当前位置:网站首页>[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 15. Basic syntax of SystemVerilog learning 2 (operators, type conversion, loops, task/function... Including practical exercises)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 15. Basic syntax of SystemVerilog learning 2 (operators, type conversion, loops, task/function... Including practical exercises)
2022-07-07 08:00:00 【luoganttcc】
Reading guide : The author has the honor to be a pioneer in the field of electronic information in China “ University of electronic technology ” During postgraduate study , Touch the cutting edge Numbers IC Verification knowledge , I heard something like Huawei Hisilicon 、 Tsinghua purple light 、 MediaTek technology And other top IC related enterprises in the industry , Pairs of numbers IC Verify some knowledge accumulation and learning experience . Want to get started for help IC Verified friends , After one or two thoughts , This column is specially opened , In order to spend the shortest time , Take the least detours , Most learned IC Verify technical knowledge .
List of articles
- One 、 Description of content
- Two 、 The operator (Operation)
- 3、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Procedure statement (Procedural Statements)
- Four 、 Variable type conversion (Type Casting)
- 5、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Loop control statement
- 6、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Mission (task) And the function (function)
- 7、 ... and 、 Practice
One 、 Description of content
- SystemVerilog The operator
- SystemVerilog Procedure statement
- SystemVerilog Variable type conversion
- SystemVerilog Loop control statement
- SystemVerilog enhance case sentence
- SystemVerilog Mission (task) And the function (function)
Two 、 The operator (Operation)

- All equal to
===I will also comparex/z
3、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Procedure statement (Procedural Statements)
3.1、 Autoincrement and autodecrement operators
- similar C Language

- First increase / Use after reduction and use before increase / reduce

notes :SystemVerilog Self increase and self decrease of are usually used in TB in , Will not be used in RTL In the code !

3.2、 Logical comparison operator
be equal to
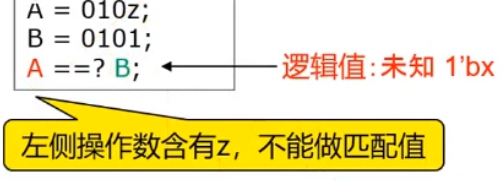
==, It's not equal to!=( It's used a lot , Generally speaking, there arexThere is something wrong with the state )- Logical truth 1, Logic assumes that 0;
- If the compared value There is x and z, Then the logical value is 1’bx
- eg:
a=4'b000xandb=4'b000xThe two comparison results are1'bx, Then there is a pit here ifif(a == b), Be careful1'bxIs it true !
- eg:
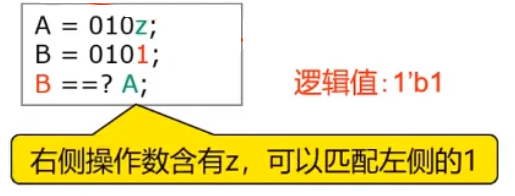
Congruence
===, Incongruence!==- perfect match Four state values :
0,1,x,z- eg:
a=4'b000xandb=4'b000xThe two comparison results are1'b1
- eg:
- perfect match Four state values :
Wildcard logical comparison
- Match, etc
==?And match!=?- Compare by bit , hold
xandzValue should be matched - Just put Right operand Medium
xandzAs a shielding symbol- eg:
4‘b1010 ==? 4'b101xMatch and return1'b1;4‘b1011 ==? 4'b101xMatch and return1'b1
- eg:
- Compare by bit , hold
- Match, etc
- Examples of logical comparison of matchers
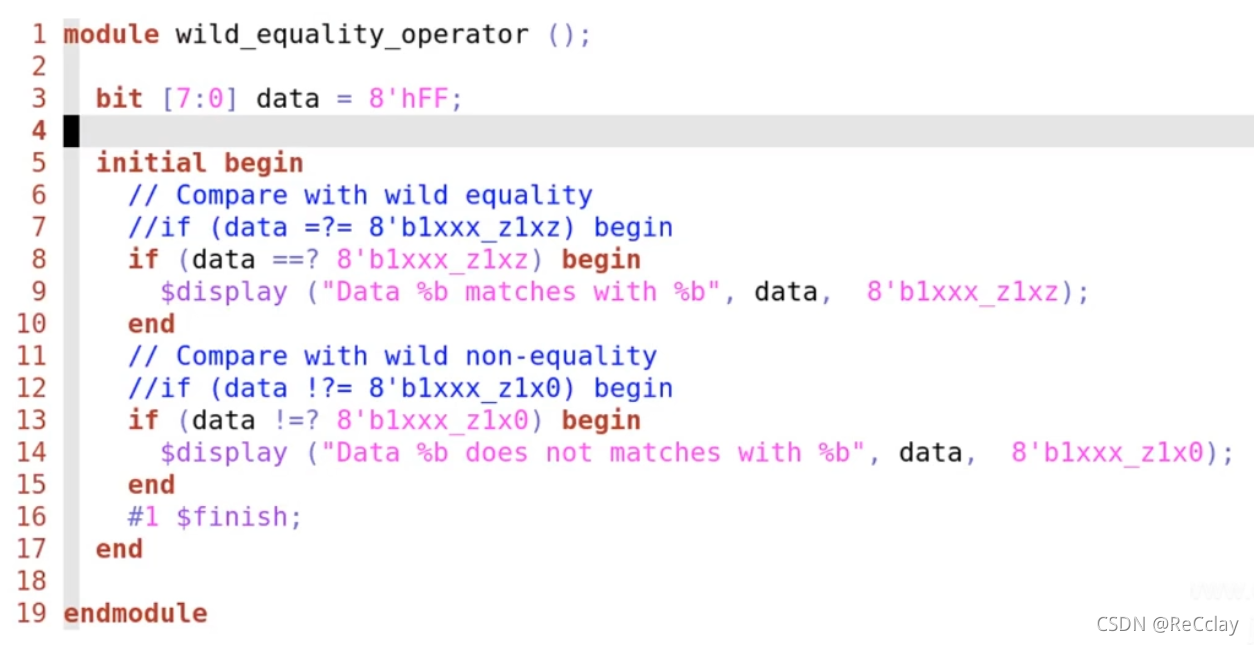
- Print out the first
$display
notes : The comments in the screenshot above and
displayThere is a slight problem with grammar .
3.3、inside keyword
- inside Sure Match any value in a set of data range

