当前位置:网站首页>Thoroughly understand LRU algorithm - explain 146 questions in detail and eliminate LRU cache in redis
Thoroughly understand LRU algorithm - explain 146 questions in detail and eliminate LRU cache in redis
2022-07-06 13:36:00 【Li bohuan】
LRU(Least Recently Used, Most recently unused ) Is a common page replacement algorithm , His thought is very simple : It thinks that the data that has just been accessed , It will definitely be visited again , Data that has not been accessed for a long time , I'm sure I won't be interviewed again , When the cache is full , Delete it first .
This is a data structure problem Splicing with simple data structures Here we use Double linked list Add Hashtable (key Data storage key value Storage node ( data key and value Packaged as a node )) Guarantee put get The time complexity of O(1). Use a hash table and a bidirectional linked list to maintain all key value pairs in the cache . The bidirectional list stores these key value pairs in the order they are used , The key value pairs near the tail are recently used , The key value pair near the head is the longest unused .
Leetcode146:

Code implementation :
First, we write the node class of the bidirectional linked list : Include key,value( The default is int type ), And the precursor node and the successor node
public static class Node{
public int key;
public int value;
public Node pre;
public Node next;
public Node(int key, int value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}Then build a two-way linked list according to the node class :
public static class NodeDoubleLinkedList{
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public NodeDoubleLinkedList(){
// No arguments structure
head = null;
tail = null;
}
//LRU There are three ways to cache Add a node to the tail One updates the node to the tail ( Adjust priorities ) A way to delete the header node ( It corresponds to driving out the keywords that have not been used for the longest time )
public void addNode(Node node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
if(head == null){
// That is, the bidirectional linked list has no nodes
head = node;
tail = node;
}else{
// Otherwise, put it in the tail On the left is the head , On the right is the tail
tail.next = node;
node.pre = tail;
tail = node;
}
}
//node Enter the reference Guaranteed node In a double linked list
//node Reconnect the left and right sides of the original position, and then node Separate it and hang it on your tail
// Here we need to adjust the priority according to the topic because get After the operation This node is operated Then he will put it on the tail of the two-way linked list to represent the recently operated node
public void moveNodeTotail(Node node){
// Separate
if(node == tail){
return;
}
if(head == node){
// The adjustment of the head node and the middle node are different There are nodes before and after the intermediate nodes
head = head.next;// The head is going to move to the tail So the head is moved one after another
head.pre = null;// Then point to empty , Disconnect point head The pointer to
}else{
// Will point to node The pointer of is disconnected !!
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
// add to
node.pre = tail;
node.next = null;
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
public Node removeHead(){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Node res = head;
if(head == tail){
head = null;
tail = null;
}else{
head = res.next;
// Talk about the separation of header nodes
res.next = null;
head.pre = null;
}
return res;
}
}With the realization of two-way linked list , All we need to do is LRU In the algorithm, it can be combined with hash table :
private HashMap<Integer,Node> map;
private NodeDoubleLinkedList nodelist;
int cap;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
map = new HashMap<>();
nodelist = new NodeDoubleLinkedList();
cap = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){
Node res = map.get(key);
nodelist.moveNodeTotail(res);
return res.value;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
// meanwhile put Into the map And two-way linked list
if(map.containsKey(key)){// to update
Node node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
// Recently operated Put it in the tail
nodelist.moveNodeTotail(node);
}else{
// New operation
Node newNode = new Node(key,value);
map.put(key,newNode);
nodelist.addNode(newNode);
if(map.size() == cap + 1){
// Beyond capacity Delete the header
Node remove = nodelist.removeHead();
// The hash table will also be deleted
map.remove(remove.key);
}
}
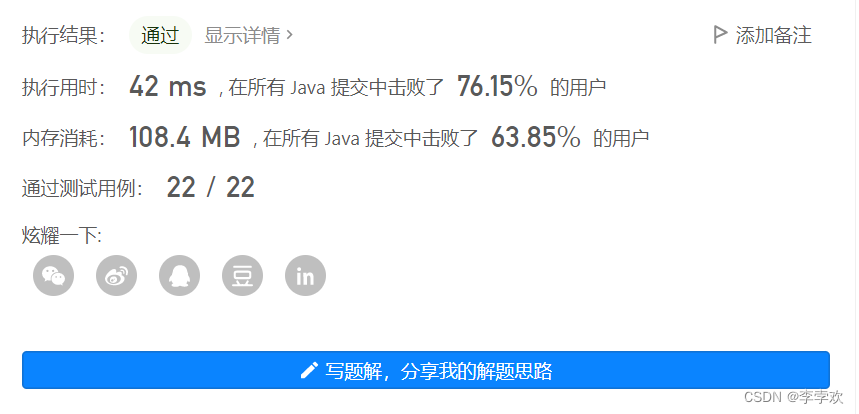
}Execution results :
So let's see Redis Medium lru cache !!
Redis 4.0 It's been realized before 6 Memory elimination strategy , stay 4.0 after , added 2 Strategies . We can divide them into two categories according to whether they will be eliminated : No data culling strategy , Only noeviction This kind of . There will be elimination 7 Two other strategies . There will be elimination 7 Strategies , We can further classify the candidate datasets into two categories according to the scope of the elimination candidate datasets : stay Set expiration time Of the data , Include volatile-random、volatile-ttl、volatile-lru、volatile-lfu(Redis 4.0 Then add ) Four kinds of . stay All data ranges To eliminate , Include allkeys-lru、allkeys-random、allkeys-lfu(Redis 4.0 Then add ) Three .
You can see ,redis There are two cache obsolescence strategies used LRU Algorithm , however ,LRU In the actual implementation of the algorithm , Need to use linked list to manage all cache data , This will bring Extra space overhead . and , When data is accessed , You need to move the data to the end of the linked list , If there's a lot of data being accessed , Will bring a lot of linked list mobile operation , It's time consuming , And then it reduces Redis Cache performance .
therefore , stay Redis in ,LRU The algorithm has been simplified , To reduce the impact of data obsolescence on cache performance . say concretely ,Redis Record by default Timestamp of the last access of each data ( By the key value of the data structure RedisObject Medium lru Field records ). then ,Redis When deciding on the data to be eliminated , First meeting Randomly choose N Data , Take them as a candidate set . Next ,Redis I'll compare this N Data lru Field , hold lru The data with the smallest field value Out of the cache .
Redis A configuration parameter is provided maxmemory-samples, This parameter is Redis The number of selected data N. for example , We execute the following order , It can make Redis elect 100 Data as candidate data sets :
CONFIG SET maxmemory-samples 100When data needs to be eliminated again ,Redis You need to pick the candidate set created when the data goes into the first elimination . The selection criteria at this time is : Data that can enter the candidate set lru The field value must be less than the smallest... In the candidate set lru value . When new data enters the candidate dataset , If the number of data in the candidate data set reaches maxmemory-samples,Redis Just put the candidate data set lru The data with the smallest field value is eliminated .
thus ,Redis Cache does not need to maintain a large linked list for all data , You don't have to move linked list items every time you access data , Improved cache performance .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
IPv6 experiment
3. C language uses algebraic cofactor to calculate determinant

