当前位置:网站首页>Service asynchronous communication
Service asynchronous communication
2022-07-07 00:38:00 【Henrik-Yao】
List of articles
MQ Some common questions about
- Message reliability issues : How to ensure that the sent message is consumed at least once
- Delayed message problem : How to realize the delayed delivery of messages
- High availability problem : How to avoid single point MQ Unavailability caused by failure
- Message stacking problem : How to solve the problem of millions of messages , The problem of not being able to consume in time
One . Message reliability
Message reliability issues
- Lost while sending :
The message sent by the producer was not delivered exchange
The news arrived exchange Not arrived after queue - MQ Downtime ,queue Lose message
- consumer Downtime without consumption after receiving the message
1. Producer message confirmation
RabbitMQ Provides publisher confirm Mechanism to avoid sending messages to MQ Lost in the process . Message sent to MQ in the future , Will return a result to the sender , Indicates whether the message is processed successfully . As a result, there are two requests :
- publisher-confirm, Sender confirms
The message was successfully delivered to the switch , return ack
The message was not delivered to the switch , return nack - publisher-return, Sender's receipt
The message was delivered to the switch , But there is no route to the queue . return ACK, And routing failure reason
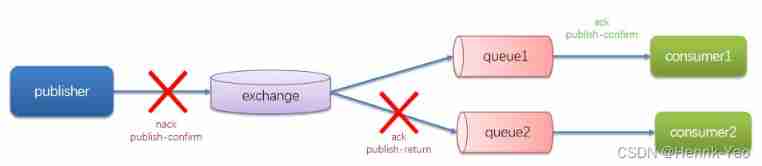
When the acknowledgement mechanism sends a message , You need to set a globally unique for each message id, To distinguish between different messages , avoid ack Conflict
SpringAMQP Implement producer validation
stay publisher Micro service application.yml Add configuration in :
spring:
rabbitmq:
publisher-confirm-type: correlated
publisher-returns: true
template:
mandatory: true
Configuration instructions :
- publish-confirm-type: Turn on publisher-confirm, Two types are supported here :
simple: Synchronization waiting confirm result , Until timeout
correlated: Asynchronous callback , Definition ConfirmCallback,MQ This... Will be called back when the result is returned ConfirmCallback - publish-returns: Turn on publish-return function , Again based on callback Mechanism , It's just a definition ReturnCallback
- template.mandatory: Define the policy when message routing fails .true, Call ReturnCallback;false: Then drop the message
Every RabbitTemplate Only one can be configured ReturnCallback, Therefore, it is necessary to configure :
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class CommonConfig implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// obtain RabbitTemplate
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RabbitTemplate.class);
// Set up ReturnCallback
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> {
// Delivery failed , Log
log.info(" Message delivery failed , The reply code {}, reason {}, Switch {}, Routing key {}, news {}",
replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey, message.toString());
// If there is a business need , You can resend the message
});
}
}
ConfirmCallback You can specify... When sending a message , Because every business process confirm The logic of success or failure is not necessarily the same
public void testSendMessage2SimpleQueue() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. Message body
String message = "hello, spring amqp!";
// 2. Globally unique message ID, It needs to be encapsulated into CorrelationData in
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
// 3. add to callback
correlationData.getFuture().addCallback(
result -> {
if(result.isAck()){
// 3.1.ack, The news is successful
log.debug(" Message sent successfully , ID:{}", correlationData.getId());
}else{
// 3.2.nack, The news failed
log.error(" Message delivery failed , ID:{}, reason {}",correlationData.getId(), result.getReason());
}
},
ex -> log.error(" Message sending exception , ID:{}, reason {}",correlationData.getId(),ex.getMessage())
);
// 4. Send a message
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("task.direct", "task", message, correlationData);
// Sleep for a while , wait for ack receipt
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
2. Message persistence
By default , Switch 、 queue 、 Messages are persistent
MQ The default is to store messages in memory , Enabling the persistence function can ensure that the cache is in MQ Messages in are not lost
Switch persistence :
@Bean
public DirectExchange simpleExchange(){
// Three parameters : Switch name 、 Persistent or not 、 When there is no queue Whether to delete it automatically when binding with it
return new DirectExchange("simple.direct", true, false);
}
Queue persistence :
@Bean
public Queue simpleQueue(){
// Use QueueBuilder Build queue ,durable It's persistent
return QueueBuilder.durable("simple.queue").build();
}
Message persistence ,SpringAMQP Messages in are persistent by default , Can pass MessageProperties Medium DeliveryMode Designated :
Message msg = MessageBuilder
.withBody(message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)) // Message body
.setDeliveryMode(MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT) // Persistence
.build();
3. Consumer message confirmation
RabbitMQ Support consumer recognition mechanism , namely : After processing the message, the consumer can report to MQ send out ack receipt ,MQ received ack The message will not be deleted until the receipt is received . and SpringAMQP Three confirmation modes are allowed to be configured :
- manual: Manual ack, After the business code is completed , call api send out ack.
