当前位置:网站首页>[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 22. Ahb-sramc of SystemVerilog project practice (2) (Introduction to AMBA bus)
[quick start of Digital IC Verification] 22. Ahb-sramc of SystemVerilog project practice (2) (Introduction to AMBA bus)
2022-07-07 15:20:00 【luoganttcc】
Reading guide : The author has the honor to be a pioneer in the field of electronic information in China “ University of electronic technology ” During postgraduate study , Touch the cutting edge Numbers IC Verification knowledge , I heard something like Huawei Hisilicon 、 Tsinghua purple light 、 MediaTek technology And other top IC related enterprises in the industry , Pairs of numbers IC Verify some knowledge accumulation and learning experience . Want to get started for help IC Verified friends , After one or two thoughts , This column is specially opened , In order to spend the shortest time , Take the least detours , Most learned IC Verify technical knowledge .
List of articles
One 、 Description of content
- AMBA Bus Overview
- AHB( A top priority )
- APB
- Different IP The interconnection between
notes :AMBA Bus except APB and AHB outside , also ASB, But it's used less , So this is no longer the focus ! in addition , We AHB-SRAMC The project only uses AHB Slave On the side , So it's not necessarily that AHB Only when you are proficient can you do this project . As a matter of fact slave Speaking of , Only AHB A simplified version of the protocol :
AHB-Lite.
Two 、AMBA Bus Overview
2.1、 Introduction to system bus
- Each module in the system chip (IP) There needs to be an interface between
- Bus as a subsystem between share The communication link of
- Share the words , Every slave Will divide the address space
- In case of direct connection ( Point to point communication ), There is no need to divide the address space , But the cost is high and it is not easy to expand
- advantage
- Low cost
- Convenient and easy to use ( Expandable )
- shortcoming
- Can cause Performance bottleneck ( Involving command allocation 、 Queuing and conflict problems )
2.2、AMBA 2.0
Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture
- On chip bus standard
Three kinds of buses are defined
- AHB(Advanced High-performance Bus)
- In practice, more variants are used :AHB-Lite
- ASB(Advanced System Bus)【 Understanding can 】
- APB(Advanced Peripheral Bus)
- Use in Slave in
- AHB(Advanced High-performance Bus)
AMBA2.0 Upgrade to AMBA3.0 Added AXI agreement , The main application scenario is complex high-speed system .
2.3、AMBA The development history
- AMBA 1.0
- ASB and APB
- AMBA 2.0
- AHB,ASB and APB
- AMBA 3.0
- AMBA Advanced eXtensible Interface(AXI)
- AMBA 4.0
- AXI Coherency Extensions(ACE)【 Multi core consistency 】
2.4、 A typical AMBA 2.0 System
notes : What we want to verify is AHB-SRAMC modular , That is to say AHB The data of the interface is converted to SRAMC And then write it in , So study AHB Is a must !
- Processors and other main devices / Slave devices can be replaced
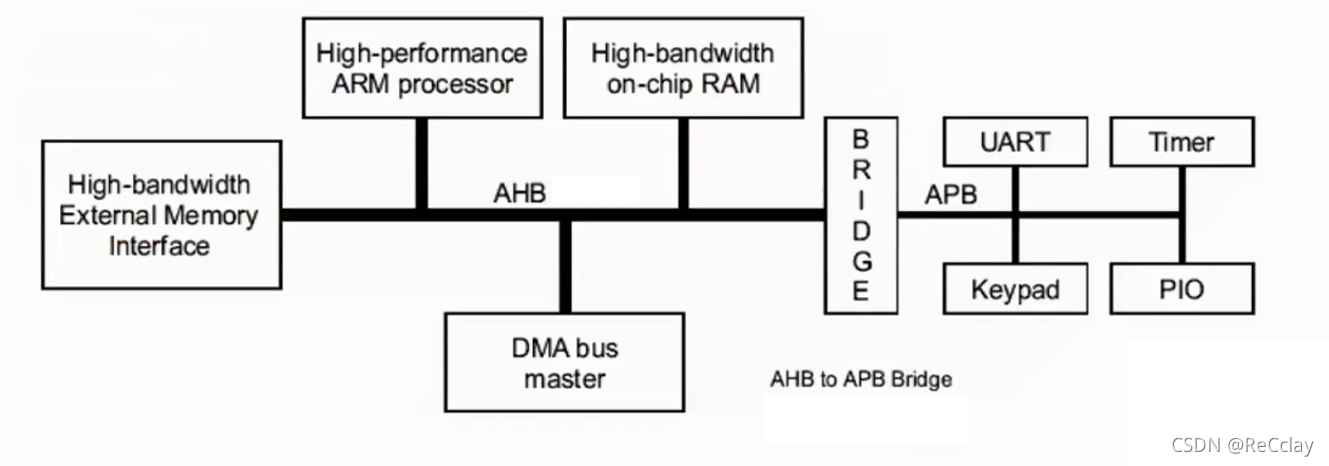
2.5、AMBA2.0 AHB
- High speed bus ( in the light of APB)、 High performance
- 2 Stage pipeline operation
- It can support multiple bus masters ( There is no limit to the quantity )
- Support burst transmission ( real Burst Transmission is carried forward in AMBA3.0 Of AXI)
- AMBA 13’00
- Bus bandwidth :8/16/32/64/128 bits(32 bits Most used )
- The rising edge triggers the operation
notes :AHB be relative to APB Promotion , It mainly lies in two-stage flow !
