当前位置:网站首页>Intensive literature reading series (I): Courier routing and assignment for food delivery service using reinforcement learning
Intensive literature reading series (I): Courier routing and assignment for food delivery service using reinforcement learning
2022-07-06 13:50:00 【zhugby】
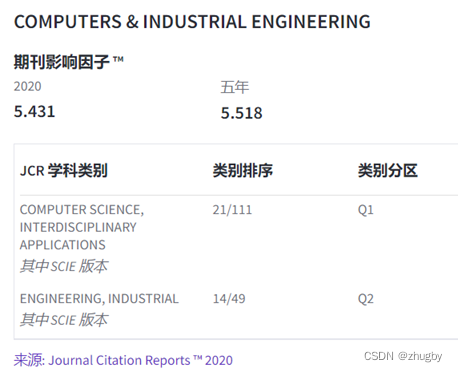
source : Article on 2022 Published in the Journal of COMPUTERS & INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING , The basic information and influence factors of periodicals are shown in the figure below :
Catalog
3.2 The question assumes / Prerequisite
4.1 Basic framework of reinforcement learning
6.3 Average harvest reward comparison results
6.4 Comparison results of average delivery orders
Abstract
Markov decision process is used to represent the takeout delivery service in the real world , Express the delivery problem as Deep reinforcement learning ask leg . The system assigns orders to the takeout , The delivery clerk picks up the order in the designated restaurant and delivers it to the destination , The goal is to have limited time and limited takeout , Maximize total meal delivery revenue . This article USES the Three methods Try to solve this problem :1.Q-learning_ single agent 2.DDQN_ single agent 3.DDQN_ many agent, Use simulation experiments to learn the three algorithms policy And with rule_based policy Contrast . Results found ,1. Allowing takeout staff to reject orders and move in idle state can effectively improve revenue ;2. Of the three methods DDQN_ single agent The algorithm has the best performance ,RL_based Methods are better than rule_based Policy.
1. Research contribution
- And the shortest path VRP The questions are different , This article maximizes the total expected return by reducing delivery time ; Different from the traditional delivery of goods , Do not know the order information in advance , Orders are generated randomly ;
