当前位置:网站首页>Lecture 3 Gradient Tutorial Gradient Descent and Stochastic Gradient Descent
Lecture 3 Gradient Tutorial Gradient Descent and Stochastic Gradient Descent
2022-08-05 05:24:00 【A long way to go】
Gradient Tutorial
The main difference between the gradient descent algorithm and the stochastic gradient descent algorithm is that:
- The loss function of the gradient descent algorithm is cost函数 ,cost是计算所有训练数据的损失
- The loss function of the stochastic gradient descent algorithm is loss函数,loss是计算一个训练函数的损失
- 由于随机梯度下降no need for reconciliation,Therefore, the loss function and gradient update can be reducedfor循环部分
梯度下降
Gradient descent loss function formula: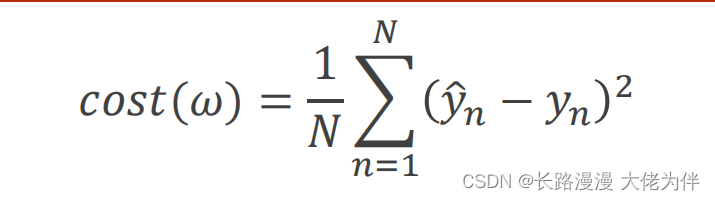
梯度公式: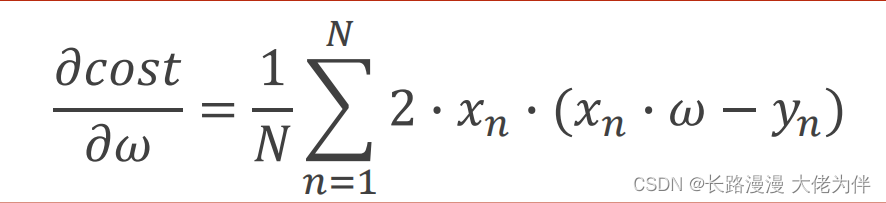
梯度下降算法(cost函数)
算法代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 准备x,y的数据
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
# 猜测初始权重
w = 1.0
#定义学习率,This is a hyperparameter,Manual definition is required
learning_rate=0.05
# 前馈计算
def forward(x):
return x * w
# 计算平均损失函数
# Because of the need for reconciliation,所以需要将x,yTake in the entire dataset
def cost(xs, ys):
cost = 0
#使用zipfunctions are extracted separatelyx,y
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
y_pred = forward(x)
cost += (y_pred - y) ** 2
return cost / len(xs)
# 计算梯度,Also sum and average
def gradient(xs, ys):
grad = 0
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
grad += 2 * x * (x * w - y)
return grad / len(xs)
epoch_list = []
cost_list = []
print('predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
#更新梯度
for epoch in range(80):
cost_val = cost(x_data, y_data)
grad_val = gradient(x_data, y_data)
w -= learning_rate * grad_val # 0.01 learning rate
print('epoch:', epoch, 'w=', w, 'loss=', cost_val)
#Load the count and average loss into a list,for later drawing use
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(cost_val)
print('predict (after training)', 4, forward(4))
#画出cost与epoch的平面图
plt.plot(epoch_list, cost_list)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
结果如下:
predict (before training) 4 4.0
epoch: 0 w= 1.4666666666666668 loss= 4.666666666666667
epoch: 1 w= 1.7155555555555557 loss= 1.3274074074074067
epoch: 2 w= 1.8482962962962963 loss= 0.3775736625514398
epoch: 3 w= 1.9190913580246913 loss= 0.10739873068129853
epoch: 4 w= 1.9568487242798354 loss= 0.030548972282680543
epoch: 5 w= 1.976985986282579 loss= 0.008689485449295776
...................
epoch: 55 w= 1.9999999999999996 loss= 3.681350891031389e-30
epoch: 56 w= 1.9999999999999998 loss= 1.3805065841367707e-30
epoch: 57 w= 2.0 loss= 3.4512664603419266e-31
epoch: 58 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
epoch: 59 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
...................
epoch: 77 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
epoch: 78 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
epoch: 79 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
predict (after training) 4 8.0
cost与epoch关系如图: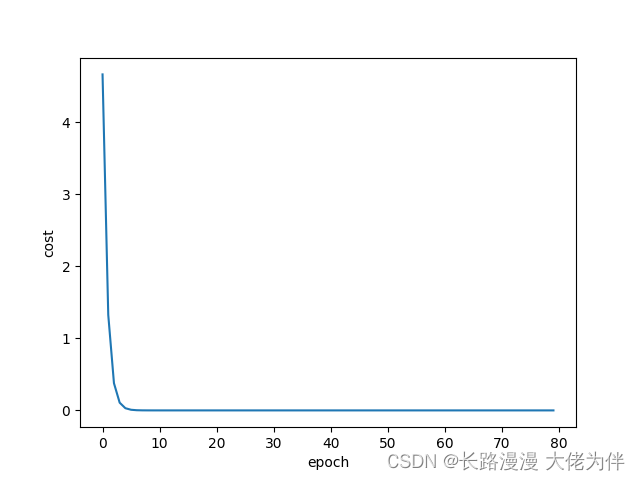
随机梯度下降
损失函数公式: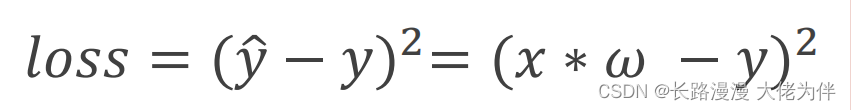
梯度公式: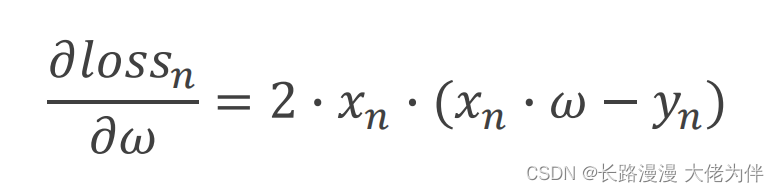
运行代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 准备x,y的数据
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
# 猜测初始权重
w = 1.0
#定义学习率,This is a hyperparameter,Manual definition is required
learning_rate=0.03
# 前馈计算
def forward(x):
return x * w
# 计算损失函数
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y)**2
# 计算梯度,Also sum and average
def gradient(x, y):
return 2*x*(x*w - y)
epoch_list = []
loss_list = []
print('predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