- Q: What is? Burst transmission ?
A: The command of the bus is nothing more than address (ADDR) And data (DATA). During bus transmission ,single The timing regulation is relatively dead , It takes two beats to complete the address and timing transmission , As shown in the figure below .
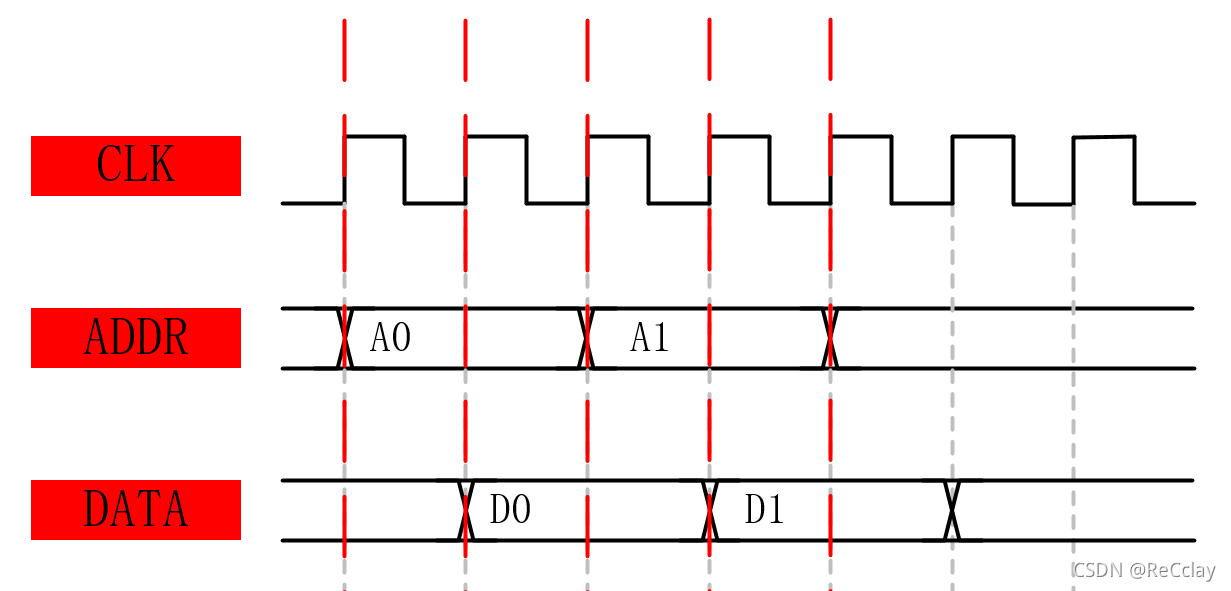
Generally, the bus bandwidth is 32bits, That is, you can read 4 Data of addresses . For tradition single transmission , It needs to be sent in the first address cycle ADDR = 0x50, You can read the address in the second data cycle 0x50/0x51/0x52/0x53 Composed of 32 Bit data . I want to read the next 4 Address data , It needs to be sent in the first address cycle ADDR = 0x54, You can read the address in the second data cycle 0x54/0x55/0x56/0x57 Composed of 32 Bit data . Read it like this , Total cost 4 pat .