- Problem: when the salesmen are idle, they can choose to stay where they are or go to the restaurant , It is expected to shorten the delivery time of the next order ; Allow the takeout to reject the order allocated for delivery , It is expected that the total revenue of the system ;
- Try to use machine learning method to solve the delivery path problem of takeout , It is beneficial to expand to the research of other problems in the future ;
- For large-scale problems , simplify Q-learning The algorithm uses single agent Training can significantly speed up training and get better results .
2. Literature review
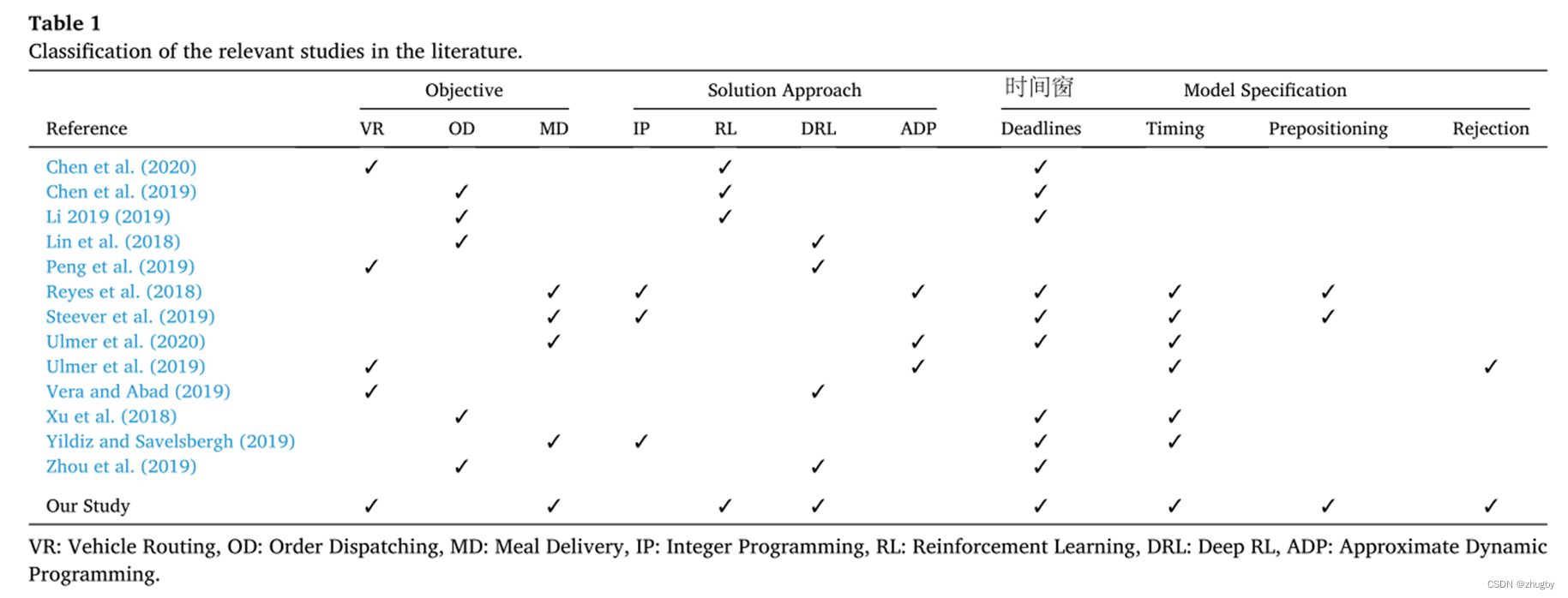
The common method to solve the problem of food distribution in the existing literature is Linear programming and Approximate dynamic planning (ADP),RL Few algorithms are used , This paper uses reinforcement learning and deep reinforcement methods at the same time, and compares the performance of different methods ; Reject orders and with reservation ( Predict the next order generation location , The delivery clerk moves to the restaurant when he is free ) Very little is considered in the literature , This paper considers four attributes at the same time , Perfect model .
3. Problem description
3.1 Problem description
N A takeout takes food from the restaurant through m*m Grid map for customers , The goal is to find an action that maximizes the total income of the takeout policy Guide the decision-making behavior of the takeout .
3.2 The question assumes / Prerequisite
Orders are part of the environment , According to minimization sum( The distance between the takeout and the order ) In principle, the order is allocated to the takeout
After the order is assigned to the takeout, the takeout can refuse to deliver the order
The rejected order is returned to the order list and reassigned to other takeaway
If the order is rejected by all assigned takeaways within a certain period of time , Orders leave the system and will not be delivered .
