当前位置:网站首页>[robot hand eye calibration] eye in hand
[robot hand eye calibration] eye in hand
2022-07-06 02:12:00 【Ten year dream laboratory】
/*hand-eye calibration using TSAI method*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Geometry>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/LU>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/StdVector>
#include <opencv2/core/eigen.hpp>
#define PI 3.1415926
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace Eigen;
//https://www.cnblogs.com/long5683/p/10094122.html
int num_of_all_images = 70;// shooting 70 Time ?
// Number of inner corners in row and column direction
cv::Size board_size = cv::Size(9, 7);//9 That's ok 7 Column Corner point
// Calibrate the actual size of the checkerboard ( The unit should be connected with pose.txt The units of robot position in the are the same ) mm
cv::Size2f square_size = cv::Size2f(25, 25);//25x25mm
Eigen::Matrix3d skew(Eigen::Vector3d V);// Antisymmetric matrix . Generated by vectors
Eigen::Matrix4d quat2rot(Eigen::Vector3d q);// Unit quaternion turns Rotation matrix
Eigen::Vector3d rot2quat(Eigen::MatrixXd R);
Eigen::Matrix4d transl(Eigen::Vector3d x);
Eigen::Matrix4d handEye(std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > bHg,
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > cHw);
Eigen::Matrix4d handEye1(std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > bHg,
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > cHw);
int handEye_calib(Eigen::Matrix4d &gHc, std::string path);
// skew - returns skew matrix of a 3x1 vector.
// cross(V,U) = skew(V)*U Cross product calculation
// S = skew(V)
// 0 -Vz Vy
// S = Vz 0 -Vx
// -Vy Vx 0
// See also: cross
Eigen::Matrix3d skew(Eigen::Vector3d V)// Antisymmetric matrix
{
Eigen::Matrix3d S;
S <<
0, -V(2), V(1),
V(2), 0, -V(0),
-V(1), V(0), 0;
return S;
}
// quat2rot - a unit quaternion(3x1) to converts a rotation matrix (3x3)
// The unit is 4 yuan (3x1) Transform rotation matrix (3x3)
// R = quat2rot(q)
//
// q - 3x1 unit quaternion The unit is 4 yuan
// R - 4x4 homogeneous rotation matrix (translation component is zero) 4x4 Homogeneous rotation matrix ( The translation segment is 0)
// q = sin(theta/2) * v The unit is 4 yuan :
// theta - rotation angle Rotation angle
// v - unit rotation axis, |v| = 1 Unit rotation axis
//
// See also: rot2quat, rotx, roty, rotz, transl, rotvec
Eigen::Matrix4d quat2rot(Eigen::Vector3d q)
{
double p = q.transpose()*q;// Unit quaternion length
if (p > 1)
std::cout << "Warning: quat2rot: quaternion greater than 1";// Make sure it's a unit quaternion
double w = sqrt(1 - p); // Calculation q.w // w = cos(theta/2)
Eigen::Matrix4d R;
R << Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(4, 4);// Initialize homogeneous identity matrix
Eigen::Matrix3d res;
res = 2 * (q*q.transpose()) + 2 * w*skew(q);
res = res + Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(3, 3) - 2 * p*Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(3, 3);
R.topLeftCorner(3, 3) << res;// Replace the rotation matrix
return R;
}
// rot2quat - converts a rotation matrix (3x3) to a unit quaternion(3x1)
//
// q = rot2quat(R)
//
// R - 3x3 rotation matrix, or 4x4 homogeneous matrix
// q - 3x1 unit quaternion
// q = sin(theta/2) * v
// teta - rotation angle
// v - unit rotation axis, |v| = 1
// See also: quat2rot, rotx, roty, rotz, transl, rotvec
Eigen::Vector3d rot2quat(Eigen::MatrixXd R)
{
// can this be imaginary? Can this be imagined ?
double w4 = 2 * sqrt(1 + R.topLeftCorner(3, 3).trace());
Eigen::Vector3d q;
q << (R(2, 1) - R(1, 2)) / w4,
(R(0, 2) - R(2, 0)) / w4,
(R(1, 0) - R(0, 1)) / w4;
return q;// The unit is 4 yuan
}
// TRANSL Translational transform Translation transformation
//
// T= TRANSL(X, Y, Z)
// T= TRANSL( [X Y Z] )
//
// [X Y Z]' = TRANSL(T)
//
// [X Y Z] = TRANSL(TG)
//
// Returns a homogeneous transformation representing a
// translation of X, Y and Z.
//
// The third form returns the translational part of a
// homogenous transform as a 3-element column vector.
//
// The fourth form returns a matrix of the X, Y and Z elements
// extracted from a Cartesian trajectory matrix TG.