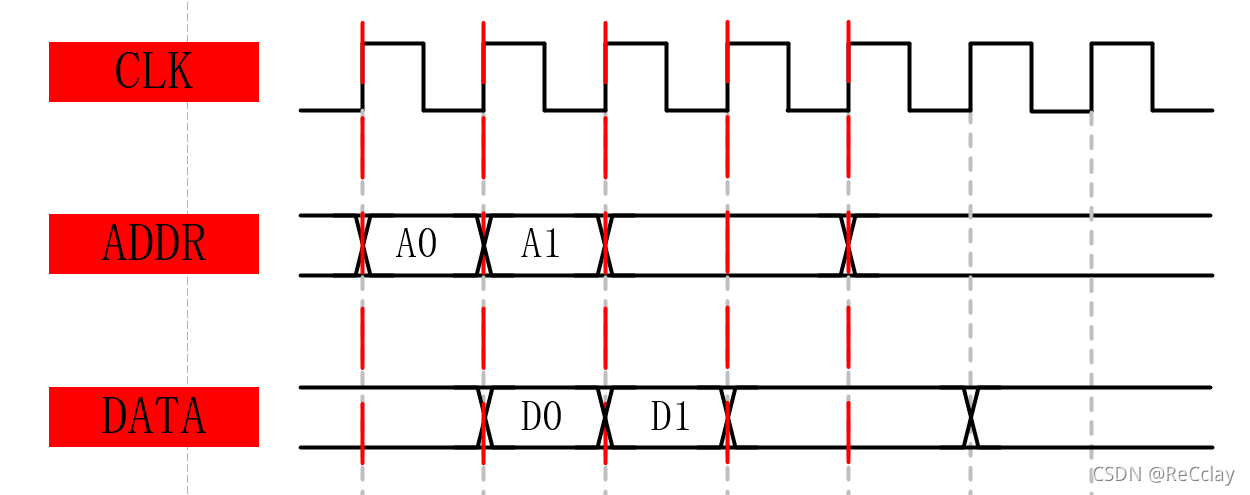
and Burst The transmission wants to read the above 2 individual 32 Bit data , It needs to be sent in the first address cycle ADDR = 0x50 and INC2( Indicates that you need to start from 0x50 Read this address consecutively 2 individual 32 Bit data ), Then you can read one in the second data cycle 32 Bit data , Read another one in the third data cycle 32 For data , Total cost 3 pat .
Empathy , Read more N Data , Then send it in addition to the sending address INCN that will do , Total needs N+1 pat .
- Q:2 What does stage pipeline operation mean ?
A: Pipeline operation is directly reflected in the address 1 At the time of sending , You can read the address 0 Corresponding data , As shown in the figure below .
2.6、AMBA2.0 APB
- Low speed bus 、 low power consumption
- The interface is simple