Four 、 Variable Type conversion (Type Casting)
4.1、 Variable type converter type' (expression)
- SystemVerilog Added Variable type converter :
type' (expression)- The variable type converter can type the expression at any time
- Not like Verilog The same can only happen in assignment statements

4.2、$cast Cast
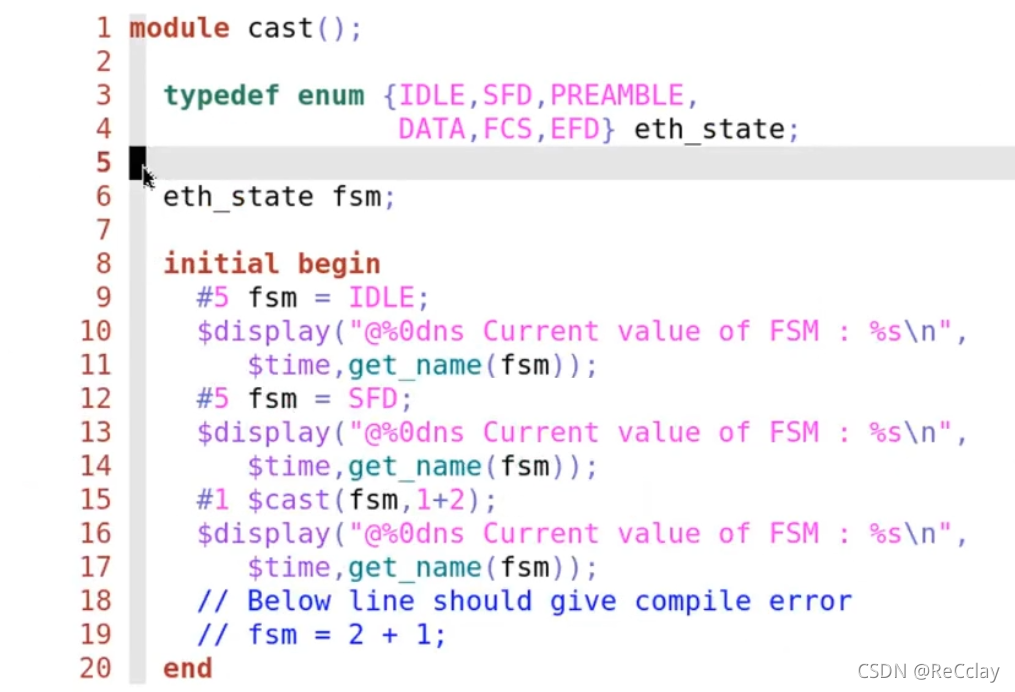
$cast(fsm, 1+2): hold3Assign a value to fsm, And convert the integer mandatory type to the enumeration type , Is this time fsm byDATA
4.3、 Variable bit width conversion (Size Casting)
- SystemVerilog Added Vector bit width transformation
size' (expression)- The expression is converted to Small Bit width hour , Left The bits on the side are Delete
- The expression is converted to Big Bit width hour , Left The bits on the side are expand
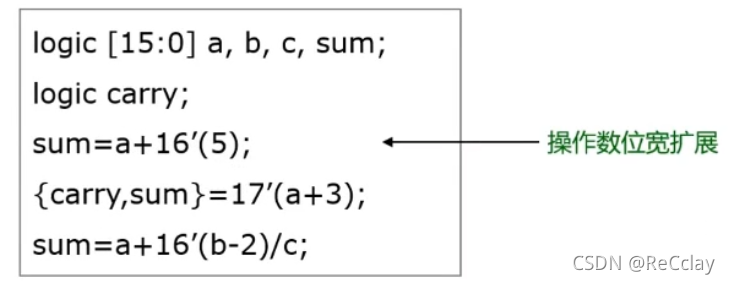
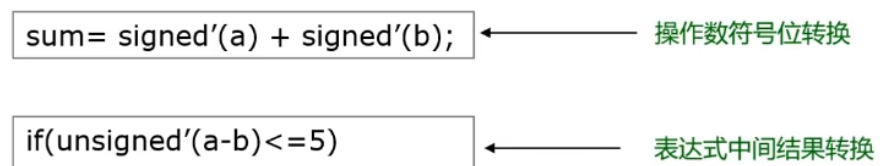
4.4、 Variable sign bit conversion
- SystemVerilog Sign bits can be converted
signed' (expression)andunsigned' (expression)- Operand sign bit conversion
- Expression result sign bit conversion
5、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Loop control statement
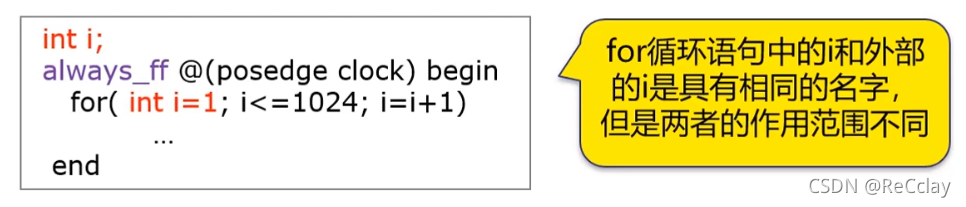
5.1、for Loop statement
Verilog The loop variable in must be in for Statement
- The current loop interacts with other statements
SystemVerilog Can be in for Loop variables are declared inside the loop
- Each variable is a unique local variable , So variables with the same name used externally will not affect each other
- Local loop variables are automated (automatic)
- for The local variables declared inside the loop do not exist outside the loop statement
- stay Verilog Both combinatorial logic and temporal logic are described in
alwayskeyword , Sequential logicalways @(posedge clk); Combinatorial logicalways @(*) - stay SystemVerilog in , Describe temporal logic with
always_ff @(posedge clk)perhapsalways @(posedge clk); Combinatorial logicalways_comb @(*)oralways @(*)

continue
- Can only be used for circular statements
- End this cycle , So let's go to the next loop
break
- Can only be used for circular statements
- Break the cycle , Out of the loop , Do not execute this loop statement
return
- Can be used for loop statements
- End of cycle
- It can also be used for task and function
- end task and function
- Can be used for loop statements
5.2、do...while Loop statement
- Verilog Medium while The loop does not necessarily execute
- If the value of the first loop expression is false , Then the loop statement will not execute
- SystemVerilog Added
do...whileLoop statement ( similar C Language )- Execute the loop statement at least once
- Judge the loop variable at the end of the loop statement

