当前位置:网站首页>Dark horse -- redis
Dark horse -- redis
2022-07-06 19:13:00 【Hu Yuqiao】
Learning links :https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cr4y1671t?p=1&vd_source=510ec700814c4e5dc4c4fda8f06c10e8
Crazy God notes :https://www.cnblogs.com/meditation5201314/p/14882992.html#redis%E4%BA%94%E7%A7%8D%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%B1%BB%E5%9E%8B
Code address :https://gitee.com/empirefree/SpringBoot-summarize
It may be because the teacher said according to the project code , The playback volume is so low , In fact, the teacher spoke very well , It is completely possible not to depend on the project , Build a small project by yourself and simply use basic redis Just go . In the advanced chapter, build clusters 、canal These are skipped , First get familiar with the record , Let's talk about it later
List of articles
1. The basic chapter
1.1 Preface
Madness theory –Redis Learning notes :https://www.cnblogs.com/meditation5201314/p/14882992.html
I learned what crazy God said before Redis, Just feel yourself Redis Learned , I saw what Shang Silicon Valley sent Redis Chapter , I found that I just learned some basic skills , Actual advanced content 、 Practical drill 、 I didn't understand the principle , Sure enough, you have to move forward modestly .
1.2 Basic types
1.2.1 String
setnx mykey 111
1.2.2 List
Go first and come out later , It can be regarded as a stack , You can also make queues
1.2.3 set
Value cannot be repeated
1.2.4 Hash
key map
1.2.5 Zset
zset key score value
-- z1 Set add elements m2, The score is 2
zadd z1 2 m2
-- Reverse order from index 1 Start to output 2 Elements
zrevrange z1 1 2 withscores
-- Inquire about z1 The largest of 1000 The smallest score 0 branch ,0: The offset is less than or equal to 1000 Of 3 Elements
zrevrangeByScore z1 1000 0 withscores limit 0 3
-- 1: Represents less than the last returned maximum score 3 Elements ( If the scores are the same, there will be repeated returns )
zrevrangeByScore z1 The maximum score returned last time 0 withscores limit 1 3
1.3 Connection pool
1.3.1 Connection pool type
1.jedis
2.SpringDataRedis: Provides redisTemplate
1.3.2 RedisTempalte
1.3.2.1 Basic concepts
1. Internally implemented jdk serialize
2. About random code : because SpringMVC Built in jackson-Binder Such serialization
2. Actual combat
2.1. SMS login ( A little )
I've done a lot before , I simply read the writing principle and skipped
2.2. Data caching
2.2.1 Basic concepts
2.2.1.1 Cache update strategy
- Use delete cache
- How to ensure the consistency of cache and database data
- Single project : Cache and database are put into the same transaction
- Distributed transactions :TCC Business plan
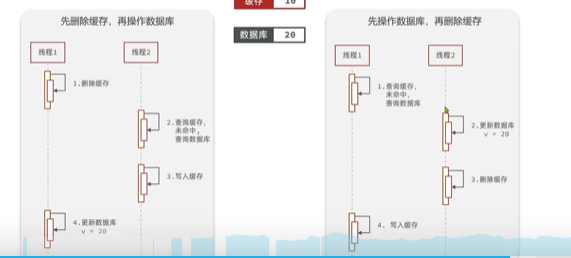
- Database first or So let's delete the cache ( This generally refers to user requests , Business background update data , Of course , The whole operation transaction or distributed lock implementation is also ok )
- Delete cache first , Rework database :A Delete first ,B stay A Reading and writing the cache before updating will write error data
- Database first , Reoperation cache :A Database first ,B stay A Reading the database and writing the cache before the operation will also read the wrong data
- Delay double delete ( Delete before request , Delay after updating the Library 3~5 second , And then delete ): The reason for the delay is to ensure A Deleting the cache operation database is not completed ,B Then read the wrong data , Then dirty reading occurs , Just to make sure B After execution , But I don't think it's meaningful , In the case of concurrency, you still have to use transactions or distributed locks . Let's have a brief understanding .
