当前位置:网站首页>[oiclass] share prizes
[oiclass] share prizes
2022-07-06 14:48:00 【Liujincheng LJC】
Share prizes
Title Description
In the school creative knowledge competition , Mingming and Wenwen got a total of n(1≦ n≦250) A prize , Every prize has a value Vi (1 ≦ Vi ≦ 2,000). They want to share these prizes equally by value , If you can't score equally, try to minimize the gap between them . Now give the number of prizes and their value , Clearly want to calculate the minimum difference after division , And the number of schemes divided .
for example : Yes 5 The value of each prize is :2, 1,8, 4, 16. Mingming and Wenwen are divided into two parts , The first four are part 1+2+4+8=15,16 As a separate part , Then the difference between the two parts :16-15 = 1. This is the division scheme with the smallest gap , And the division method of this scheme is only 1 Kind of .
Prizes of the same value intersect and convert into different schemes , Such as : There are four prizes worth {1, 1, 1, 1}, Yes 6 There are different division schemes , Divide these prizes into two parts , Every part of it 2 A prize .
Input
first line : An integer n(1≦n≦250);
Then there was n That's ok , One integer per row Vi (1 ≦ Vi ≦ 2,000) Represents the value of each prize .
Output
first line : An integer , Represents the minimum difference between the two parts of the division .
The second line : An integer , The number of division schemes representing the minimum difference , The result is right 1,000,000 Seeking remainder (mod 1,000,000).
The sample input #1:
5
2
1
8
4
16
Sample output #1:
1
1
The sample input #2:
4
1
1
1
1
Sample output #2:
0
6
Ideas
First, we can use the idea of dynamic programming :
set up f[i][j] For the former i The value of these prizes is j Different schemes
So the equation of state transition is going to be :
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j]+f[i-1][j-a[i]]
The code written at this time is like this :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000;
const int N = 300;
int n,a[N],f[N][2000*N];
int maxn = 0;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin >> a[i],maxn+=a[i];
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=maxn;j++){
f[i][j] = (f[i-1][j]+f[i-1][j-a[i]])%MOD;
}
}
int ans=2000*N,cnt=-1;
for(int j=0;j<=maxn;j++){
if(abs((maxn-j)-j)<ans){
ans = abs((maxn-j)-j);
cnt = f[n][j];
}
}
cout << ans << endl << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
result : MLE
The space complexity of this code is too high . So I put f The first dimension of is changed to a scrolling array :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000;
const int N = 260;
int n,a[N],f[3][2000*N];
bool vis[3][2000*N];
int maxn = 0;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin >> a[i],maxn+=a[i];
f[0][0] = 1;
vis[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=maxn;j++){
if(j-a[i]>=0){
f[i%2][j] = (f[(i-1)%2][j]+f[(i-1)%2][j-a[i]])%MOD;
vis[i%2][j]= vis[(i-1)%2][j] || vis[(i-1)%2][j-a[i]];
}
else{
f[i%2][j] = f[(i-1)%2][j];
vis[i%2][j] = vis[(i-1)%2][j];
}
}
}
int ans=2000*N,cnt=-1;
for(int j=0;j<=maxn;j++){
if(abs((maxn-j)-j)<ans and vis[n%2][j]!=0){
ans = abs((maxn-j)-j);
cnt = f[n%2][j];
}
}
cout << ans << endl << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
This time it became TLE
Time optimization , take mod The final answer is :
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 1000000;
const int N = 260;
int n,a[N],sum[N],f[3][2000*N];
bool vis[3][2000*N];
int maxn = 0;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin >> a[i];
maxn+=a[i];
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+a[i];
}
f[0][0] = 1;
vis[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int I2=i%2,I12=(i-1)%2;
for(int j=0;j<=sum[i];j++){
if(j-a[i]>=0){
f[I2][j] = f[I12][j]+f[I12][j-a[i]];
if(f[I2][j]>=MOD) f[I2][j]-=MOD;
vis[I2][j]= vis[I12][j] || vis[I12][j-a[i]];
}
else{
f[I2][j] = f[I12][j];
vis[I2][j] = vis[I12][j];
}
}
}
int ans=2000*N,cnt=-1;
for(int j=0;j<=maxn;j++){
if(abs((maxn-j)-j)<ans and vis[n%2][j]!=0){
ans = abs((maxn-j)-j);
cnt = f[n%2][j];
}
}
cout << ans << endl << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
Turned into AC !
边栏推荐
- Sword finger offer 23 - print binary tree from top to bottom
- How to earn the first pot of gold in CSDN (we are all creators)
- 5分钟掌握机器学习鸢尾花逻辑回归分类
- What is the transaction of MySQL? What is dirty reading and what is unreal reading? Not repeatable?
- Numpy Quick Start Guide
- With 27K successful entry ByteDance, this "software testing interview notes" has benefited me for life
- Pointer -- output all characters in the string in reverse order
- Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 7 Summary of knowledge points and answers to exercises after class
- 数字电路基础(一)数制与码制
- Flash implements forced login
猜你喜欢

