same field , The value is different 了 . That means that non repeatable . We are Session B Submitted several Implicit transaction ( Note that implicit transactions , It means that the transaction is committed when the statement ends ), These transactions have been modified studentno As a 1 The column of the record for name Value , After each transaction commit , If Session A You can view the latest values for all transactions in , This phenomenon is also called It can't be read repeatedly .
- Fantasy reading ( Phantom ): For two things Session A、Session B, Session A From a table Read It's a field , then Session B In the table Insert Some new ones . after , If Session A Read again The same watch , There will be more lines . That means unreal reading .Session A According to the conditions, the transaction in studentno > 0 This conditional query table student, Got it name The column value is ’ Zhang San ’ The record of ; after Session B Submitted a Implicit transaction , The transaction reports to the table student A new record has been inserted into ; after Session A The transactions in are then processed under the same conditions studentno > 0 Query table student, The result set contains Session B The record newly inserted by the transaction in , This phenomenon is also called Fantasy reading . We call the newly inserted records Phantom recording .
3.3. SQL Four isolation levels in
The above describes some problems that may be encountered during the execution of several concurrent transactions , These problems can be prioritized , Let's rank these problems according to their severity :
Dirty write > Dirty reading > It can't be read repeatedly > Fantasy reading
We are willing to give up some isolation in exchange for some performance, which is reflected in : Set up some isolation levels , The lower the isolation level . The more concurrency problems occur . SQL standard Set up in 4 individual Isolation level :
- READ UNCOMMITTED : Read uncommitted , At this isolation level , All transactions can see the results of other uncommitted transactions . Can't avoid dirty reading 、 It can't be read repeatedly 、 Fantasy reading .
- READ COMMITTED : Read submitted , It satisfies the simple definition of isolation : A transaction can only see changes that have been committed by the transaction . This is the default isolation level for most database systems ( But it's not MySQL default ). Avoid dirty reading , But not repeatable 、 The unreal reading problem still exists .
- REPEATABLE READ : Repeatable , Business A After reading a piece of data , At this point, the transaction B This data has been modified and submitted , The transaction A Reread the data , Read the original content . Avoid dirty reading 、 It can't be read repeatedly , But the problem of unreal reading still exists . This is a MySQL The default isolation level of .
- SERIALIZABLE : Serializable , Make sure that transactions can read the same rows from a table . During the duration of this transaction , Prevent other transactions from inserting into the table 、 Update and delete operations . All concurrency problems can be avoided , But the performance is very low . It can avoid dirty reading 、 No repeated reading or phantom reading .
SQL standard Specified in the , For different isolation levels , Concurrent transactions can have different severity problems , The details are as follows :
| Isolation level | Possibility of dirty reading | The possibility of non repetition | The possibility of unreal reading | Lock reading |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| READ UNCONMITED | YES | YES | YES | NO |
| READ COMNITED | NO | YES | YES | NO |
| REPEATABLE READ | NO | NO | YES | NO |
| SERIALIZABLE | NO | NO | NO | YES |
Dirty write Why didn't it involve ? Because the problem of dirty writing is too serious , Whatever the isolation level , Dirty writing is not allowed .
Different isolation levels have different phenomena , And there are different locking and concurrency mechanisms , Higher isolation level , The worse the concurrency performance of the database ,4 The relationship between transaction isolation level and concurrency performance is as follows :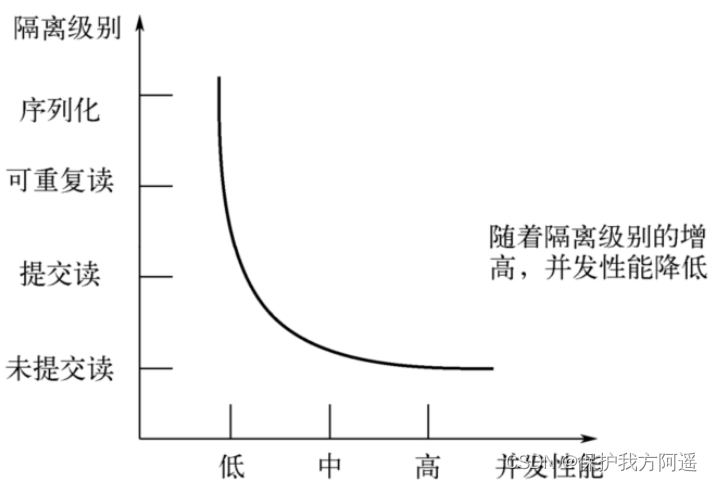
3.4. MySQL Four isolation levels supported
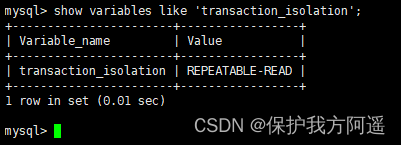
MySQL The default isolation level for is REPEATABLE READ, We can manually modify the isolation level of transactions .
