当前位置:网站首页>Execution process of MySQL query request - underlying principle
Execution process of MySQL query request - underlying principle
2022-07-06 18:33:00 【@Positive_ function】
Come and explore MySQL Well !
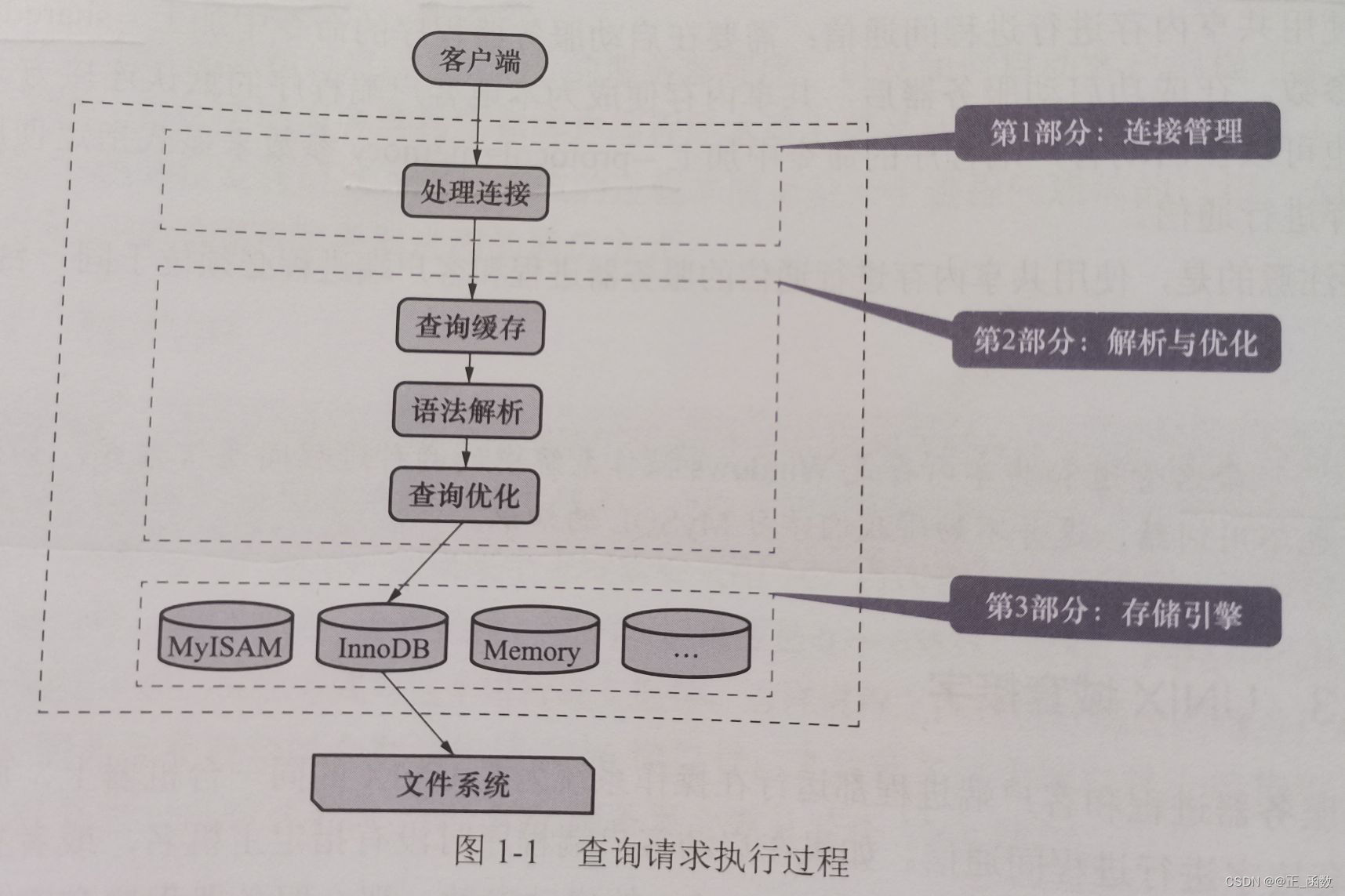
One 、 Connection management
Client processes can adopt TCP/IP、 Named pipes or shared memory 、UNIX Domain socket And other communication methods to establish a connection with the server process . Whenever a client process connects to a server process , The server process will create a thread to deal with the interaction with the client ; When the client exits, it will disconnect from the server , The server does not immediately destroy the threads that interact with the client , Instead, cache it , When another new client connects , The cached thread will be allocated to the new client . This eliminates the need to create and destroy threads frequently , So it saves money . From this we can also see ,MySQL The server will assign a thread to each connected client , However, too many threads will seriously affect the system performance , So we also need to limit the number of clients that can connect to the server at the same time . When the client program initiates a connection , Need to carry host information 、 user name 、 Password and other information , The server program authenticates the information provided by the client program . If authentication fails , The server program will reject the connection . in addition , If the client program and the server program do not run on the same computer , We can also adopt Transport layer security (TransportLayer Security,TLS) The protocol encrypts the connection , So as to ensure the security of data transmission .