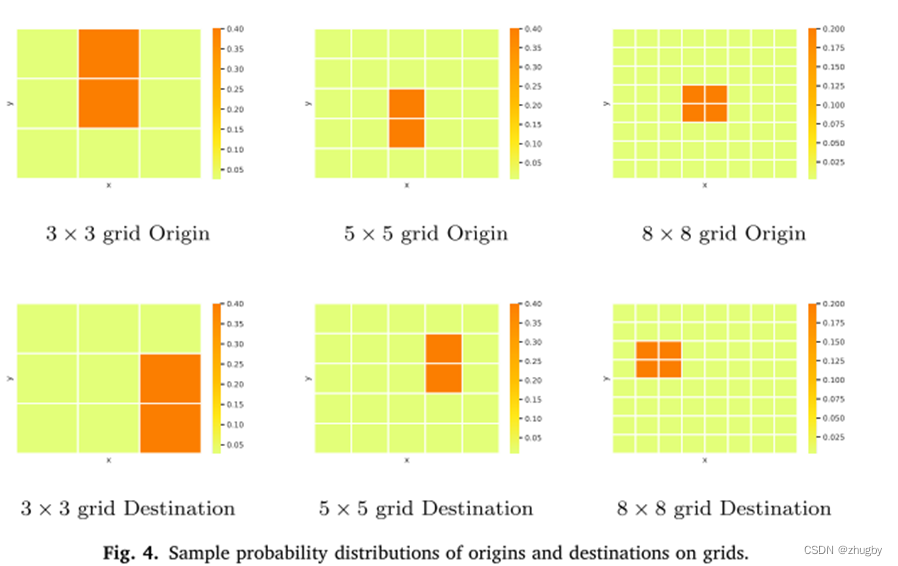
Each grid on the map becomes the starting point of the order ( The restaurant ) And destination ( Customer point ) The probability is different ,(1) Restaurants are mostly concentrated in a certain area (2) Destinations with large orders tend to be concentrated in a certain area ( university )
3.3 Problem definition
To use RL Method to solve the delivery route problem of takeout , We need to turn this problem into RL problem , Definition RL Elements of :
State
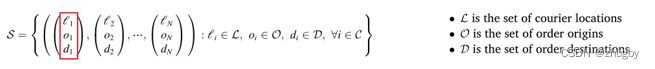

in the light of  , Each triplet records the i The current position of takeout , Takeaway i The starting point of the delivery order ( The restaurant ), And the destination of the order .、
, Each triplet records the i The current position of takeout , Takeaway i The starting point of the delivery order ( The restaurant ), And the destination of the order .、
The size of the state space :
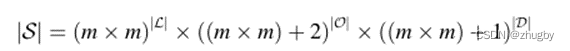
Order starting space +2: The starting position of the order belongs to m*m Grid points are located outside the space , Two new statuses :1) Take the meal / On the way to deliver meals ;2) Idle no order status
Order destination space +1: The starting position of the order belongs to m*m Grid points are located outside the space , Added a new status , The delivery clerk is idle, no order delivery, no destination .
Besides , Takeout orders include five attributes : Order starting point 、 Order destination 、 Order duration 、 Rejected times 、 Deliver the order to the delivery clerk ID
Actions
For each takeout , Action options
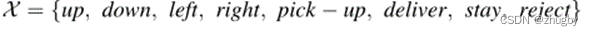
Rewards <state,action>--reward
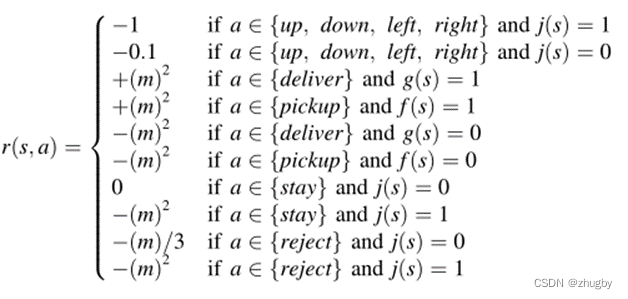

The delivery clerk moves every step after accepting the order reward yes -1, Move one step in idle state -0.1; Every time the order is successfully picked up and delivered, positive reward by m2; Failed to extract and deliver the order ( Pick up the wrong goods 、 Deliver the wrong goods ) Get negative reward/penalty by -m2; Stay idle and wait for nothing reward; The allocation order chooses to wait in place without moving to get negative reward/penalty by -m2; Once the order is allocated, it will be rejected -m/3; Reject the order in the process of delivering the order and get negative reward/penalty by -m2;
besides , If the order is not effectively allocated to the takeout during the service time, leave the system , Additional punishment . in real life , Every customer usually has a level of patience , If he / She didn't get the service within a certain time , He / She will leave the system .