5.3、SystemVerilog enhance case sentence - case/casex/casez
- default Optional. , In a case In the sentence Cannot use more than one default
- First calculate case Value of expression , Then match with the actual branch below , When the match is reached, the corresponding statement will be executed
- case The value of the expression is Assign by bit , Can handle
x and z
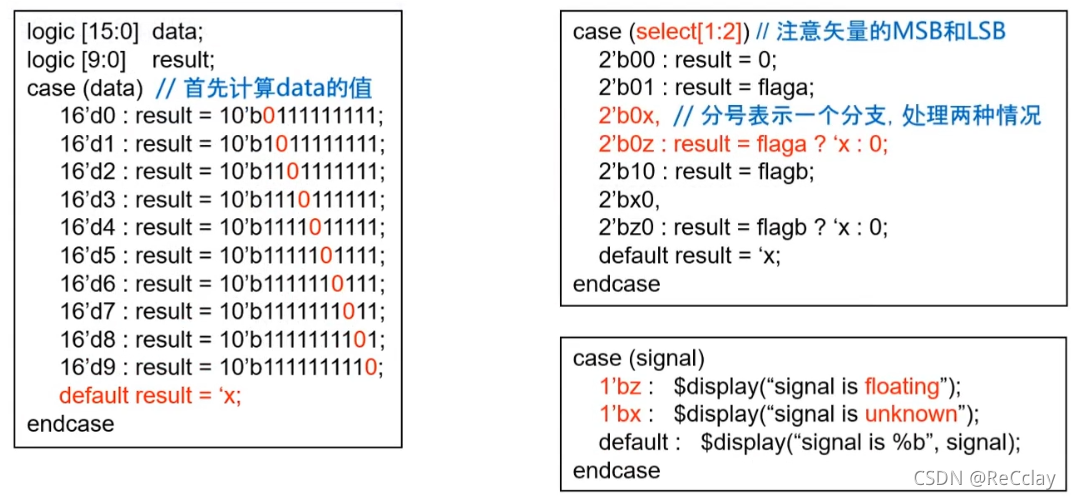
casez- No concern
z
- No concern

notes : Question marks indicate wildcards
casex- No concern
zandx
- No concern

- When
field = 8'b01100110when ,casex Select branch statement2 perform field ^ mask = x1x0x1x0
6、 ... and 、SystemVerilog Mission (task) And the function (function)
6.1、Verilog task and function summary
function
- Function execution time No simulation time is consumed
- Function There cannot be a statement that controls the simulation time
- No simulation time delay :#100 =(`timescale 1ns/10ps)
- There must be no blocking statements :
@(posedge clock)perhapswait(ready) - Cannot call task
void functionno return value- Verilog Of
functionThere must be a return value (Verilog Return by function name !)
- Verilog Of
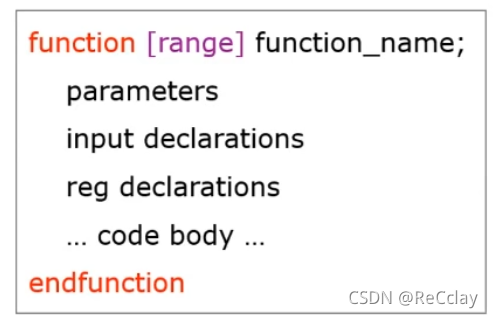
function int sum(input x, y);
sum = x + y;
return sum;
endfunction
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- task
- task contain input、output and inout sentence
- task Consume simulation time
- Delay :#20
- Clock cycle :@(posedge clock)
- event :event

6.2、SystemVerilog task and function
- tasks and function
- No Need to use begin…end sentence
- Added
returnsentence- The return value is only 1 with return; return
bit/logicThis simple type of variable
- The return value is only 1 with return; return
void functionno return valuefunctionThere can beoutputandinoutAs a formal parameter- Return value greater than 1 Time , use output It is convenient to return ; return
array/queue/structComplicated use output
- Return value greater than 1 Time , use output It is convenient to return ; return

You can make an analogy like this ,function Without timing information , Generally speaking, describe combinatorial logic ;task You can bring timing information , It can describe combinatorial logic , It can also describe temporal logic !
- return sentence
- SystemVerilog Added return sentence
- return Statement execution time Returns the value of an expression , Otherwise, the last returned value Assign to function name
- return Statement is used to exit task and function