2.2.1.2 Optimism lock / Pessimistic locking
Optimism lock + Business : Data consistency can be achieved , It is suitable for the situation of small concurrent competition ( Because it avoids frequent data updates , It's using CAS capare and swap Spin or version number mechanism 2 Ways of planting )
Pessimistic locking + Business : Lock before each reading
2.3 Distributed lock
2.3.1 Basic concepts
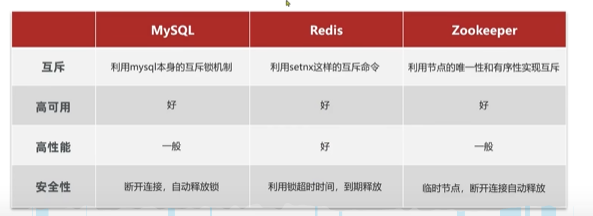
Distributed lock : The mutually visible and mutually exclusive locks between multithreads in the distributed system or cluster mode
2.3.2 Redisson principle
2.3.2.0 Distributed lock problem
be based on setnx The resulting distributed lock exists 4 A question , and Redisson Can solve :
1. Do not reenter :setx Thread the same thread can repeatedly acquire the same lock
1. Can't try again :setnt Only try to acquire the lock once without retrying
1. Time out release :setnx If the business execution is too long, the lock will be automatically deleted .( But if you do not set the timeout and the service restarts, then follow up key The value always exists )
1. Master slave consistency :setnx in , The master set the lock , Change from library to main library after downtime , Then the outside can still get the lock
2. Redisson Reentrant lock
Get the lock :
// Judge whether it exists , If you can get it, you can get
if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0)
then
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
// according to threadid Judge whether the lock is your own , Add one to the number of locks obtained , Then reset the validity
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)
then
redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1);
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);
return nil;
end;
// Otherwise, the lock acquisition fails
return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);
Release the lock :
// If the number of locks =0, Then release directly
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0)
then return nil;
end;
// If the number of locks is greater than 0, Reset validity , Subtract one from the number and return . Otherwise, it means the lock ==0, You can directly delete publications and subscriptions
local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1);
if (counter > 0)
then
redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]);
return 0;
else
redis.call('del', KEYS[1]);
redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); // Delete lock subscription , It is used by the thread of the retry mechanism for subsequent lock acquisition failure
return 1;
end;
return nil;
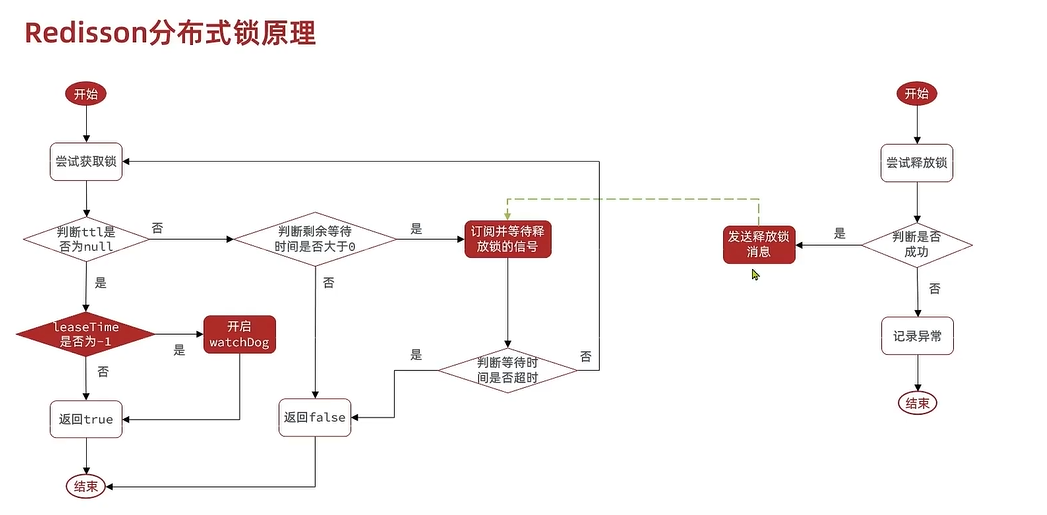
2.3.2.2 The basic flow
// The source code of obtaining and releasing locks is here 2 Function contents
// tryLock Of 3 Parameters : Get lock wait time ( The default is not to wait ) Release lock time , Time unit
boolean isLock = rLock.tryLock(1, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
rLock.unlock();
1. Lock
1. Threads a Execute first Lua Script get lock , To be successful ( Default lock release time 30 second )LUA The script guarantees the same thread id Get the lock ** Reentrant **
