当前位置:网站首页>Chain team implementation (C language)
Chain team implementation (C language)
2022-07-06 14:16:00 【An Ruoxi~】
We have known about stack before , We know , Stack is first in first out , Last in, first out
Then the team is first in, first out , last in last out
It's like we go to the queue to buy food , The person in the front row will buy it first , It's natural, right >-<
So we know the principle of team , It is relatively easy to realize the chain team .
Here we should pay attention to : The head node here cannot be the same as the previous head node , Because this is a chain queue , The required operation is first in, first out , last in last out , Tail plug deletion , So here our head node should have two pointer fields , Point to the position to be inserted and the position to be deleted respectively .
Let's declare the function in the header file first
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
typedef struct Node {
ELEM_TYPE data;
struct Node* next;
}Node,*PNode;
typedef struct Head {
struct Node* front;
struct Node* rear;
}Head,*Plist;
void Init(Plist plq);
bool Push(Plist plq,ELEM_TYPE val);
bool Pop(Plist plq);
bool Top(Plist plq,ELEM_TYPE* rtval);
int Getlength(Plist plq);
bool IsEmpty(Plist plq);
void Clear(Plist plq);
void Destory(Plist plq);
void Show(Plist plq);Function definition in header file
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"list_queue.h"
void Init(Plist plq) {
assert(plq!=NULL);
plq->front = NULL;
plq->rear = NULL;
}
bool Push(Plist plq, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plq != NULL);
struct Node* pnewnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
assert(pnewnode!=NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
if (IsEmpty(plq)) {
pnewnode->next = NULL;
plq->front = plq->rear = pnewnode;
return true;
}
pnewnode->next = plq->rear->next;
plq->rear->next = pnewnode;
plq->rear = pnewnode;
return true;
}
bool Pop(Plist plq) {
assert(plq!=NULL);
if (IsEmpty(plq)) {
return false;
}
if (plq->front->next==NULL){//plq->front==plq->rear
free(plq->front);
plq->front = plq->rear = NULL;
return true;
}
struct Node* p = plq->front;
plq->front = p->next;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return true;
}
bool Top(Plist plq, ELEM_TYPE* rtval) {
assert(plq != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(plq)) {
return false;
}
*rtval = plq->front->data;
return true;
}
int Getlength(Plist plq) {
assert(plq!=NULL);
int count = 0;
for (struct Node* p = plq->front; p!= NULL;p=p->next) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
bool IsEmpty(Plist plq) {
assert(plq!=NULL);
return plq->front == NULL;
}
void Clear(Plist plq) {
assert(plq!=NULL);
Destory(plq);
}
void Destory(Plist plq) {
assert(plq != NULL);
/*while (plq->front!=NULL) {
struct Node* p = plq->front;
plq->front = p->next;
free(p);
}
plq->rear =plq->front= NULL;*/
struct Node* p = plq->front;
struct Node* q;
plq->front = plq->rear = NULL;
while (p!=NULL) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
void Show(Plist plq) {
assert(plq != NULL);
for (struct Node* p = plq->front; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
printf("%5d",p->data);
}
printf("\n");
}The test file
The test case
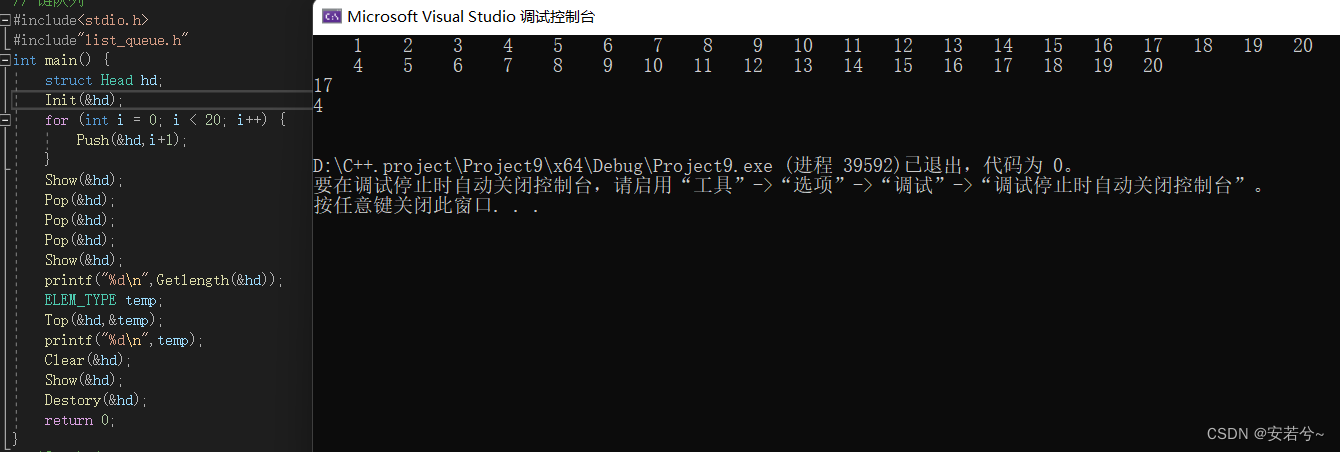
#include<stdio.h>
#include"list_queue.h"
int main() {
struct Head hd;
Init(&hd);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
Push(&hd,i+1);
}
Show(&hd);
Pop(&hd);
Pop(&hd);
Pop(&hd);
Show(&hd);
printf("%d\n",Getlength(&hd));
ELEM_TYPE temp;
Top(&hd,&temp);
printf("%d\n",temp);
Clear(&hd);
Show(&hd);
Destory(&hd);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Analysis of penetration test learning and actual combat stage
[experiment index of educator database]
Sqqyw (indifferent dot icon system) vulnerability recurrence and 74cms vulnerability recurrence
7-7 7003 组合锁(PTA程序设计)
浅谈漏洞发现思路
XSS之冷门事件
sqqyw(淡然点图标系统)漏洞复现和74cms漏洞复现
[insert, modify and delete data in the headsong educator data table]
HackMyvm靶机系列(1)-webmaster
Xray and Burp linked Mining
Xray and burp linkage mining
JS several ways to judge whether an object is an array
Hackmyvm target series (4) -vulny
外网打点(信息收集)
Feature extraction and detection 14 plane object recognition
记一次api接口SQL注入实战
C language file operation
Harmonyos JS demo application development
The difference between layer 3 switch and router
实验七 常用类的使用(修正帖)
![[paper reproduction] cyclegan (based on pytorch framework) {unfinished}](/img/16/43d8929d1a37c1c68e959d5854e18c.jpg)