当前位置:网站首页>Strengthen basic learning records
Strengthen basic learning records
2022-07-06 13:52:00 【I like the strengthened Xiaobai in Curie】
Strengthening learning Q-learning and Saras Comparison of
Multi agent reinforcement learning small white one , Recently, I am learning to strengthen the foundation of learning , Record here , In case you forget .
One 、Q-learning
Q-learing The most basic reinforcement learning algorithm , adopt Q Table storage status - Action value , namely Q(s,a), It can be used for problems with small state space , When the dimension of state space is large , Need to cooperate with neural network , Expanded into DQN Algorithm , Dealing with problems .
- Value-based
- Off-Policy
Read a lot about On-Policy and Off-Policy The blog of , I haven't quite understood the difference between the two , I'm confused , I read a blogger's answer two days ago , Only then have a deeper understanding , A link is attached here .
link : on-policy and off-policy What's the difference? ?
When Q-learning update , Although the data used is current policy Produced , But the updated strategy is not the one that generates this data ( Pay attention to the... In the update formula max), It can be understood here : there max The operation is to select a larger Q A worthy action , to update Q surface , But the actual round may not be changed , So it is Off-Policy Of . - Pseudo code

- Realization
The environment used here is the treasure hunt game in the teacher's tutorial , Maintain through lists ,—#-T, The last position T It's a treasure ,# Represents the current position of the player , Go to the rightmost grid , Find the treasure , Game over .
The code implementation refers to a blogger , Can't find the link .....
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
N_STATES = 6 # 6 Status , One dimensional array length
ACTIONS = [-1, 1] # Two states ,-1:left, 1:right
epsilon = 0.9 # greedy
alpha = 0.1 # Learning rate
gamma = 0.9 # Diminishing reward value
max_episodes = 10 # Maximum rounds
fresh_time = 0.3 # Move interval
# q_table
q_table = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((N_STATES, len(ACTIONS))), columns=ACTIONS)
# choose action: 1. Explore randomly and explore locations that have not been explored , Otherwise select reward The biggest move
def choose_action(state, table):
state_actions = table.iloc[state, :]
if np.random.uniform() > epsilon or state_actions.all() == 0:
action = np.random.choice(ACTIONS)
else:
action = state_actions.argmax()
return action
def get_env_feedback(state, action):
# New status = current state + Move status
new_state = state + action
reward = 0
# Shift right plus 0.5
# Move to the right , Closer to the treasure , get +0.5 Reward
if action > 0:
reward += 0.5
# Move to the left , Stay away from the treasure , get -0.5 Reward
if action < 0:
reward -= 0.5
# The next step is to reach the treasure , Give the highest reward +1
if new_state == N_STATES - 1:
reward += 1
# If you go all the way to the left , And move left , Get the lowest negative reward -1
# At the same time pay attention to , It's still here to define the new state , Otherwise, it will report a mistake
if new_state < 0:
new_state = 0
reward -= 1
return new_state, reward
def update_env(state, epoch, step):
env_list = ['-'] * (N_STATES - 1) + ['T']
if state == N_STATES - 1:
# Reach your destination
print("")
print("epoch=" + str(epoch) + ", step=" + str(step), end='')
time.sleep(2)
else:
env_list[state] = '#'
print('\r' + ''.join(env_list), end='')
time.sleep(fresh_time)
def q_learning():
for epoch in range(max_episodes):
step = 0 # Move steps
state = 0 # The initial state
update_env(state, epoch, step)
while state != N_STATES - 1:
cur_action = choose_action(state, q_table)
new_state, reward = get_env_feedback(state, cur_action)
q_pred = q_table.loc[state, cur_action]
if new_state != N_STATES - 1:
q_target = reward + gamma * q_table.loc[new_state, :].max()
else:
q_target = reward
q_table.loc[state, cur_action] += alpha * (q_target - q_pred)
state = new_state
update_env(state, epoch, step)
step += 1
return q_table
q_learning()
Two 、Saras
Saras It is also the most basic algorithm in reinforcement learning , Also use Q Table is stored Q(s,a), The reason why it's called Saras, It's because of one transition contain (s,a,r,a,s) Quintuples , namely Saras.
