当前位置:网站首页>相机标定(1): 单目相机标定及张正友标定基本原理
相机标定(1): 单目相机标定及张正友标定基本原理
2022-07-07 09:41:00 【@BangBang】
为什么需要标定相机
相机的数学意义:
- 真实世界是三维的,拍摄照片是二维的
- 相机(
看成一个广义函数):输入三维场景,输出是二维图片(灰度值) - 彩色图是
RGB三通道,每个通道可以认为是一张灰度图 函数(映射关系)是不可逆的,也就是说我们无法从二维照片恢复出三维世界(二维照片没有深度信息)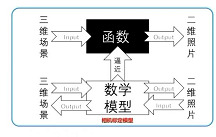
相机标定的意义
相机标定:使用带有pattern的标定板来求解相机参数的过程- 用一个简化的数学面模型来代表复杂的三维到二维成像过程
- 相机的参数包括:
相机内参(焦距)、相机外参(旋转、平移矩阵),镜头的畸变参数 用途:畸变矫正,双目视觉,结构光,三维重建,SLAM,都需要相机标定,获得相机的参数才可以进行应用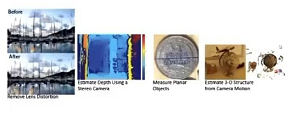
坐标系变换
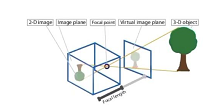
小孔成像原理
小孔成像说明
- 简单没镜头
- 有一个小的光源 (蜡烛)
- 真实世界的3D物体,发出光线通过光圈(小孔)
- 相机的另一侧,像平面位置,得到一个倒立的实像
坐标系介绍
必知的专用术语:
世界坐标系(World Coords):点在真实世界中的位置,描述相机的位置,单位是m相机坐标系(Camera Coords):以相机的sensor中心为原点,简历相机坐标系,单位m图像物理坐标系:经过小孔成像后得到的二维坐标系,单位是mm,坐标元旦是图中的点 C C C像素坐标系(Pixel Coords): 成像点在相机sensor上像素的行数和列数,不带任何的物理单位主点:光轴与图像平面的交点,图中的点p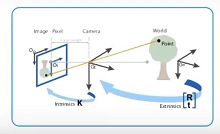
在双目或多目系统中,世界坐标系和相机坐标系是不重合的,需要对世界坐标系通过旋转矩阵R和平移矩阵T,变换到相机坐标系。
上图二维平面中, O i O_{i} Oi为图像坐标系原点, O d O_{d} Od是像素坐标系,像素坐标系相对于图像坐标系原点有些偏移。
(1)世界坐标系到相机坐标系
点p在不同坐标系的表示
- 世界坐标系(World Coords): P ( x w , y w , z w ) P(x_{w},y_{w},z_{w}) P(xw,yw,zw)
- 相机坐标系(World Coords): P ( x c , y c , z c ) P(x_{c},y_{c},z_{c}) P(xc,yc,zc)
世界坐标系与相机坐标系之间的转换矩阵:
- R R R:相机坐标系相对于世界坐标系的旋转矩阵
- T T T: 相机坐标系相对于世界坐标系的平移矩阵
转换关系数学表达:
[ x c y c z c 1 ] = [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 O 1 ] ⋅ [ x w y w z w 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ O & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤=[R3×3OT3×11]⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤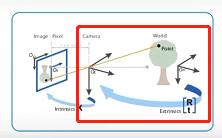
世界坐标系通过旋转矩阵R和偏移矩阵T,转换为相机坐标系 ,如果世界坐标系和相机坐标系重合,则R是一个单位矩阵,T是零矩阵,这样就可以把真实世界的点,转换为相机坐标系中的点
(2) 相机坐标系到图像坐标系
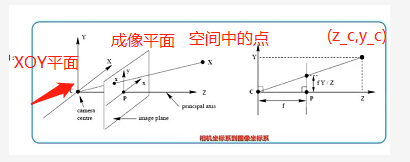
- 假设相机上的点 p ( x c , y c , z c ) p(x_c,y_c,z_c) p(xc,yc,zc) 在图像坐标系的成像点是 p ′ ( x , y ) p^{'}(x,y) p′(x,y)
- 基于小孔成像的原理
- 空间中一点成像在平面中,与 X c Y XcY XcY平面(镜头)平行,距离原点 f f f的平面
- 取一个截面 Z c Y ZcY ZcY,可以得到右图,右图中的黑点 ( z c , y c ) (z_c,y_c) (zc,yc),根据相似三角形关系可以计算得到:
y y c = f z c \frac{y}{y_c}=\frac{f}{z_c} ycy=zcf - 取一个截面 X c Y XcY XcY,根据相似三角形关系可以计算得到:
x x c = y y c \frac{x}{x_c}=\frac{y}{y_c} xcx=ycy - 结合两个三角变换关系,有:
x x c = y y c = f z c \frac{x}{x_c}=\frac{y}{y_c}=\frac{f}{z_c} xcx=ycy=zcf
简化后可以得到:
x = f z c ⋅ x c x=\frac{f}{z_c} \cdot x_{c} x=zcf⋅xc
