当前位置:网站首页>Advanced length of redis -- deletion strategy, master-slave replication, sentinel mode
Advanced length of redis -- deletion strategy, master-slave replication, sentinel mode
2022-07-05 04:26:00 【acwing】
Redis————— Deletion policy
** Expired data **
Redis It's a memory level database , All data is stored in memory , The data in memory can be used by him TTL Command gets its state
XX Have timeliness
-1 Permanent data
-2 Expired data Or deleted data Or undefined data
The goal of the data deletion strategy
In memory footprint and CPU Find a balance between occupation , Taking care of one thing and losing the other will result in the whole redis‘ Performance degradation
Even cause server downtime or memory leakage
Data deletion strategy
Delete regularly
** Create a timer When key Set the expiration time And when the expiration time reaches , Delete the key immediately by the scheduled task **
advantage To save memory Then delete Free up unnecessary memory quickly
shortcoming CPU Under great pressure No matter what cpu How high is the load at this time All occupied cpu It will affect redis Server response time and instruction throughput
summary Exchange processor performance for storage time ( Time for space )
Lazy deletion
Data arrival expiration time Don't deal with it The next time you access the data
Judge whether it is overdue expirelNeeded()
1. If it is found that it has not expired Return the data
2. It is found that the data has expired Delete Return does not exist
advantage save cpu Delete when you find that you have to delete
shortcoming There's a lot of memory pressure Data that has occupied memory for a long time
summary Swapping memory for processor performance ( Exchange space for time )
Delete periodically
Redis’ When starting server initialization 、 Reading configuration server.hz Value The default is 10
To perform a second server.hz Time serverCron() Frequency --databaseCron()---activeExpireCycle() For each expires[*] Test them one by one Every time you execute 250ms/server.hz Duration of work execution
To someone expires[*] Random selection W individual key testing
1. If a key Overtime Delete key
2. If you delete in a round key The number of >W*25% Cycle the process
Parameters current_db Used to record activeExpireCycle() Into that expires[*] perform
If activeExpireCycle() Execution time expired Next time from current_db Keep going down
Delete periodically
Periodic polling redis Time sensitive data in the library Qualification by random sampling Use the proportion of expired data to control the frequency of deletion
characteristic cpu Performance occupancy settings have peaks The detection frequency can be set by yourself
Memory pressure is not great The cold data of long-term temporary memory will be continuously cleaned
summary Periodically spot check storage space ( Random sampling 、 Focus on spot check )
Data elimination strategy ( Data expulsion algorithm )
When new data enters redis when , If there is not enough memory ?
Redis Using memory to store data Before executing every command Would call freeMemioryifNeeded() Check if there is enough memory If the memory does not meet the minimum storage requirements for newly added data redis To snack, delete some data and clear the storage space for the current instruction The strategy of cleaning up data is eviction algorithm Eviction strategy
Be careful The process of evicting data is not 100% Be able to clean up enough usable memory space If not, repeat When all the data is tried If the requirement of memory cleaning cannot be met An error message will appear

Related configurations that affect data obsolescence
Maximum available memory That is, the proportion of physical memory occupied The default value is 0 Means unrestricted In the production environment, set according to the demand Usually set at 50% above
Maxmemory ? mb
Select the number of data to be deleted each time Random data acquisition Delete data to be detected
Maxmemory-samples count
Selection strategy for data deletion
Maxmemory-polioy policy
Detect volatile data ( Data sets that may be out of date server.db[i].expires)
1.volatile-lru Choose the one that is least used for a period of time
2.volatile-lfu Select the data that has been used least for a period of time to eliminate
3.volatile-ttl Select the data that will be out of date
4.volatile-random Choose any data to eliminate
Expand the scope
1. Check the whole database data ( All data sets server.db[i].dict)
2.Alkeys-lru Choose the one that is least used for a period of time
3.Alkeys-lfu Select the data that has been used least for a period of time to eliminate
4.Alkeys-ttl Select the data that will be out of date
Give up data
No-enviction( deportation ) Exclusion data (redis4.0 Default policy in ) Error will be raised OOM(out of Memory)
Corresponding settings
Maxmemory-policy volatile-lru Make property settings
stay redis Use in INFO Command output monitoring information The query cache hit and miss The number of times Tune according to business needs Redis To configure
Redis————— Master slave copy
Introduction to master-slave replication
Internet three high architecture
High concurrency
High performance
High availability The server Normal operation time Ratio of time in the whole year
Industry availability goals 99.999% That is to say, the annual downtime of the server is less than 315 second
Redis High availability ?
