当前位置:网站首页>[groovy] closure (closure parameter binding | curry function | rcurry function | ncurry function | code example)
[groovy] closure (closure parameter binding | curry function | rcurry function | ncurry function | code example)
2022-07-05 04:40:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 Closure parameter binding
- 1、 Closure parameter binding curry function
- 2、 Closure parameter binding rcurry function
- 3、 Closure parameter binding ncurry function
- Two 、 Complete code example
One 、 Closure parameter binding
Closure Closure Provides curry , ncurry , rcurry Method , this
3
3
3 There are two ways to Closure Conduct Parameter binding ;
- curry function : From left to right binding Closure parameters ;
- rcurry function : From right to left binding Closure parameters ;
- ncurry function : Specify from
n
n
n Start binding with two parameters Closure parameters ;
Above
3
3
3 Both methods will Create a new closure , Need to use The new variable receives the newly created closure , The original closure variable remains unchanged ;
1、 Closure parameter binding curry function
Binding parameters from left to right ;
Closure parameter binding curry The function prototype :
/** * Bind parameters from left to right * <p> * characteristic use : * <pre class="groovyTestCase"> * def multiply = { a, b {@code ->} a * b } * def doubler = multiply.curry(2) * assert doubler(4) == 8 * </pre> * notes : Pair closure vararg Types of functions are specially handled . * If you use vararg Parameters , The whole... Will not be used vararg Array , * But use vararg The first parameter of the array , * As shown in the following example : * <pre class="groovyTestCase"> * def a = { one, two, Object[] others {@code ->} one + two + others.sum() } * assert a.parameterTypes.name == ['java.lang.Object', 'java.lang.Object', '[Ljava.lang.Object;'] * assert a(1,2,3,4) == 10 * def b = a.curry(1) * assert b.parameterTypes.name == ['java.lang.Object', '[Ljava.lang.Object;'] * assert b(2,3,4) == 10 * def c = b.curry(2) * assert c.parameterTypes.name == ['[Ljava.lang.Object;'] * assert c(3,4) == 10 * def d = c.curry(3) * assert d.parameterTypes.name == ['[Ljava.lang.Object;'] * assert d(4) == 10 * def e = d.curry(4) * assert e.parameterTypes.name == ['[Ljava.lang.Object;'] * assert e() == 10 * assert e(5) == 15 * </pre> * * * @param arguments Closure parameters to bind * @return Return a new closure with bound parameters */ public Closure<V> curry(final Object... arguments) {
return new CurriedClosure<V>(this, arguments); }Code example :
// Define closure variables , Declare two parameters a, b // And specify the default value for the closure def closure5 = {
a = 0, b = "Groovy" -> println "${a} : ${b}" } // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure5() // Bind from left to right Closure parameters def closure6 = closure5.curry(1, "Gradle") // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure6()Execution results :
0 : Groovy1 : Gradle2、 Closure parameter binding rcurry function
Closure parameter binding rcurry The function binds parameters from right to left , however The order of parameters is from left to right , This is something to be aware of ;
Closure parameter binding rcurry The function prototype :
/** * Bind closure parameters from right to left * According to ordinary curry() Method , Parameters are provided on the right instead of the left . * characteristic use : * <pre class="groovyTestCase"> * def divide = { a, b {@code ->} a / b } * def halver = divide.rcurry(2) * assert halver(8) == 4 * </pre> * * curried The position of the parameter will be delayed , * for example , If there are two overloaded doCall Method available , * Add... To the parameters provided curried Parameters will be connected , The results will be used for method selection . * * @param arguments Binding parameters * @return New closure after binding parameters * @see #curry(Object...) */ public Closure<V> rcurry(final Object... arguments) {
return new CurriedClosure<V>(-arguments.length, this, arguments); }Code example :
// Define closure variables , Declare two parameters a, b // And specify the default value for the closure def closure5 = {
a = 0, b = "Groovy" -> println "${a} : ${b}" } // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure5() // Bind from right to left Closure parameters def closure7 =closure5.rcurry(2, "Java") // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure7()Execution results :
0 : Groovy2 : Java3、 Closure parameter binding ncurry function
From
n
n
n Start binding the parameters in the closure with two parameters ;
Notice that curry / ncurry / rcurry After the method , All default values are overwritten and cleared , If From
2
2
2 Start binding closure parameters with parameters , Then the first parameter has no default value , Invocation time , The first parameter must be passed in before you can only , Otherwise, the runtime will report an error ;
Closure parameter binding ncurry The function prototype :
/** * Bind closure parameters from the given index * * @param argument The closure of the parameter to be bound * @return the The newly created closure after binding parameters * @see #ncurry(int, Object...) */ public Closure<V> ncurry(int n, final Object argument) {
return ncurry(n, new Object[]{
argument}); }Code example :
// Define closure variables , Declare two parameters a, b // And specify the default value for the closure def closure5 = {
a = 0, b = "Groovy" -> println "${a} : ${b}" } // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure5() // From n Start binding closure parameters with parameters , // Notice that curry / ncurry / rcurry After the method , The previous default value overrides // At this time, the first parameter has no value // Invocation time , The first parameter must be passed in before you can only def closure8 =closure5.ncurry(1, "Kotlin") // The first default value of the closure is cancelled , At this point, the value of the first parameter must be passed in to execute the closure // Otherwise, the report will be wrong closure8(3)Execution results :
0 : Groovy3 : KotlinTwo 、 Complete code example
Complete code example :
import org.codehaus.groovy.ant.Groovyclass Test {
static void main(args) {
// I. Receive the thinning of a default parameter // Define closure variables def closure = {
println "Accept One Arguments : ${it}" } // Call closure closure.call("Hello"); closure("Hello"); // II. A closure that does not accept any parameters // Define closure variables , Parameters are not allowed to be passed in def closure2 = {
-> println "Not Accept Arguments" } // An error will be reported when the parameter is passed in //closure2("Hello") // Call closure , Cannot pass in parameters closure2.call(); closure2(); // III. Receive a closure of a custom parameter // Define closure variables , Declare a parameter a def closure3 = {
a -> println "${a}" } // Call closure , Cannot pass in parameters closure3.call(1); closure3(2); // IV. Receive the closure of two custom parameters // Define closure variables , Declare two parameters a, b // Print these two parameters in the closure def closure4 = {
a, b -> println "${a} : ${b}" } // Call closure , Cannot pass in parameters closure4.call(1, 2); closure4(3, 4); // V. Specify default values for closure parameters // Define closure variables , Declare two parameters a, b // And specify the default value for the closure def closure5 = {
a = 0, b = "Groovy" -> println "${a} : ${b}" } // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure5() // Bind from left to right Closure parameters def closure6 = closure5.curry(1, "Gradle") // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure6() // Bind from right to left Closure parameters def closure7 =closure5.rcurry(2, "Java") // Closures have default values , You can call without passing in parameters closure7() // From n Start binding closure parameters with parameters , // Notice that curry / ncurry / rcurry After the method , The previous default value overrides // At this time, the first parameter has no value // Invocation time , The first parameter must be passed in before you can only def closure8 =closure5.ncurry(1, "Kotlin") // The first default value of the closure is cancelled , At this point, the value of the first parameter must be passed in to execute the closure // Otherwise, the report will be wrong closure8(3) }}Execution results :
Accept One Arguments : HelloAccept One Arguments : HelloNot Accept ArgumentsNot Accept Arguments121 : 23 : 40 : Groovy1 : Gradle2 : Java3 : Kotlin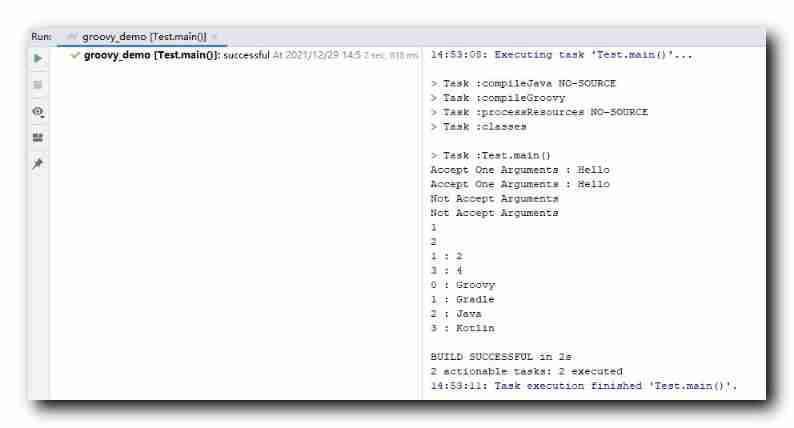
边栏推荐
- Invalid bound statement (not found) in idea -- problem solving
- Official announcement! The third cloud native programming challenge is officially launched!
- C26451: arithmetic overflow: use the operator * on a 4-byte value, and then convert the result to an 8-byte value. To avoid overflow, cast the value to wide type before calling the operator * (io.2)
- All in one 1413: determine base
- windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
- You Li takes you to talk about C language 7 (define constants and macros)
- Wan broadband access technology V EPON Technology
- Live broadcast preview | container service ack elasticity prediction best practice
- 取余操作是一个哈希函数
- English topic assignment (27)
猜你喜欢