- auto: Automatically ack, from spring monitoring listener Whether there are exceptions in the code , If there is no exception, return ack; Throw an exception and return nack
- none: close ack,MQ It is assumed that the consumer will successfully process after obtaining the message , Therefore, the message is deleted immediately after delivery
The configuration method is to modify application.yml file , Add the following configuration :
modify consumer Service application.yml file , Add the following :
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: none # close ack
4. Consumption failure retry mechanism
When consumers are abnormal , The news will continue requeue( Rejoin the team ) To queue , And resend it to the consumer , Then again , Again requeue, Infinite loop , Lead to mq Message processing soared , Bring unnecessary pressure
You can use Spring Of retry Mechanism , Use local retry when the consumer has an exception , Not unlimited requeue To mq queue
modify consumer Service application.yml file , Add content :
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
retry:
enabled: true # Failed to open consumer. Try again
initial-interval: 1000 # The waiting time for the first failure is 1 second
multiplier: 1 # Multiple of failed waiting time , Next waiting time = multiplier * last-interval
max-attempts: 3 # max retries
stateless: true # true No state ;false A stateful . If the business contains transactions , Here instead false
restart consumer service , Repeat the previous test . You can find :
- Trying again 3 Next time ,SpringAMQP It throws an exception AmqpRejectAndDontRequeueException, This indicates that the local retry triggered
- see RabbitMQ Console , Found that the message was deleted , Explain finally SpringAMQP The return is ack,mq The message was deleted
Consumer failure message processing strategy
After turning on Retry mode , Out of retries , If the message still fails , You need to have MessageRecoverer Interface to handle , It contains three different implementations :
- RejectAndDontRequeueRecoverer: Retry after exhaustion , direct reject, Discard the message . The default is this way
- ImmediateRequeueMessageRecoverer: Retry after exhaustion , return nack, The news rejoined the team
- RepublishMessageRecoverer: Retry after exhaustion , Post the failure message to the specified switch
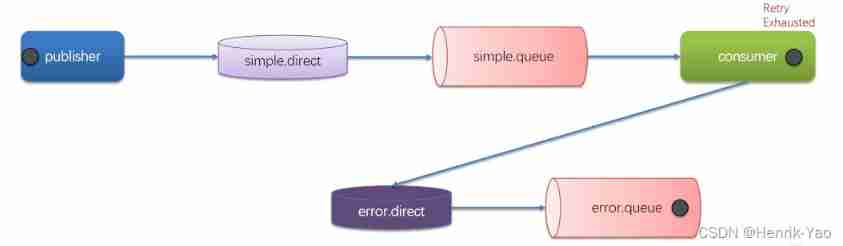
A more elegant solution is RepublishMessageRecoverer, After failure, the message is delivered to a specified , A queue dedicated to storing exception messages , Subsequently, it will be handled manually
1) stay consumer The service defines the switch and queue for processing failure messages
@Bean
public DirectExchange errorMessageExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("error.direct");
}
@Bean
public Queue errorQueue(){
return new Queue("error.queue", true);
}
@Bean
public Binding errorBinding(Queue errorQueue, DirectExchange errorMessageExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(errorQueue).to(errorMessageExchange).with("error");
}
2) Define a RepublishMessageRecoverer, Associate queues and switches
@Bean
public MessageRecoverer republishMessageRecoverer(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate){
return new RepublishMessageRecoverer(rabbitTemplate, "error.direct", "error");
}
How to ensure RabbitMQ The reliability of the message ?