//
// See also ROTX, ROTY, ROTZ, ROTVEC.
// Copyright (C) Peter Corke 1990
Eigen::Matrix4d transl(Eigen::Vector3d x)// Homogeneous form 3D vector
{
Eigen::Matrix4d r;
r << Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(4, 4);
r.topRightCorner(3, 1) << x;
return r;
}
//Eigen Memory allocator aligned_allocator
// Use every two K = (M*M - M) / 2
// Parameters : gHg: Robot end pose vector . cHw: The pose vector of the image pixel coordinate system in the camera coordinate system . Output : The pose matrix of the camera in the robot terminal coordinate system .
Eigen::Matrix4d handEye(std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > bHg,
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > cHw)
{
int M = bHg.size();
// Number of unique camera position pairs Number of unique camera position pairs
int K = (M*M - M) / 2;
// will store: skew(Pgij+Pcij)
Eigen::MatrixXd A;
A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(3 * K, 3);
// will store: Pcij - Pgij
Eigen::MatrixXd B;
B = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(3 * K, 1);
int k = 0;
// Now convert from wHc notation to Hc notation used in Tsai paper. Now from wHc The symbol is converted to Tsai Used in the paper Hc Symbol .
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > Hg = bHg;
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > Hc = cHw;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < M; j++)
{
//Transformation from i-th to j-th gripper pose and the corresponding quaternion From i One to the first j The transformation of the positions and postures of the grippers and the corresponding quaternions
Eigen::Matrix4d Hgij = Hg.at(j).lu().solve(Hg.at(i));
Eigen::Vector3d Pgij = 2 * rot2quat(Hgij);
// Transformation from i-th to j-th camera pose and the corresponding quaternion
Eigen::Matrix4d Hcij = Hc.at(j)*Hc.at(i).inverse();
Eigen::Vector3d Pcij = 2 * rot2quat(Hcij);
// Form linear system of equations
k = k + 1;
// left-hand side
A.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 3) << skew(Pgij + Pcij);
// right-hand side
B.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 1) << Pcij - Pgij;
}
}
// Rotation from camera to gripper is obtained from the set of equations: The rotation from the camera to the fixture is obtained from a set of equations :
// skew(Pgij+Pcij) * Pcg_ = Pcij - Pgij
// Gripper with camera is first moved to M different poses, then the gripper
// .. and camera poses are obtained for all poses. The above equation uses
// .. invariances present between each pair of i-th and j-th pose.
// Solve the equation A*Pcg_ = B
Eigen::Vector3d Pcg_ = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(B);
// Obtained non-unit quaternin is scaled back to unit value that
// .. designates camera-gripper rotation
Eigen::Vector3d Pcg = 2 * Pcg_ / sqrt(1 + (double)(Pcg_.transpose()*Pcg_));
// Rotation matrix
Eigen::Matrix4d Rcg = quat2rot(Pcg / 2);
// Calculate translational component Calculate translation segments
k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < M; j++)
{
// Transformation from i-th to j-th gripper pose
Eigen::Matrix4d Hgij = Hg.at(j).lu().solve(Hg.at(i));
// Transformation from i-th to j-th camera pose
Eigen::Matrix4d Hcij = Hc.at(j)*Hc.at(i).inverse();
k = k + 1;
// Form linear system of equations
// left-hand side
A.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 3) << Hgij.topLeftCorner(3, 3) - Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(3, 3);
// right-hand side
B.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 1) << Rcg.topLeftCorner(3, 3)*Hcij.block(0, 3, 3, 1) - Hgij.block(0, 3, 3, 1);
}
}
Eigen::Vector3d Tcg = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(B);
// incorporate translation with rotation
Eigen::Matrix4d gHc = transl(Tcg) * Rcg;
return gHc;
}
// Only two adjacent K = M-1
// Parameters : gHg: Robot end pose vector . cHw: The pose vector of the image pixel coordinate system in the camera coordinate system . Output : The pose matrix of the camera in the robot terminal coordinate system .
Eigen::Matrix4d handEye1(std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > bHg,
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > cHw)
{
int M = bHg.size();
// Number of unique camera position pairs
int K = M - 1;
// will store: skew(Pgij+Pcij)
Eigen::MatrixXd A;
A = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(3 * K, 3);
// will store: Pcij - Pgij
Eigen::MatrixXd B;
B = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(3 * K, 1);
int k = 0;
// Now convert from wHc notation to Hc notation used in Tsai paper.
