当前位置:网站首页>Experiment 4 array
Experiment 4 array
2022-07-06 13:55:00 【Wen Wen likes Guo Zia】
Experiment four : Array
The experiment purpose
1. Master array declaration 、 Definition 、 Initialize and use .
2. Master the access method of one-dimensional or two-dimensional array elements .
Experimental content
1. Programming , Complete the following functions :
(1) Input 20 An integer into the array ;
(2) Yes 20 The number is sorted from large to small , Output sorted array ;
(3) Enter an integer x;
(4) Look for... In an array x. If output is found x Subscript in array , Output not found -1.
package code41;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays; // Import Arrays class
public class code41 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int []numbers=new int[20];
System.out.println(" Please enter 20 It's an integer :");
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
numbers[i]=in.nextInt(); // adopt nextInt Method to read the number entered by the user in turn and store it in the array
}
Arrays.sort(numbers); // take 20 An integer is sorted from small to large
for(int i = 19;i>=0;i--) {
System.out.println(numbers[i]); // Output in reverse order , That is, convert it to sort from large to small
}
System.out.println(" Please enter an integer x:");
int x=in.nextInt(),j=0;
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
if(x==numbers[i]) // Look for... In an array x
{
System.out.println(i); // Output x Subscript in array
j=1;
}
}
if(j!=1)
{
System.out.println("-1"); // Output if you can't find it -1
}
}
}
- Output a stored in a two-dimensional array 3*3 matrix , And find the sum of diagonal elements .
package code42;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class code42 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
int numbers[][]=new int[3][3]; // Define this array and allocate memory space to it
int i,j,sum=0;
System.out.println(" Please enter 3*3 The elements of a matrix :");
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
for(i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
numbers[i][j]=in.nextInt(); // Input array elements
if(i==j) // Determine whether it is a diagonal element
{
sum+=numbers[i][j]; // Sum up
}
}
}
System.out.println(" The sum of diagonal elements is :"+sum);
System.out.println(" Output 3*3 Array of :");
for(i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
System.out.print(" "+numbers[i][j]); // Output two-dimensional array
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
3. Print Yang Hui triangle in the following form
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
........................
Before output 10 That's ok .
package code43;
public class code43 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
int[][]num=new int[10][10]; // Define a Yang Hui triangle with ten rows and ten columns
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<num.length;j++) {
num[i][0]=1;
num[i][j]=1; // The first and last columns of each row are 1
}
}
for(int i=2;i<num.length;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<i;j++) {
num[i][j]=num[i-1][j]+num[i-1][j-1]; // Each number is equal to the sum of the two numbers above it
}
}
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print(num[i][j]+" "); // Output Yang Hui triangle
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
4. Yes M A circle of individuals , Each person has a number (1.2.3.....M), Count from the first person , To report for duty N This person is out of the circle . Continue counting , Count to N At that time, this man made a circle again . Until there's only one left , Output the order of the circle .M、N Input from keyboard .
package code44;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class code44 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Automatically generated method stubs
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(" Please enter the total number of people :");
int M=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(" This person will leave the circle as soon as he reports for duty :");
int N=in.nextInt();
int num[]=new int[M];
int a=M,b=-1,c=0;
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
c++;
num[i]=c; // Number the array
}
System.out.println(" Original sort :");
for(int i=0;i<M;i++) {
System.out.print(num[i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(" Output the order of the circle :");
while(a!=1) { // End of control cycle
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
b++;
if(b==M)
{
b=0; // Count
}
if(num[b]==0)
{
i--; // Prevent double counting
}
}
if(num[b]!=0)
{
System.out.print(num[b]+"\t"); // The sorting number of the output number
num[b]=0; // Exclude the selected number
}
a--;
}
}
}
Summary of experiments
- When defining an array , Except to give the name of the array 、 Member type , Also allocate memory space for it , And initialize ;
- When defining an array , Do not allow the [] Specify the number of array elements in ;
- Arrays cannot be assigned as a whole ;
- Import Arrays class , Use Arrays.sort() Method can sort the elements in the specified array from small to large ;
- Java Some examples of array experiment problems, such as matrix 、 Yang hui triangle 、 Joseph Ring problem has its fixed Algorithm .