4. resolvent
4.1 Basic framework of reinforcement learning
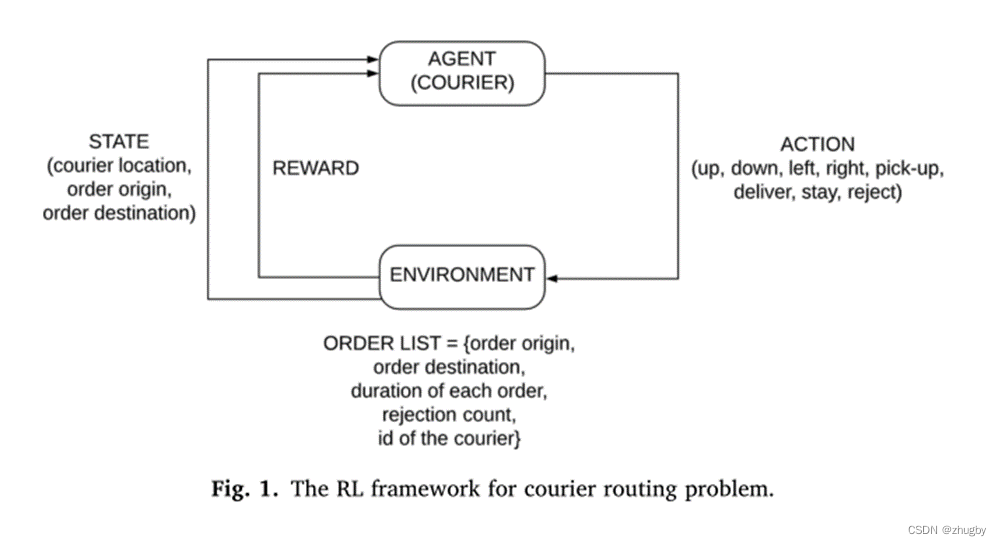
Reinforcement learning is agent In the process of interaction with the environment, the learning process to achieve a goal .agent Observe the environment environment Change according to your current situation state To make a action Every time you make one action,environment Will change ,agent Will get a new state, Then choose the new action Keep implementing .
4.2 Q-learning

Q-learning The detailed introduction of the algorithm can be seen blog Reinforcement learning series ( Two ):Q learning Algorithm introduction and python Realization Q learning solve TSP problem
Q-learning Algorithm shortcoming : Only applicable to small-scale problems , Large scale problems Q The table has the disaster of state explosion ;
Trick: Simplification problem , Homogeneous takeout ,Q-Learning Just train one agent/ The action choice strategy of takeout , Apply to all takeout staff ; namely Q-learning single agent.
4.3 DDQN
To make up for Q-learning Disadvantages of the algorithm , Replace with two deep Neural Networks Q surface , Neural network input state value , Output the corresponding action action Of Q value .