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > Hg = bHg;
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > Hc = cHw;
for (int i = 0; i < M - 1; i++)
{
//Transformation from i-th to j-th gripper pose and the corresponding quaternion
Eigen::Matrix4d Hgij = Hg.at(i + 1).lu().solve(Hg.at(i));
Eigen::Vector3d Pgij = 2 * rot2quat(Hgij);
// Transformation from i-th to j-th camera pose and the corresponding quaternion
Eigen::Matrix4d Hcij = Hc.at(i + 1)*Hc.at(i).inverse();
Eigen::Vector3d Pcij = 2 * rot2quat(Hcij);
//Form linear system of equations
k = k + 1;
//left-hand side
A.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 3) << skew(Pgij + Pcij);
//right-hand side
B.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 1) << Pcij - Pgij;
}
// Rotation from camera to gripper is obtained from the set of equations:
// skew(Pgij+Pcij) * Pcg_ = Pcij - Pgij
// Gripper with camera is first moved to M different poses, then the gripper
// .. and camera poses are obtained for all poses. The above equation uses
// .. invariances present between each pair of i-th and j-th pose.
// Solve the equation A*Pcg_ = B
Eigen::Vector3d Pcg_ = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(B);
// Obtained non-unit quaternin is scaled back to unit value that
// .. designates camera-gripper rotation
Eigen::Vector3d Pcg = 2 * Pcg_ / sqrt(1 + (double)(Pcg_.transpose()*Pcg_));
// Rotation matrix
Eigen::Matrix4d Rcg = quat2rot(Pcg / 2);
// Calculate translational component
k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < M - 1; i++)
{
// Transformation from i-th to j-th gripper pose
Eigen::Matrix4d Hgij = Hg.at(i + 1).lu().solve(Hg.at(i));
// Transformation from i-th to j-th camera pose
Eigen::Matrix4d Hcij = Hc.at(i + 1)*Hc.at(i).inverse();
// Form linear system of equations
k = k + 1;
// left-hand side
A.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 3) << Hgij.topLeftCorner(3, 3) - Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(3, 3);
B.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 1) << Rcg.topLeftCorner(3, 3)*Hcij.block(0, 3, 3, 1) - Hgij.block(0, 3, 3, 1);
B.block(3 * k - 3, 0, 3, 1) << Rcg.topLeftCorner(3, 3)*Hcij.block(0, 3, 3, 1) - Hgij.block(0, 3, 3, 1);
}
Eigen::Vector3d Tcg = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(B);
// incorporate translation with rotation
Eigen::Matrix4d gHc = transl(Tcg) * Rcg;
return gHc;
}
// Parameters : Calibration results . Data directory path
int handEye_calib(Eigen::Matrix4d &gHc, std::string path)
{
ofstream ofs(path + "/output.txt");// File output stream : Log during calibration . And calibration results Internal parameter distortion coefficient .
std::vector<cv::Mat> images;// Picture vector
// Read in the picture
std::cout << "****************** Read in the picture ......******************" << std::endl;
ofs << "****************** Read in the picture ......******************" << std::endl;// output to a file
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_all_images; i++)// Go through all the pictures
{
std::string image_path;
image_path = path + "/" + std::to_string(i) + ".png";//1.png 2.png Picture path
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(image_path, 0);// Read pictures into memory image
std::cout << "image_path: " << image_path << std::endl;// Output picture path
if (!image.empty())// The picture is not empty
images.push_back(image);// Add to vector
else
{
std::cout << "can not find " << image_path << std::endl;// Unable to find the picture
exit(-1);
}
}
// Update the actual number of pictures
int num_of_images = images.size();
std::cout << "****************** Read in the picture ******************" << std::endl;
ofs << "****************** Read in the picture !******************" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Actual number of pictures : " << num_of_images << std::endl;
ofs << " Actual number of pictures : " << num_of_images << std::endl;
// Extract corners
std::cout << "****************** Start corner extraction ......******************" << std::endl;
ofs << "****************** Start corner extraction ......******************" << std::endl;
// Image size
cv::Size image_size;
std::vector<cv::Point2f> image_points_buff;// Two dimensional point vector
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point2f>> image_points_seq;// Image point set Sequence
int num_img_successed_processing = 0;// Number of pictures processed successfully
for (int i = 0; i < images.size(); i++)// Go through all the pictures
{
cv::Mat image = images[i];// Take a picture
if (i == 0)
{
// First image
image_size.width = image.cols;// The width of the image : Pixels
image_size.height = image.rows;// Height of the image
}
//9 That's ok 7 Column corner , Find out the corners of the checkerboard , write in image_points_buff.
/*flags: The checkerboard corner detection method sets the marker position
CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH Use adaptive threshold to transform gray image into binary image , Instead of a fixed threshold calculated from the average brightness of the image
CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE Before binarization with fixed threshold or adaptive threshold , First use equalizeHist To equalize the image gamma value .
CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS Use other guidelines ( Such as contour area , Perimeter , Like a square shape ) To remove the error blocks detected in the contour detection stage .
CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK Quickly detect the corners of the checkerboard on the image , If no checkerboard corner is found , Bypass other time-consuming function calls , This can shorten the execution time of the whole function in case that the image is not observed and in bad circumstances .*/
if (0 == cv::findChessboardCorners(image, board_size, image_points_buff,
cv::CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH | cv::CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE /*+ cv::CALIB_CB_FAST_CHECK*/))
{
std::cout << "can not find chessboard corners! " << std::endl;
ofs << "can not find chessboard corners! " << std::endl;
continue;
}
else// Find the corner of the chessboard
{ // Accurate corner position in corner detection
// Parameters image: The input image . image_points_buff: Input the initial coordinates of the corner and the accurate coordinates for output
//winSize: Half the side length of the search window , For example, if winSize=Size(5,5), Then a size is : The search window of will be used .
//zeroZone: In the middle of the search area dead region Half the side length , Sometimes used to avoid the singularity of autocorrelation matrix . If the value is set to (-1,-1) It means there is no such area .
//criteria: The termination condition of the iteration . That is, when the number of iterations exceeds criteria.maxCount, Or the change of corner position is less than criteria.epsilon when , Stop the iteration process .
cv::cornerSubPix(image, image_points_buff, cv::Size(3, 3), cv::Size(-1, -1),
cv::TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_EPS + CV_TERMCRIT_ITER, 30, 0.1));// Extract sub-pixel corner information
// Refine the corners of rough extraction
// cv::find4QuadCornerSubpix(image, image_points_buff, cv::Size(5, 5));
// Save subpixel corners
image_points_seq.push_back(image_points_buff);// Corners are added to the sequence first
std::cout << "successed processing :" << num_img_successed_processing++ << std::endl;
cv::Mat image_color;
cv::cvtColor(image, image_color, CV_GRAY2BGR);// Conversion used to convert an image from one color space to another , From gray space to RGB and BGR Color space
cv::drawChessboardCorners(image_color, board_size, image_points_buff, true);// Corner drawing
std::stringstream namestream;// Character stream
std::string name;// character string
namestream << "/" << i << "_corner.png";// Build character stream
namestream >> name;// Assign a value to the character thick
cv::imwrite(path + name, image_color);// Store the color image drawn with corners in disk
}
}
// The number of images is updated again according to the number of images in which corners are detected
num_of_images = image_points_seq.size();// Number of images with corners detected
std::cout << "****************** Corner extraction complete !******************" << std::endl;
ofs << "****************** Corner extraction complete !******************" << std::endl;
// Camera calibration
std::cout << "****************** Start camera calibration ......******************" << std::endl;
ofs << "****************** Start camera calibration ......******************" << std::endl;
// Save the three-dimensional coordinates of the corners on the calibration plate
std::vector<std::vector<cv::Point3f>> object_points;
// Internal and external references
// Internal reference
cv::Mat camera_matrix = cv::Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, cv::Scalar::all(0));//3x3 Zero matrix
std::vector<int> point_counts;// points vector
// Distortion coefficient : k1, k2, p1, p2, k3
cv::Mat dist_coeff = cv::Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, cv::Scalar::all(0));//1x5 Zero matrix
// Translation vector
std::vector<cv::Mat> t_vec;//
// Rotating vector
std::vector<cv::Mat> r_vec;
// Initialize the 3D coordinates of the corner on the calibration board
int i, j, k;
for (k = 0; k < num_of_images; k++)// Traverse the image with corner detected
{
//std::cout << "image.NO:" << k << std::endl;
std::vector<cv::Point3f> temp_point_set;
for (i = 0; i < board_size.height; i++)// Every line
{
for (j = 0; j < board_size.width; j++)// Each column
{
cv::Point3f real_point;
real_point.x = j * square_size.width;// theory x spot
real_point.y = i * square_size.height;// theory y spot
real_point.z = 0;// Default in z Plane
// std::cout << "real_point cordinates" << real_point << std::endl;
temp_point_set.push_back(real_point);// Set of theoretical points
}
}
object_points.push_back(temp_point_set);// Image theoretical corner coordinates vector . ( initialization ) The world coordinates of each inner corner
}
// Initialize the number of corners on each image
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_images; i++)
{
point_counts.push_back(board_size.width*board_size.height);// Number of image corners vector
}
// Start calibration
std::cout << "****************** Began to run calibrateCamera!******************" << std::endl;
// Parameters : object_points: All image theoretical corner coordinates . Corner coordinates in the image coordinate system .