- Value-based
- On-Policy
Here's a comparison Q-learning, Then we can know , The data used here is the current policy Produced , And updated Q When it's worth it , It is based on new actions and new States Q value , New actions will be performed ( Note that there is no max), So it is On-Policy. - Pseudo code
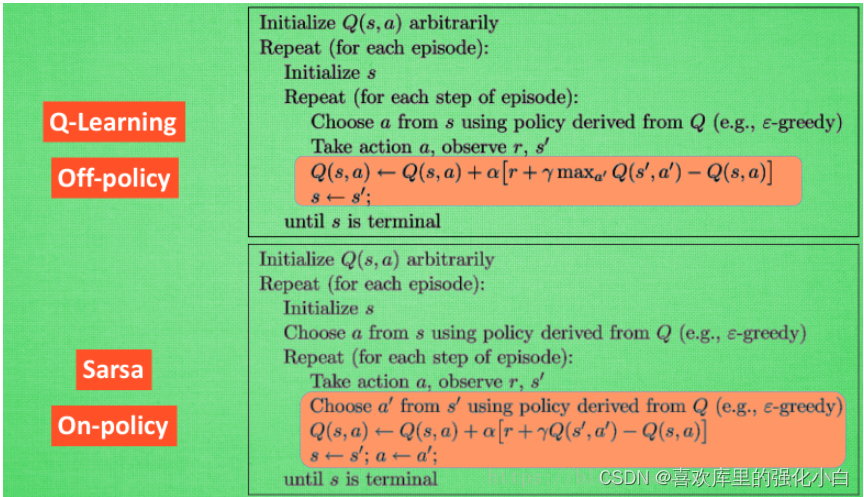
- Realization
Reference here Q-learning Made simple changes , This is based on the new state , Choose another action , And perform the action , In addition, update Q When it's worth it , Directly based on the corresponding Q Value update .
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
N_STATES = 6 # 6 Status , One dimensional array length
ACTIONS = [-1, 1] # Two states ,-1:left, 1:right
epsilon = 0.9 # greedy
alpha = 0.1 # Learning rate
gamma = 0.9 # Diminishing reward value
max_episodes = 10 # Maximum rounds
fresh_time = 0.3 # Move interval
# q_table
# Generate (N_STATES,len(ACTIONS))) Of Q Empty value table
q_table = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((N_STATES, len(ACTIONS))), columns=ACTIONS)
# choose action:
#0.9 Probability greed ,0.1 Probabilistic random selection of actions , Be exploratory
def choose_action(state, table):
state_actions = table.iloc[state, :]
if np.random.uniform() > epsilon or state_actions.all() == 0:
action = np.random.choice(ACTIONS)
else:
action = state_actions.argmax()
return action
def get_env_feedback(state, action):
# New status = current state + Move status
new_state = state + action
reward = 0
# Shift right plus 0.5
# Move to the right , Closer to the treasure , get +0.5 Reward
if action > 0:
reward += 0.5
# Move to the left , Stay away from the treasure , get -0.5 Reward
if action < 0:
reward -= 0.5
# The next step is to reach the treasure , Give the highest reward +1
if new_state == N_STATES - 1:
reward += 1
# If you go all the way to the left , And move left , Get the lowest negative reward -1
# At the same time pay attention to , It's still here to define the new state , Otherwise, it will report a mistake
if new_state < 0:
new_state = 0
reward -= 1
return new_state, reward
# Maintain the environment
def update_env(state, epoch, step):
env_list = ['-'] * (N_STATES - 1) + ['T']
if state == N_STATES - 1:
# Reach your destination
print("")
print("epoch=" + str(epoch) + ", step=" + str(step), end='')
time.sleep(2)
else:
env_list[state] = '#'
print('\r' + ''.join(env_list), end='')
time.sleep(fresh_time)
# to update Q surface
def Saras():
for epoch in range(max_episodes):
step = 0 # Move steps
state = 0 # The initial state
update_env(state, epoch, step)
cur_action = choose_action(state, q_table)
while state != N_STATES - 1:
new_state, reward = get_env_feedback(state, cur_action)
new_action = choose_action(new_state,q_table)
q_pred = q_table.loc[state, cur_action]
if new_state != N_STATES - 1:
q_target = reward + gamma * q_table.loc[new_state, new_action]
else:
q_target = reward
q_table.loc[state, cur_action] += alpha * (q_target - q_pred)
state,cur_action = new_state,new_action
update_env(state, epoch, step)
step += 1
return q_table
Saras()
Blog for the first time , It may be understood that there is a problem , Please correct your mistakes .