When the connection is established , The server thread associated with the client will always wait for the request sent by the client .MySQL The request received by the server is just a text message , The text message has to go through various processes . What if you want to know what happened , Please read on .
Two 、 Analysis and optimization
Up to now ,MySQL The server has obtained the request in text form , Then I have to go through “ Ninety-eight is difficult ” To deal with , Some of the more important parts are The query cache 、 Syntax parsing and Query optimization . Let's take a closer look at .
2.1 The query cache
If I ask you 9 + 8 * 16- 3 * 2 * 17 What's the value of , You may use a calculator to calculate , Or more powerful, direct mental arithmetic , Finally, we got the result 357. If I ask you again 9 + 8 * 16 - 3 * 2 * 17 What's the value of , Will you still calculate foolishly ? We have just calculated , Just say the answer directly .
MySQL The same is true for the server program to process query requests , It will cache the query requests and results that have just been processed . If you have the same request next time , Just look up the results directly from the cache , There is no need to look up in the underlying table . This query cache can be shared between different clients . in other words . If the client A Just sent a query request , And the client B Then the same query request is sent , So the client B You can directly use the data in the query cache for this query .
Of course ,MySOL The server is not as smart as anyone , If there is any character difference between the two query requests ( for example , Space 、 notes 、 Case write ), Will cause the cache to miss . in addition , If the query request contains some system functions 、 User defined variables and functions 、 The system tables , Such as myql、information_schema、performance_schema Tables in the database , Then the request will not be cached . Take some system functions as an example , Two calls to the same function may produce different results . Like functions NOW, Each call will generate the latest current time . If this function is called in two query requests , Even if the text information of the query request is the same , Then two queries at different times should also get different results . If the results are cached at the first query , Using the result of the first query directly in the second query is wrong !
But since it's caching , Then there is a time when the cache fails .MySQL Our caching system monitors every table involved , As long as the structure or data of the table is modified , For example, we used INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、TRUNCATE TABLE、ALTER TABLE、DROP TABLE or DROP DATABASE sentence , Then all query caches related to the table will become invalid and be deleted from the query cache !
Although query caching can sometimes improve system performance , But it also has to incur some overhead due to maintaining this cache . For example, we need to search in the query cache every time , After the query request is processed, the query cache needs to be updated , The memory area corresponding to the query cache needs to be maintained 、 from MySQL 5.7.20 Start , Query caching is not recommended , stay MySQL 8.0 Delete it directly in .
2.2 Syntax parsing
If the query cache misses , Next, you need to enter the formal query stage . Because the request sent by the client program is just a piece of text , therefore MySQL The server program first analyzes this text , Determine whether the syntax of the request is correct , Then the table to be queried from the text 、 All kinds of query conditions are extracted and put into MySQL Some data structures used inside the server .
essentially , Extracting the required information from the specified text is a compilation process , Involving lexical analysis 、 Syntax analysis 、 Semantic analysis and other stages . These issues do not fall within the scope of our discussion , You just need to understand that this step is required in the process of processing requests .
