当前位置:网站首页>A Cooperative Approach to Particle Swarm Optimization
A Cooperative Approach to Particle Swarm Optimization
2022-07-06 01:19:00 【身影王座】
0、论文背景
CPSO是基于标准PSO变形而来的,本文提出了一种对传统的PSO算法的变体,称为协作粒子群优化器,或CPSO。利用协作行为来显著提高原始算法的性能,这是通过使用多个群来协同优化解向量的不同分量来实现的。
Van den Bergh F, Engelbrecht A P. A cooperative approach to particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation, 2004, 8(3): 225-239.
1、CPSO
1.1 标准PSO
有关PSO算法以及具体实现,参见本人之前写的博客:标准PSO。
速度更新公式:
![\begin{aligned} v_{i, j}(t+1)=w v_{i, j}(t)+c_{1} r_{1, i}(t) & {\left[y_{i, j}(t)-x_{i, j}(t)\right] } +c_{2} r_{2, i}(t)\left[\hat{y}_{j}(t)-x_{i, j}(t)\right] &(1)\end{aligned}](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202207/06/202207060119162576_7.gif)
位置更新公式:

pbest更新公式:

gbest更新公式:


1.2 CPSO_Sk
CPSO算法将较大的搜索空间分解为几个较小的空间,因此每个子群收敛到其子空间中包含的解的速度明显快于标准PSO在原始n维搜索空间上的收敛速度。
如果每个子空间维度设置为1维,那么整个n维的空间就划分为n个1维的子空间。

-
 表示的是s*1维的样本子空间,s代表粒子的总个数,1代表n维中的一维变量。
表示的是s*1维的样本子空间,s代表粒子的总个数,1代表n维中的一维变量。  代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的位置。
代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的位置。 代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的pbest。
代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的pbest。 代表第j个子空间gbest。
代表第j个子空间gbest。 该函数返回一个n维向量,通过连接所有子空间的所有全局最佳向量,除了第j个分量,它被替换为z。
该函数返回一个n维向量,通过连接所有子空间的所有全局最佳向量,除了第j个分量,它被替换为z。
如果每个子空间维度设置为k维,那么整个n维的空间就划分为 个k维的子空间。
个k维的子空间。