#更新梯度
for epoch in range(100):
for x,y in zip(x_data, y_data):
grad = gradient(x,y)
w = w - learning_rate*grad # update weight by every grad of sample of training set
print("\tgrad:", x, y,grad)
l = loss(x,y)
print('epoch:', epoch, 'w=', w, 'loss=', l)
#Load the count and average loss into a list,for later drawing use
epoch_list.append(epoch)
loss_list .append(l)
print('predict (after training)', 4, forward(4))
#画出cost与epoch的平面图
plt.plot(epoch_list, loss_list )
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
predict (before training) 4 4.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 -2.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 -7.52
grad: 3.0 6.0 -12.859199999999998
epoch: 0 w= 1.671376 loss= 0.9719436003840011
grad: 1.0 2.0 -0.657248
grad: 2.0 4.0 -2.4712524800000004
grad: 3.0 6.0 -4.2258417408
epoch: 1 w= 1.8920062666239998 loss= 0.10496381803637934
grad: 1.0 2.0 -0.2159874667520003
grad: 2.0 4.0 -0.8121128749875215
grad: 3.0 6.0 -1.3887130162286585
epoch: 2 w= 1.9645106673630452 loss= 0.011335434579147843
grad: 1.0 2.0 -0.0709786652739095
grad: 2.0 4.0 -0.26687978142989977
grad: 3.0 6.0 -0.4563644262451305
epoch: 3 w= 1.9883373535515134 loss= 0.0012241558996415386
grad: 1.0 2.0 -0.02332529289697316
grad: 2.0 4.0 -0.08770310129261993
grad: 3.0 6.0 -0.14997230321038302
...............
epoch: 31 w= 1.9999999999999996 loss= 3.1554436208840472e-30
grad: 1.0 2.0 -8.881784197001252e-16
grad: 2.0 4.0 -3.552713678800501e-15
grad: 3.0 6.0 -1.0658141036401503e-14
epoch: 32 w= 1.9999999999999998 loss= 7.888609052210118e-31
grad: 1.0 2.0 -4.440892098500626e-16
grad: 2.0 4.0 -1.7763568394002505e-15
grad: 3.0 6.0 -5.329070518200751e-15
epoch: 33 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 0.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 0.0
grad: 3.0 6.0 0.0
epoch: 34 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 0.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 0.0
grad: 3.0 6.0 0.0
epoch: 35 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 0.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 0.0
grad: 3.0 6.0 0.0
...............
epoch: 97 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 0.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 0.0
grad: 3.0 6.0 0.0
epoch: 98 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
grad: 1.0 2.0 0.0
grad: 2.0 4.0 0.0
grad: 3.0 6.0 0.0
epoch: 99 w= 2.0 loss= 0.0
predict (after training) 4 8.0
平面图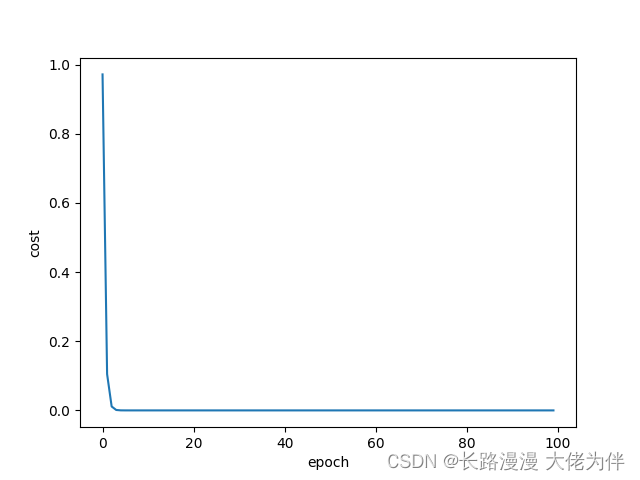
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Calling Matlab configuration in pycharm: No module named 'matlab.engine'; 'matlab' is not a package
2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi-School 1st Session 01
Matplotlib(二)—— 子图
![[Let's pass 14] A day in the study room](/img/fc/ff4161db8ed13a0c8ef75b066b8eab.png)
[Let's pass 14] A day in the study room
Structured Light 3D Reconstruction (2) Line Structured Light 3D Reconstruction
【过一下10】sklearn使用记录
Pycharm中使用pip安装第三方库安装失败:“Non-zero exit code (2)“的解决方法

Reverse theory knowledge 4

The difference between span tag and p
软件设计 实验四 桥接模式实验
随机推荐
学习总结week2_1
Returned object not currently part of this pool
Returned object not currently part of this pool
Analysis of Mvi Architecture
学习总结week2_4
redis 持久化
浅谈Servlet生命周期
学习总结day5
Mysql5.7 二进制 部署
redis 缓存清除策略
位运算符与逻辑运算符的区别
phone call function
RL reinforcement learning summary (1)
1.3 mysql批量插入数据
Requests the library deployment and common function
2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi-School 1st Session 01
分布式和集群
【过一下7】全连接神经网络视频第一节的笔记
day12函数进阶作业
2022杭电多校第一场01