当前位置:网站首页>C Primer Plus Chapter 14 (structure and other data forms)
C Primer Plus Chapter 14 (structure and other data forms)
2022-07-07 00:49:00 【His Last Bow】
Catalog
- 1. Create a structure statement
- 2. Define structural variables
- 4. Structure array
- 5. Nested structure
- 6. Pointer to structure
- 7. Passing information about structures to functions
- 7.1 Pass structure members
- 7.2 The address of the delivery structure
- 7.3 Transmission structure
- 7.4 Other structural features
- 7.5 Structure and structure pointer selection
- 7.6 The character array and character pointer in the structure
- 7.7 structure 、 Pointers and malloc()
- 7.8 Compound literals and structures (C99)
- 7.9 Scalable array members (C99)
- 7.10 Anonymous structure (C11)
- 8. The chain structure
- 9. Joint profile
- 10. Enumeration type
- 11. typedef brief introduction
- 12. Other complex statements
1. Create a structure statement
- Structure statement (structure declaration) Describes the organizational layout of a structure
- Each part of the structure is called member (member) or Field (field)
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
struct animal dog;
struct animal cat;
Structure declarations are sometimes called templates , Because it outlines how the structure stores data
If you put a structure declaration inside a function , Its tag is limited to the internal use of the function
If you put the structure declaration outside a function , All functions after this declaration can use its tag
2. Define structural variables
structure There are two meanings
Structural layout : Tell the compiler how to represent data , But it doesn't make the compiler for data Distribute Space
Create a Structural variables
struct animal { char name[50]; int age; char sex; }; struct animal dog;The compiler creates a structure variable dog
The compiler uses animal The template allocates space for this variable
- One contains 50 An element of char Array
- One int Variable of type
- One char Variable of type
These storage spaces are associated with a name dog Bind together
You can define two struct animal Variable of type , Or point to struct animal Pointer to type structure
struct animal dog; struct animal cat; struct animal *a;- The pointer a Can point to dog 、cat Or any other animal Structural variables of type
From the nature ,animal The structure declaration creates a structure called struct animal New type of
struct animal dog;
- Is a simplification of the following statement
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
} dog;
struct {
// No structural markers
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
} dog;
3.1 Initialization structure
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
struct animal dog = {
"abc",
1,
'M'
};
- If you initialize the structure of a static storage period , The value in the initialization list must be a constant expression
3.2 Access structure members
#include <stdio.h>
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
int main() {
struct animal dog = {
"abc",
1,
'M'
};
printf("name = %s, age = %d, sex = %c\n", dog.name, dog.age, dog.sex);
}
3.3 Structure initializer
- C90 and C11 It provides Specify initializer (designated initializer)
struct animal dog = {
.age = 1,
.name = "abc",
2,
.sex = 'M'
};
- Dot operator + The member name method does not need to consider the order of members in the structure
- name The next one is age, therefore age From the original 1 Modified into 2
4. Structure array
4.1 Declare structure array
struct animal zoo[10];
- Every element in an array is a animal The structure of the type
4.2 Identify the members of the structure array
zoo; // animal Array of structures
zoo[0] // animal Elements of the structure
zoo[0].name = "abc"; // char Array
zoo[0].name[1] = 'b'; // char
5. Nested structure
struct name {
char first[10];
char last[10];
};
struct animal {
struct name dog;
int age;
char sex;
};
6. Pointer to structure
- Pointers to structures are usually easier to manipulate than the structure itself
- You can pass a pointer to a structure to a function
- Passing pointers is more efficient
- The structure representing data contains pointers to other structures
6.1 Declare and initialize structure pointers
struct animal* p;
p = &dog;
printf("%#x\n", p);
- The structure variable name is not the address of the structure variable
6.2 Use pointers to access members
Access member's 2 Methods
The first 1 Methods : Use -> Operator
printf("%s\n", p->name);The first 2 Methods : Quoting
printf("%s\n", (*p).name);
7. Passing information about structures to functions
7.1 Pass structure members
#include <stdio.h>
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
void sout(char);
int main() {
struct animal dog = {
.name = "abc",
.age = 1,
.sex = 'M'