1.3 CPSO_Hk
在前一节中,CPSO_Sk算法容易陷入子空间局部最优的位置,全局搜索能力相较于PSO下降了。为了提高CPSO_Sk的全局搜索能力,将CPSO_Sk和PSO结合起来,形成了CPSO_Hk算法。

- P和Q的种群个数加起来是s,这里P和Q的种群个数统统设置为s/2。
- k是随机抽取的种群中的一个样本,并进行Q和P种群之间相对应的信息交互。
1.4 算法的复现和实验
文章中的算法实验比较复杂,不打算按照文中的思路进行复现。我这里复现算法以及进行简单的实验,看看是否有一些效果,有效果的话便于将其思想应用到其他地方。因此本文的复现仅仅停留于思想的理解和借鉴。
PSO(重复实验100次,取平均值):
function f = Rastrigin(x)
% the Rastrigin function
% xi = [-5.12,5.12]
d = size(x,2);
f = 10*d + sum(x.^2 - 10*cos(2*pi*x),2);
endclc;clear;clearvars;
% 随机生成5个数据
num_initial = 20;
num_vari = 60;
% 搜索区间
upper_bound = 5.12;
lower_bound = -5.12;
iter = 12000;
w = 1;
% 随机生成5个数据,并获得其评估值
sample_x = lhsdesign(num_initial, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial, num_vari);
sample_y = Rastrigin(sample_x);
Fmin = zeros(iter, 1);
aver_Fmin = zeros(iter, 1);
for n = 1 : 100
k = 1;
% 初始化一些参数
pbestx = sample_x;
pbesty = sample_y;
% 当前位置信息presentx
presentx = lhsdesign(num_initial, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial, num_vari);
vx = sample_x;
[fmin, gbest] = min(pbesty);
fprintf("n: %.4f\n", n);
% fprintf("iter 0 fmin: %.4f\n", fmin);
for i = 1 : iter
r = rand(num_initial, num_vari);
% pso更新下一步的位置,这里可以设置一下超过搜索范围的就设置为边界
vx = w.*vx + 2 * r .* (pbestx - presentx) + 2 * r .* (pbestx(gbest, :) - presentx);
vx(vx > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
vx(vx < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presentx = presentx + vx;
presentx(presentx > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
presentx(presentx < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presenty = Rastrigin(presentx);
% 更新每个单独个体最佳位置
pbestx(presenty < pbesty, :) = presentx(presenty < pbesty, :);
pbesty(presenty < pbesty, :) = presenty(presenty < pbesty, :);
% 更新所有个体最佳位置
[fmin, gbest] = min(pbesty);
% fprintf("iter %d fmin: %.4f\n", i, fmin);
Fmin(k, 1) = fmin;
k = k +1;
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin + Fmin;
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin ./ 100;
% disp(pbestx(gbest, :));
plot(aver_Fmin);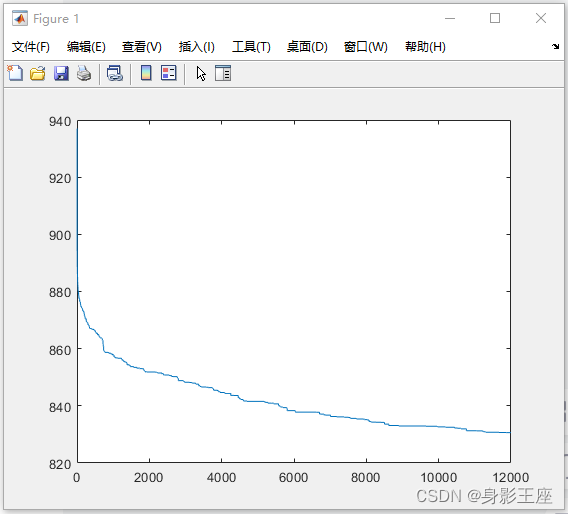
CPSO_Sk(重复实验100次,取平均值):
clc;clear;clearvars;
% 随机生成20个数据
num_initial = 20;
num_vari = 60;
% 搜索区间
upper_bound = 5.12;
lower_bound = -5.12;
% 迭代时计算y值总的个数
eval_num = 12000;
% K表示划分子空间的个数,sub_num表示每个子空间的维度
K = 5;
sub_num = num_vari / K;
% 算法的迭代次数
iter = eval_num / K;
w = 1;
% 随机生成20个数据,并获得其评估值
sample_x = lhsdesign(num_initial, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial, num_vari);
sample_y = Rastrigin(sample_x);
Fmin = zeros(eval_num, 1);
aver_Fmin = zeros(eval_num, 1);
for n = 1 : 100
n1 = 1;
% 初始化一些参数
pbestx = sample_x;
pbesty = sample_y;
% 当前位置信息presentx
presentx = lhsdesign(num_initial, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial, num_vari);
vx = sample_x;
[fmin, gbest] = min(pbesty);
global_best_x = pbestx(gbest, :);
fprintf("n: %.4f\n", n);
% fprintf("iter 0 fmin: %.4f\n", fmin);
for i = 1 : iter
for i1 = 1 : K
ind = ((1 + (i1 - 1) * sub_num) : i1 * sub_num);
r = rand(num_initial, sub_num);
% pso更新下一步的位置,这里可以设置一下超过搜索范围的就设置为边界
vx(:, ind) = w.*vx(:, ind) + 2 * r .* (pbestx(:, ind) - presentx(:, ind)) + 2 * r .* (pbestx(gbest, ind) - presentx(:, ind));
vx1 = vx(:, ind);
vx1(vx1 > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
vx1(vx1 < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
vx(:, ind) = vx1;
presentx(:, ind) = presentx(:, ind) + vx1;
presentx1 = presentx(:, ind);
presentx1(presentx1 > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
presentx1(presentx1 < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presentx(:, ind) = presentx1;
presentx2 = repmat(global_best_x, num_initial, 1);
presentx2(:, ind) = presentx1;
presenty = Rastrigin(presentx2);
% 更新每个单独个体最佳位置
pbestx1 = pbestx(:, ind);
pbestx1(presenty < pbesty, :) = presentx1(presenty < pbesty, :);
pbestx(:, ind) = pbestx1;
pbesty(presenty < pbesty, :) = presenty(presenty < pbesty, :);
% 更新所有个体最佳位置
[fmin, gbest] = min(pbesty);
global_best_x = pbestx(gbest, :);
Fmin(n1, 1) = fmin;
n1 = n1 +1;
% fprintf("iter %d fmin: %.4f\n", i, fmin);
end
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin + Fmin;
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin ./ 100;
plot(aver_Fmin);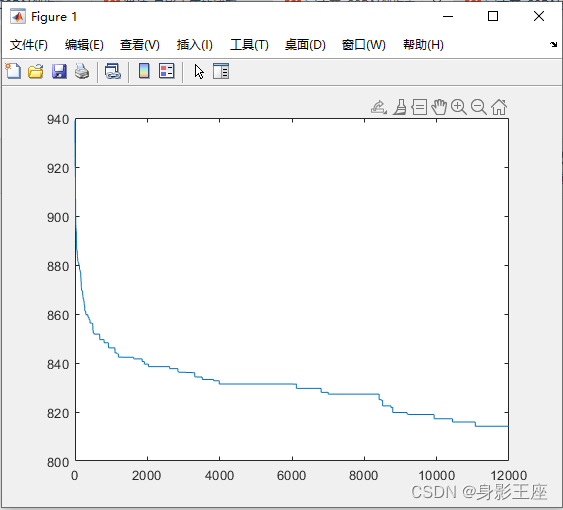
CPSO_Hk(重复实验100次,取平均值):评估次数相较于上面两个要少一半左右。
clc;clear;clearvars;
% 随机生成20个数据,P10个,Q10个
num_initial1 = 10;
num_initial2 = 10;
