当前位置:网站首页>【离散化+前缀和】Acwing802. 区间和
【离散化+前缀和】Acwing802. 区间和
2022-08-02 14:11:00 【超级码力奥】
参考题解:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/13511/

// 很好的分析过程:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/13511/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010; //n次插入和m次查询相关数据量的上界
int n, m;
// 存离散化之后的插入的值
int a[N];
// 存数组a的前缀和
int s[N];
vector<int> alls; // 存所有与插入和查询相关的坐标
vector<pair<int, int>> add, query; // 存储插入和询问操作的数据
// 返回输入的坐标离散化之后的下边
int find(int x)
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
// 至于为啥返回r + 1,是因为让a和前缀和数组从1开始处理
// 方便使用前缀和运算。
return r + 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
int x, c;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &c);
add.push_back({
x, c});
alls.push_back(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++)
{
int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
query.push_back({
l, r});
alls.push_back(l);
alls.push_back(r);
}
// 对需要操作的下标排序,去重
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
// 执行前n次插入操作
for(auto item : add)
{
int x = find(item.first);
a[x] += item.second;
}
// 处理前缀和
for(int i =1; i <= alls.size(); i ++ ) s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i];
// 处理后m次询问操作
for(auto item : query)
{
int l = find(item.first);
int r = find(item.second);
printf("%d\n", s[r] - s[l - 1]);
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- How to reinstall Win7 system with U disk?How to reinstall win7 using u disk?
- What is Win10 God Mode for?How to enable God Mode in Windows 10?
- 利用plot_surface命令绘制复杂曲面入门详解
- Masters and Masters
- Letter combination of LeetCode2 phone number
- Detailed introduction to the hierarchical method of binary tree creation
- In-depth understanding of Golang's Map
- Software Testing Basics (Back)
- Win10上帝模式干嘛的?Win10怎么开启上帝模式?
- How to simulate 1/3 probability with coins, and arbitrary probability?
猜你喜欢
Detailed introduction to drawing complex surfaces using the plot_surface command
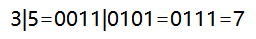
奇技淫巧-位运算
Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
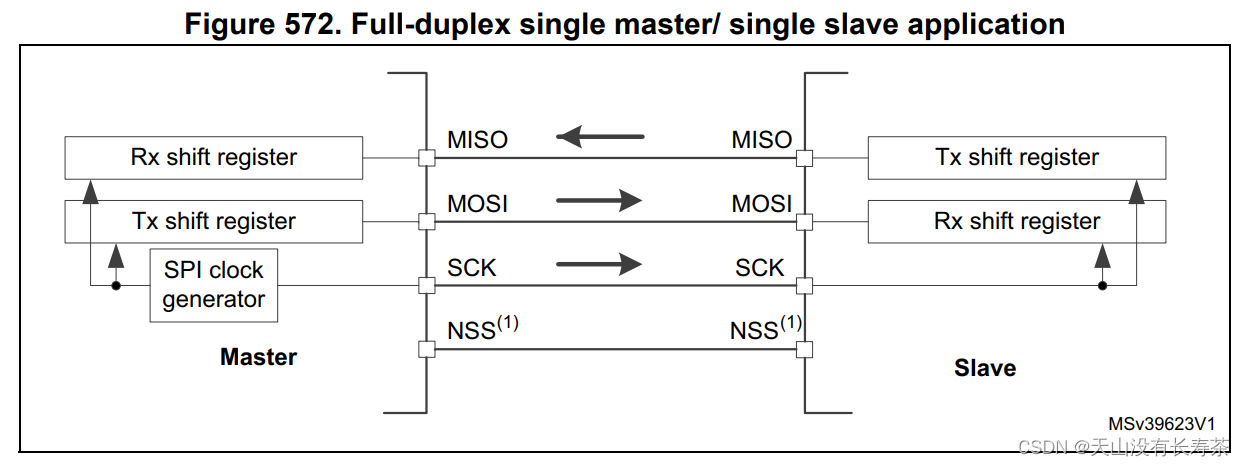
STM32LL library use - SPI communication

Win11系统找不到dll文件怎么修复

Win11 computer off for a period of time without operating network how to solve

Win11电脑一段时间不操作就断网怎么解决

win10 system update error code 0x80244022 how to do
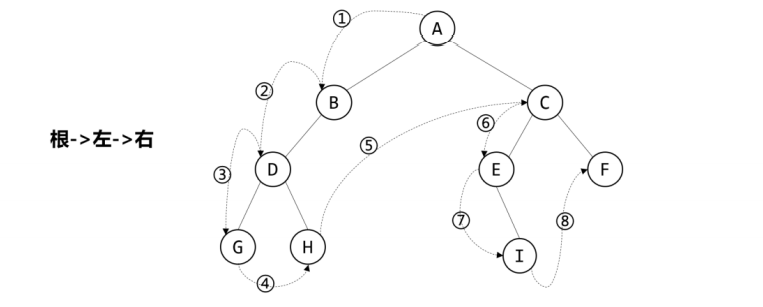
第三十二章:二叉树的存储与遍历
第二十五章:一文掌握while循环
随机推荐
Open the door of electricity "Circuit" (1): voltage, current, reference direction
1. Development community homepage, register
MATLAB绘图函数ezplot入门详解
3.用户上传头像
cmake configure libtorch error Failed to compute shorthash for libnvrtc.so
Exotic curiosity-a solution looking - bit operations
模板系列-二分
关于c语言的调试技巧
Win10电脑需要安装杀毒软件吗?
A clean start Windows 7?How to load only the basic service start Windows 7 system
casbin模型
二叉树遍历之后序遍历(非递归、递归)入门详解
永久更改pip源
Mysql connection error solution
Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
网络安全抓包
二叉树的遍历:递归法/ 迭代法/ 统一迭代法(强QAQ)
第三十章:普通树的存储和遍历
MATLAB制作简易小动画入门详解
In-depth understanding of Golang's Map