- Turn on the producer confirmation mechanism , Ensure that the producer's message can reach the queue
- Turn on persistence , Ensure that messages are not lost in the queue before they are consumed
- Open the consumer confirmation mechanism to auto, from spring After confirming that the message processing is successful ack
- Enable the consumer failure retry mechanism , And set up MessageRecoverer, Post the message to the exception switch after multiple failed retries , Leave it to manual treatment
Two . Dead letter switch
1. Dead letter
When a message in a queue satisfies one of the following conditions , Can be a dead letter (dead letter):
- Consumer use basic.reject or basic.nack Failed to declare consumption , And the news requeue Parameter set to false
- The message is an expired message , Overtime, no consumption
- The queue of messages to be delivered is full , Undeliverable
If the queue containing dead letters is configured dead-letter-exchange attribute , A switch is specified , Then the dead letter in the queue will be delivered to the switch , And this switch is called Dead letter switch (Dead Letter Exchange, Check DLX)
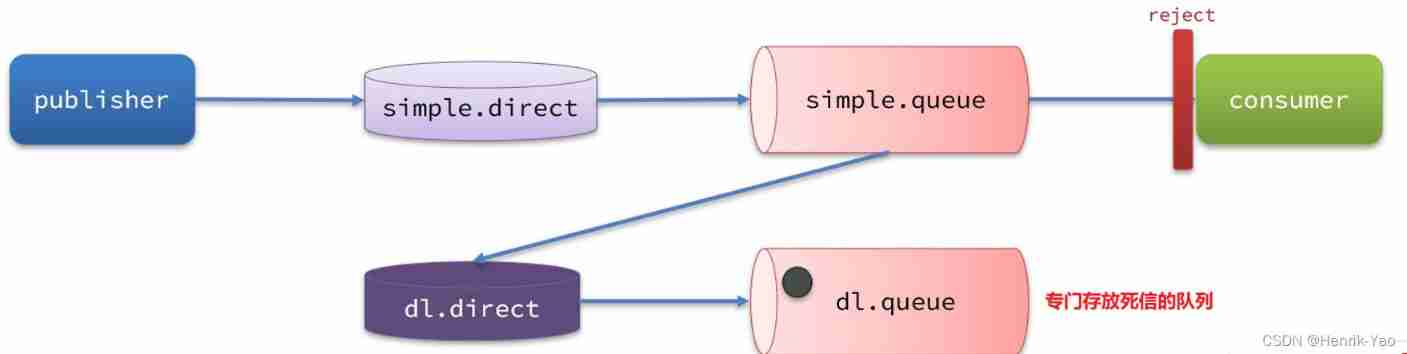
2.TTL
TTL, That is to say Time-To-Live. If a message in a queue TTL End yet to consume , Will become dead letter ,ttl Timeout can be divided into two cases :
- The queue where the message is located sets the lifetime
- The message itself sets the lifetime
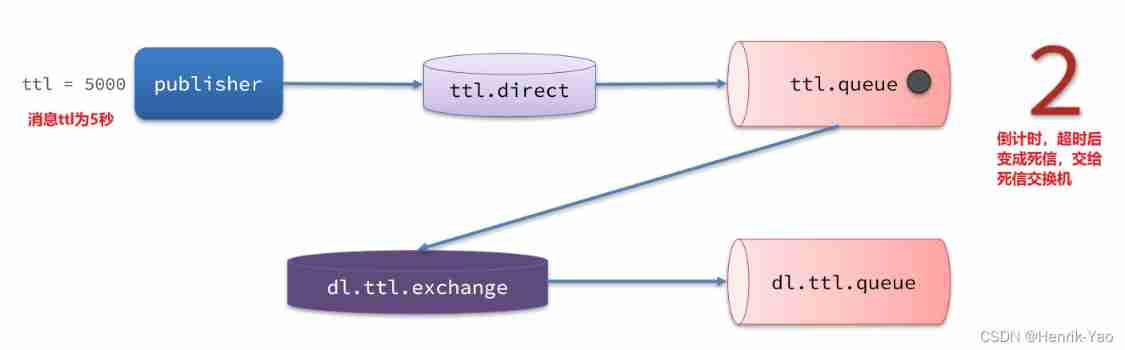
Dead letter switch for receiving dead letter with timeout
stay consumer Service SpringRabbitListener in , Define a new consumer , And declare Dead letter switch 、 Dead letter queue :
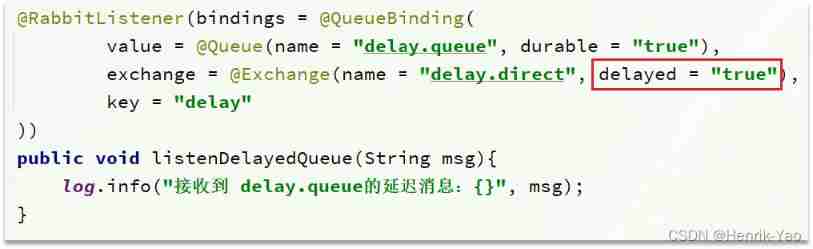
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "dl.ttl.queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "dl.ttl.direct"),
key = "ttl"
))
public void listenDlQueue(String msg){
log.info(" Received dl.ttl.queue Delay message for :{}", msg);
}
Declare a queue , And specify TTL
To set the timeout for the queue , You need to configure... When declaring the queue x-message-ttl attribute :
@Bean
public Queue ttlQueue(){
return QueueBuilder.durable("ttl.queue") // Specify the queue name , And persist
.ttl(10000) // Set the timeout of the queue ,10 second
.deadLetterExchange("dl.ttl.direct") // Specify the dead letter switch
.build();
}
Be careful , This queue sets the dead letter switch to dl.ttl.direct
Declaration switch , take ttl Bound to the switch :
@Bean
public DirectExchange ttlExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("ttl.direct");
}
@Bean
public Binding ttlBinding(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(ttlQueue()).to(ttlExchange()).with("ttl");
}
Send a message , But don't specify TTL:
@Test
public void testTTLQueue() {
// Create a message
String message = "hello, ttl queue";
// news ID, It needs to be encapsulated into CorrelationData in
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
// Send a message
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("ttl.direct", "ttl", message, correlationData);
// Log
log.debug(" Message sent successfully ");
}
Send message log :
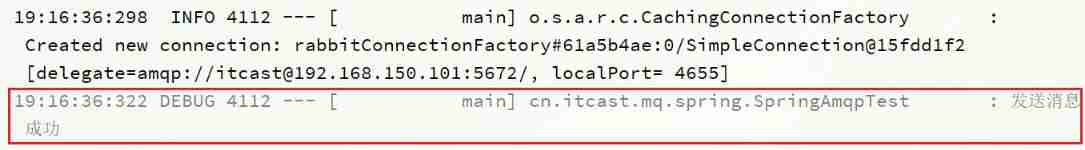
View the log of received messages :
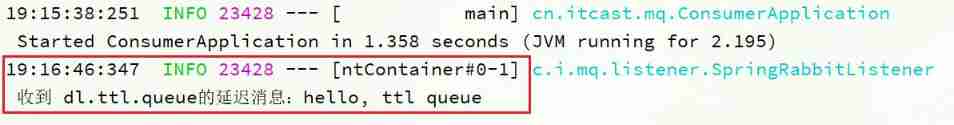
Because of the queue TTL The value is 10000ms, That is to say 10 second . You can see that the time difference between sending and receiving messages is just 10 second .
