当前位置:网站首页>Relationship between hashcode() and equals()
Relationship between hashcode() and equals()
2022-07-06 13:41:00 【Wake up duck, did you program today?】
stay java in , Each object can call its own hashcode() Method to get its own hash value
- If I have two objects hashcode inequality , Then these two objects must be different objects
- If I have two objects hashcode identical , It does not mean that these two objects must be the same object , It can also be two objects
- If two objects are equal , So their hashCode It must be the same
stay java In the implementation class of some collection classes , When comparing whether two objects are equal , According to the above principles , Will call the object first hashCode() Method to get hashCode Compare , If hashCode If you are different, you can directly think that the two objects are different , If hashCode Same value , Then it will call further equals() Methods for comparison , and equals() Method , It is used to finally determine whether two objects are equal , Usually equals Implementation will be heavy , More logic , and hashCode() The main thing is to get a hash value , It's actually a number , Relatively light , So when comparing two objects , Usually use it first hashCode
Be careful : We rewrote equals() Method , Then pay attention to hashCode() Method , Be sure to follow the above rules .
Here's the picture :
package com.ws;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<User,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(new User("wangshun"),"123");
System.out.println(hashMap.get(new User("wangshun")));
}
}
class User {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
User user = (User) obj;
return user.getName().equals(this.name);
}
}
No rewriting hashcode The previous running result is null
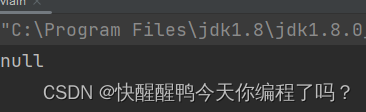
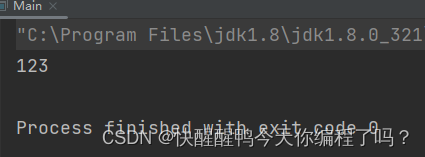
package com.ws;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<User,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(new User("wangshun"),"123");
System.out.println(hashMap.get(new User("wangshun")));
}
}
class User {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
User user = (User) obj;
return user.getName().equals(this.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return name.hashCode();
}
}
rewrite hashcode For after 123
边栏推荐
- View UI plus released version 1.3.1 to enhance the experience of typescript
- There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
- C语言入门指南
- 更改VS主题及设置背景图片
- C language Getting Started Guide
- [during the interview] - how can I explain the mechanism of TCP to achieve reliable transmission
- 8. C language - bit operator and displacement operator
- 这次,彻底搞清楚MySQL索引
- MySQL中count(*)的实现方式
- [modern Chinese history] Chapter 6 test
猜你喜欢

There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
MySQL lock summary (comprehensive and concise + graphic explanation)

8.C语言——位操作符与位移操作符

2.C语言初阶练习题(2)
MySQL事务及实现原理全面总结,再也不用担心面试
FAQs and answers to the imitation Niuke technology blog project (I)
MATLAB打开.m文件乱码解决办法

西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《基础实验》试题及答案

5.MSDN的下载和使用
2022泰迪杯数据挖掘挑战赛C题思路及赛后总结
随机推荐
About the parental delegation mechanism and the process of class loading
【手撕代码】单例模式及生产者/消费者模式
魏牌:产品叫好声一片,但为何销量还是受挫
Questions and answers of "Fundamentals of RF circuits" in the first semester of the 22nd academic year of Xi'an University of Electronic Science and technology
3. C language uses algebraic cofactor to calculate determinant
学编程的八大电脑操作,总有一款你不会
稻 城 亚 丁
1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method
最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-3
Service ability of Hongmeng harmonyos learning notes to realize cross end communication
[during the interview] - how can I explain the mechanism of TCP to achieve reliable transmission
C语言入门指南
凡人修仙学指针-1
(super detailed II) detailed visualization of onenet data, how to plot with intercepted data flow
Leetcode. 3. Longest substring without repeated characters - more than 100% solution
canvas基础1 - 画直线(通俗易懂)
Set container
Custom RPC project - frequently asked questions and explanations (Registration Center)
2.C语言矩阵乘法
[the Nine Yang Manual] 2017 Fudan University Applied Statistics real problem + analysis