当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode array operation
Leetcode array operation
2022-07-05 06:13:00 【Dawnlighttt】
List of articles
q54 Spiral matrix
Answer key
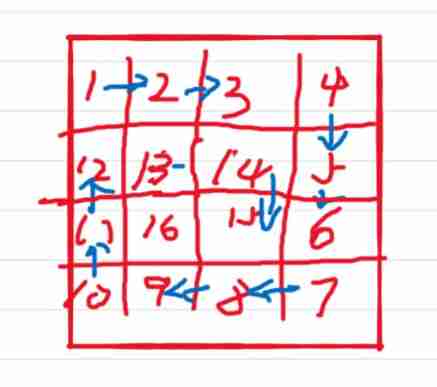
Traverse every row and column in a layer by layer way , The last element of each row or column is the beginning of the next column or row . Because the side length of the matrix in the question is not necessarily equal , So in the end, there will be an extra row or column , It can be treated separately .
func spiralOrder(matrix [][]int) []int {
if len(matrix) == 0 {
return []int{
}
}
res := make([]int, 0)
top, bottom, left, right := 0, len(matrix) - 1, 0, len(matrix[0]) - 1
// Traverse in a ring , The last element of each row or column is the beginning of the next column or row
for top < bottom && left < right {
for i := left; i < right; i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[top][i])
}
for i := top; i < bottom; i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[i][right])
}
for i := right; i > left; i-- {
res = append(res, matrix[bottom][i])
}
for i := bottom; i > top; i-- {
res = append(res, matrix[i][left])
}
right--
top++
bottom--
left++
}
// One more line
if top == bottom {
for i := left; i <= right; i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[top][i])
}
// One more column
} else if left == right {
for i := top; i <= bottom; i++ {
res = append(res, matrix[i][left])
}
}
return res
}
q73 Matrix zeroing
Answer key
Use a hash table to mark the value as 0 Coordinates of , Then traverse the hash table , Set the elements of the same row and column to 0 .
type Point struct {
x int
y int
}
func setZeroes(matrix [][]int) {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
hashTable := make(map[Point]bool)
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if matrix[i][j] == 0 && hashTable[Point{
i, j}] == false {
hashTable[Point{
i, j}] = true
}
}
}
for key, _ := range hashTable {
// The same column becomes 0
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
matrix[i][key.y] = 0
}
// Peers become 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
matrix[key.x][i] = 0
}
}
}
q78 A subset of
Answer key
This question can use dfs and bfs There are two ways to solve .
dfs:
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
res = make([][]int, 0)
dfs(nums, 0, nil)
return res
}
func dfs(nums []int, path int, prefix []int) {
if path >= len(nums) {
dst := make([]int, len(prefix))
copy(dst, prefix)
res = append(res, dst)
return
}
dfs(nums, path + 1, append(prefix, nums[path]))
dfs(nums, path + 1, prefix)
}
bfs:
func subsets1(nums []int) [][]int {
res := make([][]int, 0)
path := make([]int, 0)
var bfs func(int)
bfs = func(start int) {
if start > len(nums) {
return
}
tmp := make([]int, len(path))
copy(tmp, path)
res = append(res, tmp)
for i := start; i < len(nums); i++ {
path = append(path, nums[i])
bfs(i + 1)
path = path[:len(path) - 1]
}
}
bfs(0)
return res
}
q384 Scramble the array
Answer key
The hardest part of this problem is how to disturb the array , The strategy is like this : loop n Time , Exchange the randomly obtained array elements with the last element of the array every time .
type Solution struct {
nums []int
reNums []int
}
func Constructor(nums []int) Solution {
return Solution{
nums: nums, reNums: append([]int{
}, nums...)}
}
func (this *Solution) Reset() []int {
return this.reNums
}
func (this *Solution) Shuffle() []int {
for n := len(this.nums); n > 0; n-- {
randIndex := rand2.Intn(n)
this.nums[n - 1], this.nums[randIndex] = this.nums[randIndex], this.nums[n - 1]
}
return this.nums
}
q581 The shortest continuous unordered subarray
Answer key
First, determine the boundary of the subarray , We set it as begin and end. Actually begin Is the subscript of the last number greater than the minimum , and end In fact, it is the subscript of the last element smaller than the maximum . For example, it is easy to understand :{1, 2, 5, 4, 3, 6, 7} , In this case , The last number smaller than the maximum is actually 3, Because the array traverses to 3 When , The maximum value at this time is 5, therefore 3 Is the last number smaller than the maximum , In the following traversal , Are updated maximum . So it is the same to find the left boundary .
func findUnsortedSubarray(nums []int) int {
n := len(nums)
min, max := nums[n - 1], nums[0]
begin, end := -1, -1
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if nums[i] >= max {
max = nums[i]
} else {
end = i
}
if nums[n - i - 1] <= min {
min = nums[n - i - 1]
} else {
begin = n - i - 1
}
}
// Special judgement
if end == -1 {
return 0
}
return end - begin + 1
}
q945 Use the minimum increment unique to the array
Answer key
First, sort the array , Then iterate through the array , If the current element is less than or equal to its previous element , Then change it to the previous number +1 .
func minIncrementForUnique(nums []int) int {
sort.Ints(nums)
move := 0
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] <= nums[i - 1] {
prev := nums[i]
nums[i] = nums[i - 1] + 1
move += nums[i] - prev
}
}
return move
}
边栏推荐
- [jailhouse article] jailhouse hypervisor
- 1039 Course List for Student
- JS quickly converts JSON data into URL parameters
- leetcode-31:下一个排列
- js快速将json数据转换为url参数
- [cloud native] record of feign custom configuration of microservices
- Appium基础 — 使用Appium的第一个Demo
- LVS简介【暂未完成(半成品)】
- [rust notes] 16 input and output (Part 2)
- Flutter Web 硬件键盘监听
猜你喜欢
Navicat連接Oracle數據庫報錯ORA-28547或ORA-03135
Sqlmap tutorial (II) practical skills I

1.15 - 输入输出系统
leetcode-6111:螺旋矩阵 IV

Appium基础 — 使用Appium的第一个Demo
![[jailhouse article] look mum, no VM exits](/img/fe/87e0851d243f14dff96ef1bc350e50.png)
[jailhouse article] look mum, no VM exits
Leetcode-6110: number of incremental paths in the grid graph

Personal developed penetration testing tool Satania v1.2 update
7. Processing the input of multidimensional features
1.14 - assembly line
随机推荐
Spark中groupByKey() 和 reduceByKey() 和combineByKey()
Traditional databases are gradually "difficult to adapt", and cloud native databases stand out
Dichotomy, discretization, etc
Leetcode-6110: number of incremental paths in the grid graph
liunx启动redis
Introduction and experience of wazuh open source host security solution
leetcode-3:无重复字符的最长子串
QT判断界面当前点击的按钮和当前鼠标坐标
1041 Be Unique
Appium foundation - use the first demo of appium
Liunx starts redis
Leetcode-9: palindromes
1039 Course List for Student
Typical use cases for knapsacks, queues, and stacks
【Rust 笔记】16-输入与输出(下)
Is it impossible for lamda to wake up?
Leetcode-556: the next larger element III
[rust notes] 16 input and output (Part 2)
[cloud native] record of feign custom configuration of microservices
Control unit