The two networks are divided into online prediction Networks Eval Network obtain Q The predicted value and target network are obtained Q True value of .
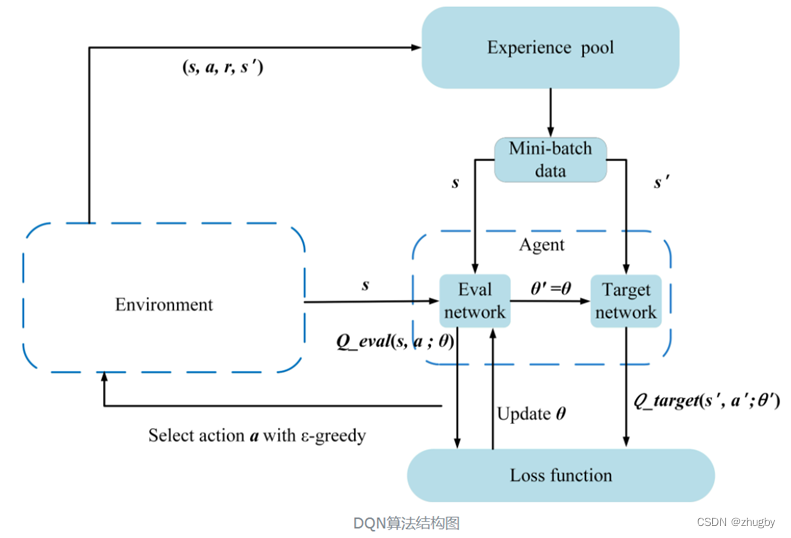
reference , The algorithm flow is summarized as follows :
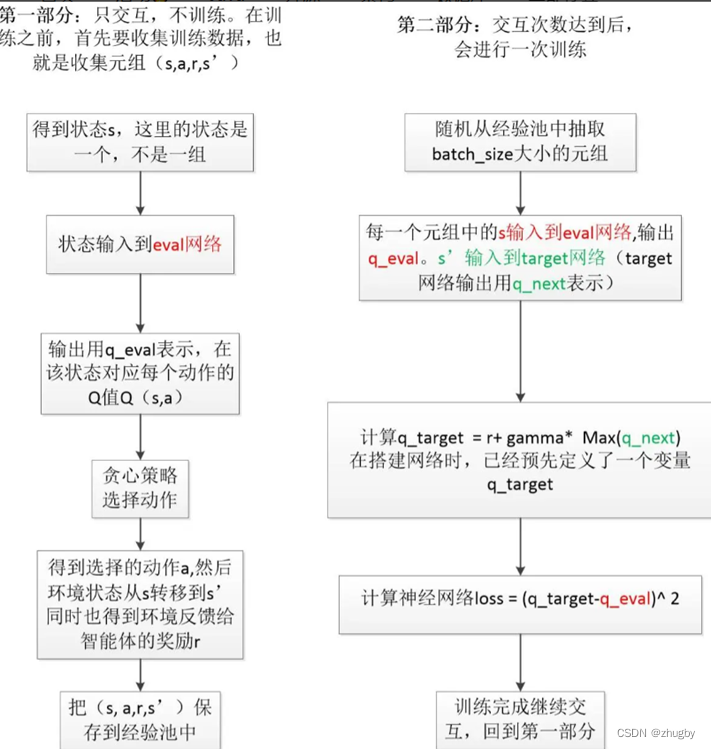
Use random gradient descent algorithm to update network parameters , The possible problems are , When the gradient is too large , Network parameters change too much , The Internet is very unstable ; therefore , This paper adopts Gradient clipping strategy , Normalize the gradient vector to 0-1 Between , bring DDQN The model is more stable .
4.4 Rule Based algorithm
For comparative evaluation RL Performance of the algorithm . The delivery clerk moves to pick up and deliver goods according to the principle of the shortest path , Choose to wait in place when there is no task assigned , It is not allowed to reject the order , In order to focus on the analysis and emphasis on whether there is stay、reject The influence of action .
5. Simulation evaluation
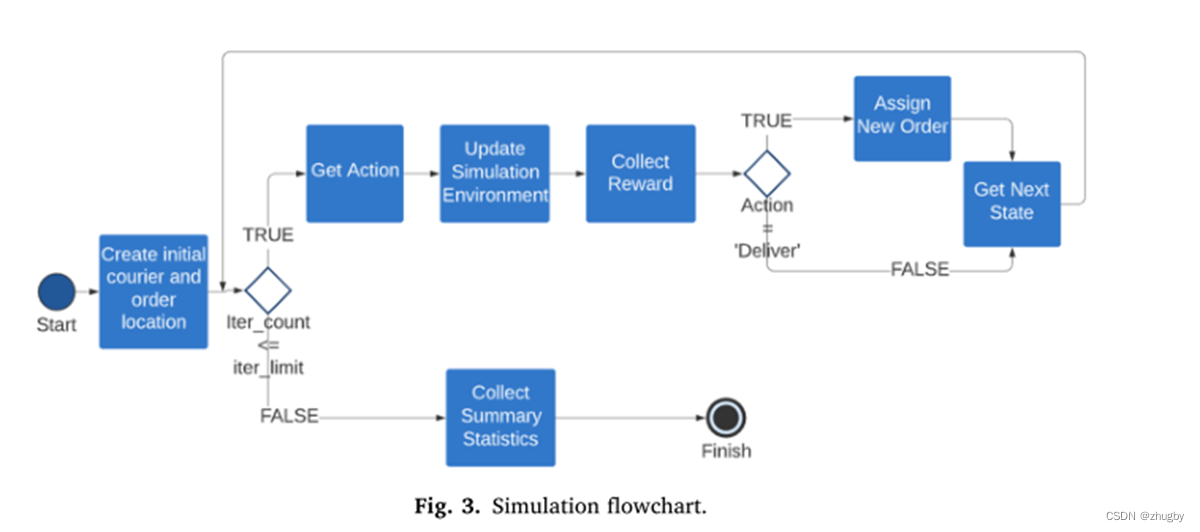
Carry out the simulation experiment according to the simulation flow chart :