Machine fault Hard disk failure System crash
Capacity of the bottleneck Out of memory
Conclusion
To avoid a single point Redis Server failure Prepare abortion server Connect with each other Copy data and save multiple copies on different servers come together And keep the data synchronized
It is considered that one of the servers is down Other servers can continue to provide services Realization redis High availability At the same time, redundant backup of data is realized
Multi server connection scheme master
master server Master node Main library
Primary client
Receiving party slave
From the server From the node Slave Library
From the client
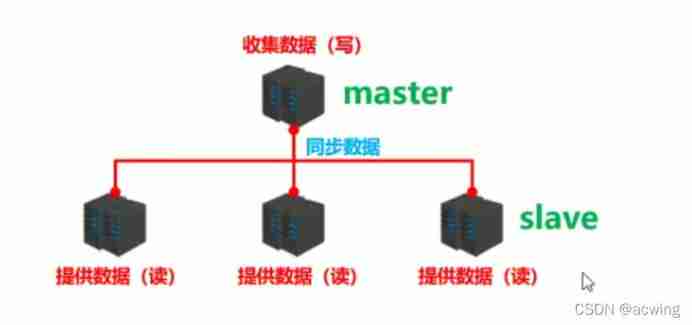
Master slave copy Timeliness and effectiveness of data
Master slave replication will master Data in real time 、 Effectively copy to slave in
One master You can have multiple slave One slave Value corresponds to a master
Master
Writing data
When writing Automatically synchronize the changed data to slave
Slave
Reading data
Writing data ( prohibit )
The role of master-slave replication
Read / write separation master Write slave read Improve the load capacity of the server Load balancing Based on the master-slave structure Cooperate with the separation of reading and writing
from slave Share responsibility master load And according to the change of demand change slave The number of Sharing the load of data reading through multiple slave nodes
Greatly improved Redis Server concurrency and data throughput Fault recovery When master When something goes wrong from slave Provide services Fast fault recovery data redundancy
Hot data backup It's a way of data redundancy beyond persistence High availability cornerstone Based on master-slave replication Construction of sentry mode and cluster Realization Redis High availability solution 、
Master slave copy workflow 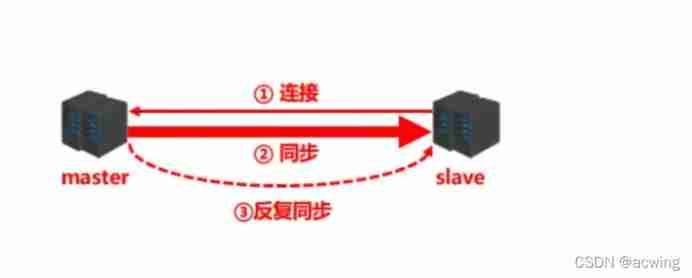
Establish connection phase ( Preparation stage )
establish slave To master The connection of send master Able to identify slave And save slave Port number
- establish master The address and port of , preservation master Information
- establish socke( Information channels ) Connect
- send out ping command ( Timing task )
- Authentication
- send out slave Port information 、
Main connection (slave Connect master)
Mode one Client sends command
Slaveof masterip masterport
Mode two Start server parameters
Redis-server-slaveof masterip masterport
Mode three Server configuration
Slaveof masterip masterport
stay redis-conf In profile Join in slaveof ip Address Port number
Info command You can view the connection information
Master slave disconnect
- To break off slave And master The connection of slave After disconnection Existing data will not be deleted Just not receiving master Data sent
- Slaveof no one slave Client execution of
Authorized access
master The client sends a command to set the password
requirepass password
mater Profile settings password
config set requirepass password
config get requirepass
slave The client sends a command to set the password
auth password
slave Profile settings password
masterauth password
slave Start the server and set the password
redis-server -a password
Data synchronization phase
stay slaver First time to condense master after Copy master All data in to slave
take slave Database update support master Current database state
Request to synchronize data
- establish RDB Synchronous data
- recovery RDB Synchronous data
- Request partial synchronization data
- Restore partially synchronized data
current state :
Slave have master Segment all data contain RDB Data received by the process
Master preservation slave The location of the current data synchronization
The overall Data cloning is completed between
Data synchronization phase master explain
If master The amount of data is huge Data synchronization phase should avoid the peak traffic , Avoid creating master Blocking Affect the normal implementation of business
The copy buffer size is not set properly Can cause data overflow If the full copy cycle is too long After partial replication, it is found that the number has been lost A second full copy is required
the slave In a dead cycleRepl-bocklog-size Set sizeMaster Single machine memory should not occupy a large proportion of main memory Use 60% or 70% of the memory
Thirty or forty percent is left for execution bgsave Command and create a copy buffer
Data synchronization phase slave explain
- To avoid slave Make full copies 、 Server response blocked or data out of sync during partial replication It is suggested to close the external service during this period
slabe-serve-stale-data yes|no - Data synchronization phase master Send to slave The information is understandable master yes slaved A client actively sends slave dispatch orders