2.3 Query optimization
After parsing , The server program gets the information it needs , For example, what are the tables and columns to query 、 What are the search criteria . But that's not enough , Because we write MySQL Statement execution efficiency may not be very high ,MySQL Our optimization program will optimize our statements , If external connection is converted to internal connection 、 Expression simplification 、 Sub query into a bunch of things such as connections . The result of optimization is to generate an execution plan , This execution plan indicates which indexes should be used to execute the query , And what is the connection order between tables . We can use EXPLAIN Statement to view the execution plan of a statement .
3、 ... and 、 Storage engine
Until the server program completes the query optimization , You haven't really accessed the data in the real table .MySQL The server encapsulates the data storage and extraction operations into a module called storage engine . We know , A table consists of row by row records , But it's just a logical concept . How to physically represent records , How to read data from the table and how to write data to specific physical memory , It's all the responsibility of the storage engine . In order to achieve different functions ,MySQL Provides a wide range of storage engines , Tables managed by different storage engines may have different storage structures , The access algorithm may also be different .
Why is it called an engine ? Maybe this name is more popular , In fact, this was called table processor before storage engine , Later, people may think it's too rustic , It becomes a storage engine . Its function is to receive instructions from the upper layer , Then read or write the data in the table .
MySQL Supported storage engines :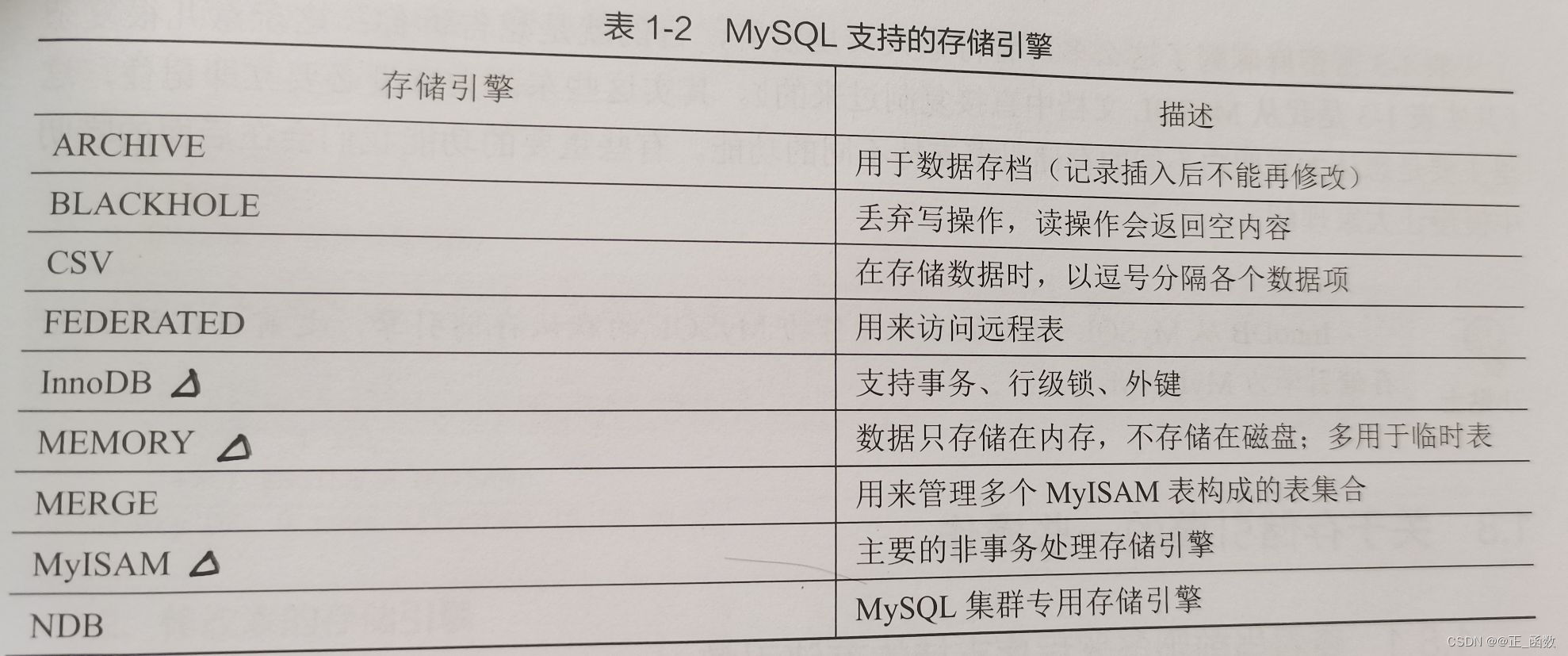
Storage engine support for some functions :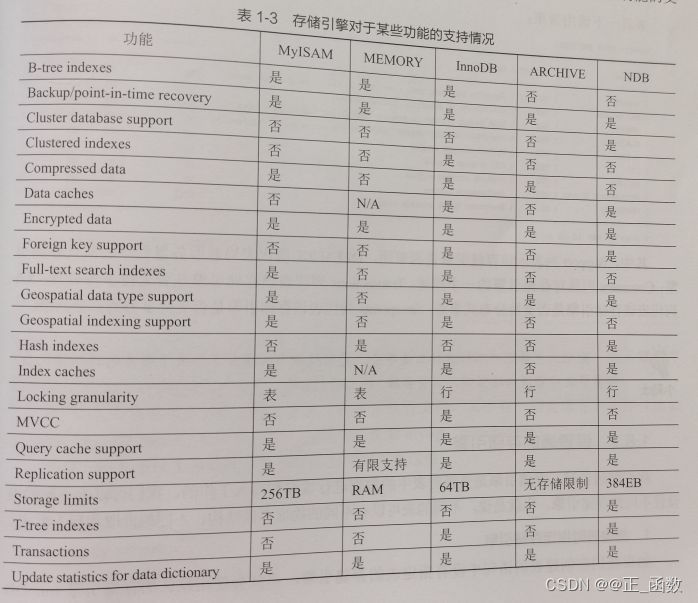
From 《MySQL How it works —— Understand from the root MySQL》.