- stay Bridge Latch address signal and control signal in
- Applicable to a variety of peripherals ( Because peripherals are interfaces made according to other people's specifications , It must be able to hang up )
- Rising edge trigger
2.7、AHB Part of the
notes : The following components are not all SoC Need to be .
- AHB Main equipment (master)
- launch Once read / Write operations
- Only one master device is allowed to use the bus at one time
- CPU、DMA、DSP…
- AHB Slave device (slave)
- Respond to Once read / Write operations
- adopt Address mapping To choose which slave device to use
- External memory controller EMI、APB bridge
- AHB Arbiter (arbiter)
- Allow a master to control the bus
- stay AMBA The arbitration algorithm is not defined in the protocol
- master Is based on fair polling
RRDispatching principle , Or according to the absolute prioritySPDispatching principle ? - In actual development , We use
RRMore
- master Is based on fair polling
- AHB Decoder (decoder)
- Determine which slave device to choose through address decoding
2.8、APB Part of the
AHB2APB Bridge
- All addresses can be locked 、 Data and control ( Read write control ) The signal
- Perform secondary decoding to generate APB Select the signal from the device
APB All other modules on the bus are APB Slave device ( There is no master device )
2.9、AMBA Other relevant issues of the agreement
- Process independent ( What the protocol realizes is logic , namely RTL Code )
- Electrical characteristics are not defined ( What is defined is only the logical temporal relationship , And the chip is used internally , Voltage independent )
- Define timing only at the clock cycle level