};
sout(dog.name);
}
void sout(char str[50]) {
printf("%s\n", str);
}
7.2 The address of the delivery structure
#include <stdio.h>
void sout(struct animal *);
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
int main() {
struct animal dog = {
.name = "abc",
.age = 1,
.sex = 'M'
};
sout(&dog);
}
void sout(struct animal *p) {
printf("%s\n", p->name);
}
7.3 Transmission structure
#include <stdio.h>
void sout(struct animal);
struct animal {
char name[50];
int age;
char sex;
};
int main() {
struct animal dog = {
.name = "abc",
.age = 1,
.sex = 'M'
};
sout(dog);
}
void sout(struct animal a) {
printf("%s\n", a.name);
}
7.4 Other structural features
Assign one structure to another
dog = cat;
7.5 Structure and structure pointer selection
The pointer :
advantage :
C A method that language can always use
Faster execution , Just pass an address
shortcoming :
- Unable to protect data
structure :
- advantage :
- The function deals with a copy of the original data , Protecting raw data
- The code style is clear
- shortcoming
- Older versions cannot be used
- Transfer structure wastes time and storage space
- advantage :
In pursuit of efficiency, structural pointers are used as function parameters , Use const Prevent accidental modification
Passing structures by value is the most common way to deal with small structures
7.6 The character array and character pointer in the structure
struct name {
char *first;
char *last;
};
struct name n = {
"abc",
"ABC"
};
printf("%s, %s\n", n.first, n.last);
7.7 structure 、 Pointers and malloc()
- Use malloc() Allocate memory and use a pointer to store the address , Allocate appropriate space for the string
struct name {
char* first;
char* last;
};
char first[5];
char last[5];
fgets(first, 5, stdin);
fgets(last, 5, stdin);
struct name n;
n.first = (char*)malloc(strlen(first) + 1);
n.last = (char*)malloc(strlen(last) + 1);
strcpy(n.first, first);
strcpy(n.last, last);
printf("%s%s\n", n.first, n.last);
7.8 Compound literals and structures (C99)
struct animal dog;
dog = (struct animal) {
.name = "abc",
.age = 1,
.sex = 'M'
};
7.9 Scalable array members (C99)
- utilize Scalable array members (flexible array member) Structure of declaration , Features of the last array member
- The array will not exist immediately
- Using this scalable array member, you can write appropriate code
- Rules for declaring scalable array members
- Must be the last member of the structure
- Structure must have at least one member
- The declaration of a scalable array is similar to an ordinary array
struct animal {
int age;
char sex;
char name[]; // Scalable array members
};
- You need to declare a struct animal Type of The pointer , And then use malloc() To allocate enough space , To store the struct animal The general contents of the type structure and the extra space required for the scalable array members
struct animal *p;
p = malloc(sizeof(struct animal) + 5 * sizeof(char));
7.10 Anonymous structure (C11)
struct animal {
struct {
char first[10];
char last[10];
};
int age;
char sex;
};
8. The chain structure
- data structure :
- Binary tree
- Pile up
- Hashtable
- Chart
- These data structures are composed of The chain structure (linked structure) form
- Each structure contains one or two data items and one or two pointers to other structures of the same type
- These pointers link one structure to another , And provide a path that can traverse the entire structure linked to each other
9. Joint profile
- union (union) It's a data type , It can store different data types in the same memory space ( Not stored at the same time )
union animal {
char name[10];
int age;
char sex;
}
- Declared unions can only store name, age, sex A value of
- The compiler allocates enough space to store the type that takes up the largest bytes in the joint declaration
9.1 Use Union
union animal dog;
dog.name = "abc"; // take "abc" Storage
dog.age = 1; // Delete "abc" , take 1 Storage
dog.sex = 'M'; // Delete 1 , take 'M' Storage
9.2 Anonymous Union (C11)
union animal {
union {
char first[10];
char last[10];
};
int age;
char sex;
};
10. Enumeration type
- Enumeration type (enumerated type) Used to represent integer constants
- Use to enum Statement (enum Constant is int type )
- Improve code readability
enum letter {
a, b, c};
enum letter abc;
- The first 1 A declaration creates letter As a tag name , Allow to put enum letter Use as type name
- Enumerated in curly brackets letter Variables may have values
- The first 2 A statement makes abc As a variable of this type
- abc Possible values make a、b、c
- These symbolic constants are called enumerator (enumerator)
10.1 enum Constant
printf("a = %d,b = %d\n", a, b);
// a = 0,b = 1
10.2 The default value is
- By default , The constants in the enumeration list are given 0、1、2 etc.