- Multiple slave At the same time master Request data synchronization master Sent RDB More documents It's going to have a huge impact on bandwidth If master Not enough bandwidth , Therefore, data synchronization needs to be based on business requirements Right amount of peak shifting
How the command propagation phase and the copy buffer work
When master After the database state is modified The server database state is inconsistent
At this point, you need to synchronize master-slave data to a consistent state Synchronous actions become command propagation \
Master Send the received data change command to slave slave After receiving the command, execute the command
Partial replication in the command propagation phase
The network is disconnected in the command stage
The network is broken and connected Ignore
Short time network outage Partial reproduction
Long time network interruption Copy in full
Three core elements of partial replication
Running the server id(run id)
Replication backlog buffer for primary server
The replication offset of the master and slave servers
Copy buffer
Copy buffer also called Copy backlog buffer It's a first in, first out (FIFO) Queues Used to store commands executed by the server Every time you pass a command master Will record the command spread And stored in the copy buffer
The default data storage size of the copy buffer is 1M
When the number of elements in the queue is greater than the queue length The first element to join the team will be ejected And new elements are put into the queue
effect
Used to hold master All instructions received ( Instructions that only affect data changes for example set sekect),
Data sources When master When receiving the instruction from the main customer In addition to executing instructions The change instruction will be stored in the buffer
Master slave copy offset (offset)
Sync information comparison master And slave The difference of When slave After the break Recover data usage
Data synchronization + Command propagation phase workflow

heartbeat
Enter the command propagation phase master And slave We need to exchange information between them Use heartbeat mechanism for maintenance Keep both sides connected online
Master heartbeat
Internal instructions ping
cycle from repl-ping-period decision Default 10s
effect Judge slave Whether online
Inquire about INFO replication obtain slave Last connection interval lag The project is maintained at 0 or 1 As normal
Slave Heartbeat task
Internal instructions replconf ack {offset}
cycle 1s
effect report slave Copy your own 、 Offset Get the latest data instructions
Judge master Whether online
Redis————— Sentinel mode
Brief introduction to sentry
When the host Downtime
close master And all slave
Who will inherit the data service during shutdown
Find one. slave As master
Find a master How to find
Modify other slave Configuration of , Connect the new master
After modifying the configuration How to restore the original Lord
Start a new master And slave
Copy in full N+ Partial reproduction N
sentry Sentinel
Sentinel is a distributed system It is used to monitor each server in the master-slave structure When there is a failure, the voting mechanism is used to select a new one master And put all slave Connect to the new master
The role of a sentry
monitor
1. Keep checking master and slave Is it working
2. Master Survival tests master And slave Operation detection
notice ( remind ) When the monitored server has problems , To the other ( The sentry room client ) Sending notice
Automatic failover : To break off master And slave Connect Pick one slave As master, Will others slave Connect new master, And inform the client of the new server address
Be careful : Sentinel is also a redis The server It just doesn't provide data related services , Usually, the number of sentries is odd
Enable sentinel mode
Configure the master-slave structure of one drag two
Three sentries ( The configuration is the same , Different ports )
Activate the sentry
Redis-sentinel filename
边栏推荐
- 托管式服务网络:云原生时代的应用体系架构进化
- 【科普】热设计基础知识:5G光器件之散热分析
- WeNet:面向工业落地的E2E语音识别工具
- [untitled]
- American 5g open ran suffered another major setback, and its attempt to counter China's 5g technology has failed
- PR video clip (project packaging)
- 长度为n的入栈顺序的可能出栈顺序种数
- 【虚幻引擎UE】打包报错出现!FindPin错误的解决办法
- 如何进行「小步重构」?
- Technical tutorial: how to use easydss to push live streaming to qiniu cloud?
猜你喜欢

取余操作是一个哈希函数

直播预告 | 容器服务 ACK 弹性预测最佳实践
![[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices](/img/45/380e739f5eed33626c363756f814d3.png)
[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices

10 programming habits that web developers should develop

首席信息官如何利用业务分析构建业务价值?