• Generate initial takeout location and order location (state)
• The delivery clerk according to Policy choice action Move
• Update environmental changes 【 Order list And the service time of all orders 】
• Calculation reward
• Once the order is delivered , Send new orders
• After reaching the number of iterations , collect data ( Number of dispatched orders 、reward The sum of the ) The standard to measure the performance of the algorithm
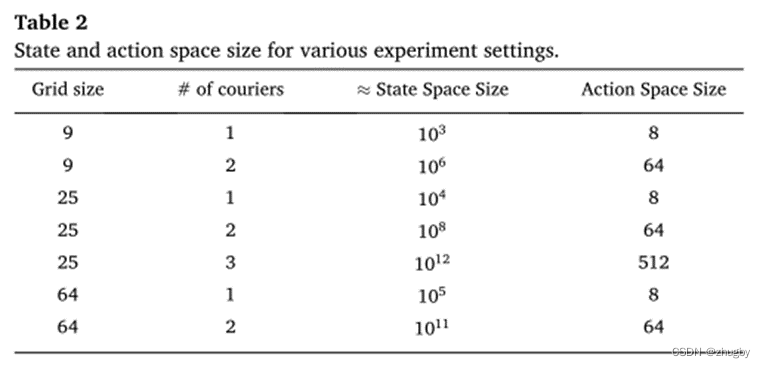
The scale of the problem
Different problem sizes ( Grid size 、 Number of takeout staff 、 Size of state space and action space ) We're going to do the experiment under the sun
Distribution heat map of restaurants and order destinations
6. experimental result
Comparison of the three methods :
1.Q-learning : Training sheet agent Of Policy, Will be applied to all takeout staff ;
2.DDQN: Training sheet agent Of Policy, Apply to all takeout staff ;
3.DDQN: More direct training agent Of Policy;
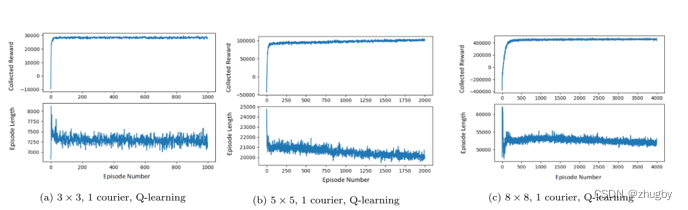
6.1 Q-learning single agent
in the light of Q-learning single agent, With the state space / The scale of the problem increases , The convergence speed of the algorithm will gradually slow down .