1. If lock release time is set , Then the lock refresh mechanism of the watchdog is not executed
2. If not set , By default, the door lock release time is used 30 second , Execute the watchdog refresh mechanism .
1. Recursion every time you look at the door / 3 = 10 Seconds to refresh the thread id The validity of the , Promised not to ** Delete the lock when it times out **( Because the default 30 Second ratio 10 A second more )
2. Threads b perform Lua Script failed , Subscribe to waiting time , Then re acquire the lock , After receiving the subscription, retry according to whether the waiting time is left , Don't receive the subscription. Quit when the time is up ---- Ensure the highest priority of waiting time , Realized ** Can try again **
2. Unlock
1. Release subscription messages
2. Cancel the watchdog
Redisson Distributed lock
1. Reentrant : utilize hash Storage thread id And reentry times
2. Can try again : Using publish subscribe and circular wait to realize lock retry ( Ensure that within the waiting time )
3. Overtime renewal : utilize watchDog, Every once in a while (releaseTime / 3) Reset
4. Master slave consistency : utilize multiLock Only by acquiring all master node locks can we succeed ( Multiple master nodes are installed )
2.4 Commodity seckill
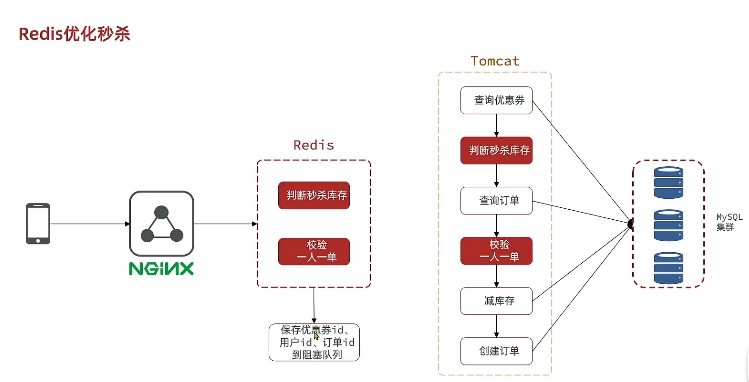
2.4.1 Basic concepts
1、Redis Second kill qualification judgment (Lua Scripts guarantee atomicity ). Save relevant information to the blocking queue
2、 Processing orders asynchronously , Deducting the inventory
2.4.2 Second kill qualification –Lua Script
-- Determine inventory 、 Judge whether the user orders , Deducting the inventory
-- Get the coupon of parameters id、 user id
local voucherId = ARGV[1]
local userId = ARGV[2]
local stockKey = 'seckill:stock:' .. voucherId
local orderKey = 'seckill:order:' .. voucherId
--
if(tonumber(redis.call('get', stockKey)) <= 0) then
return 1
end
if(redis.call("sismember", orderKey, userId) == 1) then
return 2
end
redis.call('incrby', stockKey, -1)
redis.call("sadd", orderKey, userId)
return 0
2.4.3 Order in seconds – Asynchronous implementation of blocking queue
0、 Load blocking queue read ahead
1、Redis Make qualification judgment , Put the qualified ones in the queue
2、 Thread pool reads queue data asynchronously
( problem : Blocking queues are based on jvm Memory to store data , The service outage , High concurrency will lead to data problems )
2.4.4 Redis- Message queue
2.4.4.1 Basic concepts
The queue in which messages are stored , Double linked list , use [LPush, BRPOP], or [Rpush, BLPOP] These implementations block queues .