When sending a message , Set up TTL
When sending a message , You can also specify TTL:
@Test
public void testTTLMsg() {
// Create a message
Message message = MessageBuilder
.withBody("hello, ttl message".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
.setExpiration("5000")
.build();
// news ID, It needs to be encapsulated into CorrelationData in
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
// Send a message
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("ttl.direct", "ttl", message, correlationData);
log.debug(" Message sent successfully ");
}
View send message log :
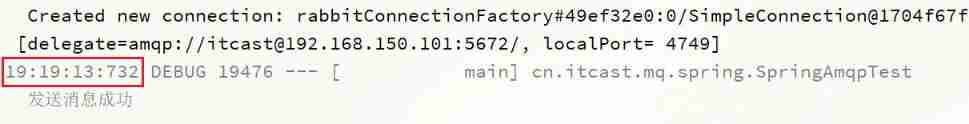
Receive message log :

)]
This time, , The delay between sending and receiving is only 5 second . Description when the queue 、 Messages are set TTL when , Any one of them will become a dead letter
There are two ways to time out messages
- Set up... For the queue ttl attribute , More than... After entering the queue ttl The news of time becomes a dead letter
- Set... For messages ttl attribute , The queue received more than ttl After time, it becomes a dead letter
3. Delay queue
utilize TTL Combined with dead letter switch , After the message is sent , The effect of consumers' delay in receiving messages . This message pattern is called delay queue (Delay Queue) Pattern
The usage scenarios of delay queue include :
- Delay sending SMS
- Users to place the order , If the user is 15 Not paid within minutes , Automatically cancel
- Make an appointment for a working meeting ,20 Automatically notify all participants in minutes
Because there is a lot of demand for delay queues , therefore RabbitMQ The official also launched a plug-in , Native supports delayed queue effects
Install the delay queue plug-in
The official installation guide address is :https://blog.rabbitmq.com/posts/2015/04/scheduling-messages-with-rabbitmq
The above documents are based on linux Native installation RabbitMQ, Then install the plug-in
The following is based on Docker To install RabbitMQ plug-in unit
Execute the following command to run MQ Containers , Note that the plugins Mount out :
docker run \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=henrik \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
-v mq-plugins:/plugins \
--name mq \
--hostname mq1 \
-p 15672:15672 \
-p 5672:5672 \
-d \
rabbitmq:3.8-management
RabbitMQ There is an official plug-in community , The address is :https://www.rabbitmq.com/community-plugins.html
It contains a variety of plug-ins , Include DelayExchange plug-in unit
Download the corresponding version and put it in the plug-in directory
To install the plug-in, you need to enter MQ Inside the container to perform the installation . My container name is mq, So execute the following command :
docker exec -it mq bash
Execution time , Please send one of the -it hinder mq Replace with your own container name .
After entering the container , Execute the following command to open the plug-in :
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange
SpringAMQP Use the delay queue plug-in
elayExchange The essence of is still the three official switches , Just add the delay function . Therefore, only one switch needs to be declared when using , The type of switch can be any type , Then we set delayed The attribute is true that will do
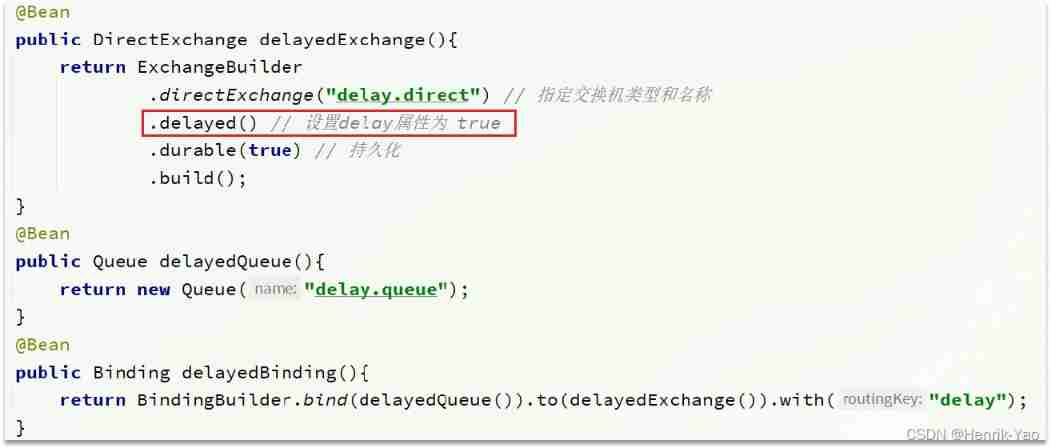
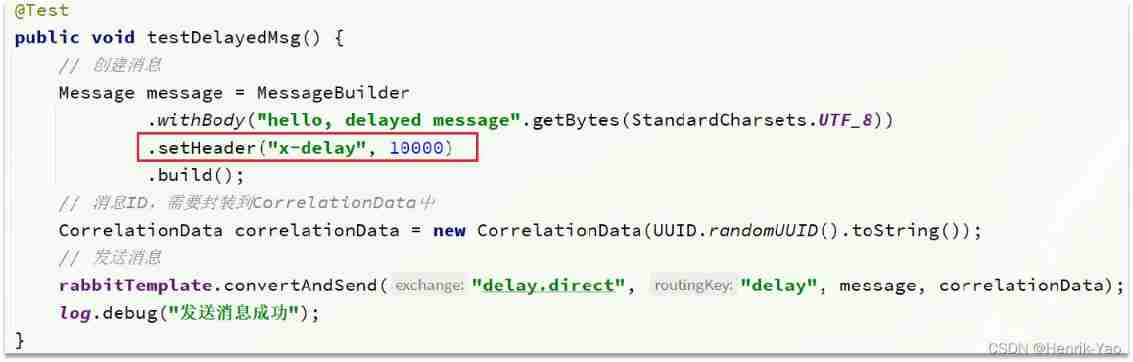
And then to this delay by true Send messages in the switch , Be sure to add one to the message header:x-delay, The value is the delay time , The unit is millisecond
3、 ... and . Lazy queue
1. Message stacking problem
When the producer sends the message faster than the consumer processes the message , It will cause messages in the queue to accumulate , Until the queue has reached the maximum number of stored messages . Then the message sent will become a dead letter , May be discarded , This is the problem of message accumulation
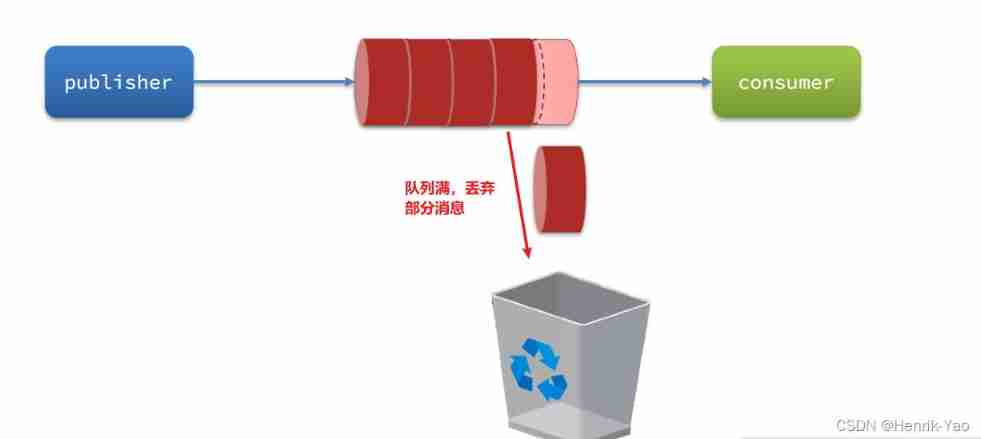
There are three ways to solve the problem of message accumulation :
- Add more consumers , Speed up consumption
- Open thread pool in consumers to speed up message processing
- Expand queue volume , Increase the upper limit of accumulation
2. Lazy queue
from RabbitMQ Of 3.6.0 Version start , It adds Lazy Queues The concept of , That is, an inert queue
The characteristics of inert queues are as follows :
- After receiving the message, it is directly stored in disk instead of memory
- Only when consumers want to consume messages will they read them from disk and load them into memory
- Support the storage of millions of messages
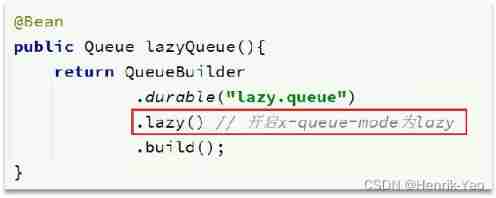
To set a queue as an inert queue , Just when declaring the queue , Appoint x-queue-mode The attribute is lazy that will do . A running queue can be changed to an inert queue through the command line :
rabbitmqctl set_policy Lazy "^lazy-queue$" '{"queue-mode":"lazy"}' --apply-to queues
Command interpretation :
rabbitmqctl:RabbitMQ Command line tools forset_policy: Add a policyLazy: Policy name , You can customize"^lazy-queue$": Match the name of the queue with a regular expression'{"queue-mode":"lazy"}': Set the queue mode to lazy Pattern--apply-to queues: The target of the policy , It's all queues
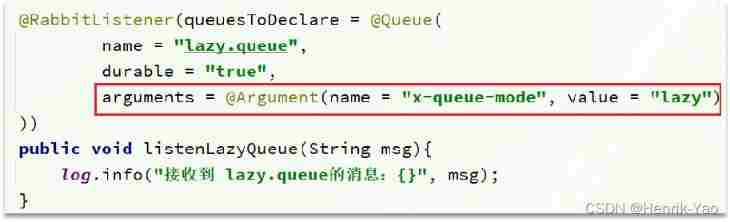
use SpringAMQP There are two ways to declare an inert queue :
@Bean The way :
Annotation mode :
Solution to message stacking problem
- Bind multiple consumers on the queue , Speed up consumption
- Using inert queues , You can do it again mq Save more messages in
Advantages of lazy queues
- Disk based storage , The message limit is high
- No intermittent page-out, Stable performance
Disadvantages of lazy queues
- Disk based storage , Message timeliness will be reduced
- Performance is limited by the size of the disk IO
Four .MQ colony
1. Cluster classification
RabbitMQ It's based on Erlang Language writing , and Erlang It's another concurrency oriented language , Natural support cluster mode .RabbitMQ There are two modes of clustering :