void function- void function no return value
outputandinoutThe formal parameters are void function Provides a way to pass variablesvoid functionCan be like task The same is called , But it must be consistent with the content constraints of the function
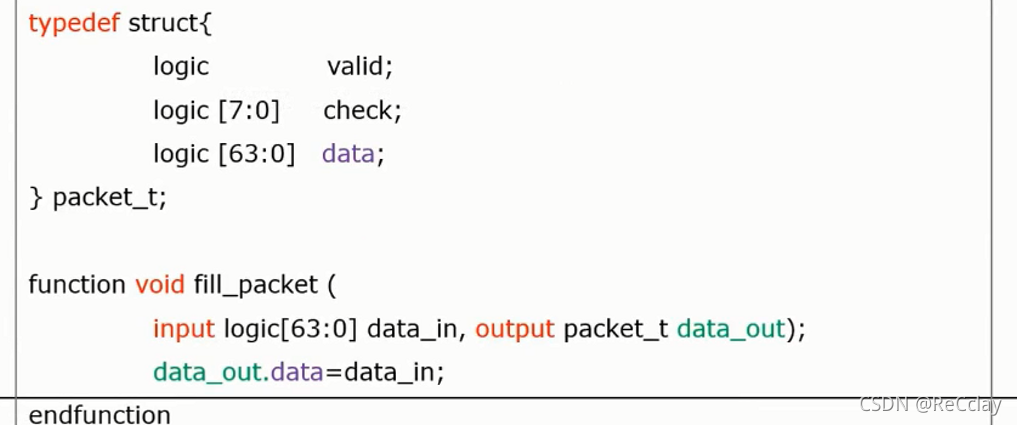
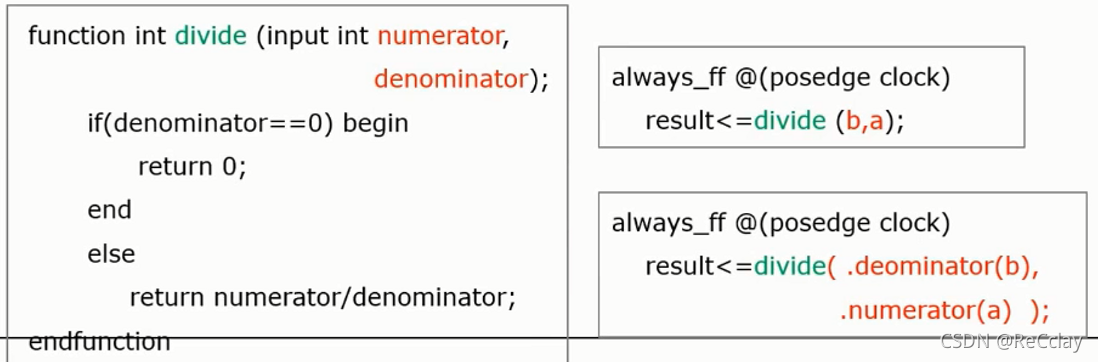
- Pass by name task and function Parameters
- SystemVerilog Pass the parameter by the name of the formal parameter
- Reduce errors
- The order of parameters is unlimited
- The syntax of passing parameters is the same as Verilog The way of port connection is the same
- SystemVerilog Pass the parameter by the name of the formal parameter
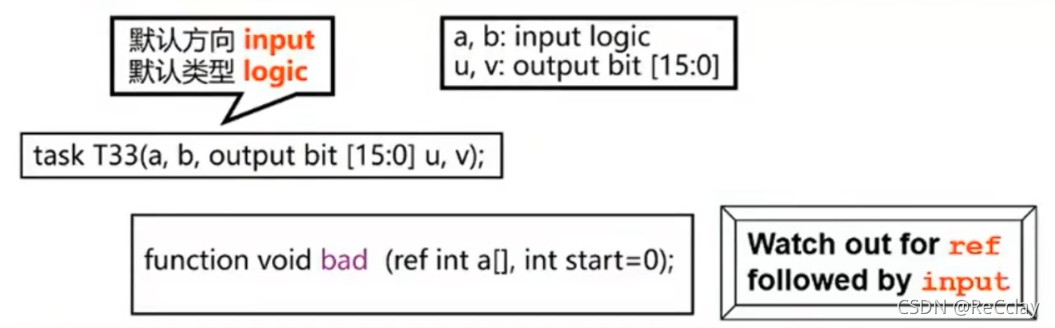
SystemVerilog Enhance function formal parameters
- Added input and output

Default direction and type of formal parameters
- Each formal parameter has a default type
- call task and function when , It is not necessary to pass parameters to parameters with default parameter values
- If the parameter value is not passed , The default value will be used

eg:
always_ff @(posedge clock)
result = incrementer(data_bus);// Parameters that are not explicitly passed use default values , namely result = data_bus + 1;
- 1
- 2
Using a reference (reference) Pass parameters instead of copying
- Common tasks (task) And the function (function) The method of passing parameter values is Copy
- Using a reference (reference) The way is explicit to the task (task) And the function (function) Pass parameters
- Keywords are :
ref( To replace the input, output perhaps inout) - Only automatic (
automatic) Tasks and functions can be usedrefParameters
- Keywords are :

(8*i)+:8Medium:meaning : hold for Loop unrolling , For example, when i=0 when ,(8*0)+:8Express0:0+8(0:8); When i Of =1 when ,(8*1)+:8Express8:16, This way for loop , Ergodicdata[63:0]- There are three ways to express a vector :
[MSB:LSB]、[MSB-:WIDTH]、[LSB+:WIDTH], For example, it corresponds to[7:0]、[7-:8]([7:0])、[0+:8]([0:7])
Using a reference (reference) Pass parameters instead of copying
- Parameters passed by reference can be read-only (read-only)
- allow task/function Reference information within the scope of the call
- prevent task/function Modify referenced information
- modify task ref Parameters are very sensitive
- ref Parameter can read the current value
- ref Parameters can immediately convey changes in information