2.4.4.2 List Message queue
advantage :
1. be based on Redis Storage , Unlimited and JVM Memory
2. be based on Redis Data persistence
shortcoming :
1. There is no way to avoid message loss
2. Only single consumers can be supported , Cannot be used by multiple consumers
2.4.4.3 PubSub Message queue
-- Release
publish order.q1.hello
-- subscribe
subscribe order.q1
-- subscribe : Support for wildcards *0 One or more ? One or more [] Meet internal conditions
PSUBSCRIBE order.*
Support multi production , Spend more
Data persistence is not supported , There is no way to avoid message loss , Messages tend to accumulate
2.4.4.4 Stream Message queue
-- add to stream queue ,* By redis Generate messages id
-- Line one : It is similar to storing all in the queue , But blocking reads read the latest , There will be overrides
xadd s1 * k1 v1
-- The queue length
xlen s1
-- Read a queue message , from 0 Start reading
xread count 1 streams s1 0
-- Read a message , Read from the latest , Wait forever
xread count 1 block 0 streams s1 $
- Messages exist forever , Go back , Blocking reads , It can be read by multiple consumers
- Because each time you read the latest , There is a risk that the message missed reading before reading will be overwritten , and pubsub type
Message diversion : Send messages to different groups
Message ID : Similar to Bookmarks , Mark which message you read , Continue to read from the identity after service downtime and restart ( This avoids missing messages )
Message confirmation : After the message is sent, it will be in pending, Send after sending XACK confirm , Then the queue removes the message
Message group mode
1、 Multiple consumers scramble to read messages
2、 Can block reading , The message can be traced back
3、 There is no risk of missing messages , The message can be traced back
-- 0 Represents the first message ,$ Represents the last message
-- > Indicates the next unused message ," other " Indicates a message that has been consumed but not confirmed . c1 Indicates the name of the consumer .
-- Queue two : The message that fails to be sent and is not confirmed enters pengding-list, Similar to a pointer marking the first position , The other pointer keeps walking backwards
-- hold stream flow s1 Put in g1 in , From the first
xgroup create s1 g1 0
xreadgroup group g1 c1 count 1 block 2000 streams s1 >
-- by the advices id Confirmation message
xack s1 g1 1655878247936-0
-- see pending-list In all time periods 10 Bar message
xpending s1 g1 - + 10
-- Read pending-list The first unconfirmed message in
xreadgroup group g1 c1 count 1 block 2000 streams s1 0
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-WWIDBab1-1656671557221)(…/…/…/…/…/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20220622145459299.png)]
actual combat
--MKSTREAM: If the stream does not exist, it will be created automatically
xgroup create stream.orders g1 0 MKSTREAM
--Lua The script throws data into the queue . Start another thread to cycle through the queue data , And do ack confirm
2.5 Business summary
2.5.1 Like function
Redis According to the article id—key Value increase or decrease , Then synchronize to the library table
2.5.2 Focus on features
After following the user every time , utilize follows-id As key, use set modify redis Pay attention to the situation , Then synchronize to the library table
2.5.3 Feed flow
2.5.3.1 Basic concepts
Feed flow : Actively push users something they are interested in
1.TimeLine: Simple content list filtering
2. Intelligent sorting : Intelligent algorithm filtering
2.5.3.2 Implementation scheme
Pull mode : Users pull their followers' information , But too much attention is easy to consume memory
Push mode : Bloggers push it to their followers every time they publish , It's unrealistic to have too many fans
Push pull mode : People are divided into big V And ordinary people , Fans are divided into active fans and zombie fans , Ordinary people just pull themselves to pay attention to people's information , Ordinary people push their own information to fans
2.5.3.3 Scroll paging
Because of tradition id When sorting in reverse order, the data will be refreshed continuously , All original limit offset Not an option , use redis in sortset, Use a fixed point score To ensure that the reading is fixed .redis Time is used as scoer
2.5.3.4 Store distance
use Geo For example, import calculation
2.5.3.5 User check-in
Because the amount of daily check-in data of each user stored in the library table is too large , So we can use bit Bits to store , Just take time as key value , It is also very convenient for subsequent query of statistical date
2.5.3.6 PV/UV
Statistics PV,UV These can be used hyperloglog Allow a little error .