• Average cluster : It is a distributed cluster , Distribute the queue to each node of the cluster , So as to improve the concurrency of the whole cluster
• Mirrored clusters : It is a master-slave cluster , Based on ordinary clusters , Added master-slave backup function , Improve the data availability of the cluster
Although the mirror cluster supports master-slave , But master-slave synchronization is not strongly consistent , In some cases, there may be a risk of data loss . So in RabbitMQ Of 3.8 After the version , Introduced new features : Arbitration queue Instead of a mirrored cluster , The underlying the Raft The protocol ensures the consistency of master-slave data
2. Average cluster
Cluster structure and characteristics
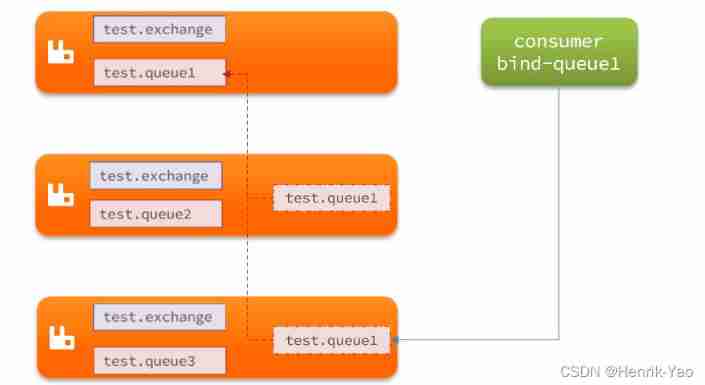
Average cluster , Or standard cluster (classic cluster), It has the following characteristics :
- Some data will be shared among the nodes of the cluster , Include : Switch 、 Queue meta information . Do not include messages in the queue .
- When accessing a node in the cluster , If the queue is not on this node , It will be transferred from the node where the data is located to the current node and return
- The node where the queue is located is down , Messages in the queue will be lost
Structure is shown in figure :
Deploy
stay RabbitMQ In the official documents of , Two cluster configuration modes are described :
- Common mode : Normal mode clusters do not perform data synchronization , Every MQ They all have their own queues 、 Data and information ( Other metadata information such as switches will be synchronized ). For example, we have 2 individual MQ:mq1, and mq2, If your message is in mq1, And you're connected to mq2, that mq2 Will go to mq1 Pull the news , Then return to you . If mq1 Downtime , The news will be lost .
- Mirror mode : Different from the normal mode , The queue will be in each mq Synchronization between mirror nodes , So you connect to any mirror node , You can get messages . And if a node goes down , It doesn't cause data loss . however , This method increases the bandwidth consumption of data synchronization .
Deploy 3 Common mode cluster of nodes
| Host name | Console port | amqp Communication port |
|---|---|---|
| mq1 | 8081 —> 15672 | 8071 —> 5672 |
| mq2 | 8082 —> 15672 | 8072 —> 5672 |
| mq3 | 8083 —> 15672 | 8073 —> 5672 |
The node labels in the cluster are... By default :[email protected][hostname], Therefore, the names of the above three nodes are :
obtain cookie
RabbitMQ The bottom layer depends on Erlang, and Erlang Virtual machine is a distributed oriented language , Cluster mode is supported by default . Each in the cluster mode RabbitMQ Node usage cookie To determine whether they are allowed to communicate with each other .
To enable two nodes to communicate , They must have the same shared secret , be called Erlang cookie.cookie Just a string of the most 255 Alphanumeric characters of characters .
Each cluster node must have same cookie. Instances also need it to communicate with each other .