Parameter passing
- The parameter type is consistent with the parameter type on the left by default
- input - By default , Enter a copy of the value at the beginning
- output - At the end of the output, copy a copy of the value
- inout - At the beginning, enter , Output at the end , A copy of the value
- ref - Pass by reference , The effect immediately appears
- When passing an array to task and function when , It can save time and content
- const - Parameter cannot be modified
Frequently asked questions :task and function difference ?
- a. Whether it consumes simulation time , namely task There can be statements that consume simulation time ,function There can be no time consuming statements ,task It does not necessarily consume simulation time .
- b. task You can call function,function Cannot call task.
- c. stay verilog in : task Multiple values can be returned (output),function Only one value can be returned
- d. task It's not return Of , void function Also no return Of
task and function Whether it can be integrated ?
- Can it be integrated , Depending on the user, the statement inside is RTL Behavior level description
- such as task or function There is
$display("xxx");, So this task or function It must not be integrated .wait/#10And so on cannot be integrated !
7、 ... and 、 Practice
7.1 Practice logical operators and arithmetic operators
7.1.1、 Comparison operator demo
sv_operation.sv
module SV_OPERATION();
bit sig_a;
bit sig_lgc_inv_a;
bit sig_bit_inv_a;
bit [2:0] sig_m_a;
bit [2:0] sig_m_lgc_inv_a;
bit [2:0] sig_m_bit_inv_a;
bit signed [7:0] sig_c;
bit signed [7:0] sig_lgc_lft_c;
bit signed [7:0] sig_lgc_rgt_c;
bit signed [7:0] sig_arth_lft_c;
bit signed [7:0] sig_arth_rgt_c;
int i;
logic [7:0] comp_a;
logic [7:0] comp_b;
logic [2:0] a;
logic comp1 [8];
logic comp2 [8];
initial begin
sig_a = 1'b0; sig_m_a = 3'b010;
sig_c = 8'sb1100_0111; sig_lgc_inv_a = !sig_a; sig_bit_inv_a = ~sig_a; sig_m_lgc_inv_a = !sig_m_a; sig_m_bit_inv_a = ~sig_m_a; comp_a = 8'b0100_1101;
comp_b = 8'b0100_1100; if(comp_a == comp_b) begin $display("******comp_a: %b == comp_b: %b", comp_a, comp_b); end else begin $display("******comp_a: %b != comp_b: %b", comp_a, comp_b); end if(comp_a === {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}) begin
$display("******comp_a: %b === {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: %b", comp_a, {
comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}); end else begin $display("******comp_a: %b !== {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: %b", comp_a, {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}); end if(comp_a ==? {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}) begin $display("******comp_a: %b ==? {
comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: %b", comp_a, {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx});
end
else begin
$display("******comp_a: %b !=? {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: %b", comp_a, {
comp_b[7:1], 1'bx});
end
end
endmodule
rslt.log
******comp_a: 01001101 != comp_b: 01001100
******comp_a: 01001101 !== {
comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: 0100110x ******comp_a: 01001101 ==? {comp_b[7:1], 1'bx}: 0100110x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Makefile Same as The first 14 Blog post , But is
comp_fileParameters changed :make comp_file=sv_operation.sv sig_aIt means single bit ,sig_m_aIndicates multiple bitssig_c = 8'sb1100_0111;Medium s It means that there is a sign- Single bit logic negates
!And bitwise inversion~equally ; But multi bits are different ! comp_xxxRepresents the variable used for comparison
7.1.2、 Logical operators ! And arithmetic operators ~ The difference of demo
sv_operation.sv
$display("******single bit logic invertor ! :sig_a is : %b, sig_lgc_inv_a is : %b", sig_a, sig_lgc_inv_a);
$display("******single bit bit invertor ~ :sig_a is : %b, sig_bit_inv_a is : %b", sig_a, sig_bit_inv_a);
$display("******multiple bit logic invertor ! :sig_m_a is : %b, sig_m_lgc_inv_a is : %b", sig_m_a, sig_m_lgc_inv_a);
$display("******multiple bit bit invertor ~ :sig_m_a is : %b, sig_m_bit_inv_a is : %b", sig_m_a, sig_m_bit_inv_a);
rslt.log
******single bit logic invertor ! :sig_a is : 0, sig_lgc_inv_a is : 1
******single bit bit invertor ~ :sig_a is : 0, sig_bit_inv_a is : 1
******multiple bit logic invertor ! :sig_m_a is : 010, sig_m_lgc_inv_a is : 000
******multiple bit bit invertor ~ :sig_m_a is : 010, sig_m_bit_inv_a is : 101
- For single bit logic, negate
!And bitwise inversion~No difference ; And multi bits are different
7.1.3、 Shift operation demo
sv_operation.sv
sig_lgc_lft_c = sig_c << 5; sig_lgc_rgt_c = sig_c >> 5; sig_arth_lft_c = sig_c <<< 5; sig_arth_rgt_c = sig_c >>> 5; $display("******logical left shift << :sig_c is : %b, sig_lgc_lft_c is : %b", sig_c,sig_lgc_lft_c); $display("******logical right shift >> :sig_c is : %b, sig_lgc_rgt_c is : %b", sig_c,sig_lgc_rgt_c); $display("******arithmetic left shift <<< :sig_c is : %b, sig_arth_lft_c is : %b", sig_c,sig_arth_lft_c); $display("******arithmetic right shift >>> :sig_c is : %b, sig_arth_rgt_c is : %b", sig_c,sig_arth_rgt_c);
rslt.log******logical left shift << :sig_c is : 11000111, sig_lgc_lft_c is : 11100000 ******logical right shift >> :sig_c is : 11000111, sig_lgc_rgt_c is : 00000110 ******arithmetic left shift <<< :sig_c is : 11000111, sig_arth_lft_c is : 11100000 ******arithmetic right shift >>> :sig_c is : 11000111, sig_arth_rgt_c is : 11111110
- Logic shift left / Move right , After moving, use
0To mend - Arithmetic left shift is the same as logical left shift ; Move arithmetic right if the highest bit is
1, Then make up1. Similarly, if the highest bit is0, Then make up0
7.1.4、++i and i++ difference demo
sv_operation.sv
i = 0;
while(i++ < 5) begin
$display("****** the i++ i %d", i);
end
i = 0;
while(++i < 5) begin
$display("****** the ++i i %d", i);
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
rslt.log
****** the i++ i 1
****** the i++ i 2
****** the i++ i 3
****** the i++ i 4
****** the i++ i 5
****** the ++i i 1
****** the ++i i 2
****** the ++i i 3
****** the ++i i 4
7.1.5、inside keyword demo
sv_operation.sv
for(int i=0; i<8; i++) begin a = i[2:0]; if(a==3'b100 || a==3'b101 || a==3'b011) begin comp1[i] = 1'b1; end else begin comp1[i] = 1'b0; end if(a inside{3'b100, 3'b101, 3'b011}) begin comp2[i] = 1'b1; end else begin comp2[i] = 1'b0; end end if(comp1 == comp2) begin $display("******comp1 == comp2"); end else begin $display("******comp1 != comp2"); end
rslt.log******comp1 == comp2
- 1
7.2、 Circulation practice
7.2.1、 Different initial Blocks share the same global variable demo
sv_loop_case.sv
module sv_loop_case();
int j;
int i;
initial begin : loop0
for(i=0; i<5; i++) begin
#1;
$display("******loop0 i = %0d", i);
end
end
initial begin : loop1
for(i=0; i<5; i++) begin
#1;
$display("******loop1 i = %0d", i);
end
end
endmodule
******loop0 i = 0
******loop1 i = 1
******loop0 i = 2
******loop1 i = 3
******loop0 i = 4
******loop1 i = 5
- You can see two initial Blocks share the same global variable i,for Circulation has an effect !
7.2.2、 Different initial Blocks use local variables demo
sv_loop_case.sv
module sv_loop_case(); //int j; //int i; initial begin : loop0 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) begin // Notice that it defines int, This is called a local variable ! #1; $display("******loop0 i = %0d", i); end end initial begin : loop1 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) begin #1; $display("******loop1 i = %0d", i); end end endmodule
