当前位置:网站首页>二叉树基本性质+oj题解析
二叉树基本性质+oj题解析
2022-08-05 04:37:00 【影子,你陪着我累吗?】

写在前面:
博主主页:戳一戳,欢迎大佬指点!
博主秋秋:QQ:1477649017 欢迎志同道合的朋友一起加油喔
目标梦想:进大厂,立志成为一个牛掰的Java程序猿,虽然现在还是一个小菜鸟嘿嘿
-----------------------------谢谢你这么帅气美丽还给我点赞!比个心-----------------------------
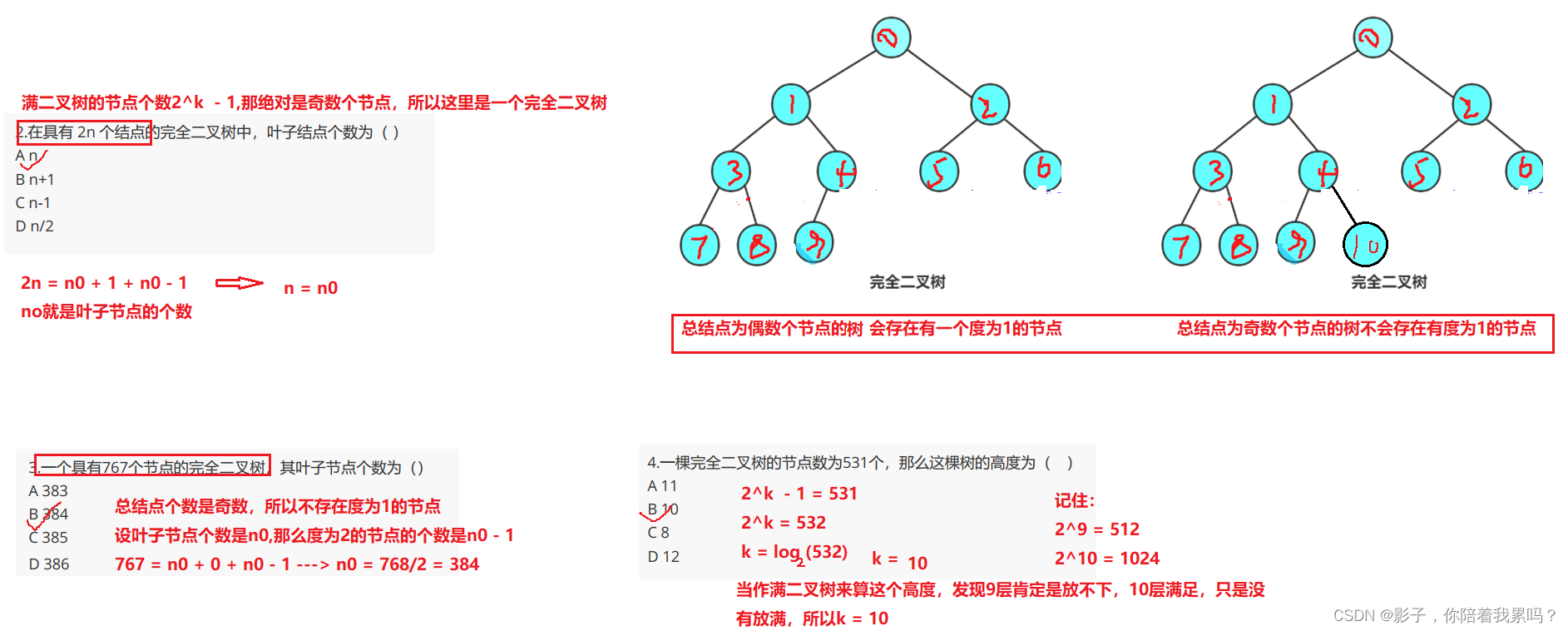
一,有关二叉树性质的证明

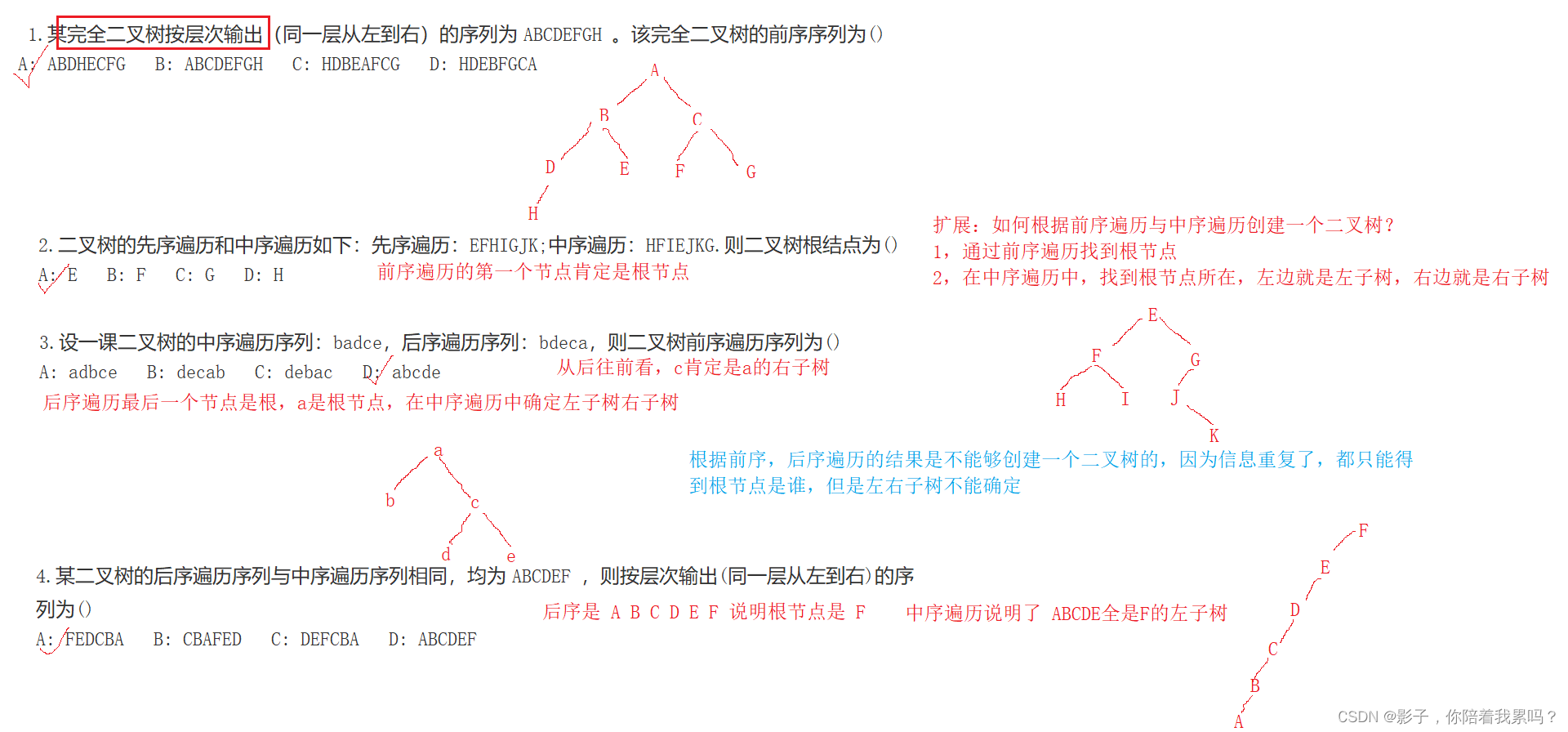
二,实题解析
三,二叉树相关oj题
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p != null && q == null || p == null && q != null){
//一个为空,一个不为空的情况
return false;
}
if(p == null && q == null){
//两个都为空的情况
return true;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
//能走到这就说明两个都不为空
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);//继续去判断左子树,然后判断右子树
}
}
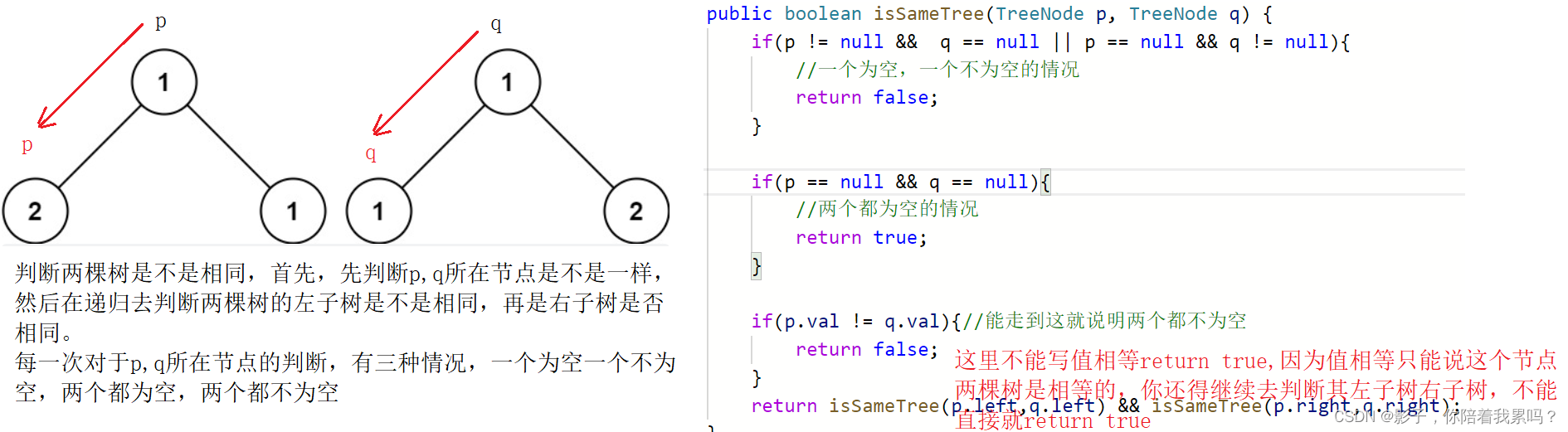
判断一下这题的时间复杂度为:O(min(m,n)),其中m是左边的树的节点个数,n是右边的树的节点个数,因为我们这里的最坏情况肯定是要把小的那棵树遍历完,而不是看大的树,小的树遍历完了不相同那就直接不用比较了。
class Solution {
//这个函数用来判断两个树是不是相同的树
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p != null && q == null || p == null && q != null){
//一个为空,一个不为空的情况
return false;
}
if(p == null && q == null){
//两个都为空的情况
return true;
}
if(p.val != q.val){
//能走到这就说明两个都不为空
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
//子树的关系就是小于等于的关系
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root == null){
//判断一下是否存在空的情况,,递归的过程中root可能为空
return false;
}
//1,可能root,subRoot本身直接就是一样的
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)){
//如果说root是空,这里就为false,就跳不出去,导致root.left空指针异常
return true;
}
//然后判断subRoot是不是root的左子树的子树或者是右子树的子树
return isSubtree(root.left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right,subRoot);
}
}
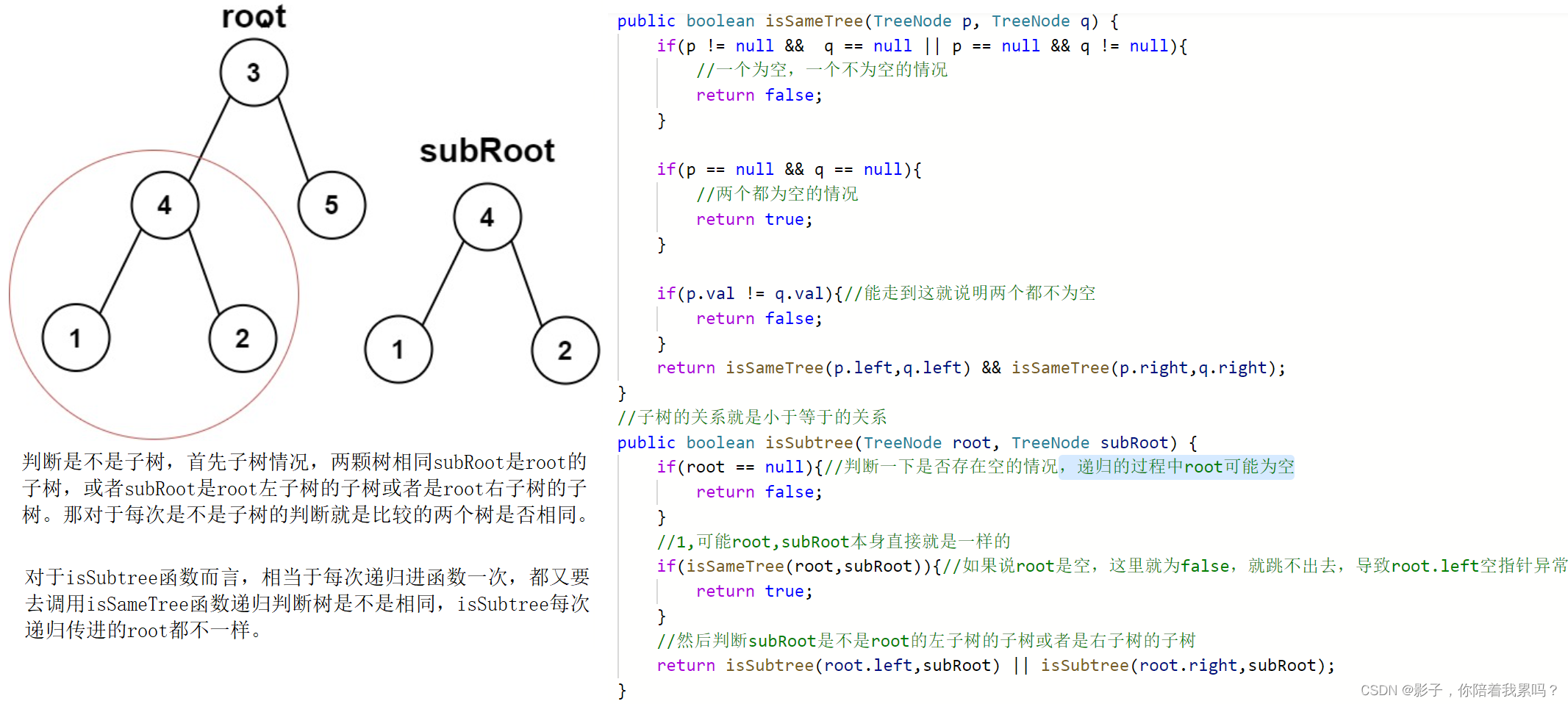