//image_points_seq: Corner coordinate vectors detected by all images
//image_size: The size of the first image . Is the pixel size of the image , This parameter needs to be used when calculating internal parameter distortion matrix of the camera ;
//camera_matrix: Camera internal parameter matrix
//dist_coeff: Distortion coefficient
//r_vec: Rotation vector : Transformation matrix from theoretical corner to photographed corner Rotation vector .
//t_vec: Translation vector
//0: Parameters flags Is the algorithm used in calibration .CV_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS: When using this parameter , stay cameraMatrix There should be... In the matrix fx,fy,u0,v0 The estimate of . Otherwise , Will initialize (u0,v0) The center point of the image , Use least squares to estimate fx,fy.
/*CV_EXPORTS_W double calibrateCamera( InputArrayOfArrays objectPoints,
InputArrayOfArrays imagePoints,
Size imageSize,
CV_OUT InputOutputArray cameraMatrix,
CV_OUT InputOutputArray distCoeffs,
OutputArrayOfArrays rvecs, OutputArrayOfArrays tvecs,
int flags=0, TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(
TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS, 30, DBL_EPSILON) );*/
cv::calibrateCamera(object_points, image_points_seq, image_size, camera_matrix, dist_coeff, r_vec, t_vec, 0);
std::cout << "****************** Calibration complete !******************" << std::endl;
std::cout << camera_matrix << std::endl;
std::cout << dist_coeff << std::endl;
// Evaluation of calibration results
std::cout << "****************** Start to evaluate the calibration results ......******************" << std::endl;
double total_err = 0.0;
double err = 0.0;
// Save the recalculated projection points
std::vector<cv::Point2f> image_points2;
std::cout << std::endl << " The calibration error of each image : " << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_images; i++)// Traverse each image
{
std::vector<cv::Point3f> temp_point_set = object_points[i];// Theoretical corner coordinates of image coordinate system
// Remap Parameters :
//temp_point_set: Three dimensional corner coordinates in the image coordinate system .
//r_vec[i]: The first i Rotation vector of image
//t_vec[i]: The first i Translation vector of image
//camera_matrix: Calibrated internal parameter matrix
//dist_coeff: Distortion coefficient after calibration .
//image_points2: The first i Recalculated projection point of image .
cv::projectPoints(temp_point_set, r_vec[i], t_vec[i], camera_matrix, dist_coeff, image_points2);
std::vector<cv::Point2f> temp_image_points = image_points_seq[i];// The first i Corner coordinates detected in the image
cv::Mat temp_image_points_Mat = cv::Mat(1, temp_image_points.size(), CV_32FC2);
cv::Mat temp_image_points2_Mat = cv::Mat(1, image_points2.size(), CV_32FC2);
for (int j = 0; j < temp_image_points.size(); j++)
{
temp_image_points_Mat.at<cv::Vec2f>(0, j) = cv::Vec2f(temp_image_points[j].x, temp_image_points[j].y);// Detection point
temp_image_points2_Mat.at<cv::Vec2f>(0, j) = cv::Vec2f(image_points2[j].x, image_points2[j].y);// Projection point
}
err = cv::norm(temp_image_points_Mat, temp_image_points2_Mat, cv::NORM_L2);// Two norms of two sets of points
total_err += err /= point_counts[i];// All images Average error of corner Accumulation .
std::cout << " The first " << i + 1 << " The average error of an image : " << err << " Pixels " << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl << " Overall average error : " << total_err / num_of_images << " Pixels " << std::endl;// Average error of all images
std::cout << "****************** Evaluation completed !******************" << std::endl;
// Output calibration results
std::cout << "****************** The calibration results are as follows :******************" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Inside the camera :" << std::endl;
std::cout << camera_matrix << std::endl;
std::cout << " Distortion coefficient :" << std::endl;
std::cout << dist_coeff.t() << std::endl;
// output to a file
ofs << "****************** The calibration results are as follows :******************" << std::endl;
ofs << " Inside the camera :" << std::endl;
ofs << camera_matrix << std::endl;
ofs << " Distortion coefficient :" << std::endl;
ofs << dist_coeff.t() << std::endl;
// Start hand eye calibration
std::cout << "****************** Began to run calibrate handEye!******************" << std::endl;
//https://blog.csdn.net/renweiyi1487/article/details/104097576
/* If STL The elements in the container are Eigen Library data structure , For example, here is a definition of vector Containers , The element is Matrix4d , As shown below :
vector<Eigen::Matrix4d>
This error is the same as the above prompt , Compilation won't go wrong , Only in the run-time error . The solution is simple , Change the definition to the following way :
vector<Eigen::Matrix4d,Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d>>;
In fact, the above code is the standard method for defining containers , But generally, the elements that define the container are C++ The type of , So you can omit , This is because in the C++11 In the standard ,aligned_allocator management C++ The memory methods of various data types in are the same , You don't have to rewrite it . But in Eigen Manage memory and C++11 The method in is different , Therefore, the memory allocation and management of elements need to be emphasized separately .