y = f z c ⋅ y c y=\frac{f}{z_c} \cdot y_{c} y=zcf⋅yc
- 写成矩阵形式:
z c ⋅ [ x y 1 ] = [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ x c y c z c 1 ] z_{c}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} zc⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤=⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤
(3) 图像坐标系到像素坐标系转换
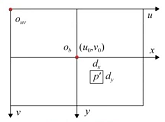
上图中,图像中点 O b O_b Ob表示图像坐标系原点, 左上角 O u v O_{uv} Ouv表示像素坐标系的原点
坐标系的转换:
- 图像坐标系的点 p ′ ( x , y ) p^{'}(x,y) p′(x,y)到像素坐标系的 ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v)的转换
- 图像坐标系的原点在sensor的中央,单位是mm
- 像素坐标系的原点在sensor的左上角,单位为Pixel,也就是像素的行数和列数
- 他们间的转换关系:
u = x d x + u 0 , v = y d y + v 0 u=\frac{x}{dx} + u_0 ,v=\frac{y}{dy} + v_0 u=dxx+u0,v=dyy+v0 - 写成矩阵形式:
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤- d x d_x dx, d y d_y dy:是sensor顾有参数,代表每个像素的毫米数
- u 0 u_0 u0, v 0 v_0 v0:代表图像坐标系原点(光心)相对像素坐标系原点的偏移量
综上:相机坐标系到像素的转换公式:
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ 1 z c ⋅ [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ x c y c z c 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \frac{1}{z_c} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_c \\ y_c \\ z_c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅zc1⋅⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xcyczc1⎦⎥⎥⎤
可以得到:
u = f x ∗ x c z c + u 0 u=f_x * \frac{x_c}{z_c}+ u_0 u=fx∗zcxc+u0
v = f y ∗ y c z c + v 0 v=f_y * \frac{y_c}{z_c}+ v_0 v=fy∗zcyc+v0
- 上式中: f x = f d x f_x=\frac{f}{dx} fx=dxf, f y = f d y f_y=\frac{f}{dy} fy=dyf,焦距除以单个像素大小
- 相机标定过程中, f , d x , d y f,dx,dy f,dx,dy不能标定得到, f x , f y f_x,f_y fx,fy可以通过标定得到
(4) 完整的坐标系转换
世界坐标系到像素坐标系转换
[ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ x y 1 ] \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡xy1⎦⎤- d x d_x dx, d y d_y dy:是sensor顾有参数,代表每个像素的毫米数
- u 0 u_0 u0, v 0 v_0 v0:代表图像坐标系原点(光心)相对像素坐标系原点的偏移量
综上:相机坐标系到像素的转换公式:
z c ⋅ [ u v 1 ] = [ 1 d x 0 u 0 0 1 d y v 0 0 0 1 ] ⋅ [ f 0 0 0 0 f 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] ⋅ [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 O 1 ] ⋅ [ x w y w z w 1 ] = M 1 M 2 [ x w y w z w 1 ] z_c\cdot\begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{1}{dx} &0&u_0 \\ 0 &\frac{1}{dy}&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} f &0&0&0 \\ 