时间复杂度分析,假设root树有m个节点,subRoot树有n个节点,因为是每次递归进去判断是不是子树,那对于每次是不是子树的判断,就是看两个树是不是相同,这个过程也是一个递归。所以最坏的情况就是subRoot和root的每一个节点都判断一下是不是子树,假设root树是n个节点,subRoot树是m个节点,那最坏就是要判断n*m次,所以时间复杂度就是O(n x m)。
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
//最大深度就是高度
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}

时间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
//最大深度就是高度
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
if(Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1){
return false;
}else{
return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
}
}
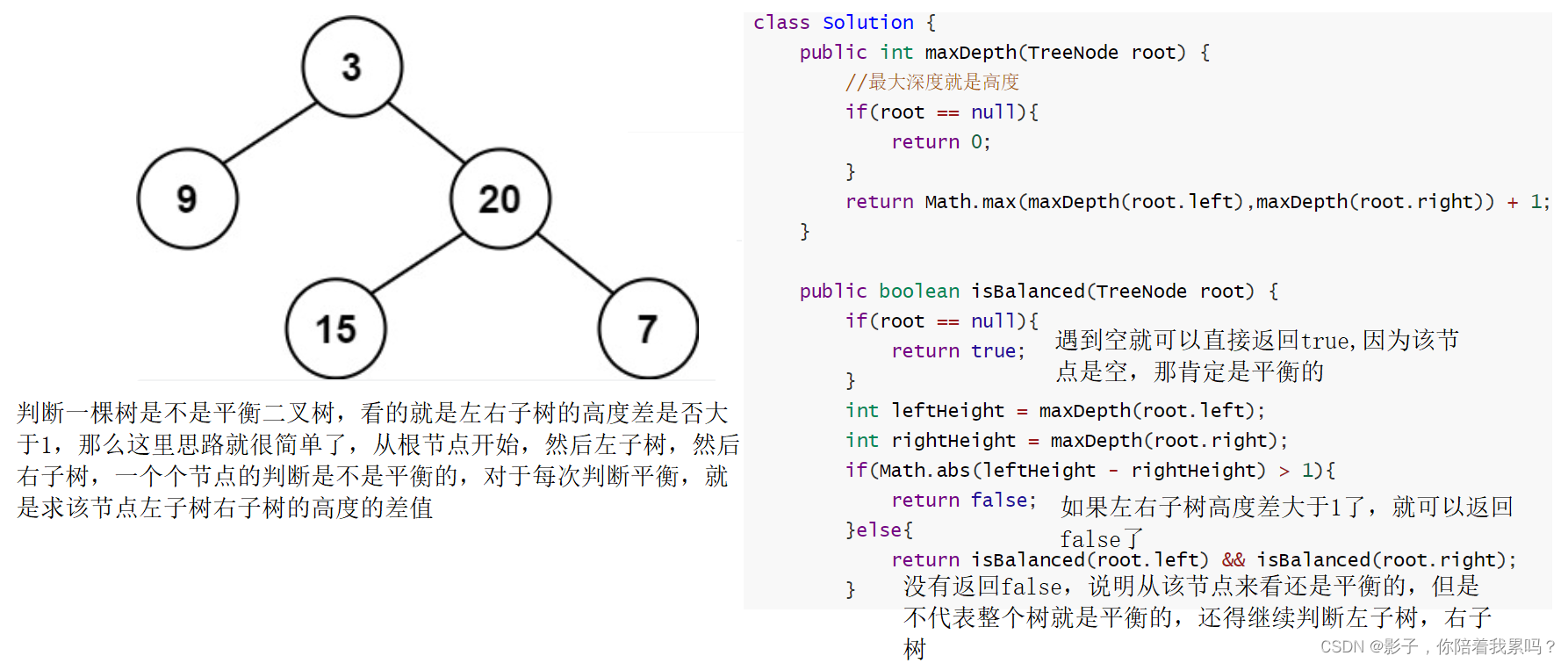
时间复杂度:O(n^2),这里也是一个嵌套的递归,isBalanced()是递归到二叉树的每一个节点,然后判断该节点是否平衡,又是要递归求左右子树的高度,所以又相当于遍历了一遍二叉树。中间存在很多的重复计算,你在计算3这个节点的左树高度时,遍历了左树,在判断9这个节点的时候,又会重复遍历到很多的节点。所以,这个方法的时间复杂度比较高,面试要求的话肯定是达不到的。
【解法优化:】
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
//最大深度就是高度
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
if(leftHeight >= 0 && rightHeight >= 0 && Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) <=1){
return (Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight)) + 1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return maxDepth(root) > 0;
}
}
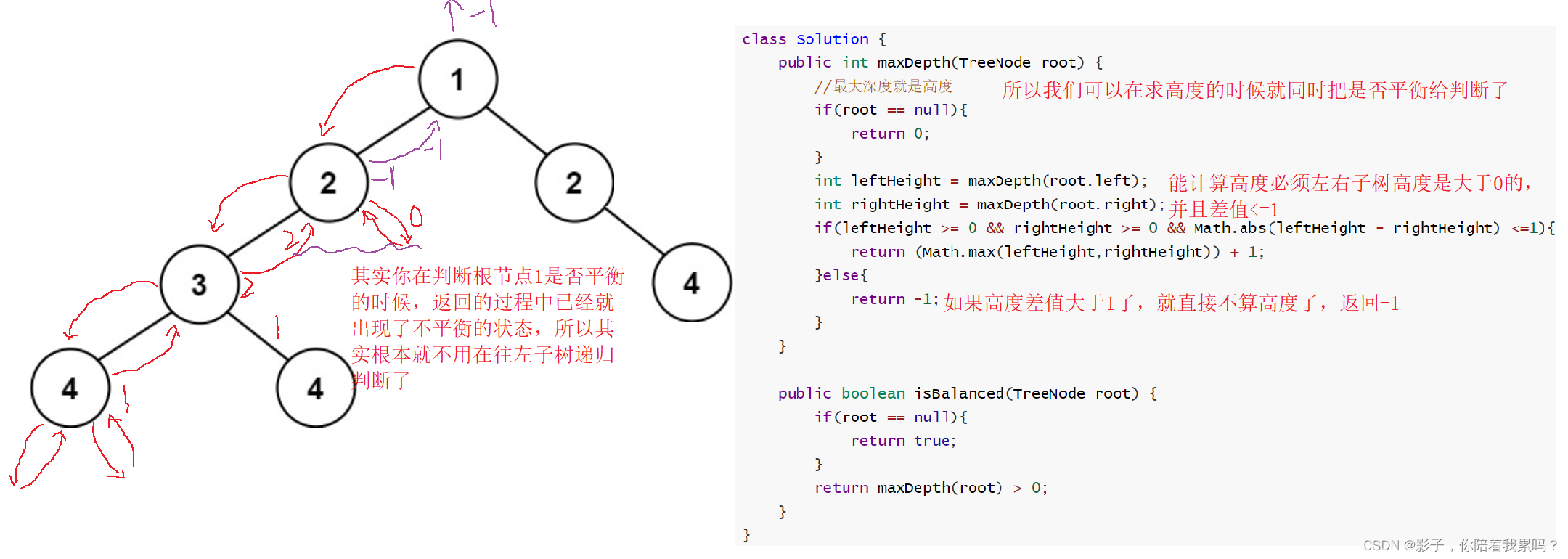
优化之后就只走了一个递归函数。因为其实对于根节点而言,你判断它是否平衡的时候,就已经把所有的节点都要遍历完,这个过程中就可能会出现不平衡的情况,这个时候这棵树已经就是不平衡的了,没必要再递归判断左子树右子树的节点了。现在的时间复杂度就降到了O(n)。
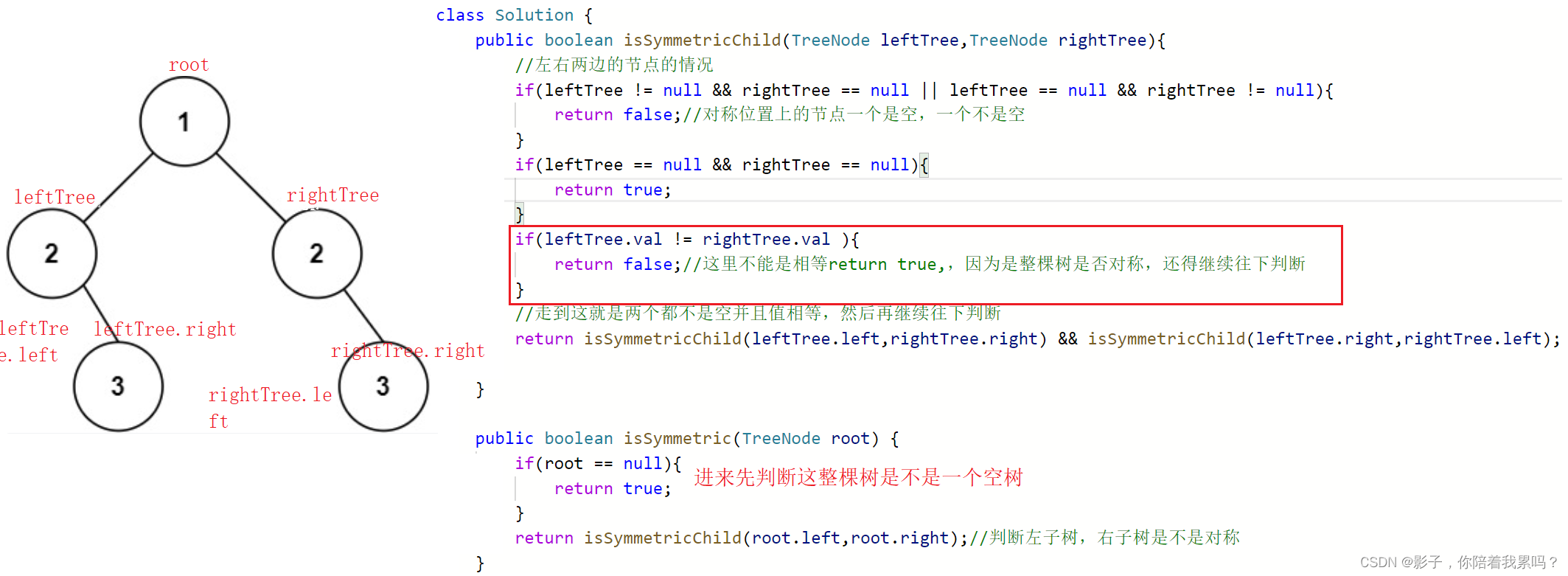
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftTree,TreeNode rightTree){
//左右两边的节点的情况
if(leftTree != null && rightTree == null || leftTree == null && rightTree != null){
return false;//对称位置上的节点一个是空,一个不是空
}
if(leftTree == null && rightTree == null){
return true;