Started before mq Get one in the container cookie value , As a cluster cookie. Execute the following command :
docker exec -it mq cat /var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie
You can see cookie Values are as follows :
FXZMCVGLBIXZCDEMMVZQ
Next , Stop and delete the current mq Containers , Let's rebuild the cluster .
docker rm -f mq
powershell
stay /tmp Create a new configuration file rabbitmq.conf:
cd /tmp
# create a file
touch rabbitmq.conf
The contents of the document are as follows :
loopback_users.guest = false
listeners.tcp.default = 5672
cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_classic_config
cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.1 = [email protected]
cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.2 = [email protected]
cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.3 = [email protected]
Create another file , Record cookie
cd /tmp
# establish cookie file
touch .erlang.cookie
# write in cookie
echo "FXZMCVGLBIXZCDEMMVZQ" > .erlang.cookie
# modify cookie File permissions
chmod 600 .erlang.cookie
Prepare three directories ,mq1、mq2、mq3:
cd /tmp
# Create directory
mkdir mq1 mq2 mq3
Then copy rabbitmq.conf、cookie File to mq1、mq2、mq3:
# Get into /tmp
cd /tmp
# Copy
cp rabbitmq.conf mq1
cp rabbitmq.conf mq2
cp rabbitmq.conf mq3
cp .erlang.cookie mq1
cp .erlang.cookie mq2
cp .erlang.cookie mq3
Start cluster
Create a network :
docker network create mq-net
docker volume create
Run the command
docker run -d --net mq-net \
-v ${
PWD}/mq1/rabbitmq.conf:/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf \
-v ${
PWD}/.erlang.cookie:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=henrik \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
--name mq1 \
--hostname mq1 \
-p 8071:5672 \
-p 8081:15672 \
rabbitmq:3.8-management
docker run -d --net mq-net \
-v ${
PWD}/mq2/rabbitmq.conf:/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf \
-v ${
PWD}/.erlang.cookie:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=henrik \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
--name mq2 \
--hostname mq2 \
-p 8072:5672 \
-p 8082:15672 \
rabbitmq:3.8-management
docker run -d --net mq-net \
-v ${
PWD}/mq3/rabbitmq.conf:/etc/rabbitmq/rabbitmq.conf \
-v ${
PWD}/.erlang.cookie:/var/lib/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=henrik \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
--name mq3 \
--hostname mq3 \
-p 8073:5672 \
-p 8083:15672 \
rabbitmq:3.8-management
3. Mirrored clusters
Mirrored clusters : The essence is the master-slave mode , Have the following characteristics :
- Switch 、 queue 、 The messages in the queue will be displayed in each mq Synchronous backup between mirror nodes .
- The node that creates the queue is called the node of the queue Master node , The other nodes backed up to are called the nodes of the queue Mirror image node .
- The primary node of one queue may be the mirror node of another queue
- All operations are completed by the master node , Then synchronize to the mirror node
- After the main outage , The mirror node is replaced with the new master node
Structure is shown in figure :
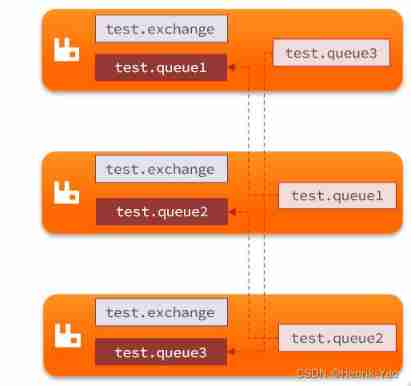
Characteristics of mirror mode
By default , The queue is only saved on the node that created it . In mirror mode , The node that creates the queue is called the node of the queue Master node , The queue is also copied to other nodes in the cluster , Also called the queue Mirror image node
however , Different queues can be created on any node in the cluster , Therefore, the master nodes of different queues can be different . even to the extent that , The primary node of one queue may be the mirror node of another queue
All requests sent by the user to the queue , For example, sending messages 、 The message receipt will be completed in the master node by default , If the request is received from the node , It will also be routed to the master node to complete . The mirror node only plays the role of backing up data
When the master node receives a message from the consumer ACK when , All mirrors delete the data in the node .
Summarized below :
- The mirror queue structure is one master and many slaves ( From is a mirror image )
- All operations are completed by the master node , Then synchronize to the mirror node
- After the main outage , The mirror node is replaced with the new master node ( If before the master-slave synchronization is completed , The Lord has been down , There may be data loss )
- No load balancing function , Because all operations will be completed by the master node ( But different queues , Its master node can be different , This can be used to improve throughput )
Mirror mode configuration
The configuration of mirror mode includes 3 Patterns :
| ha-mode | ha-params | effect |
|---|---|---|
| Accurate mode exactly | Number of copies in the queue count | Queue replica in cluster ( The sum of the primary server and the mirror server ) The number of .count If 1 Means a single copy : Queue master node .count The value is 2 Express 2 Copies :1 Queue master and 1 A mirror queue . let me put it another way :count = Number of images + 1. If the number of nodes in the cluster is less than count, The queue will be mirrored to all nodes . If the total number of clusters is greater than count+1, And the node containing the mirror fails , A new mirror will be created on another node . |