10.3 assignment
enum number {
a, b = 10, c = 100 };
printf("a = %d,b = %d, c = %d\n", a, b, c);
// a = 0,b = 10, c = 100
10.4 Shared name space
- The name space (namespace) Used to identify various parts of the program , That is, identify by name
- Scope is part of the namespace
- Variables with the same name in two different scopes do not conflict
- Two variables of the same scope with the same name conflict
- Structure tags in a specific scope 、 Both union and enumeration tags share the same namespace , This namespace is different from the space used by ordinary variables
- In the same scope, the names of variables and tags can be the same , There will be no conflict , However, you cannot declare two tags or variables with the same name in the same scope
11. typedef brief introduction
- Use typedef You can customize the name for a type
- And #define similar , But there are two 3 Different
- typedef The symbolic name created is limited to the type , Cannot be used for values
- typedef Interpreted by the compiler , It's not a preprocessor
- Within the limits ,typedef Than #define More flexible
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
// use BYTE Express 1 Byte data type
- Improve program portability
12. Other complex statements
- Symbols that can be used when declaring
| Symbol | meaning |
|---|---|
| * | It means a pointer |
| () | Represents a function |
| [] | Represents an array |
*、()、[] Rules of priority
The first 1 strip
- After the array name [] And after the function name () With the same priority
- Their ratio * ( Quoting ) High priority
int * i[10]; // An array containing pointersThe first 2 strip
- [] and () Same priority for , From left to right
int (* i)[10]; // Pointer to arrayThe first 3 strip
- [] and () From left to right
int i[10][20]; // i By 10 Contents 20 individual int A two-dimensional array consisting of an array of type values int * i[10][20]; // i By 10 Contents 20 individual int A two-dimensional array consisting of an array of pointer type values , reserve 200 Memory space for two pointers int (* i)[10][20]; // i By 10 Contents 20 individual int Pointer to a two-dimensional array consisting of an array of type values , reserve 200 individual int l Storage space
