当前位置:网站首页>Experiment 6 inheritance and polymorphism
Experiment 6 inheritance and polymorphism
2022-07-06 13:55:00 【Wen Wen likes Guo Zia】
Experiment six Inheritance and polymorphism
The experiment purpose
1. Master the use method of interface
2. Master the inheritance of subclasses 、 Subclass object creation process
3. Master the inheritance and hiding of member variables 、 Method inheritance and rewriting
Experimental hours 6 Class hours
Experimental content
1. Write a program for the elderly card of the bus 、 Student card and ordinary citizen card provide charging function . Recharge 、 Charging function extraction , Defined in an interface , Then it is implemented by these three card classes . Finally, write a test class , It is used to test the card swiping operation of bus class III cards .
package code61;
public interface Buscard { // Defining interfaces Bus card
void recharge();
void charge();
}
package code61;
public class Oldpeople implements Buscard { // Implementation interface
public void recharge() {
System.out.println(" The elderly card is recharged successfully !"); // Rewrite the recharge method of the interface
}
public void charge() {
System.out.println(" Use a senior citizen card , Deduct one yuan !"); // Rewrite the charging method of the interface
}
}
package code61;
public class People implements Buscard { // Implementation interface
public void recharge() {
System.out.println(" The ordinary citizen card has been recharged successfully !"); // Rewrite the interface recharge method
}
public void charge() {
System.out.println(" Use an ordinary citizen card , buckle 2 element !"); // Rewrite the interface charging method
}
}
package code61;
public class Student implements Buscard { // Implementation interface
public void recharge() {
System.out.println(" Student card recharge succeeded !"); // Rewrite the interface recharge method
}
public void charge() {
System.out.println(" Use student cards , buckle 1.5 element !"); // Rewrite the interface charging method
}
}
package code61;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Oldpeople O = new Oldpeople();
O.recharge();
O.charge(); // Define the elderly card object , And call recharge 、 Charging method
Student S = new Student();
S.recharge();
S.charge(); // Define student card object , And call recharge 、 Charging method
People P = new People();
P.recharge();
P.charge(); // Define the citizen card object , And call recharge 、 Charging method
}
}
2. Design four classes 、 An interface , The relationship between classes is as follows :

In the class App Use in Compute、Circle、Rectangle class , stay Compute Class Shape Interface (Shape Object as computeArea The formal parameters of the method ),Circle、Rectangle Class implementation interface Shape, rewrite area() Method . In the figure “+” It means public,“-” It means private, The upper column in the block diagram is the name of the class or interface , The middle column is the attribute , The next column is the method .
stay App Class main() in :
- Create a Compute Class object 、 One Circle Class object and a Rectangle Class object .
- call Compute Object's computeArea Method ( The actual parameters are Circle object ) Calculate the area of a circle .
- call Compute Object's computeArea Method ( The actual parameters are Rectangle object ) Calculate rectangular area .
package code62;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Compute a = new Compute();
Circle b = new Circle(2);
Rectangle c = new Rectangle(2,2);
System.out.println(" The area of the circle is :"+a.computArea(b)); // call Compute Object's computeArea Method , The argument is Circle object
System.out.println(" The area of the rectangle is :"+a.computArea(c)); // call Compute Object's computeArea Method , The argument is Rectangle object
}
}
package code62;
public class Circle implements Shape { // Implementation interface
private int radius;
public Circle(int radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double area() {
return PI*radius*radius; // Rewrite the interface area Method , Find the area of a circle
}
}
package code62;
public class Compute {
public double computArea(Shape s) { //Shape Object as the formal parameter of the method
return s.area();
}
}
package code62;
public class Rectangle implements Shape { // Implementation interface
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(int width,int height) {
this.width=width;
this.height=height;
}
public double area() {
return width*height; // Rewrite the interface area Method , Find the rectangular area
}
}
package code62;
public interface Shape { // Defining interfaces
double PI=3.14;
double area();
}
3. Ordinary door and alarm door .
(1) Define an interface Alarm( Call the police ), Contains an alarm method void alarm( );
(2) Define a class Door( Ordinary door ),Door Class has a private property name( brand ); Yes 4 Public methods getName、setName、open( Open door )、close( close );open、close The function of the method is determined by yourself .
(3) Define a class AlarmDoor( Alarm door ), Inherit Door class , Implementation interface Alarm, Override abstract methods in interfaces alarm( The function of the method is determined by yourself ).
(3) Write a test class DoorTest, stay main In the method , Give various types of alarm doors and ordinary doors , Call to open the door 、 close 、 Alarm and other actions .
package code63;
public interface Alarm { // Defining interfaces
void alarm();
}
package code63;
public class AlarmDoor extends Door implements Alarm { // Inherit Door class , Implementation interface Alarm
public void alarm() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+" Toot toot ! The alarm goes off !"); // Override abstract methods in interfaces
}
}
package code63;
public class Door {
private String name; // Private property name
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void open() {
System.out.println(this.name+" The door is open !");
}
public void close() {
System.out.println(this.name+" The door is closed !");
}
}
package code63;
public class DoorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
AlarmDoor a1 = new AlarmDoor();
a1.setName(" Low level alarm door !");
a1.open();
a1.alarm(); // Create objects a1, And call each method
AlarmDoor a2 = new AlarmDoor();
a2.setName(" Advanced alarm door !!!");
a2.open();
a2.close();
a2.alarm(); // Create objects a2, And call each method
AlarmDoor a3 = new AlarmDoor();
a3.setName(" Ordinary door .");
a3.open();
a3.close(); // Create objects a3, And call each method
}
}
4. Design five classes ( Test class 、 Computer class 、 Mobile phones 、 Chargers 、U Disk class )、 An interface (Usb Interface ), The relationships between various types are as follows :
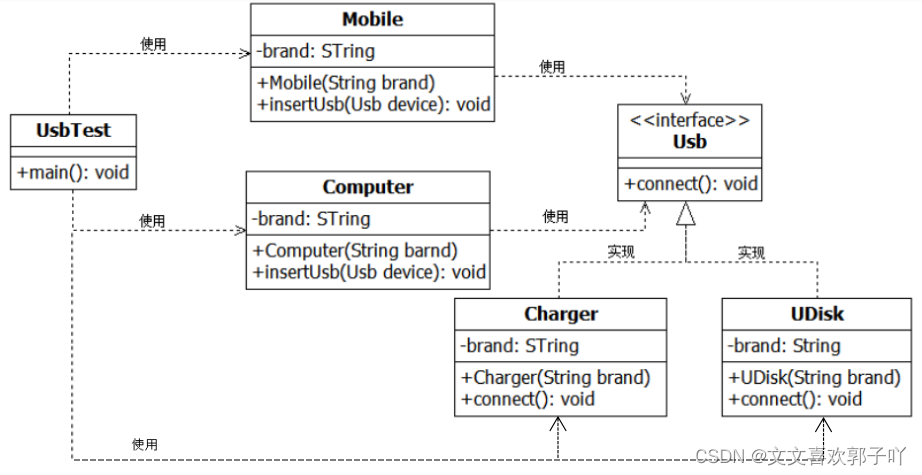
(1) stay UsbTest Class main In the method , Create a Xiaomi Mobile object 、 A millet CDQ012M Charger object 、 A Lenovo computer 、 One Kingston U Disk object . Then plug the charger into the mobile phone to charge , take U Insert the disk into the computer .
(2) stay Mobile Class InsertUsb In the method , Connect Usb.
(3) stay Computer Class InsertUsb In the method , Connect Usb.
(4) stay Charger Class connect In the method , Output “ Charger connected , Charging ...”.
(5) stay UDisk Class connect In the method , Output “ Connected U Disc apparatus , Reading data ...”.
package code64;
public class Charger implements Usb {
private String brand;
public Charger(String brand) {
this.brand=brand;
}
public void connect() {
System.out.println(" Charger connected "+this.brand+", Charging ..."); // Rewrite the interface connect Method
}
}
package code64;
public class Computer {
private String brand;
public Computer(String brand) {
this.brand=brand;
}
public void insertUsb(Usb device) {
System.out.println(this.brand);
device.connect(); // Construction connection method
}
}
package code64;
public class Moblie {
private String brand;
public void Moblie(String brand) {
this.brand=brand;
}
public void insertUsb(Usb device) {
System.out.println(this.brand);
device.connect(); // Construction connection method
}
}
package code64;
public class UDisk implements Usb {
private String brand;
public UDisk(String brand) {
this.brand=brand;
}
public void connect() {
System.out.println(" Connected U Disc apparatus "+this.brand+", Reading data ..."); // Rewrite the interface connect Method
}
}
package code64;
public interface Usb { // Defining interfaces
void connect();
}
package code64;
public class UsbTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Moblie a = new Moblie();
a.Moblie("Xiaomi"); // Create a phone object
Charger b = new Charger(" millet CDQ012M"); // Create charger object
Computer c = new Computer(" lenovo "); // Create computer objects
UDisk d = new UDisk("Kingston"); // establish U Disk object
a.insertUsb(b); // Plug the charger into the phone
c.insertUsb(d); //U Insert the disk into the computer
}
}
5. Design a weapon system , Requirements are as follows :
(1) Define an ammunition class Bullet, There is a ammo name attribute name. Design a construction method and set、get Method .
(2) Define an interface for loading ammunition Loadable, This interface has a loaded abstract method load().
(3) Define an interface that can launch ammunition Launchable, The interface has an abstract method of emission launch().
(4) Define a weapon class Weapon, It can be loaded , It can also be launched .
Weapons have an attribute name( Name of weapons )、 Usable ammunition bullet(Bullet object ) And corresponding get、set Method .
rewrite load Method , Output loaded ammunition in method .
rewrite launch Method , Output the fired ammunition in the method .
(4) Definition 3 Common weapons :Tank、Flighter、WarShip All inherit weapons Weapon. Every ordinary weapon class has a parameter name Construction method of , Create an ammunition object in the construction method .
tanks Tank The ammunition used is artillery , fighter Flighter The ammunition used is missiles , ships WarShip The ammunition used is torpedo .
(5) Define a class Army, Represents an army , Include :.
1) attribute :ArrayList<Weapon> weapon Various weapons used to store military equipment , Find the collection class by yourself ArrayList Usage and generic knowledge points ;
2) How to obtain the number of weapons owned by the army getNum;
3) How to add weapons addWeapon
4) The way to load all weapons with ammunition loadAll;
5) The way to make all weapons attack luanchAll.
(6) Write a test class , stay main In the method :
1) Build a strong army ;
2) Add various types of weapons , Including tanks 、 aircraft 、 ships .
3) Export the number of weapons owned by the army ;
4) Let all weapons be loaded with ammunition ;
5) Let all weapons be fired .

package code65;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Army {
ArrayList<Weapon> weapon;
public Army() {
weapon = new ArrayList<Weapon>(); // Store all kinds of weapons for military equipment
}
public int getNum() {
return weapon.size(); // Get the number of weapons the army has
}
public void addWeapon(Weapon weapon) {
this.weapon.add(weapon); // Add weapons
}
public void loadAll() {
System.out.println(" All weapons are ready to be loaded ...");
int a=1;
for(Weapon weapon:weapon) {
System.out.print(a+":"+weapon.getName());
weapon.load();
a++; // Let all weapons be loaded with ammunition
}
}
public void luanchAll() {
System.out.println(" All weapons are ready to fight ...");
int a=1;
for(Weapon weapon:weapon) {
System.out.print(a+":"+weapon.getName());
weapon.launch();
a++; // Let all weapons fire ammunition
}
}
}
package code65;
public class Bullet {
private String name;
public Bullet(String name) { // Construction method
this.name=name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
package code65;
public class Flighter extends Weapon { // Inherited weapon class
public Flighter(String name) {
setName(name);
Bullet bullet = new Bullet(" missile "); // Create missile object
setBullet(bullet);
}
}
package code65;
public interface Launchable { // Define an interface that can launch ammunition
void launch();
}
package code65;
public interface Loadable { // Define an interface for loading ammunition
void load();
}
package code65;
public class Tank extends Weapon { // Inherited weapon class
public Tank(String name) {
setName(name);
Bullet bullet = new Bullet(" The shells "); // Create shell object
setBullet(bullet);
}
}
package code65;
public class WarShip extends Weapon { // Inherited weapon class
public WarShip(String name) {
setName(name);
Bullet bullet = new Bullet(" torpedo "); // Create a torpedo object
setBullet(bullet);
}
}
package code65;
public class Weapon implements Loadable,Launchable { // Implement two interfaces
private String name;
private Bullet bullet;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public Bullet getBullet() {
return bullet;
}
public void setBullet(Bullet bullet) {
this.bullet=bullet;
}
public void load() {
System.out.println(" load "+this.bullet.getName()); // Rewrite the loading method of the interface
}
public void launch() {
System.out.println(" launch "+this.bullet.getName()); // Rewrite the emission method of the interface
}
}
package code65;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Tank a1 = new Tank("99 tanks ");
Flighter a2 = new Flighter(" fighters 20 ");
WarShip a3 = new WarShip(" Wuhan ship ");
WarShip a4 = new WarShip(" Wuhu ship ");
Flighter a5 = new Flighter(" fighters 31 ");
Flighter a6 = new Flighter("F35 "); // Build an army
Army a = new Army();
a.addWeapon(a1);
a.addWeapon(a2);
a.addWeapon(a3);
a.addWeapon(a4);
a.addWeapon(a5);
a.addWeapon(a6); // Add all kinds of weapons
System.out.println(" The number of weapons the army is equipped with :"+a.getNum());
a.loadAll(); // Let all weapons be loaded
a.luanchAll(); // Let all weapons fire
}
}
6. Design five classes , The relationship between classes is as follows

In the class App Use in Paint、Rectangle、Circle、Rabit class , stay paint Class AsciiArt abstract class (AsciiArt Object as setArt Method parameters ),Rectangle、Circle、Rabit Class inherits abstract class AsciiArt, And rewrite draw() Method .
Specific design steps :
- App Class main( )
1) Create a Paint object paint
2) Show the list of works
======== List of works =======
- rectangular
- round
- Little rabbit
======================
Please select :
3) According to the choice , Show different works
① Draw a rectangular
a. Create a Rectangle object rect.
b. call paint Of setArt Method , take rect Set to paint Object to display the work .
c. Call object paint Of draw Methods display works .
② A circle
a. Create a Circle object c.
b. call paint Of setArt Method , take c Set to paint Object to display the work .
c. Call object paint Of draw Methods display works .
③ Draw a little rabbit
a. Create a Rabit object rabit.
b. call paint Of setArt Method , take rabit Set to paint Object to display the work .
c. Call object paint Of draw Methods display works .
- Paint Class draw( )
① Show the name of the work 、 author .
② Calling a member variable art Of draw Methods display works .
- Rectangle Class draw( )
Output width That's ok height Columns “*”.
- Circle Class draw( )
For output “*” Composed of circles .
- Rabit Class draw( )
Output cute rabbit .