3. Advanced
3.1. Distributed cache
3.1.1 RDB
RDB: Default save It is the main process that saves ,bgsave yes fork A sub process to save
3.1.2 AOF
AOF: Record instructions , Then replace the previous aof file
3.1.3 Process cache
Distributed cache : Accessing the cache has network overhead , Clusters can share , Large amount of cache data
Process cache : Faster access to local memory , But the capacity is limited
3.1.4 Canal
canal It's simulation salve hold Redis-master Of binlog Read slave function .
Whenever the database data is modified ,canal Just listen and modify the data into the database
3.2. Practice design
3.2.1 Basic design
1.key The design of the [ Business name ]:[ Data name ]:[id]
2. Delete bigkey: Start another thread to delete the value asynchronously
2. ** It is recommended to use hash Storage **,key The amount of data that can be used %100 such ,field Use key,value( Very little memory , Because use zipList, By default, do not exceed key value 500)
2. Batch warehousing data :sadd,mset Fast warehousing
2. Redis Master and slave can reach the top w Grade QPS, Try not to build clusters .
3.2.2 Server optimization
1. Try not to enable persistence
2. Recommended Opening AOF Persistence
4. Principles
4.1 data structure
4.1.1 Basic concepts
Redis: The bottom is C Written
4.1.2 Dynamic string SDS
Redis in key, value All use single or multiple strings SDS To store ,SDS The essence is a structure , Divided into string headers ( Record string length )、 body ( Store real data )
4.1.3 IntSet
int Of set: Integer unique array , Internal binary query
4.1.4 Dict
from 3 Part of it is made up of :dictHashTable Hashtable ,dictEntry Hash node ,dict Dictionaries
The composition of hash table is dicEntry such key, value value
Dict The dictionary contains 2 Hash table , For expansion and contraction , The bottom layer is arrays + Linked list to solve hash Conflict
( summary dict The bottom is hash surface , There are arrays and one-way linked lists to realize , What's preserved is key, value Of Entry Key value pair , Use a pointer to SDS object )
4.1.5 ZipList
Compressed list is a list of contiguous memory space , Pointer links are not used , Instead, the address of the last node is recorded . Because if you use dict This pointer selection , Too many memory fragments , Pointer bytes take up too much .
4.1.6 QuickList
The node is zipList Two-way linked list , Compatible with zipList Apply for continuous excessive memory space , And the advantages of consuming too much memory space with linked list pointers .
4.1.7 SkipList Jump watch *
A jump list is a linked list , The elements are sorted in ascending order , Then keep building pointers up between elements , and MySQL Indexing is similar , Easy to find later ,CURD Efficiency is the same as that of red and black trees log(n)
4.1.8 RedisObject
RedisObject Contains 5 Data type in , then 5 The following coding method is the above skip table ,zipList,quickList these .(typerloglog,bitmap,bitmap The bottom is string,zset)
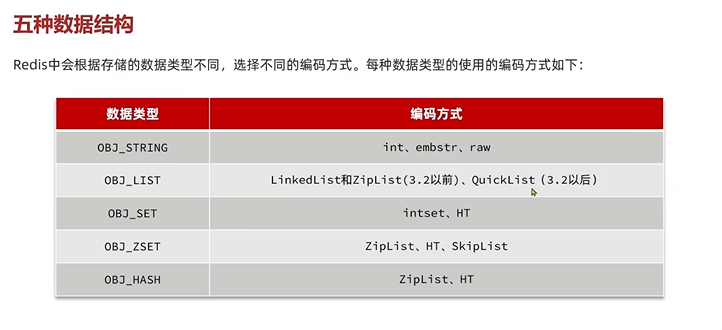
4.2 A network model
4.2.1 IO Multiplexing
Use a single thread to listen to multiple services at the same time . It is divided into select,poll, epoll.