Binary search tree concept

Summary of thread implementation
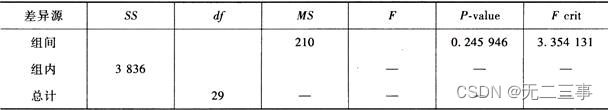
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第十章方差分析知识点总结及课后习题答案
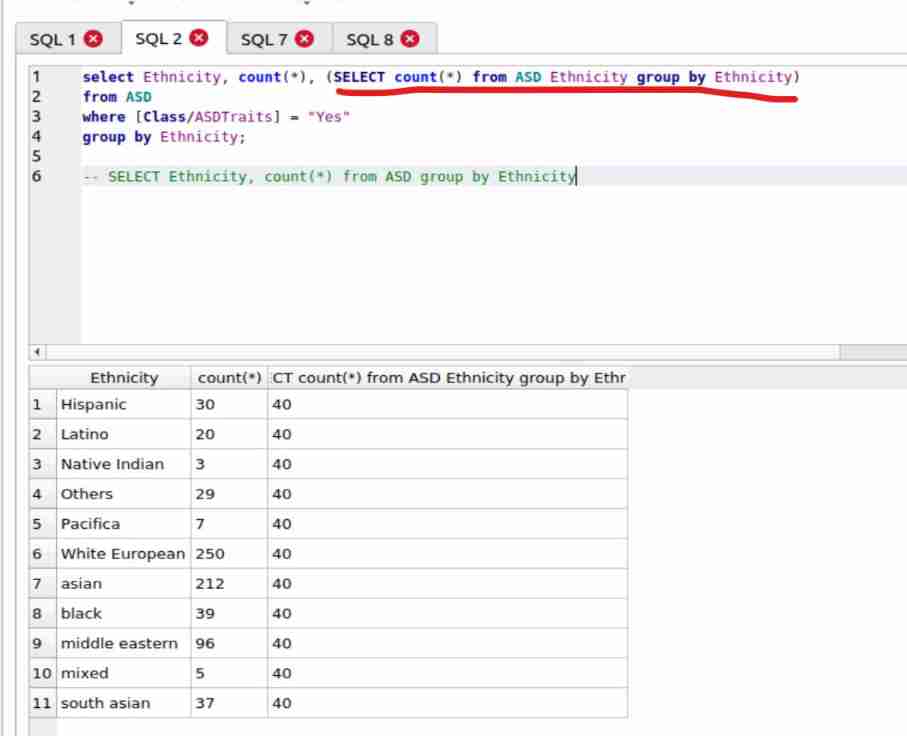
How does SQLite count the data that meets another condition under the data that has been classified once
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第三章课后习题及答案总结
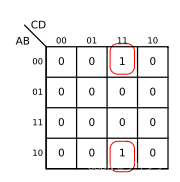
数字电路基础(二)逻辑代数
servlet中 servlet context与 session与 request三个对象的常用方法和存放数据的作用域。
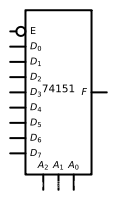
数字电路基础(四) 数据分配器、数据选择器和数值比较器

Résumé des points de connaissance et des réponses aux exercices après la classe du chapitre 7 de Jia junping dans la huitième édition des statistiques
MySQL中什么是索引?常用的索引有哪些种类?索引在什么情况下会失效?
随机推荐
函数:字符串反序存放
《统计学》第八版贾俊平第九章分类数据分析知识点总结及课后习题答案
Lintcode logo queries the two nearest saplings
Function: find 1-1/2+1/3-1/4+1/5-1/6+1/7-... +1/n
指针 --按字符串相反次序输出其中的所有字符
【指针】求解最后留下的人
Markdown font color editing teaching
浙大版《C语言程序设计实验与习题指导(第3版)》题目集
Mysql的事务是什么?什么是脏读,什么是幻读?不可重复读?
王爽汇编语言详细学习笔记二:寄存器
Statistics 8th Edition Jia Junping Chapter 10 summary of knowledge points of analysis of variance and answers to exercises after class
[pointer] find the length of the string
Zhejiang University Edition "C language programming experiment and exercise guide (3rd Edition)" topic set
1.支付系统
Captcha killer verification code identification plug-in
[pointer] find the value of the largest element in the two-dimensional array
Database monitoring SQL execution
数字电路基础(四) 数据分配器、数据选择器和数值比较器
5分钟掌握机器学习鸢尾花逻辑回归分类
Fundamentals of digital circuit (V) arithmetic operation circuit