西安电子科技大学22学年上学期《射频电路基础》试题及答案
13 power map
最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-2

C语言实现扫雷游戏(完整版)
Tyut Taiyuan University of technology 2022 introduction to software engineering summary
Common method signatures and meanings of Iterable, collection and list
View UI Plus 发布 1.3.0 版本,新增 Space、$ImagePreview 组件
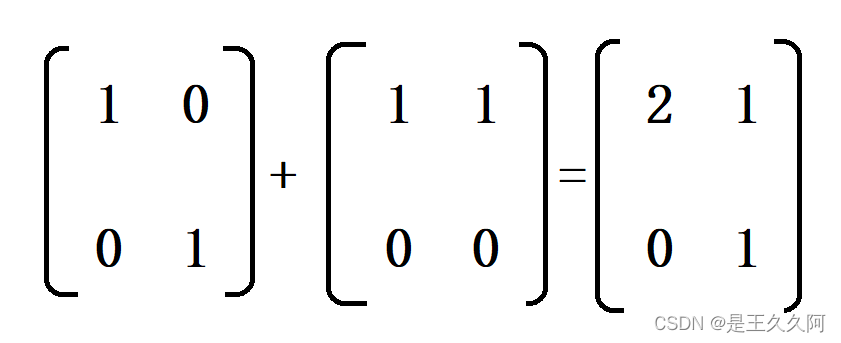
1. C language matrix addition and subtraction method
随机推荐
Redis cache obsolescence strategy
There is always one of the eight computer operations that you can't learn programming
Redis的两种持久化机制RDB和AOF的原理和优缺点
2.C语言初阶练习题(2)
1.C语言矩阵加减法
1.C语言初阶练习题(1)
【话题终结者】
View UI Plus 发布 1.3.1 版本,增强 TypeScript 使用体验
IPv6 experiment
C语言实现扫雷游戏(完整版)
5月27日杂谈
最新坦克大战2022-全程开发笔记-3
编写程序,模拟现实生活中的交通信号灯。
【九阳神功】2022复旦大学应用统计真题+解析
View UI Plus 发布 1.1.0 版本,支持 SSR、支持 Nuxt、增加 TS 声明文件
Questions and answers of "basic experiment" in the first semester of the 22nd academic year of Xi'an University of Electronic Science and technology
Network layer 7 protocol
凡人修仙学指针-2
(原创)制作一个采用 LCD1602 显示的电子钟,在 LCD 上显示当前的时间。显示格式为“时时:分分:秒秒”。设有 4 个功能键k1~k4,功能如下:(1)k1——进入时间修改。
6.函数的递归