# Check the isolation level ,MySQL 5.7.20 Before the version of :
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'tx_isolation';
# MySQL 5.7.20 After the version , introduce transaction_isolation To replace tx_isolation
# Check the isolation level ,MySQL 5.7.20 Version and later :
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'transaction_isolation';
# Or different MySQL Can be used in all versions :
SELECT @@transaction_isolation;
3.5. How to set the isolation level of transactions
Modify the isolation level of the transaction through the following statement :
SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL Isolation level ;
# among , Isolation level format :
> READ UNCOMMITTED
> READ COMMITTED
> REPEATABLE READ
> SERIALIZABLE
perhaps :
SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] TRANSACTION_ISOLATION = ' Isolation level '
# among , Isolation level format :
> READ-UNCOMMITTED
> READ-COMMITTED
> REPEATABLE-READ
> SERIALIZABLE
About using... When setting GLOBAL or SESSION Influence :
- Use GLOBAL keyword ( Affect... Globally ):
SET GLOBAL TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE;
# or
SET GLOBAL TRANSACTION_ISOLATION = 'SERIALIZABLE';
be :
- The currently existing session is invalid .
- It only works on the session after the statement has been executed .
- Use SESSION keyword ( Affect... At the session level ):
SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE;
# or
SET SESSION TRANSACTION_ISOLATION = 'SERIALIZABLE';
be :
- Valid for all subsequent transactions of the current session .
- If you execute between transactions , Is valid for subsequent transactions .
- This statement can be executed in the middle of an open transaction , But it doesn't affect the currently executing transaction .
Summary :
The database specifies multiple transaction isolation levels , Different isolation levels correspond to different interference levels , Higher isolation level , The better the data consistency , But the less concurrent .
3.6. Examples of different isolation levels
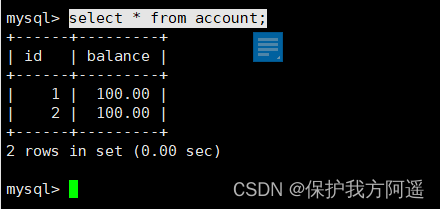
Prepare the data :
CREATE TABLE account(id int,balance decimal(10,2));
insert into account values(1,100),(2,100);
select * from account;
3.6.1. Read uncommitted dirty reads
Set the isolation level to uncommitted read :
set session transaction isolation level read uncommitted;
 Business 1 And transaction 2 The execution process of is as follows :
Business 1 And transaction 2 The execution process of is as follows :
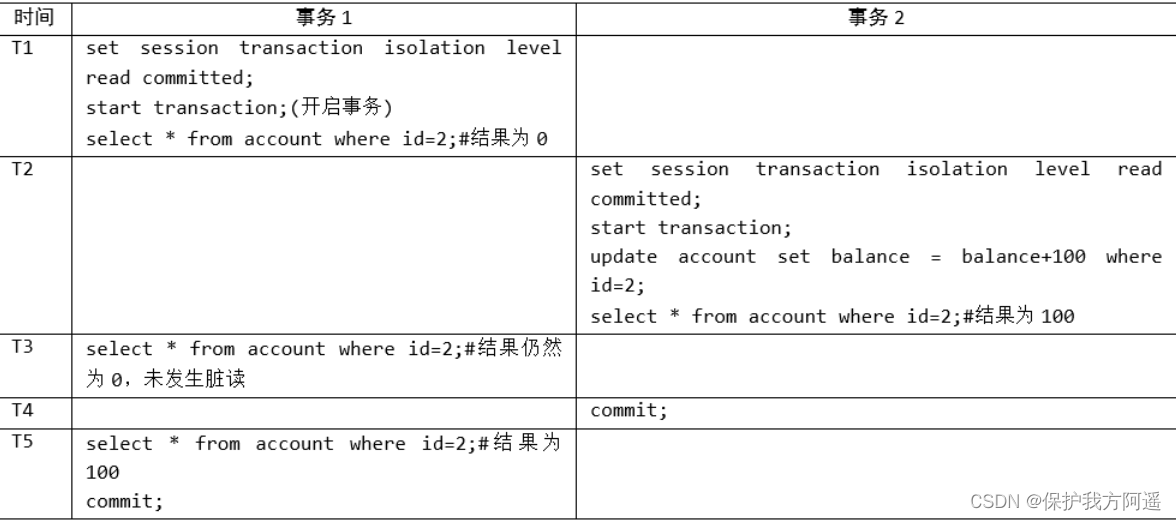
3.6.2. Read submitted
Set the isolation level to read committed :
set session transaction isolation level read committed;
3.6.3. Repeatable
Set the isolation level to repeatable read :
set session transaction isolation level repeatable read;

3.6.4. Fantasy reading

Four . Common classifications of transactions