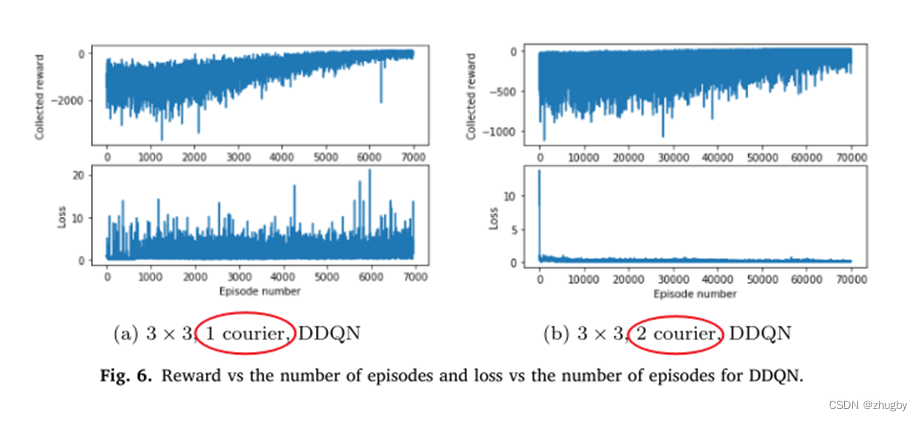
6.2 DDQN single agent vs DDQN
single agent Of reward Values converge faster
6.3 Average harvest reward comparison results
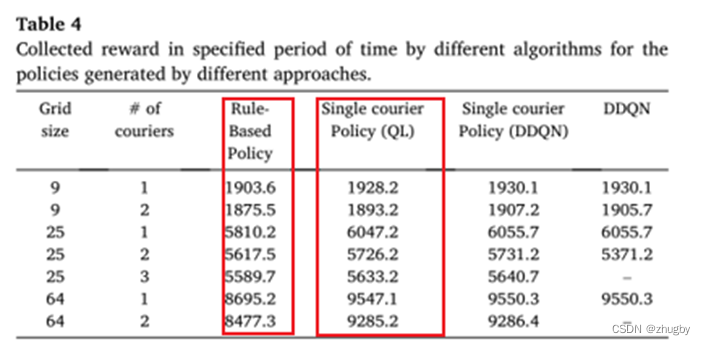
1)DDQN_ single agent>QL>Rule based learning
2)DDQN_ many agent Training on large-scale problems is too time-consuming
6.4 Comparison results of average delivery orders
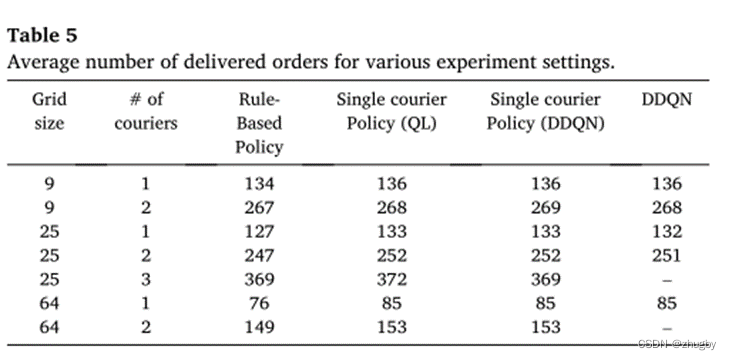
There is little difference between the average number of orders delivered by several methods
6.5 Visual display
Scene one : The delivery clerk received the order after being idle for a period of time
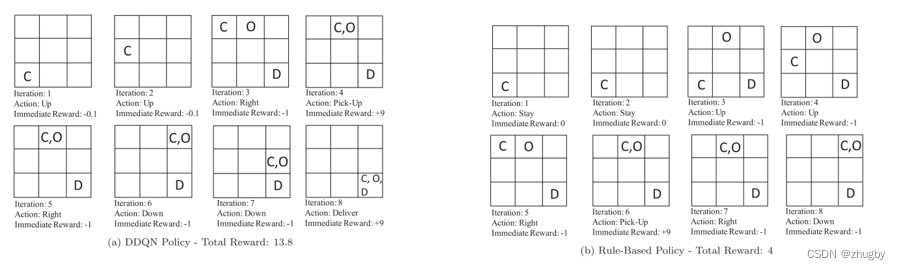
chart a Use DDQN Allow takeout staff to move in their spare time , Comparison with the use rules , It can be seen that , The penalty of allowing the takeout to move in his spare time is smaller , The higher the reward you get , And fewer iterations / Shorter time to reach the destination .