0 &f&0&0 \\ 0 &0&1&0 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ O & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} \cdot \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} = M_1M_2 \begin{bmatrix} x_w \\ y_w \\ z_w \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} zc⋅⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤=⎣⎡dx1000dy10u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡f000f0001000⎦⎤⋅[R3×3OT3×11]⋅⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤=M1M2⎣⎢⎢⎡xwywzw1⎦⎥⎥⎤
- 相机内参:相机的焦距,像素坐标的相对偏移量
M 1 = [ f x 0 u 0 0 f y v 0 0 0 1 ] M_1= \begin{bmatrix} f_x &0&u_0 \\ 0 &f_y&v_0 \\ 0 &0&1 \\ \end{bmatrix} M1=⎣⎡fx000fy0u0v01⎦⎤ - 相机外参:世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换关系,相机在世界坐标系的位姿矩阵
M 2 = [ R 3 × 3 T 3 × 1 ] = [ r 11 r 12 r 13 t 1 r 21 r 22 r 23 t 2 r 31 r 32 r 33 t 3 ] M_2=\begin{bmatrix} R_{3\times3} & T_{3\times1} \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} r_{11}&r_{12}&r_{13}&t_{1} \\ r_{21}&r_{22}&r_{23}&t_{2} \\ r_{31}&r_{32}&r_{33}&t_{3} \\ \end{bmatrix} M2=[R3×3T3×1]=⎣⎡r11r21r31r12r22r32r13r23r33t1t2t3⎦⎤
镜头畸变
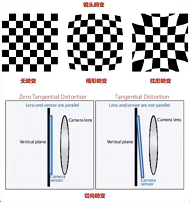
镜头畸变
超广角拍摄畸变会比较明显,越到边缘的地方畸变越明显
- 经过透镜后的实际成像和理想成像之间的误差即为镜头畸变
- 主要分为经向畸变和切向畸变
径向畸变 - 相加的透镜形状造成,沿透镜的径向分布
- 分为桶形畸变和枕形畸变
- 远离透镜中心的地方比靠近透镜中心的地方更加弯曲
- 光心处的畸变为0,距离光心越远畸变越大
- 廉价相机,畸变更严重
- 径向畸变的数学多项式描述
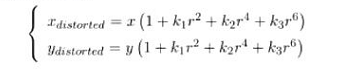
- (x,y)是没畸变的像素点, ( x d i s t o r t e d , y d i s t o r t e d ) (x_{distorted},y_{distorted}) (xdistorted,ydistorted)畸变后的位置
- k 1 , k 2 , k 3 k_1,k_2,k_3 k1,k2,k3:径向畸变系数,摄像头的内参,一般使用前两项,鱼眼相机会使用第三项
切向畸变
- 相机sensor和镜头不平行导致的,相机比较好的话一般是不存在切向畸变的。因此一般研究径向畸变的影响。
- 畸变的数学表示:
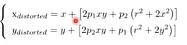
- 两个畸变合并:
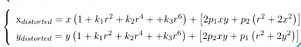
边栏推荐
- [Yugong series] go teaching course 005 variables in July 2022
- 一度辍学的数学差生,获得今年菲尔兹奖
- 聊聊SOC启动(十) 内核启动先导知识
- Unsupervised learning of visual features by contracting cluster assignments
- 常用sql语句整理:mysql
- Using ENSP to do MPLS pseudo wire test
- Onedns helps college industry network security
- Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be overwritten whenever the parent component
- R語言使用magick包的image_mosaic函數和image_flatten函數把多張圖片堆疊在一起形成堆疊組合圖像(Stack layers on top of each other)
- VIM命令模式与输入模式切换
猜你喜欢
How to use cherry pick?