}
if(leftTree.val != rightTree.val ){
return false;//这里不能是相等return true,,因为是整棵树是否对称,还得继续往下判断
}
//走到这就是两个都不是空并且值相等,然后再继续往下判断
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right) && isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);//判断左子树,右子树是不是对称
}
}
【前导:】
void levelOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;//二叉树为空,那就直接return掉
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);//首先就把root入队
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();//队头元素出队
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");//打印元素的值
if(cur.leftChild != null){
queue.offer(cur.leftChild);//如果cur的左孩子不为空就入队
}
if(cur.rightChild != null){
queue.offer(cur.rightChild);//如果cur的右孩子不为空就入队
}
}
}
层序遍历的过程得用到队列,因为队列是先进先出,符合我们层序遇到节点就打印的特点。首先把根节点入队,然后只要队列不为空就出队队头元素,出对的同时会把这个元素的左孩子,右孩子入队,就这样一直循环下去,最终的打印结果就是层序的结果。
那么下面的分层遍历,只不过是要我们把每一层都区分开。那我们只要在每次出队之前看一下队列中的元素个数,那就是这一层的个数,并且保证每次出的时候都把这一层出完,然后每层元素都会被加入到ArrayList中,这样就被区分开了。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();//用来存储整个结果
if(root == null){
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);//首先就把root入队
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();//先看一下队列中的元素
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();//用来存储每一行的结果
while(size != 0){
//把每一行元素出完
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();//队头元素出队
size--;
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);//如果cur的左孩子不为空就入队
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);//如果cur的右孩子不为空就入队
}
list.add(cur.val);//把这个出的元素加入到list中
}
ret.add(list);//把这一行的结果加入到ret中
}
return ret;
}
}
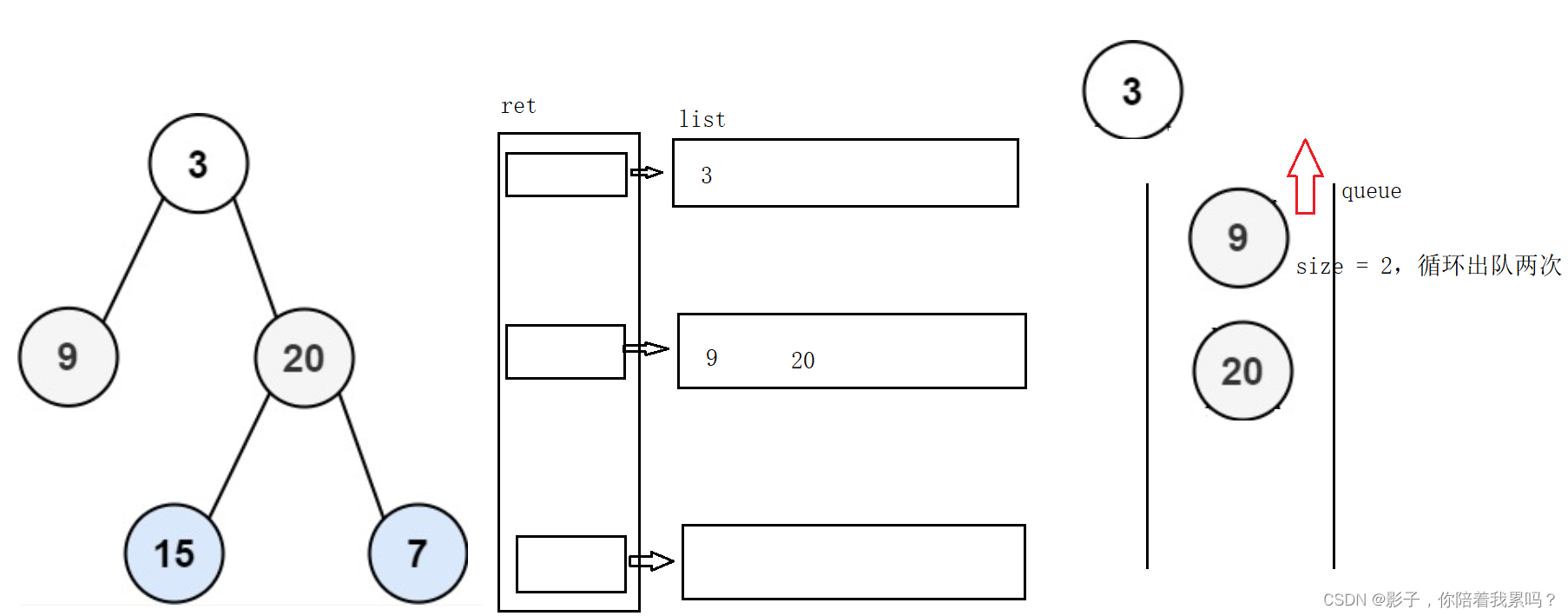
分层遍历的题记住就是用队列解,比如之前阿里考过的题,求一棵树的左视图,右视图,其实就只是上面这个题,ret这个ArrayList每一个元素的第一个元素组合起来就是左视图,最后一个元素组合起来就是右视图。
import java.util.Scanner;
class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static int i = 0;
public static TreeNode creatTree(String s){
//递归创建二叉树
TreeNode root = null;
if(s.charAt(i) != '#'){
root = new TreeNode(s.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = creatTree(s);
root.right = creatTree(s);
}else{
i++;
}
return root;
}
public static void inOrder(TreeNode root){
//中序遍历
if(root == null){
return ;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
String s = scan.nextLine();
TreeNode root = creatTree(s);
inOrder(root);
}
}
}
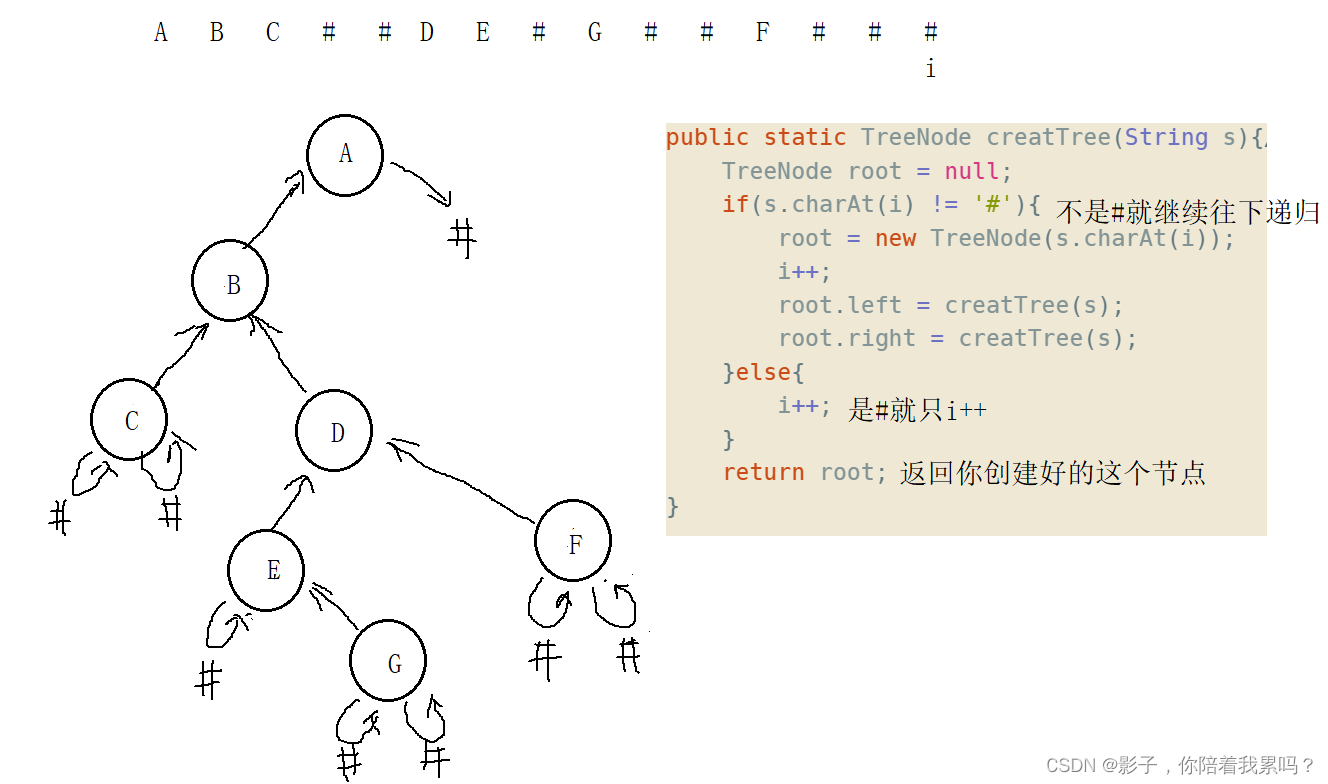
它给你的字符串是前序遍历出来的字符串顺序,所以我们就按照它的那个顺序递归创建就行。如果当前字符不是#,那就先把该节点创建,然后去递归创建其左子树,然后再是右子树。我们把每个节点串起来的过程就是你返回节点的过程。
【解法一:】
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(p == root || q == root){
//p,q就是root,那么root就是公共祖先
return root;
}
//不是,就去左右两边找
TreeNode leftFind = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightFind = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftFind !=null && rightFind != null){
//就说明在两边都找到了,所以是处在root的左右两边
return root;
}else if(leftFind != null){
return leftFind;
}else{
return rightFind;
}
}
}
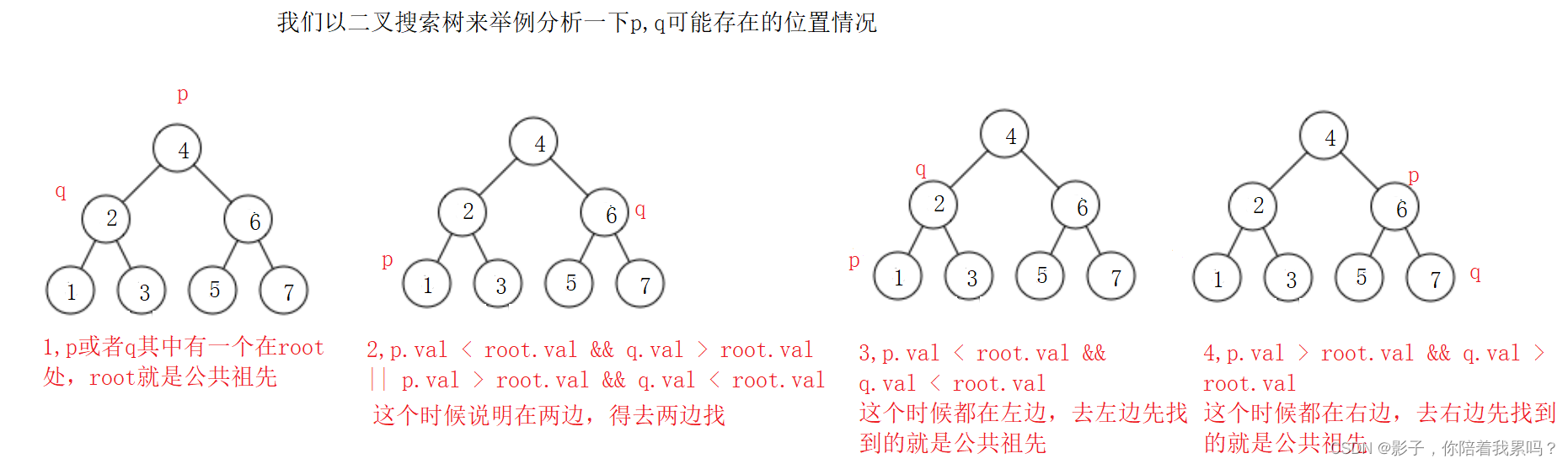
这里只是以二叉搜索树为例,其中值的比较在本题是不需要的,因为题目要求的就只是二叉树就行,但是p,q可能存在的情况就是如上。所以我们就先判断p,q是不是在root处,然后再去左边找,再去右边找,然后看两个返回值的情况。
【解法二:】
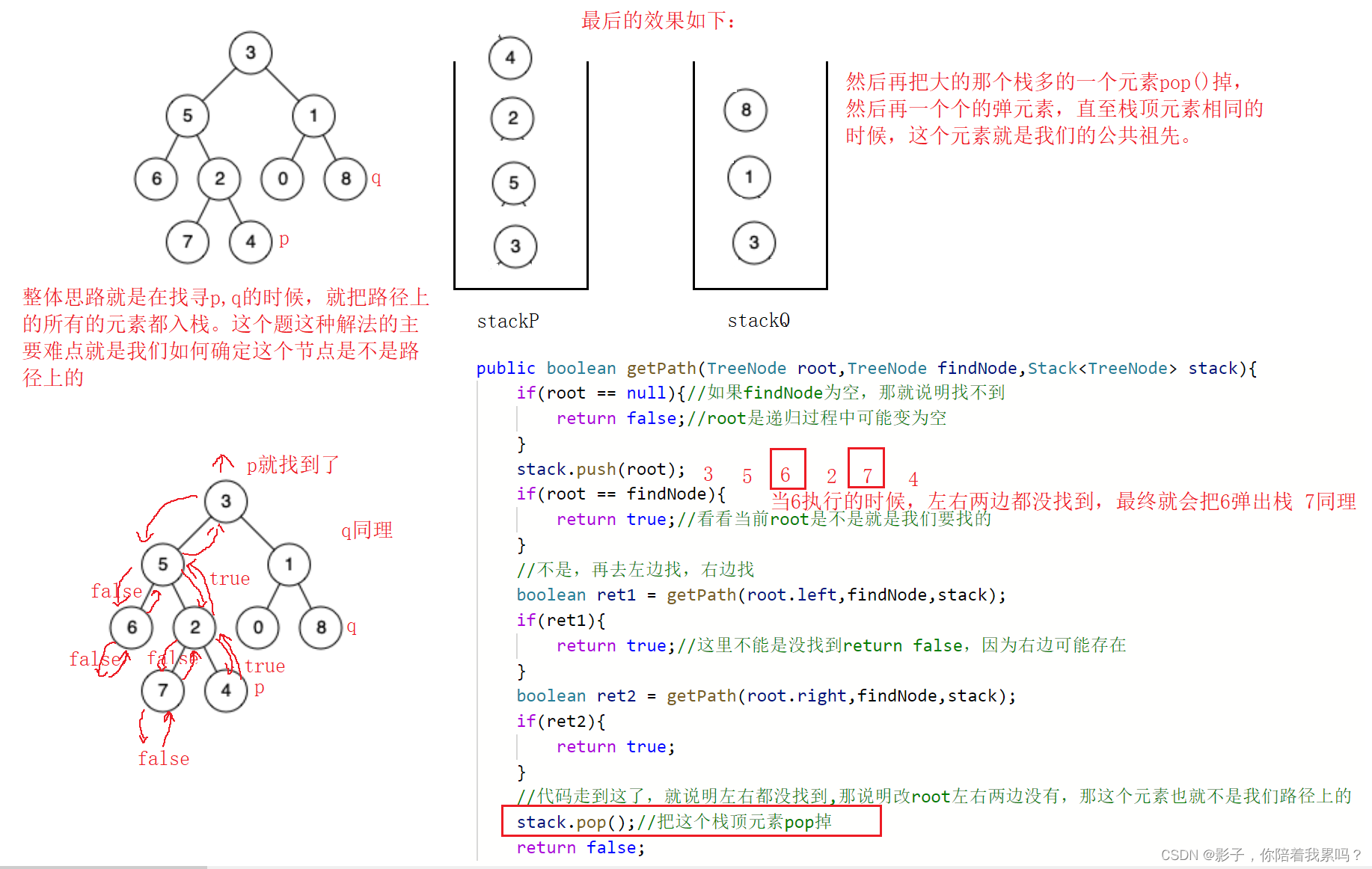
class Solution {
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode findNode,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root == null){
//如果findNode为空,那就说明找不到
return false;//root是递归过程中可能变为空
}
stack.push(root);
if(root == findNode){
return true;//看看当前root是不是就是我们要找的
}
//不是,再去左边找,右边找
boolean ret1 = getPath(root.left,findNode,stack);
if(ret1){
return true;//这里不能是没找到return false,因为右边可能存在
}
boolean ret2 = getPath(root.right,findNode,stack);
if(ret2){
return true;
}
//代码走到这了,就说明左右都没找到,那说明改root左右两边没有,那这个元素也就不是我们路径上的
stack.pop();//把这个栈顶元素pop掉
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stackP = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackQ = new Stack<>();
boolean ret1 = getPath(root,p,stackP);
boolean ret2 = getPath(root,q,stackQ);
if(ret1 == true && ret2 == true){
if(stackP.size() > stackQ.size()){
int len = stackP.size() - stackQ.size();
while(len != 0){
stackP.pop();
len--;
}
}else{
int len = stackQ.size() - stackP.size();
while(len != 0){
stackQ.pop();
len--;
}
}
}
while(!stackP.isEmpty() && !stackQ.isEmpty()){
if(stackP.peek() == stackQ.peek()){
return stackP.peek();
}
stackP.pop();
stackQ.pop();
}
return null;//到这说明没有公共祖先
}
}
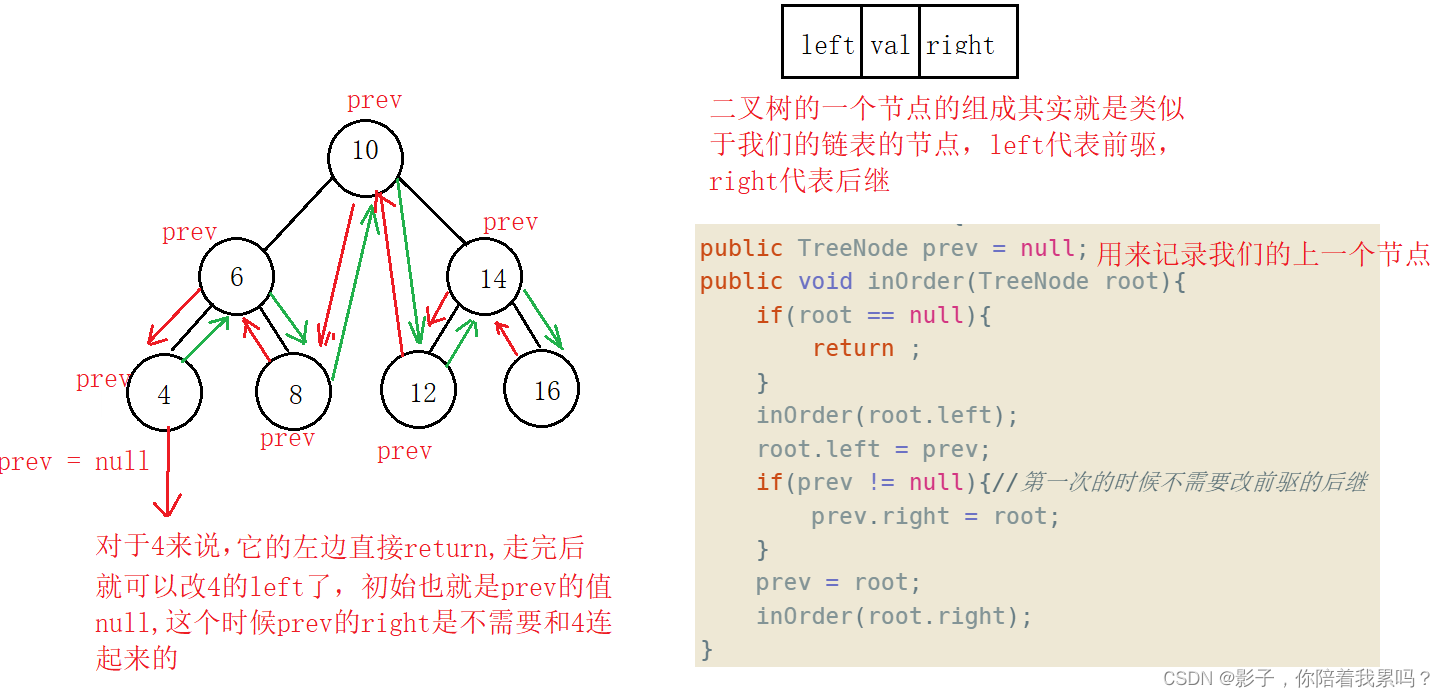
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode prev = null;
public void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return ;
}
inOrder(root.left);
root.left = prev;
if(prev != null){
//第一次的时候不需要改前驱的后继
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
inOrder(root.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree == null){
return null;
}
inOrder(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head = pRootOfTree;
while(head.left != null){
head = head.left;
}
return head;
}
}
class Solution {
public int preIndex = 0;
private TreeNode buildChildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int begin,int end){
if(begin > end){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);//首先构建根节点
int fIndex = findIndex(inorder,preorder[preIndex],begin,end);//在中序遍历的数组中找到这个头节点的位置
preIndex++;//这个节点构建完了并且找完了就把preIndex++
root.left = buildChildTree(preorder,inorder,begin,fIndex - 1);
root.right = buildChildTree(preorder,inorder,fIndex + 1,end);
return root;
}
private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int findNum,int begin,int end){
for(int i = begin;i <= end;i++){
if(inorder[i] == findNum){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildChildTree(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
}

class Solution {
public int postIndex;//记录我们前序遍历数组的下标
private TreeNode buildChildTree(int[] postorder, int[] inorder,int begin,int end){
if(begin > end){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);//首先构建根节点
int fIndex = findIndex(inorder,postorder[postIndex],begin,end);//在中序遍历的数组中找到这个头节点的位置
postIndex--;//这个节点构建完了并且找完了就把postIndex--
root.right = buildChildTree(postorder,inorder,fIndex + 1,end);//先构建右树,因为后序遍历根节点后是右子树的节点
root.left = buildChildTree(postorder,inorder,begin,fIndex - 1);
return root;
}
private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int findNum,int begin,int end){
for(int i = begin;i <= end;i++){
if(inorder[i] == findNum){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
postIndex = postorder.length - 1;
return buildChildTree(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
}
原理和上面前序中序构建是一样的,只不过后序遍历的数组我们遍历的时候是从后往前,在构建子树的时候我们也是先构建右树再构建左树。
class Solution {
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(root,stringBuilder);