package code66;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("======== List of works =======");
System.out.println("1. rectangular ");
System.out.println("2. round ");
System.out.println("3. Little rabbit ");
System.out.println("======================");
System.out.println(" Please select :");
int select=in.nextInt();
Paint paint = new Paint();
switch(select){ // According to the choice , Show different works
case 1:
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(" rectangular "," Zhang San ",3,8);
paint.setArt(rect); // Calling method , take rect Set to paint Object to display the work
paint.draw(); // call draw Method
break;
case 2:
Circle c = new Circle(" circular "," Smiles send us light ",4);
paint.setArt(c); // Calling method , take c Set to paint Object to display the work
paint.draw(); // call draw Method
break;
case 3:
Rabit rabit = new Rabit(" The rabbit "," Li Si ");
paint.setArt(rabit); // Calling method , take rabit Set to paint Object to display the work
paint.draw(); call draw Method
break;
}
}
}
package code66;
public abstract class AssciiArt { // Define an abstract class
private String title; // The name of the work
private String author; // The author's name
public AssciiArt(String title,String author) {
this.title=title;
this.author=author;
}
abstract void draw(); // Abstract drawing method
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title=title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author=author;
}
}
package code66;
public class Circle extends AssciiArt { // Inherit AssciiArt class
private int radius;
public Circle(String title,String author,int radius) {
super(title,author); // Access the overridden members in the parent class
this.radius=radius;
}
public void draw() { // Rewrite the drawing method
int d=2*radius;
for(int y=0;y<=d;y++) {
for(int x=0;x<=d;x++) {
if((x-radius)*(x-radius)+(y-radius)*(y-radius)<=radius*radius)
System.out.print("**");
else
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println(); // For output "*" Composed of circles
}
}
}
package code66;
public class Paint {
private AssciiArt art;
public void setArt(AssciiArt art) { //AsciiArt Object as setArt Method parameters
this.art=art;
}
public void draw() {
System.out.println(" works :"+this.art.getTitle());
System.out.println(" author :"+this.art.getAuthor());
this.art.draw(); // call art Of draw Methods display works
}
}
package code66;
public class Rabit extends AssciiArt { // Inherit AssciiArt class
public Rabit(String title,String author) {
super(title,author); // Access the overridden members in the parent class
}
public void draw() { // Rewrite the drawing method
System.out.println("/)/)");
System.out.println("(- -) )o");
System.out.println(" || ||"); // Draw a little rabbit
}
}
package code66;
public class Rectangle extends AssciiArt { // Inherit AssciiArt class
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(String title,String author,int width,int height) {
super(title,author); // Access the overridden members in the parent class
this.width=width;
this.height=height;
}
public void draw() { // Rewrite the drawing method
for(int a=0;a<width;a++) {
for(int b=0;b<height;b++) {
System.out.print("*"); // Output width That's ok height Columns "*" A rectangle made up of
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Summary of experiments
- Class inheritance is the most effective way to realize code reuse ;
- Java Only single inheritance is supported , That is, there can only be one parent class , But inheritance between classes can be passed ;
- Inheritance format :class Subclass name extends Parent class name ;
- keyword super It can be used to access the overridden members in the parent class in the subclass ;
- keyword abstract The decorated class is an abstract class , It is more a parent of other classes , The abstract methods must be implemented in subclasses ;
- Interface definition format :【 Modifier 】interface The interface name ;
- All methods in an interface are abstract , All abstract methods must be overridden in subclasses that implement this interface ;
- Interface implementation format :class Class name implements The interface name ;
- There can be multiple interfaces implemented , Separated by commas ;
- In addition, we need to master ArrayList How to use .
边栏推荐
- 撲克牌遊戲程序——人機對抗
- 杂谈0516
- Caching mechanism of leveldb
- ABA问题遇到过吗,详细说以下,如何避免ABA问题
- C language Getting Started Guide
- A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews
- Leetcode.3 无重复字符的最长子串——超过100%的解法
- 【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
- Differences among fianl, finally, and finalize
- 强化学习基础记录
猜你喜欢

Mixlab unbounded community white paper officially released
Meituan dynamic thread pool practice ideas, open source
. How to upload XMIND files to Jinshan document sharing online editing?