- Provide timing ( Here refers to the physical implementation timing , Don't pay too much attention ) The parameters depend on the adopted process and working frequency
- give an example : Not to say that APB Can only run 100M, And the agreement does not stipulate APB It has to be for 100M, You need to determine the frequency of operation according to the selected process and the performance requirements you want to achieve . If you choose 16nm You can run to 300M, choose 65nm You can run to 100M!【 summary : It is related to practical application , It has nothing to do with the provisions of the agreement .】
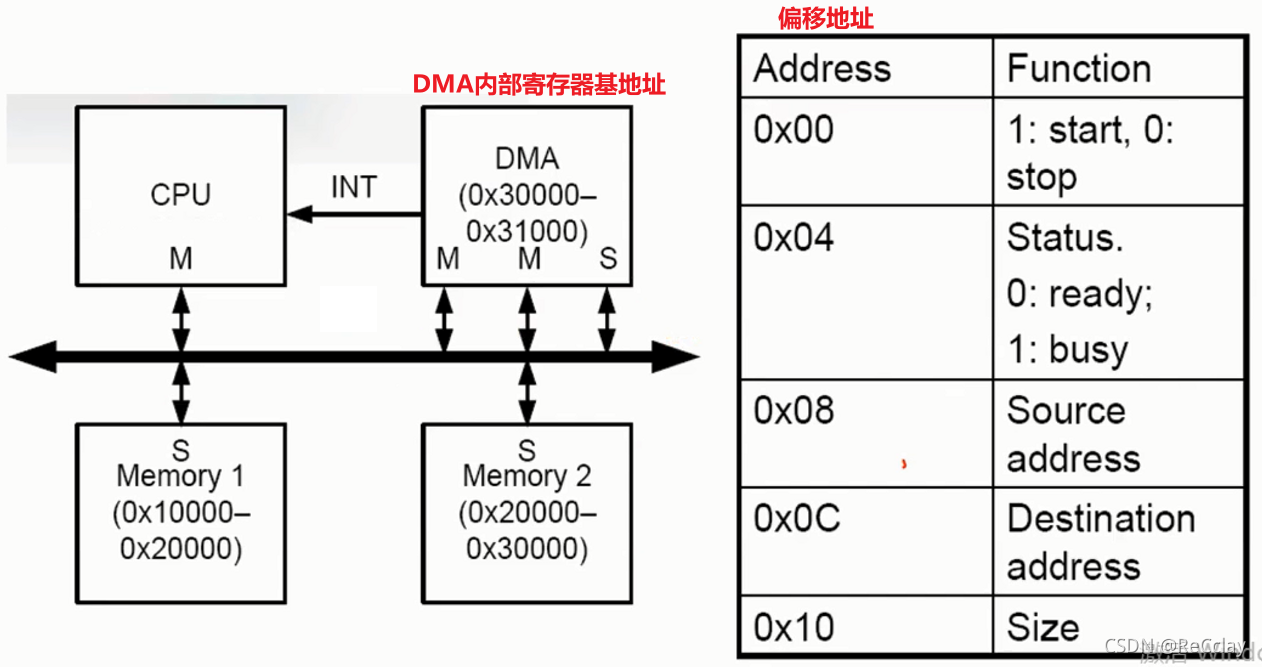
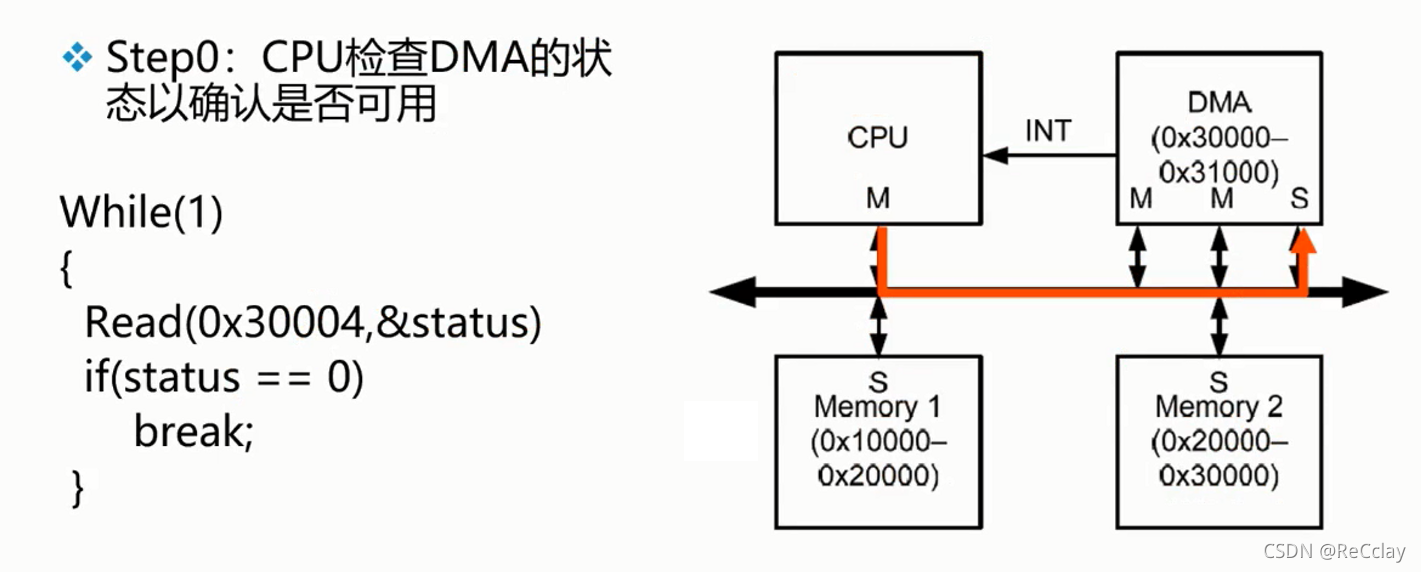
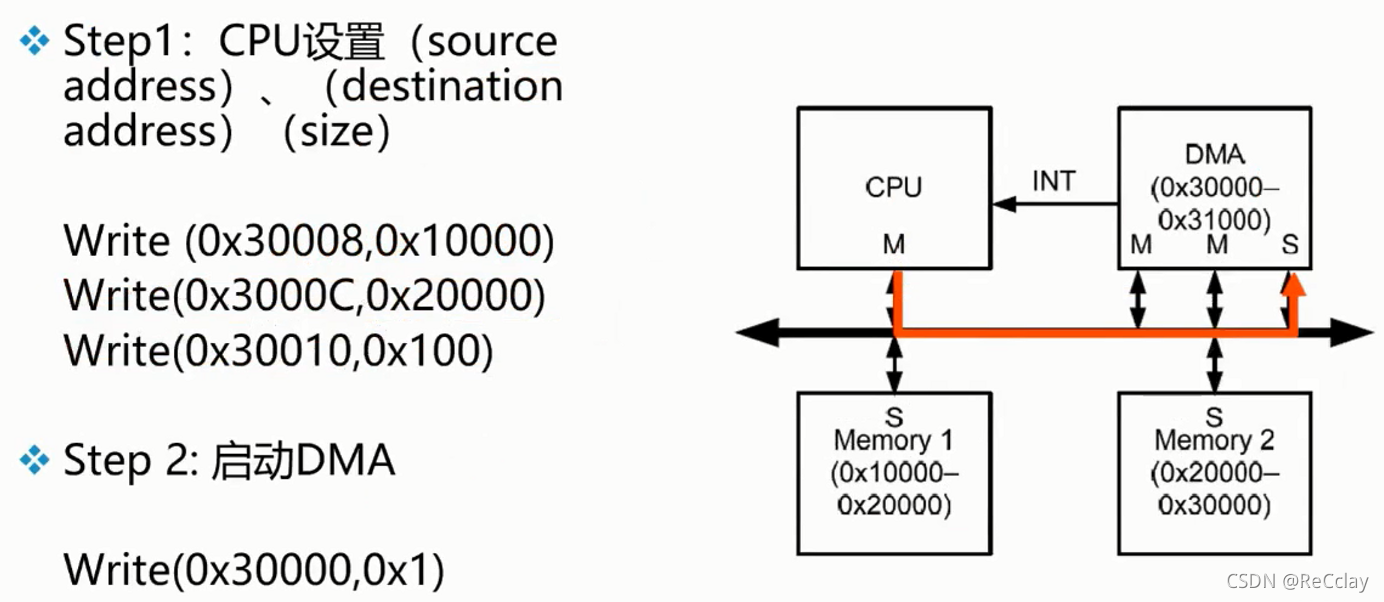
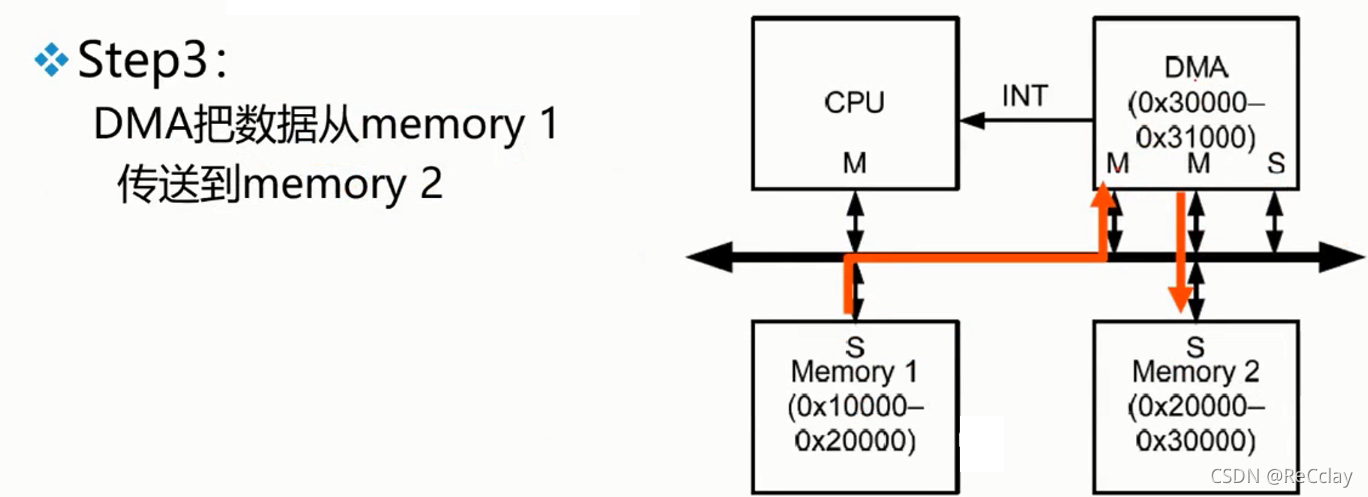
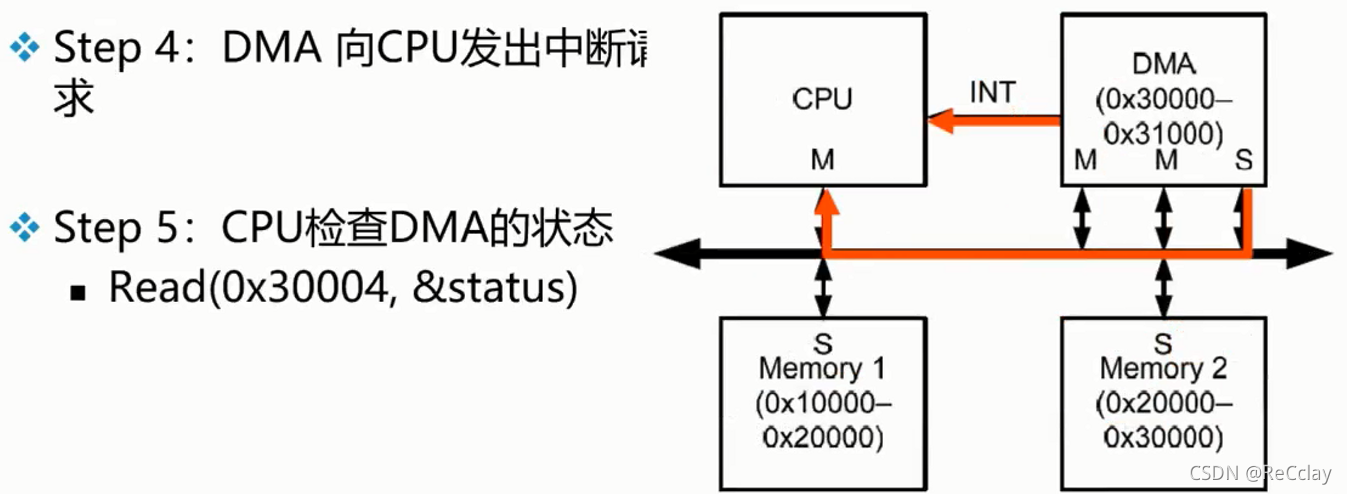
2.10、 example :DMA
notes : The following example code is pseudocode .