【FineBI】使用FineBI制作自定义地图过程
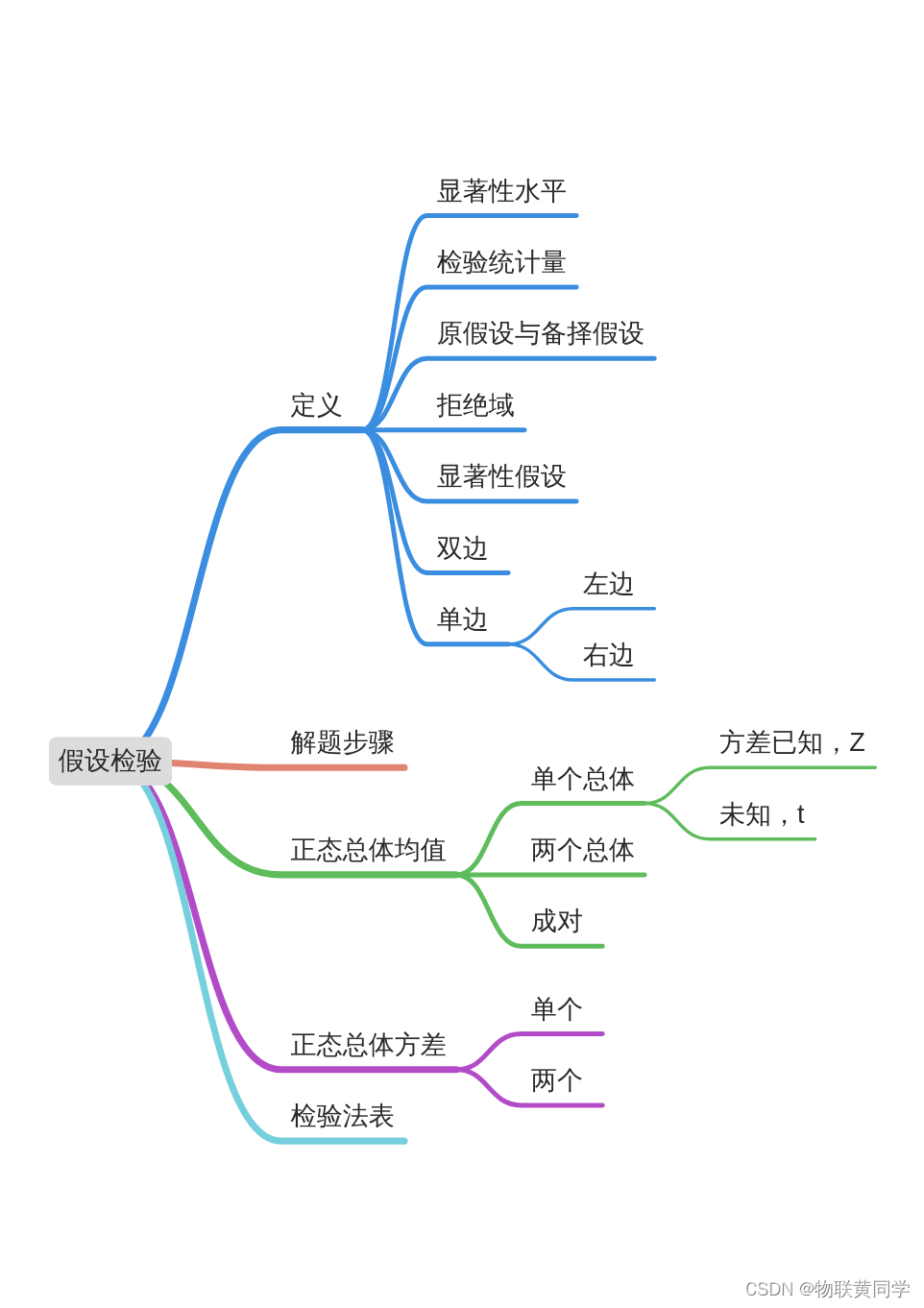
Hypothesis testing -- learning notes of Chapter 8 of probability theory and mathematical statistics
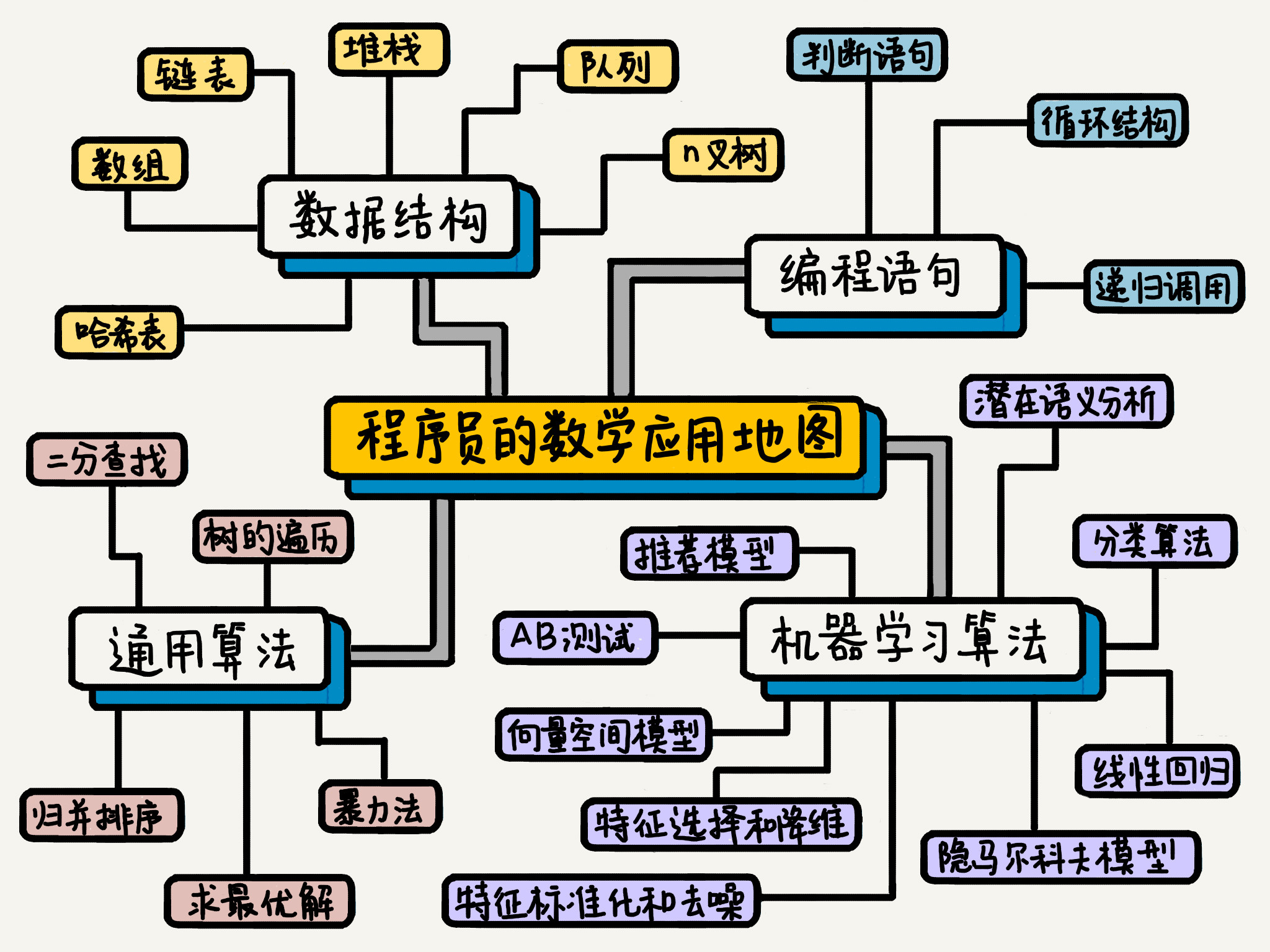
程序员应该怎么学数学
NetSetMan pro (IP fast switching tool) official Chinese version v5.1.0 | computer IP switching software download

如何优雅的获取每个分组的前几条数据
随机推荐
[uniapp] system hot update implementation ideas
蛇形矩阵
Technical tutorial: how to use easydss to push live streaming to qiniu cloud?
[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices
直播预告 | 容器服务 ACK 弹性预测最佳实践
Web开发人员应该养成的10个编程习惯
Function (error prone)
基于TCP的移动端IM即时通讯开发仍然需要心跳保活
What are the building energy-saving software
Interview related high-frequency algorithm test site 3
Threejs Internet of things, 3D visualization of farms (II)
【虛幻引擎UE】實現UE5像素流部署僅需六步操作少走彎路!(4.26和4.27原理類似)
假设检验——《概率论与数理统计》第八章学习笔记
Cookie learning diary 1
Kwai, Tiktok, video number, battle content payment
Is "golden nine and silver ten" the best time to find a job? Not necessarily
Threejs Internet of things, 3D visualization of factory
kubernetes集群之调度系统
10 programming habits that web developers should develop
OWASP top 10 vulnerability Guide (2021)