Scene two : Allow the takeout to reject the order
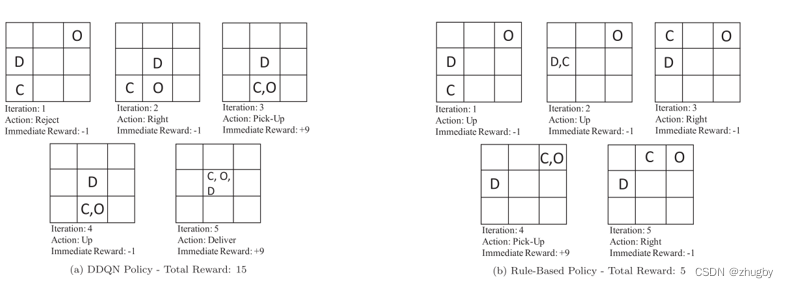
chart a Of DDQN, The takeout refused orders far away from him , Waiting for new and more recent orders , And the traditional one that cannot be refused rule comparison ,Reward More valuable , Fewer iterations / Shorter time to reach the destination .
7. Deficiency and prospect
The state space only considers orders and takeout location information , You can join the takeout staff during working hours 、 Order preparation time and other attributes improve the model
The number of takeout workers considered in this paper is too small , Every additional takeout , The state space grows exponentially ; You can aggregate the attribute characteristics of salesmen and orders to reduce dimensions , Reduce the state space
边栏推荐
- 【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
- 【九阳神功】2019复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
- 7-9 制作门牌号3.0(PTA程序设计)
- 仿牛客技术博客项目常见问题及解答(三)
- 7. Relationship between array, pointer and array
- 7-4 散列表查找(PTA程序设计)
- Mortal immortal cultivation pointer-1
- 4. Branch statements and loop statements
- About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
- [the Nine Yang Manual] 2018 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
猜你喜欢
![[hand tearing code] single case mode and producer / consumer mode](/img/b3/243843baaf0d16edeab09142b4ac09.png)
[hand tearing code] single case mode and producer / consumer mode
C language Getting Started Guide

深度强化文献阅读系列(一):Courier routing and assignment for food delivery service using reinforcement learning

2.初识C语言(2)

QT meta object qmetaobject indexofslot and other functions to obtain class methods attention

9. Pointer (upper)
![[面試時]——我如何講清楚TCP實現可靠傳輸的機制](/img/d6/109042b77de2f3cfbf866b24e89a45.png)
[面試時]——我如何講清楚TCP實現可靠傳輸的機制
4. Branch statements and loop statements
扑克牌游戏程序——人机对抗
![[dark horse morning post] Shanghai Municipal Bureau of supervision responded that Zhong Xue had a high fever and did not melt; Michael admitted that two batches of pure milk were unqualified; Wechat i](/img/d7/4671b5a74317a8f87ffd36be2b34e1.jpg)
[dark horse morning post] Shanghai Municipal Bureau of supervision responded that Zhong Xue had a high fever and did not melt; Michael admitted that two batches of pure milk were unqualified; Wechat i
随机推荐
7-9 制作门牌号3.0(PTA程序设计)
3.输入和输出函数(printf、scanf、getchar和putchar)
1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method
4. Branch statements and loop statements
js判断对象是否是数组的几种方式
Using spacedesk to realize any device in the LAN as a computer expansion screen
Poker game program - man machine confrontation
简单理解ES6的Promise
Nuxtjs快速上手(Nuxt2)
1.C语言初阶练习题(1)
Redis cache obsolescence strategy
Using qcommonstyle to draw custom form parts
使用Spacedesk实现局域网内任意设备作为电脑拓展屏
The latest tank battle 2022 - Notes on the whole development -2
[au cours de l'entrevue] - Comment expliquer le mécanisme de transmission fiable de TCP
7-11 机工士姆斯塔迪奥(PTA程序设计)
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
MySQL lock summary (comprehensive and concise + graphic explanation)
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (I)
7-7 7003 组合锁(PTA程序设计)