Thematic information | carbon, carbon neutrality, low carbon, carbon emissions - 22.1.9

如何优雅的获取每个分组的前几条数据
Is there a sudden failure on the line? How to make emergency diagnosis, troubleshooting and recovery

SQL set operation
![[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording](/img/11/b55f85ef9e1f22254218cb9083b823.png)
[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording
指针函数(基础)

官宣!第三届云原生编程挑战赛正式启动!
Uncover the seven quirky brain circuits necessary for technology leaders

Solution of circular dependency
Fonction (sujette aux erreurs)
随机推荐
Burpsuite grabs app packets
Variable category (automatic, static, register, external)
[phantom engine UE] the difference between running and starting, and the analysis of common problems
Sword finger offer 07 Rebuild binary tree
English topic assignment (26)
MacBook installation postgresql+postgis
Hexadecimal to octal
[phantom engine UE] package error appears! Solutions to findpin errors
【thingsboard】替换首页logo的方法
WeNet:面向工业落地的E2E语音识别工具
指针函数(基础)
2022-2028 global and Chinese virtual data storage Market Research Report
How can CIOs use business analysis to build business value?
Neural network and deep learning Chapter 1: introduction reading questions
Machine learning decision tree
Serpentine matrix
This is an age of uncertainty
Machine learning -- neural network
How to force activerecord to reload a class- How do I force ActiveRecord to reload a class?
Leetcode 222 number of nodes of complete binary tree