I hope my sharing above will help you , thank you !
边栏推荐
- Ms-tct: INRIA & SBU proposed a multi-scale time transformer for motion detection. The effect is SOTA! Open source! (CVPR2022)...
- 【.NET CORE】 请求长度过长报错解决方案
- 30 分钟看懂 PCA 主成分分析
- 44所高校入选!分布式智能计算项目名单公示
- [sword finger offer] 60 Points of N dice
- With the implementation of MapReduce job de emphasis, a variety of output folders
- Interview shock 62: what are the precautions for group by?
- 第三季百度网盘AI大赛盛夏来袭,寻找热爱AI的你!
- Introduction to the usage of model view delegate principal-agent mechanism in QT
- 2019 Alibaba cluster dataset Usage Summary
猜你喜欢
declval(指导函数返回值范例)
Grafana 9.0 is officially released! It's the strongest!
TOP命令详解
Implementation of queue

图之广度优先遍历
Distiller les connaissances du modèle interactif! L'Université de technologie de Chine & meituan propose Virt, qui a à la fois l'efficacité du modèle à deux tours et la performance du modèle interacti
MS-TCT:Inria&SBU提出用于动作检测的多尺度时间Transformer,效果SOTA!已开源!(CVPR2022)...
![[swoole series 2.1] run the swoole first](/img/cd/88abf7e83e9d9d416051b33263690b.png)
[swoole series 2.1] run the swoole first
![[the 300th weekly match of leetcode]](/img/a7/16b491656863e2c423ff657ac6e9c5.png)
[the 300th weekly match of leetcode]
Tree-LSTM的一些理解以及DGL代码实现
随机推荐
STM32+ESP8266+MQTT协议连接OneNet物联网平台
celery最佳实践
Recursive way
Compilation Principle -- C language implementation of prediction table
Grafana 9.0 正式发布!堪称最强!
Easy to use PDF to SVG program
HMS core machine learning service creates a new "sound" state of simultaneous interpreting translation, and AI makes international exchanges smoother
SQL优化问题的简述
Excellent open source fonts for programmers
MSF horizontal MSF port forwarding + routing table +socks5+proxychains
Automatic reservation of air tickets in C language
2022 Summer Project Training (III)
CRMEB 商城系统如何助力营销?
d绑定函数
Celery best practices
J'aimerais dire quelques mots de plus sur ce problème de communication...
atcoder它A Mountaineer
小程序在产业互联网中的作用
当保存参数使用结构体时必备的开发技巧方式
declval(指导函数返回值范例)