| all | (none) | The queue is mirrored between all nodes in the cluster . The queue will be mirrored to any newly added nodes . Mirroring to all nodes puts additional pressure on all cluster nodes , Including the network I / O, disk I / O And disk space usage . Recommended exactly, Set the number of copies to (N / 2 +1). |
| nodes | node names | Specify which nodes the queue is created to , If all the specified nodes do not exist , Then there will be an exception . If the specified node exists in the cluster , But temporarily unavailable , The node will be created to the node to which the current client is connected . |
With rabbitmqctl Command as a case
Syntax example :
exactly Pattern
rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-two "^two\." '{"ha-mode":"exactly","ha-params":2,"ha-sync-mode":"automatic"}'
rabbitmqctl set_policy: Fixed writingha-two: Policy name , Customize"^two\.": Regular expressions that match queues , Queues that conform to the naming rules take effect , Here is anything withtwo.Queue name at the beginning'{"ha-mode":"exactly","ha-params":2,"ha-sync-mode":"automatic"}': Strategy content"ha-mode":"exactly": The strategy pattern , Here is exactly Pattern , Specify the number of copies"ha-params":2: Policy parameters , Here is 2, The number of copies is 2,1 Lord 1 Mirror image"ha-sync-mode":"automatic": Synchronization strategies , The default is manual, That is, the newly added mirror node will not synchronize the old messages . If set to automatic, Then the newly added mirror node will synchronize all messages in the master node , It will bring additional network overhead
all Pattern
rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-all "^all\." '{"ha-mode":"all"}'
ha-all: Policy name , Customize"^all\.": Match all toall.The first queue name'{"ha-mode":"all"}': Strategy content"ha-mode":"all": The strategy pattern , Here is all Pattern , That is, all nodes will be called mirror nodes
nodes Pattern
rabbitmqctl set_policy ha-nodes "^nodes\." '{"ha-mode":"nodes","ha-params":["[email protected]", "[email protected]"]}'
rabbitmqctl set_policy: Fixed writingha-nodes: Policy name , Customize"^nodes\.": Regular expressions that match queues , Queues that conform to the naming rules take effect , Here is anything withnodes.Queue name at the beginning'{"ha-mode":"nodes","ha-params":["[email protected]", "[email protected]"]}': Strategy content"ha-mode":"nodes": The strategy pattern , Here is nodes Pattern"ha-params":["[email protected]", "[email protected]"]: Policy parameters , Specify the name of the node where the replica is located
4. Arbitration queue
Arbitration queue : The arbitration queue is 3.8 New features only after version , Used to replace the mirror queue , It has the following characteristics :
- Just like the mirror queue , It's all master-slave mode , Support master-slave data synchronization
- Very simple to use , No complex configuration
- Master slave synchronization is based on Raft agreement , Strong consistency
SpringAMQP Create an arbitration queue
@Bean
public Queue quorumQueue() {
return QueueBuilder
.durable("quorum.queue") // Persistence
.quorum() // Arbitration queue
.build();
}
Be careful ,yal use address Instead of host、port The way
spring:
rabbitmq:
addresses: 192.168.150.105:8071, 192.168.150.105:8072, 192.168.150.105:8073
username: itcast
password: 123321
virtual-host: /
边栏推荐
- 37页数字乡村振兴智慧农业整体规划建设方案
- Common shortcuts to idea
- Things like random
- stm32F407-------DAC数模转换
- Core knowledge of distributed cache
- Are you ready to automate continuous deployment in ci/cd?
- Amazon MemoryDB for Redis 和 Amazon ElastiCache for Redis 的内存优化
- On February 19, 2021ccf award ceremony will be held, "why in Hengdian?"
- Introduction au GPIO
- 2022/2/10 summary
猜你喜欢
Interface master v3.9, API low code development tool, build your interface service platform immediately

Devops can help reduce technology debt in ten ways

Three application characteristics of immersive projection in offline display

The programmer resigned and was sentenced to 10 months for deleting the code. Jingdong came home and said that it took 30000 to restore the database. Netizen: This is really a revenge
509 certificat basé sur Go
Everyone is always talking about EQ, so what is EQ?
iMeta | 华南农大陈程杰/夏瑞等发布TBtools构造Circos图的简单方法

Understand the misunderstanding of programmers: Chinese programmers in the eyes of Western programmers

What can the interactive slide screen demonstration bring to the enterprise exhibition hall
How to set encoding in idea
随机推荐
Leecode brush questions record interview questions 32 - I. print binary tree from top to bottom
uniapp中redirectTo和navigateTo的区别
Devops can help reduce technology debt in ten ways
Data operation platform - data collection [easy to understand]
stm32F407-------SPI通信
Data analysis course notes (V) common statistical methods, data and spelling, index and composite index
alexnet实验偶遇:loss nan, train acc 0.100, test acc 0.100情况
Advanced learning of MySQL -- Fundamentals -- concurrency of transactions
[2022 the finest in the whole network] how to test the interface test generally? Process and steps of interface test
Leecode brushes questions and records interview questions 01.02 Determine whether it is character rearrangement for each other
【vulnhub】presidential1
如何判断一个数组中的元素包含一个对象的所有属性值
2022/2/10 summary
Typescript incremental compilation
@TableId can‘t more than one in Class: “com.example.CloseContactSearcher.entity.Activity“.
【CVPR 2022】半监督目标检测:Dense Learning based Semi-Supervised Object Detection
rancher集成ldap,实现统一账号登录
【vulnhub】presidential1
Jenkins' user credentials plug-in installation
2022 PMP project management examination agile knowledge points (9)