select Copy the monitoring service every time FD It takes time from user to kernel
epoll Just put the ready monitoring service FD preserved , Then you don't have to traverse all each time FD
4.2.2 Model comparison
Currently still IO Multiplexing is used more
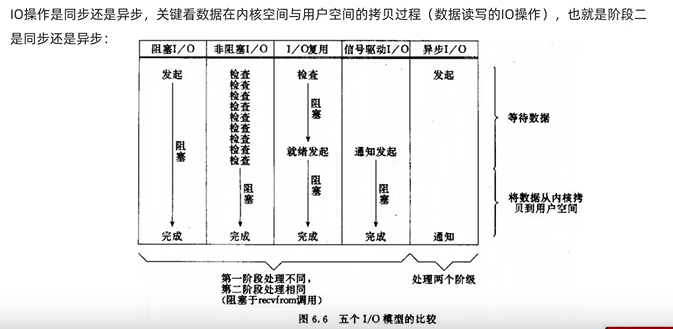
4.2.3 Redis A network model
Redis6.0 Then multithreading was introduced , It used to be single threaded
4.2.4 Redis Strategy
Redis Used in dict Recorded key Of TTL Time
4.2.4.1 Be overdue - Deletion policy
1. Inert cleaning : Every time I look up key, Delete after expiration
1. Regular clearance : Draw regularly key, Delete after expiration
4.2.4.2 Elimination strategy
8 Strategies : By default, no key, It is not allowed to write row data when the memory is full

边栏推荐
- R语言使用dt函数生成t分布密度函数数据、使用plot函数可视化t分布密度函数数据(t Distribution)
- R语言ggplot2可视化时间序列柱形图:通过双色渐变配色颜色主题可视化时间序列柱形图
- Benefit a lot, Android interview questions
- Visual Studio Code启动时提示“Code安装似乎损坏。请重新安装。”、标题栏显示“不受支持”信息的解决办法
- 黑马--Redis篇
- [depth first search] Ji suanke: find numbers
- 【论文笔记】TransUNet: Transformers Make StrongEncoders for Medical Image Segmentation
- 受益匪浅,安卓面试问题
- Modulenotfounderror: no module named 'PIL' solution
- 倒计时2天|腾讯云消息队列数据接入平台(Data Import Platform)直播预告
猜你喜欢

数学知识——高斯消元(初等行变换解方程组)代码实现

How to improve website weight
A full set of teaching materials, real questions of Android interview of 7 major manufacturers including Alibaba Kwai pinduoduo

About static type, dynamic type, ID, instancetype

Don't miss this underestimated movie because of controversy!

Mathematical knowledge -- code implementation of Gaussian elimination (elementary line transformation to solve equations)

pytorch常见损失函数

五金机电行业智能供应链管理系统解决方案:数智化供应链为传统产业“造新血”

能源行业的数字化“新”运维

ACTF 2022圆满落幕,0ops战队二连冠!!
随机推荐
LeetCode-1279. 红绿灯路口
Airiot IOT platform enables the container industry to build [welding station information monitoring system]
pytorch常见损失函数
AUTOCAD——中心线绘制、CAD默认线宽是多少?可以修改吗?
安装Mysql报错:Could not create or access the registry key needed for the...
Detailed idea and code implementation of infix expression to suffix expression
Openmv4 learning notes 1 --- one click download, background knowledge of image processing, lab brightness contrast
Countdown 2 days | live broadcast preview of Tencent cloud message queue data import platform
上海部分招工市场对新冠阳性康复者拒绝招录
Leetcode topic [array] - 119 Yang Hui triangle II
Meilu biological IPO was terminated: the annual revenue was 385million, and Chen Lin was the actual controller
提前解锁 2 大直播主题!今天手把手教你如何完成软件包集成?|第 29-30 期
MATLAB中deg2rad和rad2deg函数的使用
Interview assault 63: how to remove duplication in MySQL?
Wx applet learning notes day01
Benefit a lot, Android interview questions
MRO工业品企业采购系统:如何精细化采购协同管理?想要升级的工业品企业必看!
同宇新材冲刺深交所:年营收9.47亿 张驰与苏世国为实控人
朗坤智慧冲刺科创板:年营收4亿 拟募资7亿
Crawling data encounters single point login problem