num_vari = 60;
% 搜索区间
upper_bound = 5.12;
lower_bound = -5.12;
% 迭代时计算y值总的个数
eval_num = 12000;
% K表示划分子空间的个数,sub_num表示每个子空间的维度
K = 6;
sub_num = num_vari / K;
% 算法的迭代次数
iter = eval_num / K;
w = 1;
% 随机生成10\10个数据,并获得其评估值
sample_x1 = lhsdesign(num_initial1, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial1, num_vari);
sample_y1 = Rastrigin(sample_x1);
sample_x2 = lhsdesign(num_initial2, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial2, num_vari);
sample_y2 = Rastrigin(sample_x2);
Fmin = zeros(iter, 1);
aver_Fmin = zeros(iter, 1);
for n = 1 : 100
n1 = 1;
% 初始化一些参数
pbestx1 = sample_x1;
pbesty1 = sample_y1;
pbestxx = sample_x2;
pbestyy = sample_y2;
% 当前位置信息presentx
presentx1 = lhsdesign(num_initial1, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial1, num_vari);
presentxx = lhsdesign(num_initial2, num_vari).*(upper_bound - lower_bound) + lower_bound.*ones(num_initial2, num_vari);
vx1 = sample_x1;
vxx = sample_x2;
[fmin1, gbest1] = min(pbesty1);
[fmin2, gbest2] = min(pbestyy);
global_best_x1 = pbestx1(gbest1, :);
fprintf("n: %.4f\n", n);
% fprintf("iter 0 fmin: %.4f\n", fmin);
for i = 1 : iter
for i1 = 1 : K
ind = ((1 + (i1 - 1) * sub_num) : i1 * sub_num);
r1 = rand(num_initial1, sub_num);
% cpso更新下一步的位置,这里可以设置一下超过搜索范围的就设置为边界
vx1(:, ind) = w.*vx1(:, ind) + 2 * r1 .* (pbestx1(:, ind) - presentx1(:, ind)) + 2 * r1 .* (pbestx1(gbest1, ind) - presentx1(:, ind));
vx2 = vx1(:, ind);
vx2(vx2 > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
vx2(vx2 < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
vx1(:, ind) = vx2;
presentx1(:, ind) = presentx1(:, ind) + vx2;
presentx2 = presentx1(:, ind);
presentx2(presentx2 > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
presentx2(presentx2 < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presentx1(:, ind) = presentx2;
presentx3 = repmat(global_best_x1, num_initial1, 1);
presentx3(:, ind) = presentx2;
presenty1 = Rastrigin(presentx3);
% 更新每个单独个体最佳位置
pbestx2 = pbestx1(:, ind);
pbestx2(presenty1 < pbesty1, :) = presentx2(presenty1 < pbesty1, :);
pbestx1(:, ind) = pbestx2;
pbesty1(presenty1 < pbesty1, :) = presenty1(presenty1 < pbesty1, :);
% 更新所有个体最佳位置
[fmin1, gbest1] = min(pbesty1);
global_best_x1 = pbestx1(gbest1, :);
end
% 文中的s/2就是num_initial2,下面就是PSO算法
ki = randi(num_initial2);
while ki == gbest2
ki = randi(num_initial2);
end
% 信息交互
presentxx(ki, :) = global_best_x1;
r2 = rand(num_initial2, num_vari);
% pso更新下一步的位置,这里可以设置一下超过搜索范围的就设置为边界
vxx = w.*vxx + 2 * r2 .* (pbestxx - presentxx) + 2 * r2 .* (pbestxx(gbest2, :) - presentxx);
vxx(vxx > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
vxx(vxx < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presentxx = presentxx + vxx;
presentxx(presentxx > upper_bound) = upper_bound;
presentxx(presentxx < lower_bound) = lower_bound;
presentyy = Rastrigin(presentxx);
% 更新每个单独个体最佳位置
pbestxx(presentyy < pbestyy, :) = presentxx(presentyy < pbestyy, :);
pbestyy(presentyy < pbestyy, :) = presentyy(presentyy < pbestyy, :);
% 更新所有个体最佳位置
[fmin2, gbest2] = min(pbestyy);
% 信息交互
for i2 = 1 : K
kj = randi(num_initial1);
while kj == gbest1
kj = randi(num_initial1);
end
ind2 = ((1 + (i2 - 1) * sub_num) : i2 * sub_num);
presentx1(kj, ind2) = pbestxx(gbest2, ind2);
end
%获取全局最优值
if(fmin2 > fmin1)
fmin = fmin1;
else
fmin = fmin2;
end
Fmin(n1, 1) = fmin;
n1 = n1 +1;
%fprintf("iter %d fmin: %.4f\n", i, fmin);
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin + Fmin;
end
aver_Fmin = aver_Fmin ./ 100;
plot(aver_Fmin);
虽然CPSO_Sk和CPSO_Hk的性能相较于PSO并没有提升很多,但是其划分子空间的思想还是很难得。实际上随着问题维度的提升,CPSO_Sk和CPSO_Hk的运行时间是小于PSO的,因为总体运算减少了。而且从最终结果来看CPSO_Hk的性能>CPSO_Sk>PSO。
边栏推荐
- Modify the ssh server access port number
- [day 30] given an integer n, find the sum of its factors
- What is the most suitable book for programmers to engage in open source?
- 基于DVWA的文件上传漏洞测试
- CocoaPods could not find compatible versions for pod 'Firebase/CoreOnly'
- Leetcode 208. Implement trie (prefix tree)
- Interview must brush algorithm top101 backtracking article top34
- Cf:h. maximum and [bit operation practice + K operations + maximum and]
- Remember that a version of @nestjs/typeorm^8.1.4 cannot be obtained Env option problem
- Nmap: network detection tool and security / port scanner
猜你喜欢
电气数据|IEEE118(含风能太阳能)
基于DVWA的文件上传漏洞测试
BiShe - College Student Association Management System Based on SSM