边栏推荐
- Get started with typescript
- 简述xhr -xhr的基本使用
- Implementation of count (*) in MySQL
- [dark horse morning post] Shanghai Municipal Bureau of supervision responded that Zhong Xue had a high fever and did not melt; Michael admitted that two batches of pure milk were unqualified; Wechat i
- Implementation principle of automatic capacity expansion mechanism of ArrayList
- Read only error handling
- Service ability of Hongmeng harmonyos learning notes to realize cross end communication
- The latest tank battle 2022 full development notes-1
- 稻 城 亚 丁
- 1. First knowledge of C language (1)
猜你喜欢
A comprehensive summary of MySQL transactions and implementation principles, and no longer have to worry about interviews

QT meta object qmetaobject indexofslot and other functions to obtain class methods attention
C language Getting Started Guide
Mode 1 two-way serial communication is adopted between machine a and machine B, and the specific requirements are as follows: (1) the K1 key of machine a can control the ledi of machine B to turn on a
Differences among fianl, finally, and finalize

甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1
Leetcode. 3. Longest substring without repeated characters - more than 100% solution
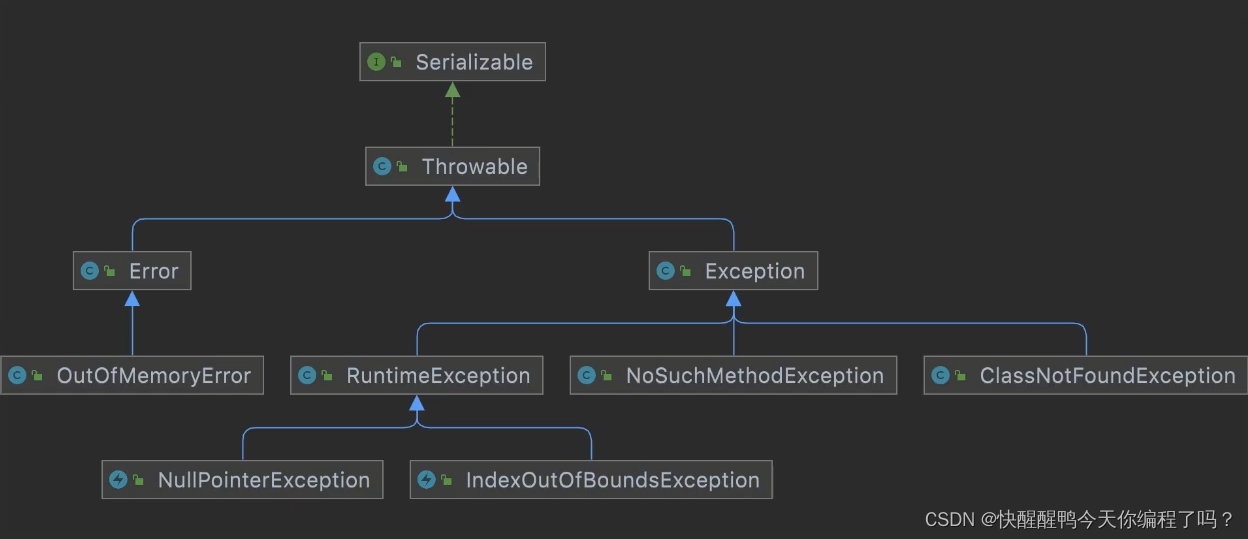