*/
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > bHg;// Robot end pose matrix vector
std::vector<Eigen::Matrix4d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Matrix4d> > cHw;// The transformation matrix between the pixel coordinate system of the image and the camera coordinate system vector
std::ifstream ifs;
ifs.open(path + "/pose.txt", std::ios::in);
if (!ifs.is_open())
{
std::cout << "pose file not found" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
std::cout << "pose file found" << std::endl;// Find the robot end pose file
}
// Read the robot posture and convert it into eigen matrix
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_images; i++)// Several images Several robot positions
{
double temp;
Eigen::Vector3d trans_temp;// Translation vector
std::cout << "pose[" << i << "]:\n";
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
ifs >> temp;// Read translation vector segments x /y/z
std::cout << temp << " ";
trans_temp(j) = temp;
}
std::vector<double> v(3, 0.0);
ifs >> v[0] >> v[1] >> v[2];// Read RPY Three angles ( Rotate around the fixed coordinate system in turn : roll:X-V[0] Pitch:Y-V[1] Yaw:Z-V[2])
std::cout << "RPY: " << v[0] << " " << v[1] << " " << v[2] << " " << std::endl;
// Calculate the attitude quaternion : RotZ(V[2])*RotY(V[1])*RotX(V[0]) Euler Angle RPY Represent the Roll( Roll angle ),Pitch( Pitch angle ),Yaw( Yaw angle ), Respectively corresponding to XYZ Shaft rotation
Eigen::Quaterniond m = Eigen::AngleAxisd(v[2] / 180 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ())
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(v[1] / 180 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY())\
* Eigen::AngleAxisd(v[0] / 180 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
double w, x, y, z;
x = m.x(); y = m.y(); z = m.z(); w = m.w();
Eigen::Quaterniond rot_temp(w, x, y, z);// Temporary posture quaternion
Eigen::Matrix4d pose_temp;// Pose matrix 4X4
pose_temp << Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(4, 4);// Basis,
// Quaternion rotation matrix
pose_temp.topLeftCorner(3, 3) << rot_temp.toRotationMatrix();
pose_temp.topRightCorner(3, 1) << trans_temp;
std::cout << "bHg:" << std::endl;
std::cout << pose_temp << "\n" << std::endl;
bHg.push_back(pose_temp);// Robot end pose matrix vector
}
ifs.close();
//r_vec and t_vec Turn into Eigen matrix
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_images; i++)// Traverse Number of shots
{
Eigen::Matrix4d pose_temp;
cv::Mat rot_temp;
// Rodriguez transformation , Rotation vector rotation matrix
cv::Rodrigues(r_vec.at(i), rot_temp);// The length of the rotation vector ( model ) Represents the angle of counterclockwise rotation around the axis ( radian )
Eigen::MatrixXd rot_eigen;
Eigen::MatrixXd trans_eigen;
cv::cv2eigen(rot_temp, rot_eigen);//cv::Mat -> Eigen::MatrixXd
cv::cv2eigen(t_vec.at(i), trans_eigen);
pose_temp.topLeftCorner(3, 3) << rot_eigen;
pose_temp.topRightCorner(3, 1) << trans_eigen;
pose_temp(3, 0) = 0;
pose_temp(3, 1) = 0;
pose_temp(3, 2) = 0;
pose_temp(3, 3) = 1;
cHw.push_back(pose_temp);// The transformation matrix between the pixel coordinate system of the image and the camera coordinate system vector
}
Eigen::AngleAxisd v;// horn - Axis vector
for (int m = 0; m < bHg.size(); m++)// Traverse the end pose of the robot
{// write file output.txt
ofs << "num:" << m << std::endl;// The first m A robot pose
ofs << "bHg" << std::endl;
ofs << bHg.at(m) << std::endl;// The first m A robot terminal pose matrix
v.fromRotationMatrix((Matrix3d)bHg.at(m).topLeftCorner(3, 3));// Robot end pose rotation matrix corresponding Space axis angle vector
ofs << "axis: " << v.axis().transpose() << std::endl << "angle: " << v.angle() / PI * 180 << std::endl;// write file : Space rotation axis , Rotation Angle
ofs << "cHw" << std::endl;
ofs << cHw.at(m) << std::endl;// Transformation matrix from image pixel coordinate system to camera coordinate system
v.fromRotationMatrix((Matrix3d)cHw.at(m).topLeftCorner(3, 3));// Space axis angle
ofs << "axis: " << v.axis().transpose() << std::endl << "angle: " << v.angle() / PI * 180 << std::endl;
}
gHc = handEye(bHg, cHw);// Calculate the transformation matrix from the end of the robot to the camera
std::cout << "\n\n\nCalibration Finished: \n" << std::endl;// Calibration completed
std::cout << "gHc" << std::endl;
ofs << std::endl << "gHc" << std::endl;
std::cout << gHc << std::endl;
ofs << gHc << std::endl;// The pose matrix of the camera relative to the end of the robot , write in output.txt
v.fromRotationMatrix((Matrix3d)gHc.topLeftCorner(3, 3));// Space axis angle vector
std::cout << "axis: " << v.axis().transpose() << std::endl << "angle: " << v.angle() / PI * 180 << std::endl;
ofs << "axis: " << v.axis().transpose() << std::endl << "angle: " << v.angle() / PI * 180 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Eigen::Matrix4d gHc;//camera relative hand Pose matrix .