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
private void tree2strChild(TreeNode t,StringBuilder stringBuilder){
if(t == null){
return ;
}
stringBuilder.append(t.val);
if(t.left != null){
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.left,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else{
if(t.right != null){
stringBuilder.append("()");
}else{
return;//左右两边都为空,什么也不做
}
}
if(t.right != null){
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.right,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else{
return ;
}
}
}

class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.empty()){
while(cur != null){
//能压入栈一定是不为空
stack.push(cur);
list.add(cur.val);//遇到就入栈
cur = cur.left;
}
//如果cur为空了
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
return list;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur != null || !stack.empty()){
while(cur != null){
//能压入栈一定是不为空
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
//如果cur为空了,也就是左边为空
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);//中间就可以加入到list里面了
cur = top.right;//继续去访问右边
}
return list;
}
}
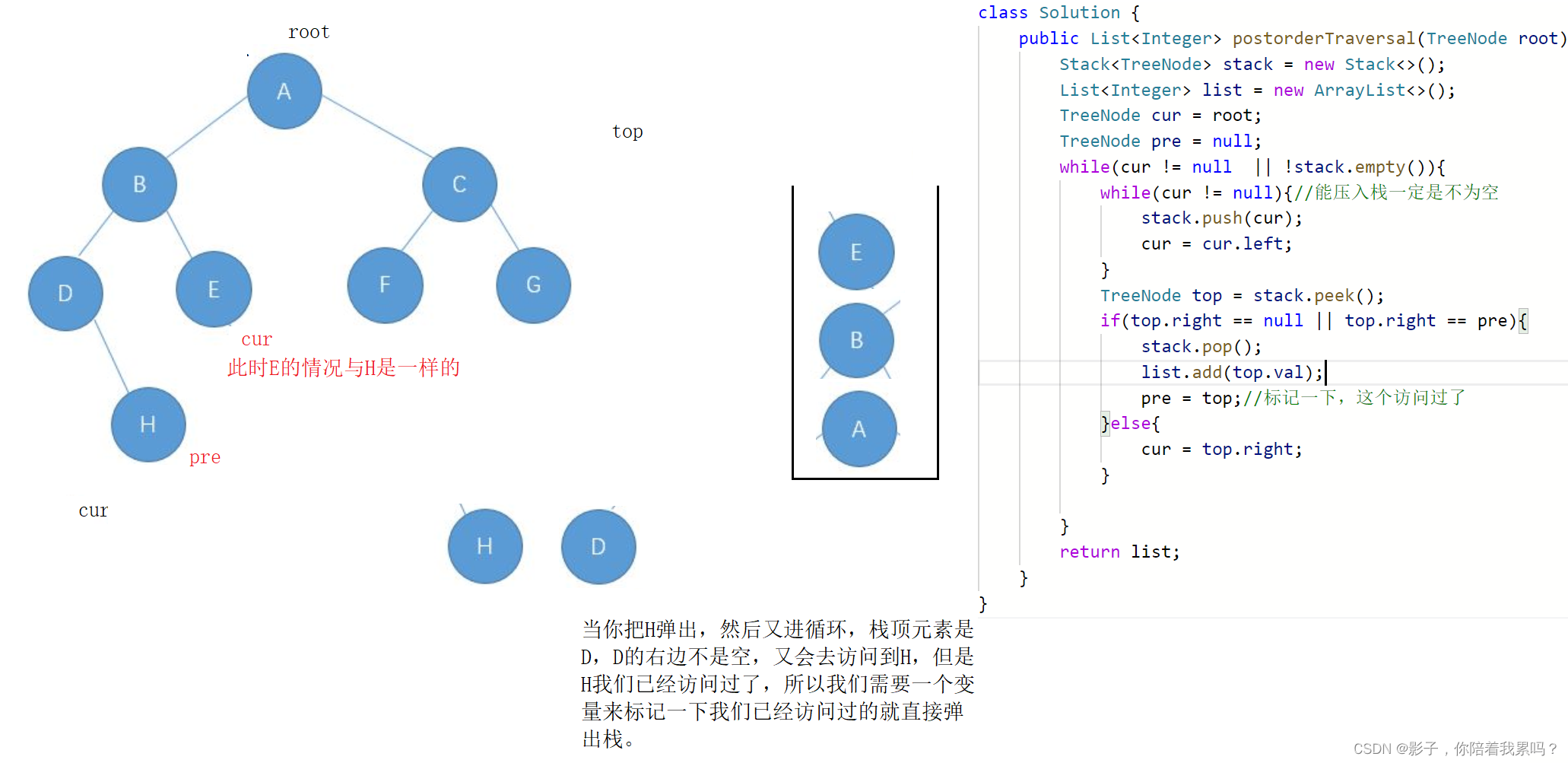
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while(cur != null || !stack.empty()){
while(cur != null){
//能压入栈一定是不为空
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == pre){
stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);
pre = top;//标记一下,这个访问过了
}else{
cur = top.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}
今天关于二叉树的分享就到这了,后面会陆陆续续的恢复更新了的,大家持续关注哟,如果觉得写的不错的话还请点点赞咯,十分感谢呢!🥰🥰🥰
边栏推荐
- 8.04 Day35-----MVC三层架构
- Why did you start preparing for the soft exam just after the PMP exam?
