当前位置:网站首页>Half of the people don't know the difference between for and foreach???
Half of the people don't know the difference between for and foreach???
2022-07-07 11:30:00 【Java technology stack】
Click on the official account ,Java dried food Timely delivery 
Recommended reading :Spring Cloud Alibaba Finally unify the Jianghu !
A colleague suddenly asked me a question , Said in foreach Can I delete it list The elements inside , I said about whether I could delete , And why ; Next, let's explore whether this can be done ;
(1) Traversing elements
First , Let's take a piece of code as an example :
String[] array = {"1", "2", "3"};
for (String i : array) {
System.out.println(i);
}
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
for (String i : list) {
System.out.println(i);
}After traversal, the results are as follows :
1
2
3
111
222
333String[] array = new String[]{"1", "2", "3"};
String[] var2 = array;
int var3 = array.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
String i = var2[var4];
System.out.println(i);
}
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
Iterator var7 = list.iterator();
while(var7.hasNext()) {
String i = (String)var7.next();
System.out.println(i);
}so , Traversing the array uses the original for loop , The collection uses Iterator iterator . The latest interview questions have been sorted out , You can Java Interview library applet online brush questions .
(2) Remove elements
Oh, yes k! Next, let's delete the element :
Use for loop :
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
log.info(list.toString());
for (int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
list.remove("222");
}
log.info(list.toString());11:11:52.532 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]
11:11:52.539 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 333]Use foreach:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
log.info(list.toString());
for (String i : list) {
list.remove("222");
}
log.info(list.toString());11:50:48.333 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:909)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:859)
at com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord.main(HelloWord.java:30)Obviously, wood has success !
Click on the official account ,Java dried food Timely delivery 
reason :
Every traversal inside the iterator will record List Inside modcount As expected , Then use the expected value and in each cycle List Member variables of modCount The comparison , But ordinary list.remove It's called List Of remove, At this time modcount++, however iterator The expected value recorded in = There is no change , So there's an error .
If you want to delete an element, you need to use the inside of the iterator remove Method :
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
log.info(list.toString());
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
String next = it.next();
//if For external use list Of remove The method will still report an error
if(next.equals("222")){
it.remove();// Here we use the inside of the iterator remove() Method ,
// Of course if you use list Of remove If the method deletes texture elements here, it is successful , such as :list.remove("222")
}
}
log.info(list.toString());result :
12:06:14.042 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]
12:06:14.046 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 333](3) Modifying elements
Use primitive for:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
log.info(list.toString());
for (int i = 0; i <list.size(); i++) {
list.set(i,"444");
}
log.info(list.toString());result :
12:12:56.910 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]
12:12:56.915 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [444, 444, 444]Oh, yes k! You can modify elements ;
Use foreach:
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("111");
list.add("222");
list.add("333");
log.info(list.toString());
for (String i : list) {
i="444";
}
log.info(list.toString());result :
12:34:47.207 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]
12:34:47.211 [main] INFO com.xiaolinge.com.hello.HelloWord - [111, 222, 333]See , No way .
Spicy? , You can't modify elements , Can you modify the attributes of an element ? Let's take a look . The latest interview questions have been sorted out , You can Java Interview library applet online brush questions .
(4)foreach Modify element properties
(for I won't test it )
public class Student {
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private String name;
public Student(){};
public Student(int age,String name){
this.age=age;
this.name=name;
}
}Oh, yes k, Next, test the code :
Student student=new Student(1,"huge");
Student student1=new Student(1,"xiaoyao");
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<Student>();
studentList.add(student);
studentList.add(student1);
System.out.println(student.getName());
System.out.println(student1.getName());
for(Student stu:studentList)
{
stu.setName("jingtian");
}
System.out.println(student.getName());
System.out.println(student1.getName());huge
xiaoyao
jingtian
jingtian484 Amazing ! Can't modify the object , But you can modify the properties of the object .
summary
for And foreach Can traverse arrays / aggregate , however for It is more efficient in more complex cycles .
foreach Cannot delete / Modify set elements , and for Sure
foreach and for You can modify the attributes in the element
So by comparison for More flexible loops .
Copyright notice : This paper is about CSDN Blogger 「coder Brother Xiao Lin 」 The original article of , follow CC 4.0 BY-SA Copyright agreement , For reprint, please attach the original source link and this statement . Link to the original text :https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40521656/article/details/90749927


Spring Cloud Alibaba Finally unify the Jianghu !
Spring Boot After the scheduled task is started , How to stop automatically ?
23 Design mode and Practice ( Very comprehensive )
Spring Boot Protect sensitive configurations 4 Methods !
Face a 5 year Java, Neither thread can exchange data !
Why does Ali recommend LongAdder?
A new technical director : No code writing with headphones ..
Don't use it. System... It's time ,StopWatch Good use of explosion !
Java 8 Sort of 10 A pose , What a show !
Spring Boot Admin Born in the sky !
Spring Boot Learning notes , This is so complete !
Focus on Java Technology stack, see more dry goods

Spring Cloud Alibaba The latest combat !
边栏推荐
- [C #] the solution of WinForm operation zoom (blur)
- Add a self incrementing sequence number to the antd table component
- 分布式数据库主从配置(MySQL)
- STM32 entry development NEC infrared protocol decoding (ultra low cost wireless transmission scheme)
- Blog moved to Zhihu
- Web端自动化测试失败的原因
- Input type= "password" how to solve the problem of password automatically brought in
- Using ENSP to do MPLS pseudo wire test
- Easyui学习整理笔记
- STM32入门开发 NEC红外线协议解码(超低成本无线传输方案)
猜你喜欢
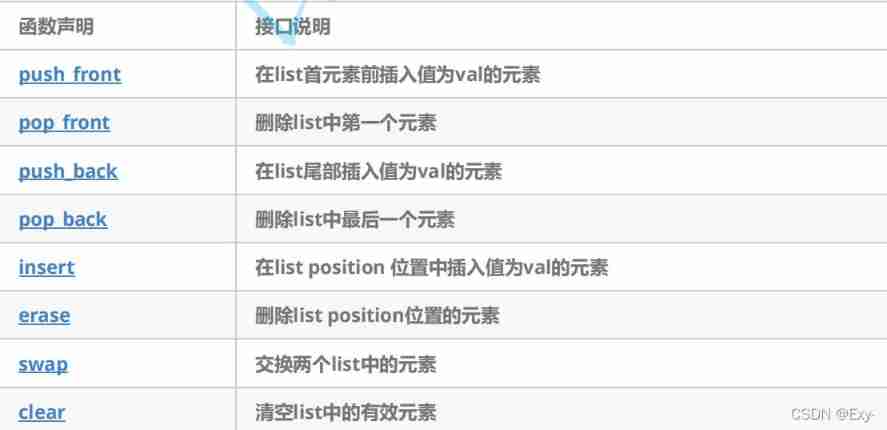
The use of list and Its Simulation Implementation
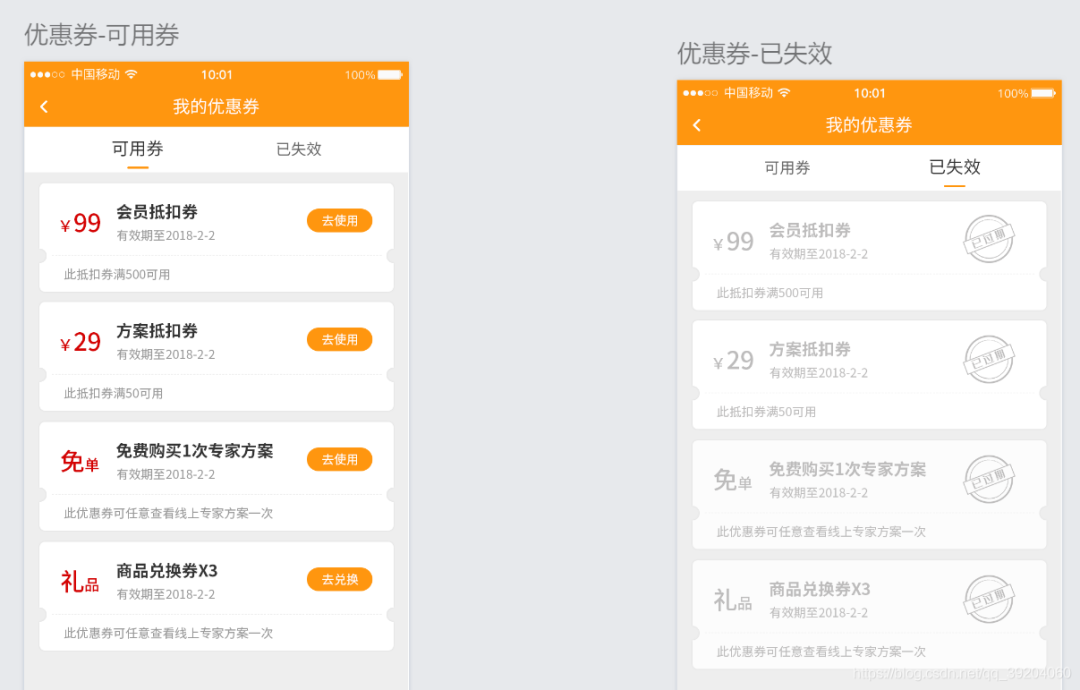
测试优惠券要怎么写测试用例?

Technology sharing | packet capturing analysis TCP protocol
About the application of writing shell script JSON in JMeter
![Verilog realizes nixie tube display driver [with source code]](/img/ad/be94912bedc738f4b5f97138db7352.png)
Verilog realizes nixie tube display driver [with source code]
请查收.NET MAUI 的最新学习资源
Table replication in PostgreSQL
![[untitled]](/img/a0/29975bc0f9832e1640cc39dfce4a71.jpg)
[untitled]
在我有限的软件测试经历里,一段专职的自动化测试经验总结

学习笔记|数据小白使用DataEase制作数据大屏
随机推荐
There are ways to improve self-discipline and self-control
[encapsulation of time format tool functions]
oracle常见锁表处理方式
Socket socket programming
什么是高内聚、低耦合?
The annual salary of general test is 15W, and the annual salary of test and development is 30w+. What is the difference between the two?
對比學習之 Unsupervised Learning of Visual Features by Contrasting Cluster Assignments
关于在云服务器上(这里用腾讯云)安装mysql8.0并使本地可以远程连接的方法
Easyui学习整理笔记
Vuthink正确安装过程
LeetCode - 面试题17.24 最大子矩阵
CentOS系统下Redis安装和自启动配置的步骤
聊聊SOC启动(十一) 内核初始化
Two week selection of tdengine community issues | phase II
【系统设计】指标监控和告警系统
[untitled]
‘module‘ object is not callable错误
RationalDMIS2022阵列工件测量
基于DE2 115开发板驱动HC_SR04超声波测距模块【附源码】
[untitled]