handEye_calib(gHc, "./data");
return 1;
}
边栏推荐
- 01. Go language introduction
- 1. Introduction to basic functions of power query
- Global and Chinese market of wheelchair climbing machines 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- How does redis implement multiple zones?
- 【coppeliasim】高效传送带
- Grabbing and sorting out external articles -- status bar [4]
- Unity learning notes -- 2D one-way platform production method
- Selenium waiting mode
- Ali test Open face test
- Overview of spark RDD
猜你喜欢
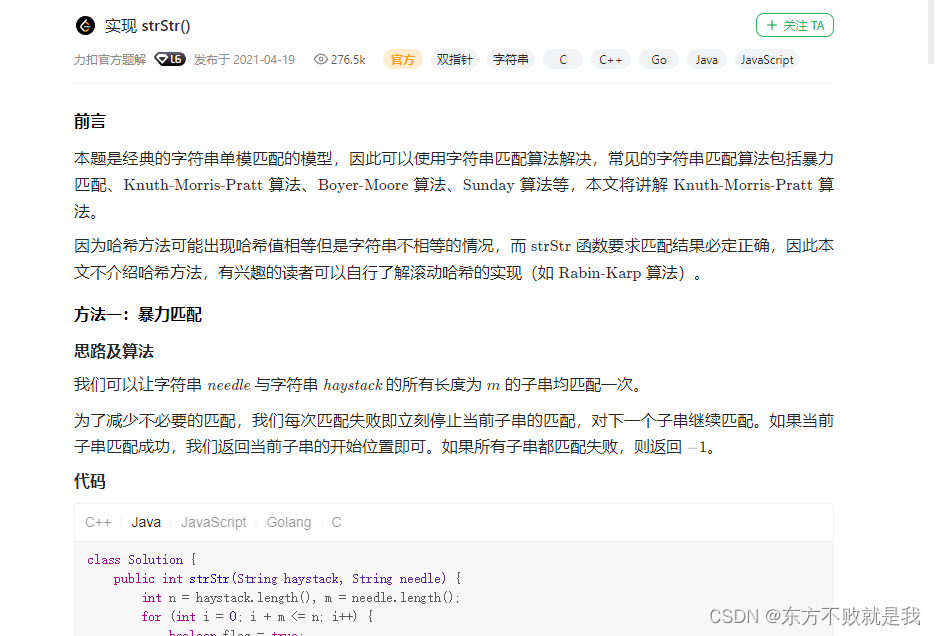
Leetcode3. Implement strstr()

Leetcode3, implémenter strstr ()
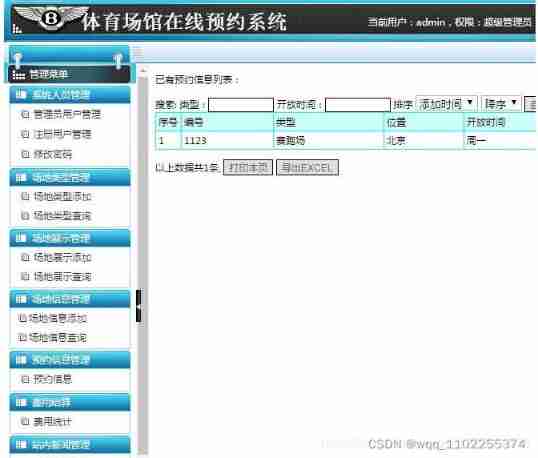
Online reservation system of sports venues based on PHP

【社区人物志】专访马龙伟:轮子不好用,那就自己造!