- Four-digit display header design
- Develop your own node package
- Cron(Crontab)--使用/教程/实例
- Talk about 20 common problems in data governance
- Feature preprocessing
- Qixi Festival earn badges
- Event parse tree Drain3 usage and explanation
- 小程序_动态设置tabBar主题皮肤
猜你喜欢
Four-digit display header design
UE4 在游戏运行时更改变量 (通过鼠标滑轮来更改第一人称角色的最大行走速度)
特征预处理
作业8.4 进程间的通信 管道与信号
UE4 通过重叠事件开启门
从企业的视角来看,数据中台到底意味着什么?
bytebuffer internal structure

How to solve the three major problems of bank data collection, data supplementary recording and index management?
upload上传图片到腾讯云,如何上传图片

The production method of the powered small sailboat is simple, the production method of the electric small sailboat
随机推荐
动力小帆船制作方法简单,电动小帆船制作方法
多御安全浏览器 V10.8.3.1 版正式发布,优化多项内容
bytebuffer internal structure
小程序_动态设置tabBar主题皮肤
In the hot summer, teach you to use Xiaomi smart home accessories + Raspberry Pi 4 to connect to Apple HomeKit
ansible各个模块详解
Shell(4) Conditional Control Statement
多列属性column元素的可见性:display、visibility、opacity、垂直对齐方式:vertical-align、z-index 越大越显示在上层
Qixi Festival earn badges
第一次性能测试实践,有“亿”点点紧张
How to deal with DNS hijacking?
There are a lot of 4T hard drives remaining, prompting "No space left on device" insufficient disk space
AUTOCAD——标注关联
How to identify false evidence and evidence?
Spark Basics [Introduction, Getting Started with WordCount Cases]
The first performance test practice, there are "100 million" a little nervous
pyqt5 + socket 实现客户端A经socket服务器中转后主动向客户端B发送文件
【 8.4 】 source code - [math] [calendar] [delete library 】 【 is not a simple sequence (Bonus) 】
flink读取mongodb数据源
Mini Program_Dynamic setting of tabBar theme skin