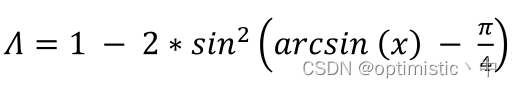
关于SIoU《SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression Zhora Gevorgyan 》的一些看法及代码实现

Poor math students who once dropped out of school won the fields award this year
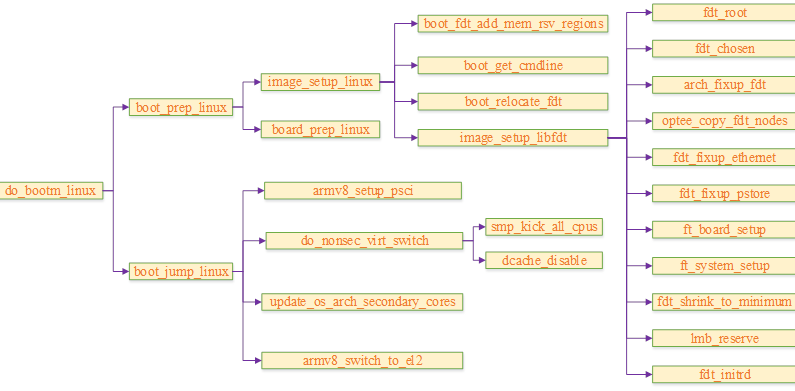
聊聊SOC启动(七) uboot启动流程三

Automated testing framework
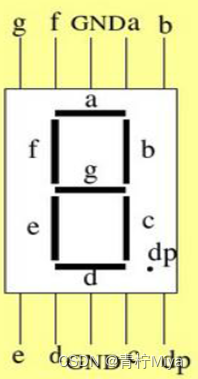
verilog设计抢答器【附源码】

自动化测试框架
![Verilog design responder [with source code]](/img/91/6359a2f3fa0045b4a88956a475488c.png)
Verilog design responder [with source code]

OneDNS助力高校行业网络安全
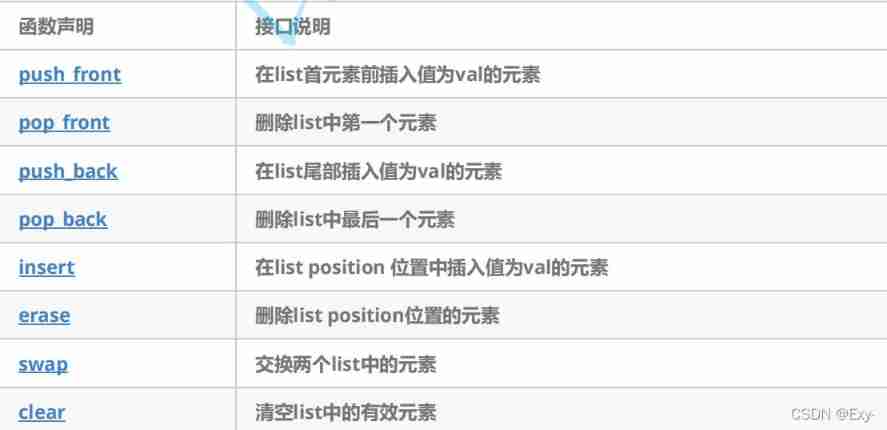
The use of list and Its Simulation Implementation
随机推荐
Android interview knowledge points
什么是高内聚、低耦合?
Vuthink proper installation process
The post-90s resigned and started a business, saying they would kill cloud database
Le Cluster kubernets en cours d'exécution veut ajuster l'adresse du segment réseau du pod
Two week selection of tdengine community issues | phase II
Case study of Jinshan API translation function based on retrofit framework
Leetcode - interview question 17.24 maximum submatrix
关于jmeter中编写shell脚本json的应用
Template initial level template
VIM命令模式与输入模式切换
About the application of writing shell script JSON in JMeter
Drive HC based on de2115 development board_ SR04 ultrasonic ranging module [source code attached]
通过 Play Integrity API 的 nonce 字段提高应用安全性
分布式数据库主从配置(MySQL)
JS array delete the specified element
关于SIoU《SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression Zhora Gevorgyan 》的一些看法及代码实现
JS add spaces to the string
Enclosed please find. Net Maui's latest learning resources
Talk about SOC startup (VI) uboot startup process II