282. Stone consolidation (interval DP)
Introduction to robotics I. spatial transformation (1) posture, transformation
![Cf:h. maximum and [bit operation practice + K operations + maximum and]](/img/c2/9e58f18eec2ff92e164d8d156629cf.png)
Cf:h. maximum and [bit operation practice + K operations + maximum and]

Exciting, 2022 open atom global open source summit registration is hot

General operation method of spot Silver
MATLB | real time opportunity constrained decision making and its application in power system
95后CV工程师晒出工资单,狠补了这个,真香...
随机推荐
Basic process and testing idea of interface automation
After 95, the CV engineer posted the payroll and made up this. It's really fragrant
SSH login is stuck and disconnected
Introduction to robotics I. spatial transformation (1) posture, transformation
Docker compose配置MySQL并实现远程连接
MYSQL---查询成绩为前5名的学生
FFT learning notes (I think it is detailed)
Leetcode 208. Implement trie (prefix tree)
In the era of industrial Internet, we will achieve enough development by relying on large industrial categories
Use of crawler manual 02 requests
95后CV工程师晒出工资单,狠补了这个,真香...
ORA-00030
Five challenges of ads-npu chip architecture design
Cannot resolve symbol error
The growth path of test / development programmers, the problem of thinking about the overall situation
什么是弱引用?es6中有哪些弱引用数据类型?js中的弱引用是什么?
The basic usage of JMeter BeanShell. The following syntax can only be used in BeanShell
Who knows how to modify the data type accuracy of the columns in the database table of Damon
BiShe - College Student Association Management System Based on SSM
cf:D. Insert a Progression【关于数组中的插入 + 绝对值的性质 + 贪心一头一尾最值】
 表示的是s*1维的样本子空间,s代表粒子的总个数,1代表n维中的一维变量。
表示的是s*1维的样本子空间,s代表粒子的总个数,1代表n维中的一维变量。 代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的位置。
代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的位置。 代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的pbest。
代表第j个子空间中第i个粒子的pbest。 代表第j个子空间gbest。
代表第j个子空间gbest。 该函数返回一个n维向量,通过连接所有子空间的所有全局最佳向量,除了第j个分量,它被替换为z。
该函数返回一个n维向量,通过连接所有子空间的所有全局最佳向量,除了第j个分量,它被替换为z。