当前位置:网站首页>Spark中groupByKey() 和 reduceByKey() 和combineByKey()
Spark中groupByKey() 和 reduceByKey() 和combineByKey()
2022-07-05 05:50:00 【YaoYong_BigData】
一、groupByKey:
在一个(K,V)的RDD上调用,返回一个(K, Iterator[V])的RDD,也是对每个key进行操作,但只生成一个sequence,groupByKey本身不能自定义函数,需要先用groupByKey生成RDD,然后才能对此RDD通过map进行自定义函数操作。
作用:
GroupByKey 算子的主要作用是按照 Key 分组, 和 ReduceByKey 有点类似, 但是 GroupByKey 并不求聚合, 只是列举 Key 对应的所有 Value。
注意点:
GroupByKey 是一个 Shuffled。
GroupByKey 和 ReduceByKey 不同, 因为需要列举 Key 对应的所有数据, 所以无法在 Map 端做 Combine, 所以 GroupByKey 的性能并没有 ReduceByKey 好。
二、reduceByKey:
是对key的value进行merge操作,在一个(K,V)的RDD上调用,返回一个(K,V)的RDD,使用指定的reduce函数,将相同key的值聚合到一起,与groupByKey类似,reduce任务的个数可以通过第二个可选的参数来设置,最重要的是它能够在本地先进行merge操作,并且merge操作可以通过函数自定义。

作用:
首先按照 Key 分组生成一个 Tuple, 然后针对每个组执行
reduce算子。
调用:
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) ⇒ V): RDD[(K, V)]
参数:
func → 执行数据处理的函数, 传入两个参数, 一个是当前值, 一个是局部汇总, 这个函数需要有一个输出, 输出就是这个 Key 的汇总结果。
注意点:
ReduceByKey 只能作用于 Key-Value 型数据, Key-Value 型数据在当前语境中特指 Tuple2。
ReduceByKey 是一个需要 Shuffled 的操作。
和其它的 Shuffled 相比, ReduceByKey是高效的, 因为类似 MapReduce 的, 在 Map 端有一个 Cominer, 这样 I/O 的数据便会减少。
三、combineByKey()
spark根据key做聚合的aggregateByKey,groupByKey,reduceByKey等常用算子其底层本质都是调用combineByKey实现的,即都是combineByKey的一种特殊情况,下面介绍下combineByKey算子:
源码有两种方式:
/**
*
* @param createCombiner
* @param mergeValue
* @param mergeCombiners
* @tparam C
* @return
*/
def combineByKey[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners)(null)
/**
*
* @param createCombiner
* @param mergeValue
* @param mergeCombiners
* @param partitioner
* @param mapSideCombine
* @param serializer
* @tparam C
* @return
*/
def combineByKey[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true,
serializer: Serializer = null): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners,
partitioner, mapSideCombine, serializer)(null)
}
}
参数说明:
1、createCombiner:V => C ,分区内创建组合函数。这个函数把当前的值作为参数,此时我们可以对其做些附加操作(类型转换)并把它返回 (这一步类似于初始化操作)。
说明:同一分区内,同一个key,只有第一次出现的value才会运行此函数。
2、mergeValue: (C, V) => C,分区内合并值函数。该函数把元素V合并到之前的元素C(createCombiner)上 (这个操作在每个分区内进行)。
说明:同一分区内,同一个key,非第一次出现value运行此函数,其中C为上次的结果,V为本次值。
3、mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,多分区合并组合器函数。该函数把2个元素C合并。
说明:这个操作在不同分区间进行。
4、partitioner:自定义分区数,默认为HashPartitioner。
5、mapSideCombine:是否在map端进行Combine操作,默认为true。
过一下图,逻辑应该就清晰了:
补充一个更详细的图:

四、实例
/**
* ------输出结果------
* (tim,1)
* (lucy,1)
* (Hello,3)
* (lily,1)
*/
@Test
def reduceByKeyTest():Unit = {
// 1. 创建 RDD
val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Seq("Hello lily", "Hello lucy", "Hello tim"))
// 2. 处理数据
val rdd2 = rdd1.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_ + _)
// 3. 得到结果
val result = rdd2.collect()
result.foreach(println(_))
// 4. 关闭sc
sc.stop()
}
/**
* ------输出结果------
* (a,CompactBuffer(1, 1))
* (b,CompactBuffer(1))
*/
@Test
def groupByKey(): Unit = {
val rdd: RDD[(String, Int)] = sc.parallelize(Seq(("a", 1), ("a", 1), ("b", 1)))
val rdd1: RDD[(String, Iterable[Int])] = rdd.groupByKey()
val rdd2: Array[(String, Iterable[Int])] = rdd1.collect()
rdd2.foreach(println(_))
}
/**
* ------输出结果------
* (zhangsan,97.33333333333333)
* (lisi,97.5)
* ---求每个学生的平均成绩
*/
@Test
def combineByKey(): Unit = {
// 1. 准备集合
val rdd: RDD[(String, Double)] = sc.parallelize(Seq(
("zhangsan", 99.0),
("zhangsan", 96.0),
("lisi", 97.0),
("lisi", 98.0),
("zhangsan", 97.0))
)
// 2. 算子操作
// 2.1. createCombiner 转换数据
// 2.2. mergeValue 分区上的聚合
// 2.3. mergeCombiners 把所有分区上的结果再次聚合, 生成最终结果
val combineResult = rdd.combineByKey(
createCombiner = (curr: Double) => (curr, 1),
mergeValue = (curr: (Double, Int), nextValue: Double) => (curr._1 + nextValue, curr._2 + 1),
mergeCombiners = (curr: (Double, Int), agg: (Double, Int)) => (curr._1 + agg._1, curr._2 + agg._2)
)
/**
* ------输出结果------
* (zhangsan,(292.0,3))
* (lisi,(195.0,2))
*/
//val resultRDD = combineResult
val resultRDD = combineResult.map( item => (item._1, item._2._1 / item._2._2) )
// 3. 获取结果, 打印结果
resultRDD.collect().foreach(println(_))
}边栏推荐
- YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2
- sync. Interpretation of mutex source code
- Codeforces Round #716 (Div. 2) D. Cut and Stick
- PC register
- After setting up the database and website When you open the app for testing, it shows that the server is being maintained
- Fried chicken nuggets and fifa22
- Dynamic planning solution ideas and summary (30000 words)
- Wazuh開源主機安全解决方案的簡介與使用體驗
- Daily question 1688 Number of matches in the competition
- Educational Codeforces Round 107 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Colorings and Dominoes
猜你喜欢
![[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?](/img/a3/7a1564cd9eb564abfd716fef08a9e7.jpg)
[practical skills] how to do a good job in technical training?
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
Reader writer model
Graduation project of game mall
Pointnet++ learning
Implement a fixed capacity stack
In this indifferent world, light crying

个人开发的渗透测试工具Satania v1.2更新
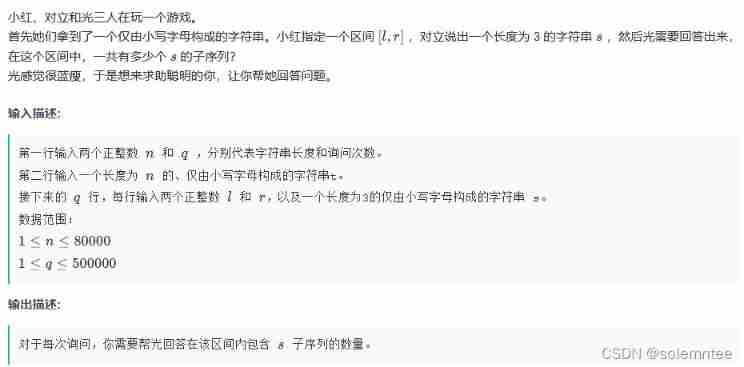
从Dijkstra的图灵奖演讲论科技创业者特点
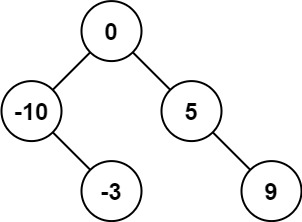
LeetCode 0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 数组中值为根,中值左右分别为左右子树
随机推荐
sync. Interpretation of mutex source code
Little known skills of Task Manager
1.15 - 输入输出系统
The sum of the unique elements of the daily question
Sword finger offer 35 Replication of complex linked list
Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
挂起等待锁 vs 自旋锁(两者的使用场合)
YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2
游戏商城毕业设计
Educational Codeforces Round 116 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Arena
ALU逻辑运算单元
Daily question 1688 Number of matches in the competition
2022 pole technology communication arm virtual hardware accelerates the development of Internet of things software
Sword finger offer 09 Implementing queues with two stacks
LeetCode 1200.最小绝对差
Convolution neural network -- convolution layer
QT判断界面当前点击的按钮和当前鼠标坐标
A misunderstanding about the console window
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
Analysis of backdoor vulnerability in remote code execution penetration test / / phpstudy of national game title of national secondary vocational network security B module