From the perspective of transaction theory , Transactions can be divided into the following types :
- Flat affairs (Flat Transactions).
- Flat transactions with savepoints (Flat Transactions with Savepoints).
- Transaction chain (Chained Transactions).
- Nested transactions (Nested Transactions).
- Distributed transactions (Distributed Transactions).
边栏推荐
- MySQL combat optimization expert 05 production experience: how to plan the database machine configuration in the real production environment?
- 14 medical registration system_ [Alibaba cloud OSS, user authentication and patient]
- MNIST implementation using pytoch in jupyter notebook
- Time complexity (see which sentence is executed the most times)
- MySQL combat optimization expert 07 production experience: how to conduct 360 degree dead angle pressure test on the database in the production environment?
- MySQL31-MySQL事务日志
- [unity] simulate jelly effect (with collision) -- tutorial on using jellysprites plug-in
- Set shell script execution error to exit automatically
- Time in TCP state_ The role of wait?
- NLP routes and resources
猜你喜欢
![14 medical registration system_ [Alibaba cloud OSS, user authentication and patient]](/img/c4/81f00c8b7037b5fb4c5df4d2aa7571.png)
14 medical registration system_ [Alibaba cloud OSS, user authentication and patient]
如何搭建接口自动化测试框架?
实现以form-data参数发送post请求
Not registered via @enableconfigurationproperties, marked (@configurationproperties use)
MySQL combat optimization expert 04 uses the execution process of update statements in the InnoDB storage engine to talk about what binlog is?
Ueeditor internationalization configuration, supporting Chinese and English switching
UnicodeDecodeError: ‘utf-8‘ codec can‘t decode byte 0xd0 in position 0成功解决
PyTorch RNN 实战案例_MNIST手写字体识别
If someone asks you about the consistency of database cache, send this article directly to him

The 32-year-old fitness coach turned to a programmer and got an offer of 760000 a year. The experience of this older coder caused heated discussion
随机推荐
17 medical registration system_ [wechat Payment]
安装OpenCV时遇到的几种错误
基于Pytorch的LSTM实战160万条评论情感分类
jar运行报错no main manifest attribute
Good blog good material record link
MySQL34-其他数据库日志
MySQL combat optimization expert 07 production experience: how to conduct 360 degree dead angle pressure test on the database in the production environment?
MySQL36-数据库备份与恢复
高并发系统的限流方案研究,其实限流实现也不复杂
Typescript入门教程(B站黑马程序员)
Carolyn Rosé博士的社交互通演讲记录
基于Pytorch肺部感染识别案例(采用ResNet网络结构)
15 医疗挂号系统_【预约挂号】
A necessary soft skill for Software Test Engineers: structured thinking
MySQL combat optimization expert 12 what does the memory data structure buffer pool look like?
[C language] deeply analyze the underlying principle of data storage
Chrome浏览器端跨域不能访问问题处理办法
实现微信公众号H5消息推送的超级详细步骤
MySQL33-多版本并发控制
Technology | diverse substrate formats