边栏推荐
- Lidar Knowledge Drop
- MySQL bit类型解析
- Niuke real problem programming - day13
- [target detection] yolov5 Runtong voc2007 data set
- Niuke real problem programming - day18
- Ctfshow, information collection: web10
- [understanding of opportunity -40]: direction, rules, choice, effort, fairness, cognition, ability, action, read the five layers of perception of 3GPP 6G white paper
- TypeScript 发布 4.8 beta 版本
- 全日制研究生和非全日制研究生的区别!
- Why do we use UTF-8 encoding?
猜你喜欢
Unity之ASE实现全屏风沙效果
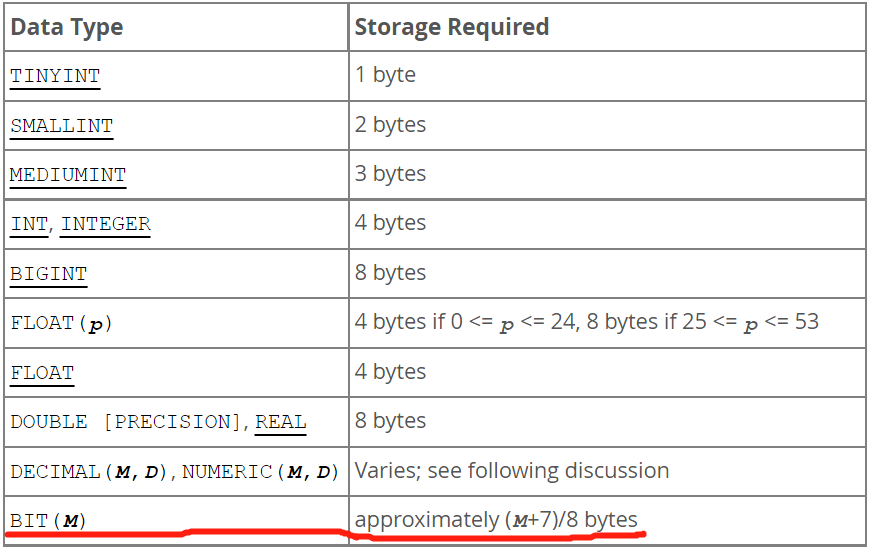
MySQL bit type resolution
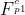
Deformable convolutional dense network for enhancing compressed video quality
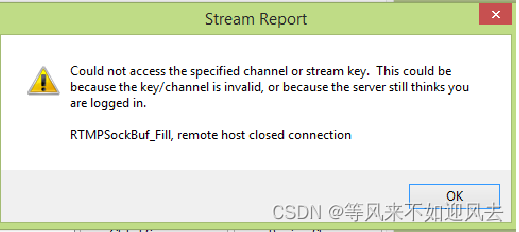
【OBS】RTMPSockBuf_Fill, remote host closed connection.

Guangzhou Development Zone enables geographical indication products to help rural revitalization
![[deep learning] image hyperspectral experiment: srcnn/fsrcnn](/img/84/114fc8f0875b82cc824e6400bcb06f.png)
[deep learning] image hyperspectral experiment: srcnn/fsrcnn
Ctfshow, information collection: web14

Ctfshow, information collection: web10
如何在opensea批量发布NFT(Rinkeby测试网)
简述keepalived工作原理
随机推荐
Connecting FTP server tutorial
写一篇万字长文《CAS自旋锁》送杰伦的新专辑登顶热榜
Mathematical modeling -- what is mathematical modeling
Niuke real problem programming - Day9
CTFshow,信息搜集:web9
[Data Mining] Visual Pattern Mining: Hog Feature + cosinus Similarity / K - means Clustering
激光雷達lidar知識點滴
asp. Netnba information management system VS development SQLSERVER database web structure c programming computer web page source code project detailed design
Niuke real problem programming - day20
Stream learning notes
Use cpolar to build a business website (2)
Delete a whole page in word
Niuke real problem programming - day15
What are PV and UV? pv、uv
Qu'est - ce qu'une violation de données
众昂矿业:萤石继续引领新能源市场增长
STM32F103C8T6 PWM驱动舵机(SG90)
Pat grade a 1103 integer factorizatio
2. Heap sort "hard to understand sort"
Niuke real problem programming - day16