rslt.log******loop0 i = 0 ******loop1 i = 0 ******loop0 i = 1 ******loop1 i = 1 ******loop0 i = 2 ******loop1 i = 2 ******loop0 i = 3 ******loop1 i = 3 ******loop0 i = 4 ******loop1 i = 4
- You can see two intial The block for Circulation does not affect !
7.2.3、 Different initial Block use automatic Defining variables demo
sv_loop_case.sv
module sv_loop_case(); //int j; //int i; initial begin : loop0 automatic int i; for(i=0; i<5; i++) begin #1; $display("******loop0 i = %0d", i); end end initial begin : loop1 automatic int i; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) begin #1; $display("******loop1 i = %0d", i); end end endmodule
rslt.log******loop0 i = 0 ******loop1 i = 0 ******loop0 i = 1 ******loop1 i = 1 ******loop0 i = 2 ******loop1 i = 2 ******loop0 i = 3 ******loop1 i = 3 ******loop0 i = 4 ******loop1 i = 4
- You can see the use of automatic Defining variables has the same effect as using local variables , Two initial The block for Cycles also do not affect each other
7.2.4、while and do...while Execution process demo
sv_loop_case.sv
initial begin j = 0; do begin $display("******%d th loop in do while loop", j); j++; end while(j<0); j=0; while(j<0) begin $display("******%d th loop in while loop", j); j++; end end
rslt.log****** 0 th loop in do while loop
- 1
- You can see
do...whileI'm going to execute it first , Then judge
7.3、case/casez/casex Branch differentiation exercise
sv_loop_case.sv
logic [3:0] sel_z = 4'bz01z; logic [3:0] sel_x = 4'bx01x;
initial begin
case(sel_z)
4'b1??? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b1??? in case selection", sel_z); 4'b01?? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b01?? in case selection", sel_z); 4'b001? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b001? in case selection", sel_z);
4'b0001 : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b0001 in case selection", sel_z); default : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is in default branch in case selection", sel_z); endcase casez(sel_z) 4'b1??? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b1??? in casez selection", sel_z); 4'b01?? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b01?? in casez selection", sel_z);
4'b001? : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b001? in casez selection", sel_z); 4'b0001 : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is 4'b0001 in casez selection", sel_z); default : $display("****** sel_z(%0b) is in default branch in case selection", sel_z); endcase case(sel_x) 4'b1??? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b1??? in case selection", sel_x);
4'b01?? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b01?? in case selection", sel_x); 4'b001? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b001? in case selection", sel_x); 4'b0001 : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b0001 in case selection", sel_x);
default : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is in default branch in case selection", sel_x);
endcase
casex(sel_x)
4'b1??? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b1??? in casex selection", sel_x); 4'b01?? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b01?? in casex selection", sel_x); 4'b001? : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b001? in casex selection", sel_x);
4'b0001 : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is 4'b0001 in casex selection", sel_x); default : $display("****** sel_x(%0b) is in default branch in case selection", sel_x);
endcase
end
rslt.log
****** sel_z(z01z) is in default branch in case selection
****** sel_z(z01z) is 4'b1??? in casez selection ****** sel_x(x01x) is in default branch in case selection ****** sel_x(x01x) is 4'b1??? in casex selection
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
casezNo concernz, namelyzCan be regarded as 0 or 1.casexNo concernzandx, namelyxandzCan be regarded as 0 or 1.- Question marks indicate wildcards ,case Inside the general configuration
?, Only for 0 and 1;casez Inside?Pass through , Can represent0/1/z;casex Inside?Pass through , Can represent0/1/x/z. z01zand001?It can also be matched , But it has matched the previous1???, So the back001?It doesn't match anymore- stay case in , If one branch is
z01z, that sel_z It can match this branch , Strictly match !
7.4、task/function practice
7.4.1、function Package structure demo
sv_function_task.sv
module sv_function_task();
typedef struct {
int height;
int weight;
logic [7:0] legs;
logic [1:0] hands;
logic [1:0] eyes;
logic noses;
}animal;
animal duck;
animal dog;
animal d;
logic [76:0] data_in;
string name;
initial begin
duck.height = 32'd132; duck.weight = 32'd200;
duck.legs = 8'd2; duck.hands = 2'd2;
duck.eyes = 2'd2; duck.noses = 1'd1;
$display("******@%0tns duck unpacked value ******", $time);
$display("******@%0tns duck height : %0d ****", $time, duck.height);
$display("******@%0tns duck weight : %0d ****", $time, duck.weight);
$display("******@%0tns duck legs : %0d ****", $time, duck.legs);
$display("******@%0tns duck hands : %0d ****", $time, duck.hands);
$display("******@%0tns duck eyes : %0d ****", $time, duck.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns duck noses : %0d ****", $time, duck.noses);
dog.height = 32'd232; dog.weight = 32'd100;
dog.legs = 8'd4; dog.hands = 2'd0;
dog.eyes = 2'd2; dog.noses = 1'd1;
$display("******@%0tns dog unpacked value ******", $time);
$display("******@%0tns dog height : %0d ****", $time, dog.height);
$display("******@%0tns dog weight : %0d ****", $time, dog.weight);
$display("******@%0tns dog legs : %0d ****", $time, dog.legs);
$display("******@%0tns dog hands : %0d ****", $time, dog.hands);
$display("******@%0tns dog eyes : %0d ****", $time, dog.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns dog noses : %0d ****", $time, dog.noses);
end
function void animal_assign (input [76:0] data_in, output animal animal_obj);
animal_obj.height = data_in[76 -: 32];
animal_obj.weight = data_in[76-32 -: 32];
animal_obj.legs = data_in[76-32-32 -: 8];
animal_obj.hands = data_in[76-32-32-8 -: 2];
animal_obj.eyes = data_in[76-32-32-8-2 -: 2];
animal_obj.noses = data_in[0];
endfunction
function void animal_display (input string name, input animal animal_obj);
$display("******@%0tns %s unpacked value animal_assign&animal_display******", $time, name);
$display("******@%0tns %s height : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.height);
$display("******@%0tns %s weight : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.weight);
$display("******@%0tns %s legs : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.legs);
$display("******@%0tns %s hands : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.hands);
$display("******@%0tns %s eyes : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns %s noses : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.noses);
endfunction
initial begin
data_in = {
32'd132, 32'd200, 8'd2, 2'd2, 2'd2, 1'd1};
animal_assign(data_in, duck);
name="duck";
animal_display(name, duck);
data_in = {
32'd132, 32'd100, 8'd2, 2'd0, 2'd2, 1'd1};
animal_assign(data_in, dog);
name="dog";
animal_display(name, dog);
end
endmodule
rslt.log
******@0ns duck unpacked value ******
******@0ns duck height : 132 ****
******@0ns duck weight : 200 ****
******@0ns duck legs : 2 ****
******@0ns duck hands : 2 ****
******@0ns duck eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns duck noses : 1 ****
******@0ns dog unpacked value ******
******@0ns dog height : 232 ****
******@0ns dog weight : 100 ****
******@0ns dog legs : 4 ****
******@0ns dog hands : 0 ****
******@0ns dog eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns dog noses : 1 ****
******@0ns duck unpacked value animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns duck height : 132 ****
******@0ns duck weight : 200 ****
******@0ns duck legs : 2 ****
******@0ns duck hands : 2 ****
******@0ns duck eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns duck noses : 1 ****
******@0ns dog unpacked value animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns dog height : 132 ****
******@0ns dog weight : 100 ****
******@0ns dog legs : 2 ****
******@0ns dog hands : 0 ****
******@0ns dog eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns dog noses : 1 ****
7.4.2、ref Parameters demo
sv_function_task.sv
module sv_function_task();
typedef struct {
int height;
int weight;
logic [7:0] legs;
logic [1:0] hands;
logic [1:0] eyes;
logic noses;
}animal;
animal duck;
animal dog;
animal d;
logic [76:0] data_in;
string name;
/*initial begin
duck.height = 32'd132; duck.weight = 32'd200;
duck.legs = 8'd2; duck.hands = 2'd2;
duck.eyes = 2'd2; duck.noses = 1'd1;
$display("******@%0tns duck unpacked value ******", $time);
$display("******@%0tns duck height : %0d ****", $time, duck.height);
$display("******@%0tns duck weight : %0d ****", $time, duck.weight);
$display("******@%0tns duck legs : %0d ****", $time, duck.legs);
$display("******@%0tns duck hands : %0d ****", $time, duck.hands);
$display("******@%0tns duck eyes : %0d ****", $time, duck.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns duck noses : %0d ****", $time, duck.noses);
dog.height = 32'd232; dog.weight = 32'd100;
dog.legs = 8'd4; dog.hands = 2'd0;
dog.eyes = 2'd2; dog.noses = 1'd1;
$display("******@%0tns dog unpacked value ******", $time);
$display("******@%0tns dog height : %0d ****", $time, dog.height);
$display("******@%0tns dog weight : %0d ****", $time, dog.weight);
$display("******@%0tns dog legs : %0d ****", $time, dog.legs);
$display("******@%0tns dog hands : %0d ****", $time, dog.hands);
$display("******@%0tns dog eyes : %0d ****", $time, dog.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns dog noses : %0d ****", $time, dog.noses);
end
function void animal_assign (input [76:0] data_in, output animal animal_obj);
animal_obj.height = data_in[76 -: 32];
animal_obj.weight = data_in[76-32 -: 32];
animal_obj.legs = data_in[76-32-32 -: 8];
animal_obj.hands = data_in[76-32-32-8 -: 2];
animal_obj.eyes = data_in[76-32-32-8-2 -: 2];
animal_obj.noses = data_in[0];
endfunction
function void animal_display (input string name, input animal animal_obj);
$display("******@%0tns %s unpacked value animal_assign&animal_display******", $time, name);
$display("******@%0tns %s height : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.height);
$display("******@%0tns %s weight : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.weight);
$display("******@%0tns %s legs : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.legs);
$display("******@%0tns %s hands : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.hands);
$display("******@%0tns %s eyes : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns %s noses : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.noses);
endfunction
initial begin
data_in = {
32'd132, 32'd200, 8'd2, 2'd2, 2'd2, 1'd1};
animal_assign(data_in, duck);
name="duck";
animal_display(name, duck);
data_in = {
32'd132, 32'd100, 8'd2, 2'd0, 2'd2, 1'd1};
animal_assign(data_in, dog);
name="dog";
animal_display(name, dog);
end*/
task automatic animal_assign(ref [76:0] data_in, ref animal animal_obj);
animal_obj.height = data_in[76 -: 32];
animal_obj.weight = data_in[76-32 -: 32];
animal_obj.legs = data_in[76-32-32 -: 8];
animal_obj.hands = data_in[76-32-32-8 -: 2];
animal_obj.eyes = data_in[76-32-32-8-2 -: 2];
animal_obj.noses = data_in[0];
endtask
task automatic animal_display(ref string name, ref animal animal_obj);
$display("******@%0tns %s unpacked value automatic animal_assign&animal_display******", $time, name);
$display("******@%0tns %s height : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.height);
$display("******@%0tns %s weight : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.weight);
$display("******@%0tns %s legs : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.legs);
$display("******@%0tns %s hands : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.hands);
$display("******@%0tns %s eyes : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.eyes);
$display("******@%0tns %s noses : %0d ****",$time, name, animal_obj.noses);
endtask
task automatic animal_assign_modified(ref [76:0] data_in, ref animal animal_obj);
animal_obj.height = data_in[76 -: 32];
animal_obj.weight = data_in[76-32 -: 32];
animal_obj.legs = data_in[76-32-32 -: 8];
animal_obj.hands = data_in[76-32-32-8 -: 2];
animal_obj.eyes = data_in[76-32-32-8-2 -: 2];
animal_obj.noses = data_in[0];
data_in = '0; endtask initial begin data_in = {32'd132, 32'd200, 8'd2, 2'd2, 2'd2, 1'd1}; animal_assign(data_in, duck); name = "duck"; animal_display(name, duck) data_in = {32'd132, 32'd100, 8'd2, 2'd0, 2'd2, 1'd1};
animal_assign(data_in, dog);
name = "dog";
animal_display(name, dog);
animal_assign_modified(data_in, dog);
animal_display(name, dog);
$display("******After data_in modified by dog structure");
animal_assign(data_in, duck);
name = "duck";
animal_display(name, duck);
end
endmodule
rslt.log
******@0ns duck unpacked value automatic animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns duck height : 132 ****
******@0ns duck weight : 200 ****
******@0ns duck legs : 2 ****
******@0ns duck hands : 2 ****
******@0ns duck eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns duck noses : 1 ****
******@0ns dog unpacked value automatic animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns dog height : 132 ****
******@0ns dog weight : 100 ****
******@0ns dog legs : 2 ****
******@0ns dog hands : 0 ****
******@0ns dog eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns dog noses : 1 ****
******@0ns dog unpacked value automatic animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns dog height : 132 ****
******@0ns dog weight : 100 ****
******@0ns dog legs : 2 ****
******@0ns dog hands : 0 ****
******@0ns dog eyes : 2 ****
******@0ns dog noses : 1 ****
******After data_in modified by dog structure
******@0ns duck unpacked value automatic animal_assign&animal_display******
******@0ns duck height : 0 ****
******@0ns duck weight : 0 ****
******@0ns duck legs : 0 ****
******@0ns duck hands : 0 ****
******@0ns duck eyes : 0 ****
******@0ns duck noses : 0 ****
- You can see the changes
refQuoted variables , Then call the variable , This variable is the changed value . refIt's easy to make mistakes , It is not recommended for actual use .
Reference resources
边栏推荐
- Installing postgresql11 database under centos7
- [OBS] win capture requires winrt
- [CV] Wu Enda machine learning course notes | Chapter 8
- A bit of knowledge - about Apple Certified MFI
- php导出百万数据
- [2022 ciscn] replay of preliminary web topics
- Linux server development, MySQL index principle and optimization
- 有 Docker 谁还在自己本地安装 Mysql ?
- Pytest+allure+jenkins environment -- completion of pit filling
- Common validation comments
猜你喜欢
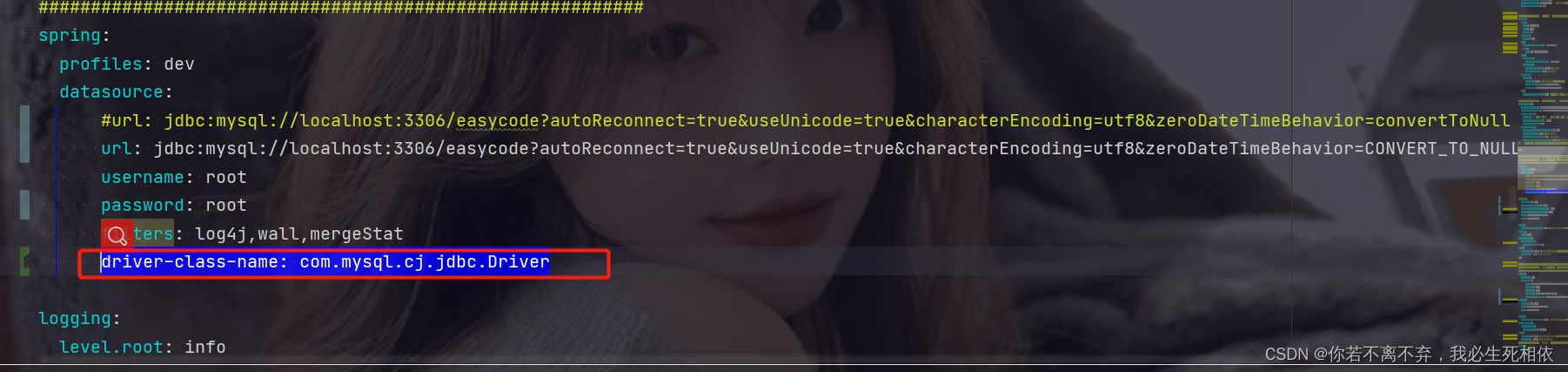
Mysql高低版本切换需要修改的配置5-8(此处以aicode为例)
![[UTCTF2020]file header](/img/e3/818e2d531a06ab90de189055f634ad.png)
[UTCTF2020]file header
Explore dry goods! Apifox construction ideas
padavan手动安装php
解决问题:Unable to connect to Redis
【斯坦福计网CS144项目】Lab3: TCPSender

Linux server development, MySQL transaction principle analysis
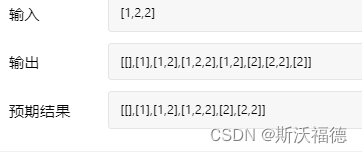
Leetcode 90: subset II

Few-Shot Learning && Meta Learning:小样本学习原理和Siamese网络结构(一)
Linux server development, MySQL index principle and optimization
随机推荐
2022焊工(初级)判断题及在线模拟考试
开源生态|打造活力开源社区,共建开源新生态!
[advanced digital IC Verification] command query method and common command interpretation of VCs tool
pytest+allure+jenkins環境--填坑完畢
Live broadcast platform source code, foldable menu bar
C语言二叉树与建堆
Cnopendata American Golden Globe Award winning data
[UVM practice] Chapter 1: configuring the UVM environment (taking VCs as an example), run through the examples in the book
[guess-ctf2019] fake compressed packets
C language communication travel card background system
Introduction to basic components of wechat applet
Téléchargement des données de conception des puces
【经验分享】如何为visio扩展云服务图标
Figure out the working principle of gpt3
Linux server development, SQL statements, indexes, views, stored procedures, triggers
Installing postgresql11 database under centos7
Rust Versus Go(哪种是我的首选语言?)
Mysql高低版本切换需要修改的配置5-8(此处以aicode为例)
C语言队列
2022-07-06: will the following go language codes be panic? A: Meeting; B: No. package main import “C“ func main() { var ch chan struct