当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode-6110: number of incremental paths in the grid graph
Leetcode-6110: number of incremental paths in the grid graph
2022-07-05 06:09:00 【Chrysanthemum headed bat】
leetcode-6110: The number of incremental paths in the grid graph
subject
To give you one m x n Integer grid graph of grid , You can move from a grid to 4 Any lattice adjacent in two directions .
Please return to the grid from arbitrarily Grid departure , achieve arbitrarily lattice , And the number in the path is Strictly increasing Number of paths for . Because the answer could be big , Please correct the results 1 0 9 + 7 10^9 + 7 109+7 Remainder After the return .
If the grids accessed in the two paths are not exactly the same , Then they are regarded as two different paths .
Example 1: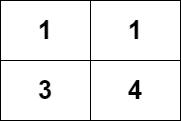
Input :grid = [[1,1],[3,4]]
Output :8
explain : Strictly incremental paths include :
- The length is 1 The path of :[1],[1],[3],[4] .
- The length is 2 The path of :[1 -> 3],[1 -> 4],[3 -> 4] .
- The length is 3 The path of :[1 -> 3 -> 4] .
Number of paths is 4 + 3 + 1 = 8 .
Example 2:
Input :grid = [[1],[2]]
Output :3
explain : Strictly incremental paths include :
- The length is 1 The path of :[1],[2] .
- The length is 2 The path of :[1 -> 2] .
Number of paths is 2 + 1 = 3 .
Problem solving
Method 1 :dfs Memory search
adopt memory Array save , The number of incremental paths per grid
such as memory[i][j], Indicates that the end point is (i,j) Number of incremental paths
class Solution {
public:
const int MOD=1e9+7;
vector<vector<int>> dirs={
{
-1,0},{
0,-1},{
1,0},{
0,1}};
vector<vector<int>> memory;
int dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid,int i,int j){
if(memory[i][j]>0) return memory[i][j];
memory[i][j]=1;
for(vector<int>& dir:dirs){
int nx=i+dir[0];
int ny=j+dir[1];
if(nx<0||nx>=grid.size()||ny<0||ny>=grid[0].size()||grid[i][j]<=grid[nx][ny]) continue;
memory[i][j]=(memory[i][j]+dfs(grid,nx,ny))%MOD;
}
return memory[i][j];
}
int countPaths(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m=grid.size();
int n=grid[0].size();
memory.resize(m,vector<int>(n));
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
res=(res+dfs(grid,i,j))%MOD;
}
}
return res;
}
};
Method 2 : Dynamic programming ( Overtime )
dp[i][j][l] Indicates that the grid point is (i,j), The path length is l The number of ,
The purpose of this is because , Only get a length of l-1 Number of paths for , To calculate the length l Number of paths for .
shortcoming :
However, for example grid[2][3]>grid[2][4]
But every time, we will make repeated comparisons , Traversing (2,3), Will compare with the right , Traversing (2,4) And compare with the left , And can't remember , because dp[i][j][l] It's just l The result of length , Just an intermediate value , Not the end result .
And method one : It directly saves the number of all incremental paths of each grid point , So it can be memorized .(dfs, Complexity O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2))
Method 2 can get the number of each path length , A small amount of data can be obtained by , But it will time out .( Matrix traversal , Complexity O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3))
class Solution {
public:
const int Mod=1e9+7;
vector<vector<int>> dirs={
{
-1,0},{
0,-1},{
1,0},{
0,1}};
int countPaths(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int res=0;
int m=grid.size();
int n=grid[0].size();
int maxPath=m*n;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m,vector<vector<int>>(n,vector<int>(m*n+1)));
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j][0]=0;
dp[i][j][1]=1;
res++;
}
}
for(int l=2;l<=maxPath;l++){
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j][l]=0;
for(vector<int>& dir:dirs){
int nx=i+dir[0];
int ny=j+dir[1];
if(nx>=0&&nx<m&&ny>=0&&ny<n&&grid[i][j]>grid[nx][ny]){
dp[i][j][l]+=dp[nx][ny][l-1];
}
}
res=(res+dp[i][j][l])%Mod;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
![[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?](/img/a3/7a1564cd9eb564abfd716fef08a9e7.jpg)
[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?
Wazuh開源主機安全解决方案的簡介與使用體驗
1.13 - RISC/CISC

AtCoder Grand Contest 013 E - Placing Squares
![Introduction to LVS [unfinished (semi-finished products)]](/img/72/d5a943a8d6d71823dcbd7f23dda35b.png)
Introduction to LVS [unfinished (semi-finished products)]
SQLMAP使用教程(二)实战技巧一
The connection and solution between the shortest Hamilton path and the traveling salesman problem
shared_ Repeated release heap object of PTR hidden danger
Erreur de connexion Navicat à la base de données Oracle Ora - 28547 ou Ora - 03135
Appium自动化测试基础 — Appium测试环境搭建总结
随机推荐
打印机脱机时一种容易被忽略的原因
【Rust 笔记】13-迭代器(中)
[rust notes] 14 set (Part 1)
【Rust 笔记】17-并发(上)
Smart construction site "hydropower energy consumption online monitoring system"
Appium自动化测试基础 — Appium测试环境搭建总结
wordpress切换页面,域名变回了IP地址
A reason that is easy to be ignored when the printer is offline
R language [import and export of dataset]
Règlement sur la sécurité des réseaux dans les écoles professionnelles secondaires du concours de compétences des écoles professionnelles de la province de Guizhou en 2022
Flutter Web 硬件键盘监听
Wazuh開源主機安全解决方案的簡介與使用體驗
884. Uncommon words in two sentences
Daily question 2006 Number of pairs whose absolute value of difference is k
1.14 - 流水线
How to adjust bugs in general projects ----- take you through the whole process by hand
Navicat連接Oracle數據庫報錯ORA-28547或ORA-03135
Groupbykey() and reducebykey() and combinebykey() in spark
leetcode-556:下一个更大元素 III
AtCoder Grand Contest 013 E - Placing Squares