Basic operations of databases and tables ----- unique constraints
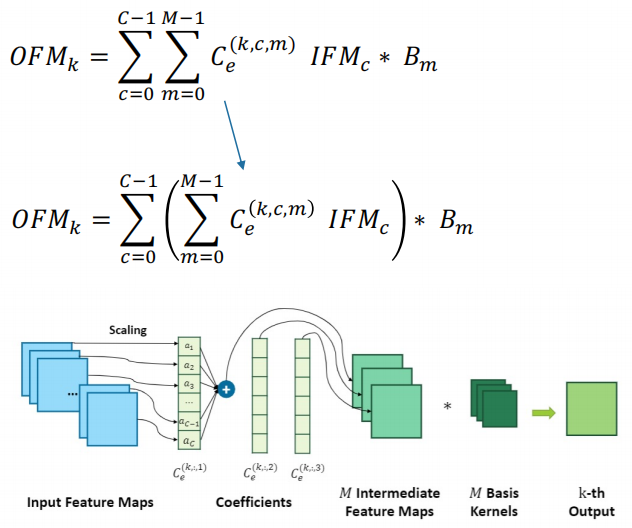
dried food! Accelerating sparse neural network through hardware and software co design
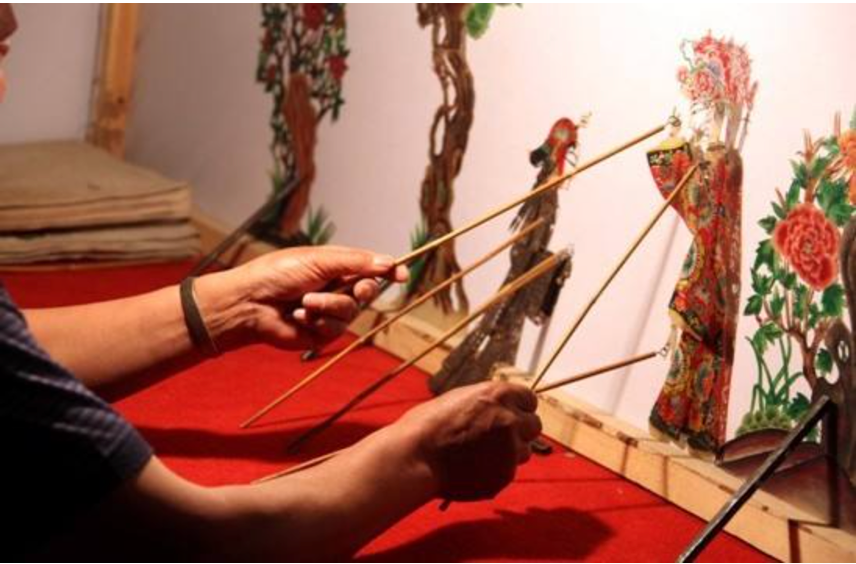

国家级非遗传承人高清旺《四大美人》皮影数字藏品惊艳亮相!
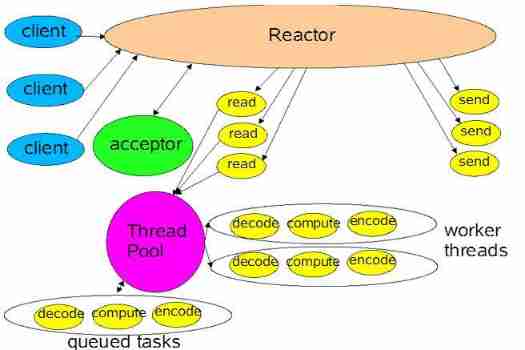
NiO related knowledge (II)
Redis-字符串类型

Overview of spark RDD
随机推荐
Dynamics 365 开发协作最佳实践思考
Grabbing and sorting out external articles -- status bar [4]
500 lines of code to understand the principle of mecached cache client driver
How to set an alias inside a bash shell script so that is it visible from the outside?
Apicloud openframe realizes the transfer and return of parameters to the previous page - basic improvement
Exness: Mercedes Benz's profits exceed expectations, and it is predicted that there will be a supply chain shortage in 2022
Online reservation system of sports venues based on PHP
Sword finger offer 12 Path in matrix
国家级非遗传承人高清旺《四大美人》皮影数字藏品惊艳亮相!
Ali test Open face test
0211 embedded C language learning
Ali test open-ended questions
阿裏測開面試題
Thinking about the best practice of dynamics 365 development collaboration
leetcode3、實現 strStr()
Spark accumulator
【网络攻防实训习题】
Global and Chinese market of wheelchair climbing machines 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Redis-字符串类型
Competition question 2022-6-26