边栏推荐
- Interface master v3.9, API low code development tool, build your interface service platform immediately
- 深度学习之数据处理
- Leecode brushes questions and records interview questions 01.02 Determine whether it is character rearrangement for each other
- Distributed cache
- ActiveReportsJS 3.1中文版|||ActiveReportsJS 3.1英文版
- @TableId can‘t more than one in Class: “com.example.CloseContactSearcher.entity.Activity“.
- C9 colleges and universities, doctoral students make a statement of nature!
- Advanced learning of MySQL -- basics -- multi table query -- inner join
- Meet the level 3 requirements of ISO 2.0 with the level B construction standard of computer room | hybrid cloud infrastructure
- Deep understanding of distributed cache design
猜你喜欢
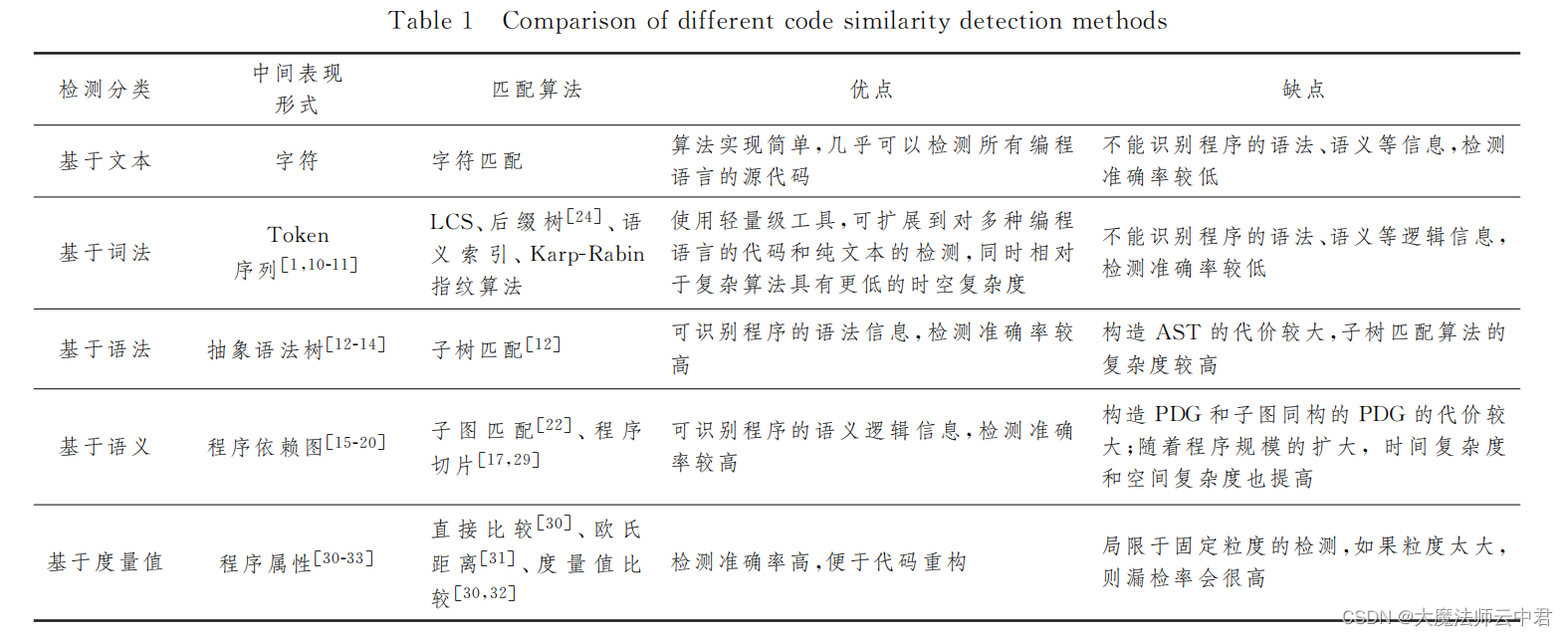
Five different code similarity detection and the development trend of code similarity detection
2022/2/10 summary

threejs图片变形放大全屏动画js特效
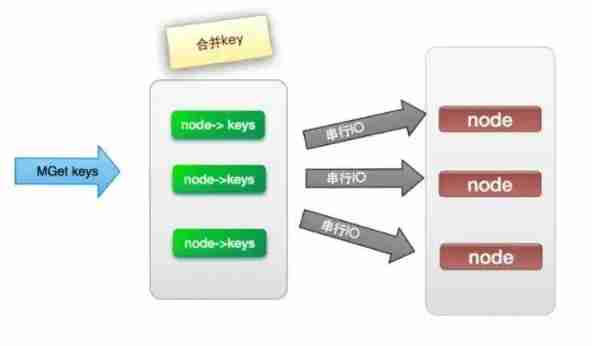
Deep understanding of distributed cache design
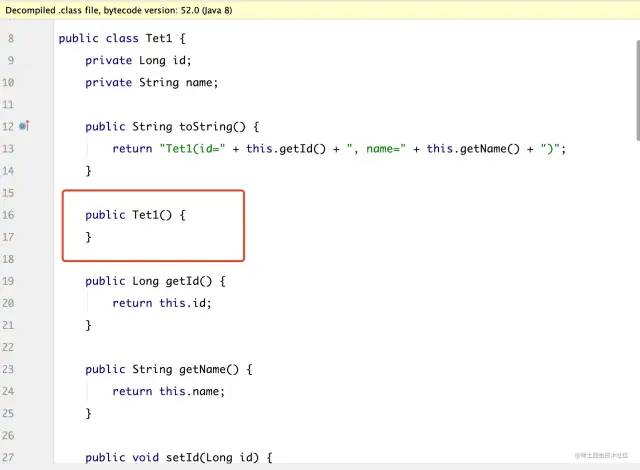
Lombok 同时使⽤ @Data 和 @Builder 的坑,你中招没?
基于GO语言实现的X.509证书
How engineers treat open source -- the heartfelt words of an old engineer
Chapter II proxy and cookies of urllib Library
ActiveReportsJS 3.1中文版|||ActiveReportsJS 3.1英文版

工程师如何对待开源 --- 一个老工程师的肺腑之言
随机推荐
Lombok 同时使⽤ @Data 和 @Builder 的坑,你中招没?
Linear algebra of deep learning
深度学习之环境配置 jupyter notebook
Configuring OSPF basic functions for Huawei devices
MySQL learning notes (mind map)
New feature of Oracle 19C: automatic DML redirection of ADG, enhanced read-write separation -- ADG_ REDIRECT_ DML
Model-Free Prediction
Markov decision process
[software reverse automation] complete collection of reverse tools
2022/2/11 summary
Basic information of mujoco
如何判断一个数组中的元素包含一个对象的所有属性值
alexnet实验偶遇:loss nan, train acc 0.100, test acc 0.100情况
Lombok makes ⽤ @data and @builder's pit at the same time. Are you hit?
2022/2/10 summary
X.509 certificate based on go language
【JokerのZYNQ7020】AXI_EMC。
Advanced learning of MySQL -- basics -- transactions
Data analysis course notes (III) array shape and calculation, numpy storage / reading data, indexing, slicing and splicing
St table