2. First knowledge of C language (2)

1. Preliminary exercises of C language (1)
一段用蜂鸣器编的音乐(成都)
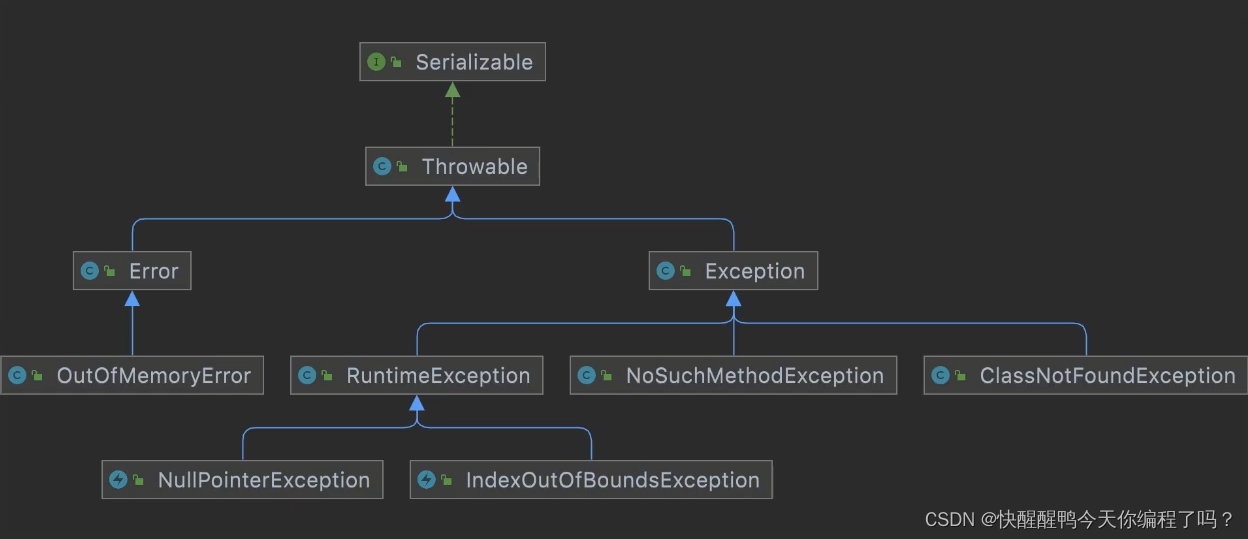
受检异常和非受检异常的区别和理解
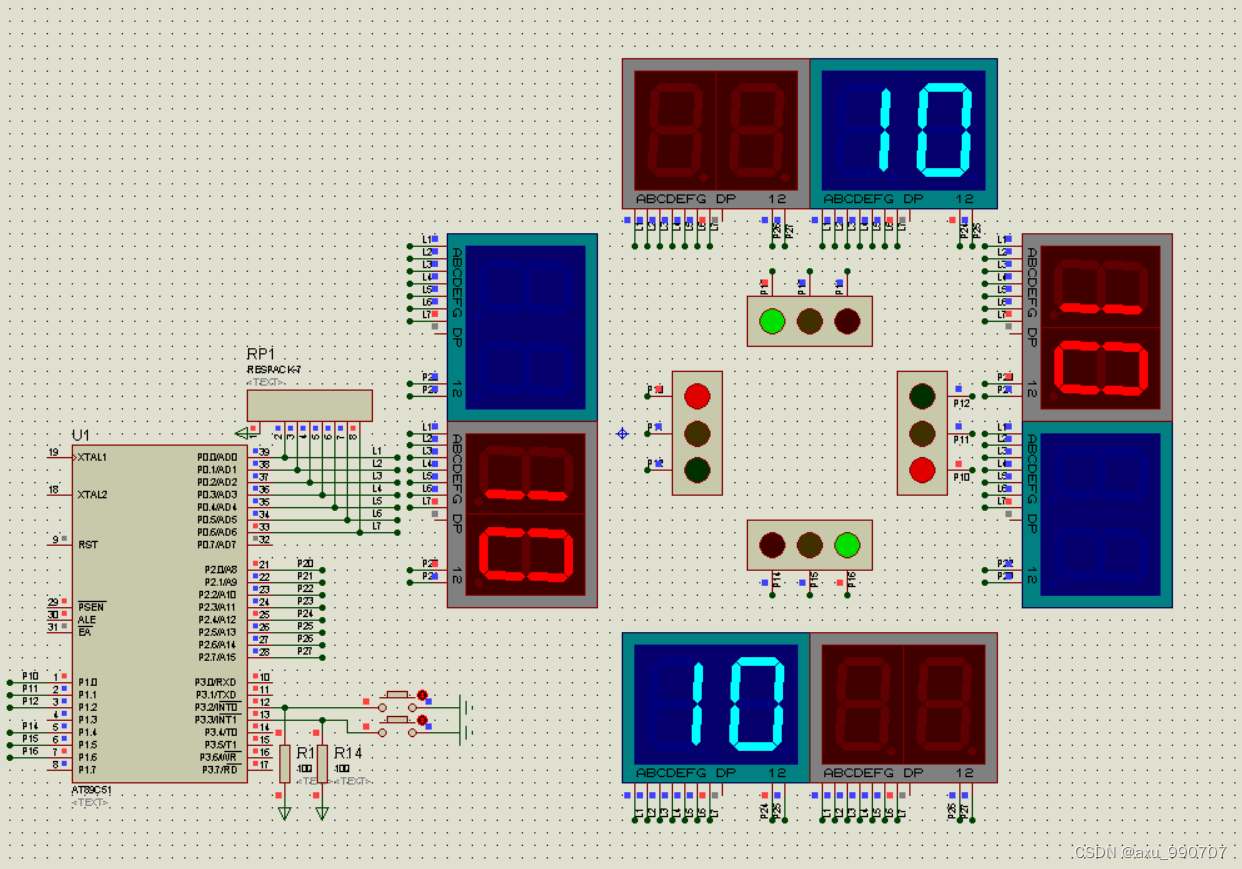
编写程序,模拟现实生活中的交通信号灯。
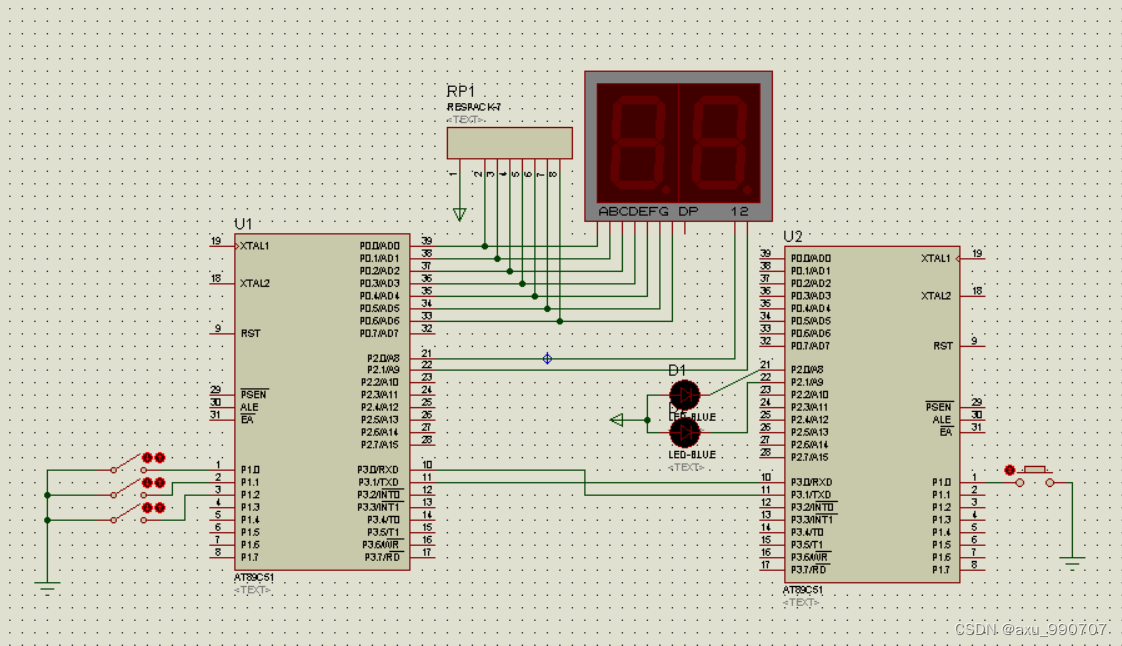
甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1

Strengthen basic learning records
随机推荐
Strengthen basic learning records
【educoder数据库实验 索引】
实验四 数组
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2016 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
Get started with typescript
Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-1
2022 Teddy cup data mining challenge question C idea and post game summary
Zatan 0516
7-4 散列表查找(PTA程序设计)
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2020 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
PriorityQueue (large root heap / small root heap /topk problem)
2. First knowledge of C language (2)
The difference between abstract classes and interfaces
[during the interview] - how can I explain the mechanism of TCP to achieve reliable transmission
C language Getting Started Guide
抽象类和接口的区别
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
ArrayList的自动扩容机制实现原理
【Numpy和Pytorch的数据处理】
强化学习基础记录