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
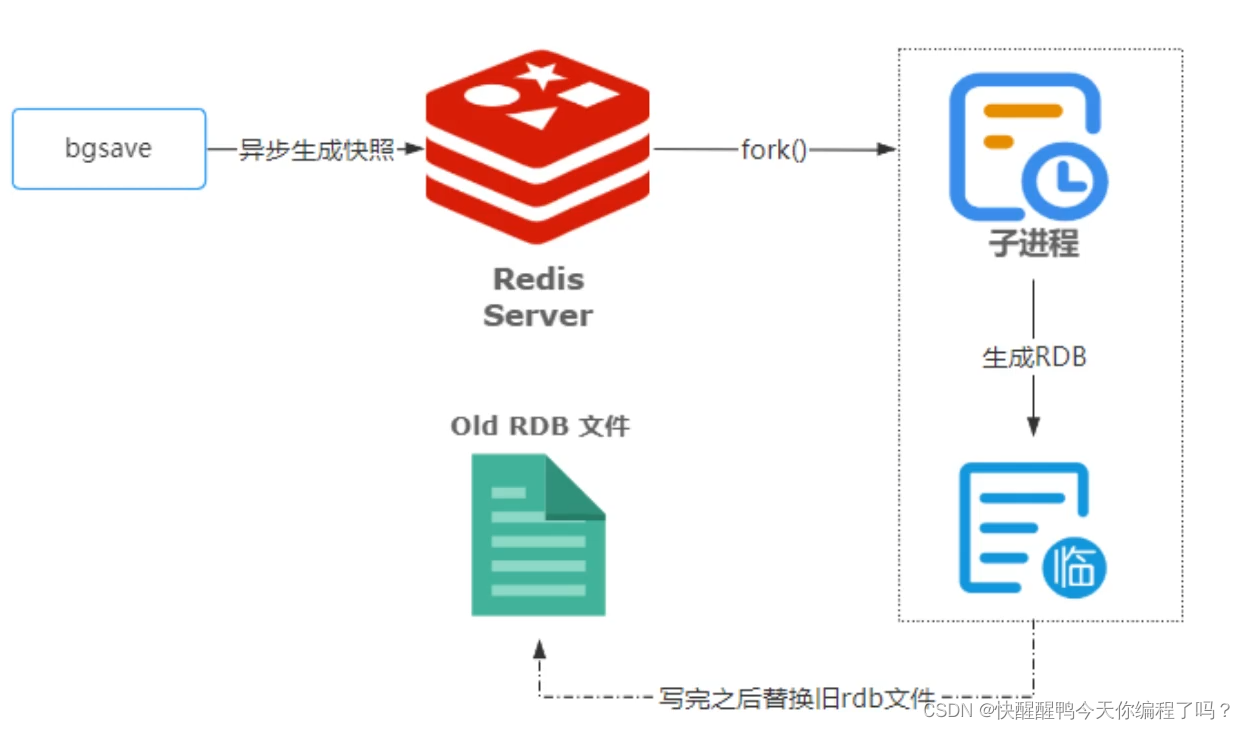
Principles, advantages and disadvantages of two persistence mechanisms RDB and AOF of redis
Cookie和Session的区别
随机推荐
甲、乙机之间采用方式 1 双向串行通信,具体要求如下: (1)甲机的 k1 按键可通过串行口控制乙机的 LEDI 点亮、LED2 灭,甲机的 k2 按键控制 乙机的 LED1
8. C language - bit operator and displacement operator
Safe driving skills on ice and snow roads
C语言入门指南
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
Nuxtjs快速上手(Nuxt2)
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2016 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
The latest tank battle 2022 - full development notes-3
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2020 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
Poker game program - man machine confrontation
About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
Canvas foundation 1 - draw a straight line (easy to understand)
受检异常和非受检异常的区别和理解
Principles, advantages and disadvantages of two persistence mechanisms RDB and AOF of redis
【九阳神功】2016复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
7-7 7003 组合锁(PTA程序设计)
为什么要使用Redis
String ABC = new string ("ABC"), how many objects are created
Inaki Ading
1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method