边栏推荐
- [modern Chinese history] Chapter 6 test
- Safe driving skills on ice and snow roads
- QT meta object qmetaobject indexofslot and other functions to obtain class methods attention
- 7-14 错误票据(PTA程序设计)
- Differences among fianl, finally, and finalize
- [modern Chinese history] Chapter 9 test
- 1. First knowledge of C language (1)
- FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (III)
- Miscellaneous talk on May 27
- Strengthen basic learning records
猜你喜欢
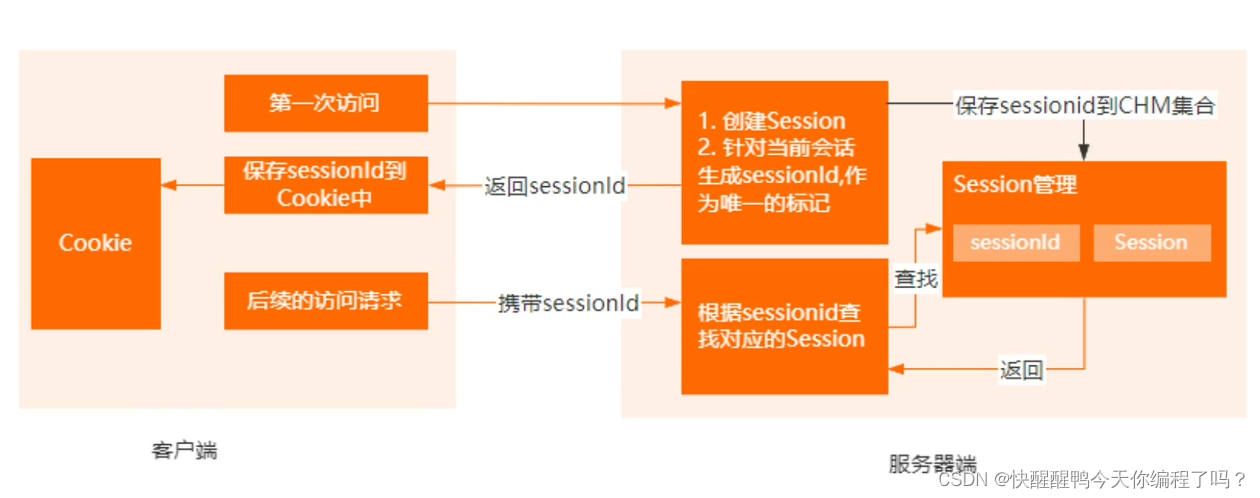
Cookie和Session的区别

使用Spacedesk实现局域网内任意设备作为电脑拓展屏
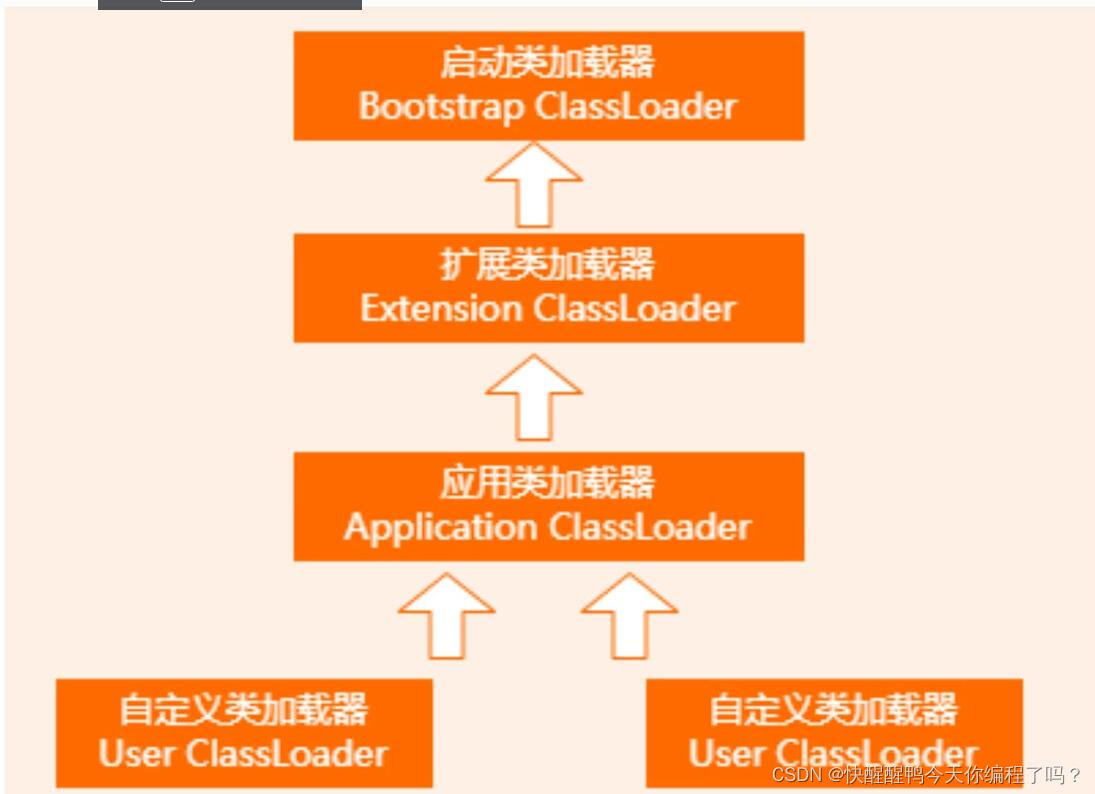
关于双亲委派机制和类加载的过程

【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
7-5 走楼梯升级版(PTA程序设计)
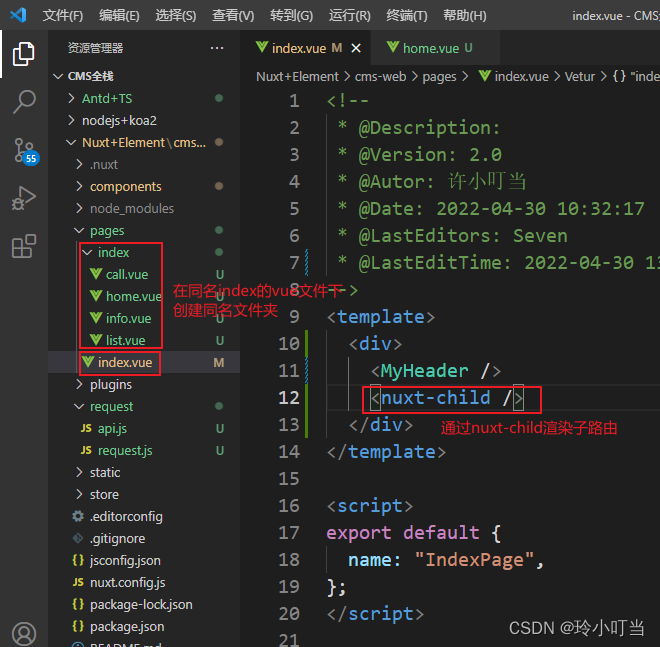
Nuxtjs快速上手(Nuxt2)
Strengthen basic learning records

Package bedding of components
Difference and understanding between detected and non detected anomalies
Intensive literature reading series (I): Courier routing and assignment for food delivery service using reinforcement learning
随机推荐
实验五 类和对象
[graduation season · advanced technology Er] goodbye, my student days
强化学习基础记录
About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
7-1 输出2到n之间的全部素数(PTA程序设计)
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2018 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2022 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
7-5 走楼梯升级版(PTA程序设计)
7-8 7104 约瑟夫问题(PTA程序设计)
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2020 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
附加简化版示例数据库到SqlServer数据库实例中
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2021 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis
[hand tearing code] single case mode and producer / consumer mode
. How to upload XMIND files to Jinshan document sharing online editing?
7-6 矩阵的局部极小值(PTA程序设计)
Brief introduction to XHR - basic use of XHR
1. First knowledge of C language (1)
The latest tank battle 2022 - Notes on the whole development -2
hashCode()与equals()之间的关系
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2017 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis