当前位置:网站首页>[rust notes] 14 set (Part 1)
[rust notes] 14 set (Part 1)
2022-07-05 06:04:00 【phial03】
14 - aggregate ( On )
14.1 - summary
aggregate : Collective generic types .
Rust The difference between sets and sets in other languages :
Rust Use Transfer To avoid deep replication .
To borrow
The checker can make Rust At compile time , Eliminate invalid errors . Invalid errors are as follows :
- Save the data pointer in the set , When the set is scaled or modified , There will be dangling pointers .
- C++ Undefined behavior in .
- Language in memory security , Invalid errors may cause
ConcurrentModificationException.
Rust No,
null- Appear in other languages
nullThe place of ,Rust useOptionInstead of .
- Appear in other languages
Standard set :
Rust aggregate explain C++ aggregate Java aggregate Python aggregate Vec<T>Increasable array vectorArrayListlistVecDeque<T>deque ( Growable ring buffer ) dequeArrayDequecollections.dequeLinkedList<T>Double linked list listLinkedList— BinaryHeap<T> where T: OrdThe biggest pile priority_queuePriorityQueueheapqHashMap<K, V> where K: Eq + Hashkey — Value hash table unordered_mapHashMapdictBTreeMap<K, V> where K: OrdOrdered bond — Value table mapTreeMap— HashSet<T> where T: Eq + HashHash table unordered_setHashSetsetBTreeSet<T> where T: OrdOrdered set setTreeSet— Vec<T>:【 Common collections 】 It can grow 、 Types allocated on the heapTAn array of values of .VecDeque<T>: AndVec<T>similar , But it is suitable for use as a first in first out queue .- Support the efficient addition and removal of values at the front and back of the list .
- It will slow down all other operations .
LinkedList<T>: Support in front of the list 、 Back end fast access .- And
VecDeque<T>The function is similar to , But it adds fast connection . - Generally speaking , Slightly slower than
Vec<T>andVecDeque<T>.
- And
BinaryHeap<T>: Priority queue . Values are always organized to find and remove maximum values .HashMap<K, V>:【 Common collections 】 It's a key — Table of value pairs , Press the key to check the value quickly . Items are stored in any order .BTreeMap<K, V>: AndHashMap<K, V>The function is similar to , But entries are stored in key order .- such as :
BTreeMap<String, i32>Compare sequential memory entries by string . - Unless you need to store entries in order , otherwise
HashMap<K, V>faster .
- such as :
HashSet<T>:【 Common collections 】 Is a group of types T Value . Commonly used in :- Quickly add and remove values .
- Quickly check whether the given value exists in the set .
BTreeSet<T>: AndHashSet<T>The function is similar to , But values are stored sequentially . Again , Unless you need to ensure the order of data , otherwiseHashSet<T>faster .
14.2-Vec<T>
The easiest way to create a vector is to use
vec!macro :// Create empty vector let mut numbers: Vec<i32> = vec![]; // Create a vector containing the given content let words = vec!["step", "on", "no", "pets"]; let mut buffer = vec![0u8; 1024]; // 1024 A filling 0 Bytes ofThe vector has 3 A field : length 、 Capacity and pointer to heap memory where its elements are stored .
VecLike all sets , Realizedstd::iter::FromIterator, So you can use iterators.collect()Method , Create a vector based on any iterator :// Convert another set into a vector let my_vec = my_set.into_iter().collect::<Vec<String>>(); // Equivalent to let my_vec: Vec<String> = my_set.into_iter().collect();
14.2.1 - Access elements
The array can be obtained intuitively through the index 、 Elements of slices or vectors :
// Get a reference to an element let first_line &lines[0]; // Get a copy of the element let fifth_number = numbsers[4]; // Realization Copy let second_line = lines[1].clone(); // Realization Clone // Get a reference to the slice let my_ref = &buffer[4..12]; // Get a copy of the slice let my_copy = buffer[4..12].to_vec(); // Realization Clone- If the index is out of bounds , Then all the above access forms will be surprised .
- The length and index of the vector are
usizedtype . You can use when necessaryn as usizetransformation . - All slicing methods can also be used on arrays and vectors .
slice.first(): Return to rightsliceReference to the first element . The return value type isOption<T>:- If
sliceIt's empty , Then return toNone. - If it's not empty , Then return to
Some(&slice[0]).
- If
slice.last(): Returns the reference to the last element .slice.get(index): returnslice[index]References to .- If you cross the border , Then return to
None. - If it works , Then return to
Some(&index)quote .
- If you cross the border , Then return to
slice.first_mut()、slice.last_mut()andslice.get_mut(): It is a variant of the above methods , returnmutquote .- return
TValue means transfer , Therefore, methods that access elements in place usually return references to elements . - Below
.to_vec()Method is an exception , It returns a copy of the element .
- return
slice.to_vec(): Clone the entire slice , Translate a new vector .- Only when elements can be cloned (
where T: Clone) Only in the case of .
- Only when elements can be cloned (
14.2.2 - iteration
- Vectors and slices can be iterated : You can iterate by value , You can also iterate by reference .
- iteration
Vec<T>produceTType of item : Elements are transferred out of the vector one by one , And be consumed . - iteration
&[T; N]、&[T]or&Vec<T>Type value : That is, for the array 、 References to slices or vectors , produce&TType of item . References to individual elements , There will be no transfer . - iteration
&mut [T: N]、&mut [T]or&mut Vec<T>Type value : produce&mut TType of item .
- iteration
- Array 、 Slices and vectors and
.iter()and.iter_mut()Method : The iterators created generate references to their elements .
14.2.3 - Growth and contraction vectors
Array 、 Length of slice and vector : Indicates the number of elements they contain .
slice.len(): returnsliceThe length of , The type isusize.slice.is_empty(): staysliceWhen no element is included , namelyslice.len() == 0when , returntrue.
The size of arrays and slices is immutable , Therefore, the following methods of enlargement and contraction are not supported .
Characteristics of vectors :
- All elements of the vector are stored in contiguous memory blocks allocated on the heap .
- The capacity of the vector is the maximum number of elements that can be contained in this block .
VecCapacity can usually be managed automatically , When more capacity is needed , Larger buffers will be allocated , And transfer the elements .
Display management The method of vector capacity :
Vec::with_capacity(n): Create a capacity ofnNew empty vector of .【 Recommended 】vec.capacity(): returnvecThe capacity of , The type isusize.vec.capacity() >= vec.len().vec.reserve(n): Make sure the vector has enough space to accommodate anothernElements .vec.capacity() >= vec.len() + n. If the capacity is enough , Just keep the status quo ; If not enough , A larger buffer will be allocated , Then transfer the vector content .vec.reserve_exact(n): tellvecThe allocated space cannot exceedn, Regardless of future growth .vec.capacity() = vec.len() + n.vec.shrink_to_fit(): Whenvec.capacity() > vec.len()when , Will try to free additional memory .
Vec<T>There are many modifiable references in vectors (&mut self) Is a method that takes a parameter , You can add and remove elements , To change the length of the vector .Add or remove a value at the end of the vector :
vec.push(value): stayvecAdd the given... At the endvaluevalue . This method obtains the value of the parameter , Not references .vec.pop(): Remove and return the last element . The type of return value isOption<T>: If the last element isx, Then return toSome(x); If the vector is empty , Then return toNone. This method returns the value of the element , Instead of quoting .
Add or remove values anywhere in the vector : The more elements to move ,
.insert()and.remove()The slower .vec.insert(index, value): stayvec[index]Insertvalue, And willvec[index..]The value in moves one position clockwise to the right . Ifindex > vec.len()Then surprise occurs .vec.remove(index): Remove and returnvec[index], And willvec[index+1..]The value in moves one position to the left . Ifindex >= vec.len()Then surprise occurs . If you want to use this method often , Then it is recommended to useVecDeque<T>To manipulate data , instead ofVec<T>.
Change the length of the vector to the specified value :
vec.resize(new_len, value): Set the vector length tonew_len, If the length increases , It will bevalueValue in the new growth position . The type of element is required to implementCloneSpecial type . Only this method can clone values , Other methods are to transfer values from one place to another .vec.truncate(new_len): Reduce the length of the vector tonew_len, And the elimination range isvec[new_len..]The elements within . Ifvec.len() <= new_len, Then keep the vector as it is .vec.clear(): fromvecRemove all elements from , amount tovec.truncate(0).
Add or remove multiple values at once :
vec.extend(iterable): Put in orderiterableAll items of are added tovecAt the end of . Similar to giving.push()Pass in multiple values .iterableParameters can be implementedIntoIterator<Item=T>Any value . All sets are implementedExtendSpecial type , This method is included .vec.split_off(index): Andvec.truncate(index)The function is similar to , But it will return a containing fromvecRemove the end of the valueVec<T>. Equivalent to multiple value versions.pop().vec1.append(&mut vec2): holdvec2(Vec<T>Vector of type ) All elements of are transferred tovec1.vec2It's going to be empty . Andvec1.extend(vec2)The difference is ,vec2It still exists after the transfer , And the capacity is not affected .vec.drain(range): fromvecRemove scopevec[range]. Returns the iterator of the removed element .rangeIt's a range value , Such as..or0..4.
Selectively remove elements from vectors :
vec.retain(test): Remove all elements that fail the given test .testParameter is an implementation ofFnMut(&T) -> boolFunction or closure of . YesvecEach element of , Will be calledtest(&element): If you return false, Then remove from the vectorelement, And clean it up . In principle, it is equivalent to the following code , But the performance should be better :vec = vec.into_iter().filter(test).collect();vec.dedup(): Clear duplicate elements . scanningvec, Compare adjacent elements , If we find equality , Then clear the extra equal value , Keep a value .let mut byte_vec = b"Missssssissippi".to_vec(); byte_vec.dedup(); assert_eq!(&byte_vec, b"Misisipi");As the result shows , This method only clears Successive duplicate value . If you want to remove all duplicate values , Then there are three ways :
1、 call
.dedupBefore sorting the vectors ;2、 Move the data into the set ;
3、 Use
.retain()Method , You can keep the original order of elements :let mut byte_vec = b"Missssssissippi".to_vec(); let mut seen = HashSet::new(); byte_vec.retain(|r| seen.insert(*r)); // .insert() Returns when the set contains items to insert false. assert_eq!(&byte_vec, b"Misp");vec.dedup_by(same): Andvec.dedup()The function is similar to , The difference is that it uses functions or closuressame(&mut elem1, &mut elem2), instead of==The operator determines whether two elements are repeated .vec.dedup_by_key(key): Andvec.dedup()The function is similar to , The difference is that it judges the repetition of two elements based onkey(&mut elem1) == key(&mut elem2). give an example : IferrorIt's aVec<Box<Error>>Type value :// Remove the error of duplicate message content errors.dedup_by_key(|err| err.description().to_string());
14.2.4 - Connect
Array of arrays : Include any array 、 Slice or vector , The element itself is also an array 、 Slice or vector .
There are two special methods for the array of arrays :
slices.concat(): Return the new vector obtained by splicing all slices .assert_eq!([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].concat(), vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]);slices.join(&separator): Andslices.concat()similar , What doesn't work is that it willseparatorA copy of is inserted between slices .assert_eq!([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]].join(&0), vec![1, 2, 0, 3, 4, 0, 5, 6]);
14.2.5 - Split
Rust Manipulate arrays by indexing 、 Considerations for slicing or vectors :
- Support to get multiple arrays of non modifiable references at the same time 、 Slice or vector :
let v = vec![0, 1, 2, 3]; let a = &v[i]; let b = &v[j]; let mid = v.len() / 2; let front_half = &v[..mid]; let back_half = &v[mid..];- It is not supported to get multiple arrays of modifiable references at the same time 、 Slice or vector :
let mut v = vec![0, 1, 2, 3]; let a = &mut v[i]; let b = &mut v[j]; // error: cannot borrow `v` as mutable more than once at a time // If i == j, Then it is equivalent to that two modifiable references operate on the same integer .Rust Supports many methods , You can not directly modify the array 、 Slice or vector , Instead, it returns a new reference to some of the data , Used to implement split operation : It ensures that the data is divided into non overlapping blocks , There are many ways to divide into
mutHe FeimutTwo versions .slice.iter()andslice.iter_mut(): The returned iterator generatessliceA reference to each element in .slice.split_at(index)andslice.split_at_mut(index): Divide the slice into two , Returns a tuple containing two parts .slice.split_at(index)Equivalent to(&slice[..index], &slice[index..]). IfindexTransboundary , These two methods will surprise .slice.split_first()andslice.split_first_mut(): Returns a tuple , Contains a reference to the first element (slice[0]) And references to all remaining element slices (slice[1..)..split_firt()The type of return value isOption<(&T, &[T])>. If the slice is empty , Then return toNone.slice.split_last()andslice.split_last_mut(): Returns a tuple , Contains a reference to the last element and a reference to all remaining element slices ..split_last()The type of return value isOption<(&[T], &T)>.slice.split(is_sep)andslice.split_mut(is_sep): Based on functions or closuresis_sep, takesliceSplit into one or more sub slices , Returns the iterator of the sub slice .When consuming the returned iterator , Will be called for each element in the slice
is_sep(&element). If you returntrue, Then this element is the separator . The separator element is not included in any sub slice of the output .The output always contains at least one sub slice , One more separator element will produce one more sub slice .
If multiple separators are adjacent or the separator is
sliceLast element of , Then the output will contain empty sub slices .slice.splitn(n, is_sep)andslice.splitn_mut(n, is_sep): Based on functions or closuresis_sep, takesliceSplit intonSub slice , Returns the iterator of the sub slice . Find frontn-1After slicing , You won't callis_sep, The last sub slice contains all the remaining elements .slice.rsplitn(n, is_sep)andslice.rsplitn_mut(n, is_sep): Reverse scan slice . Based on functions or closuresis_sep, takesliceSplit intonSub slice , Returns the iterator of the sub slice . Find aftern-1After slicing , You won't callis_sep.slice.chunks(n)andslice.chunks_mut(n): The returned iterator is a length ofnOf Non overlapping I'm going to slice it . Ifslice.len()NonMultiple , Then the length of the last sub slice is less thann.Iterative method for sub slice
slice.windows(n): The iterators returned are similarsliceSliding window of data . This iterator produces a containingsliceinnSub slices of consecutive elements ( overlap Seed slices , No returnmutQuoted variants ).The first sub slice produced is
&slice[0..n], The second sub slice is&slice[1..n+1], And so on .If
n > slice.len(), Will not produce slices ; Ifn == 0, Then this method will surprise .skill : The size is 2 Sliding window of , It can be used to detect the change of two data points in the data sequence :
let changes = daily_high_temperatures .windows(2) // Get the temperature of two adjacent days .map(|w| w[1] - w[0]) // Calculate the temperature difference .collect::<Vec<_>>();
14.2.6 - In exchange for
slice.swap(i, j): In exchange forslice[i]andslice[j]These two elements .vec.swap_remove(i): For vector , Support the item pair method of efficiently removing any element .
- Remove and return
vec[i], Followvec.remove(i)similar . - But it will not move the following elements forward , To fill the vacancy , But simply put
vecThe last element of moves to the empty position . - You can use .
- Remove and return
14.2.7 - Sort and search
Common sorting methods :
slice.sort(): Sort elements incrementally . You need to ensure that the element type implementsOrdSpecial type .slice.sort_by(cmp): Use a function or closure that specifies the sort methodcmp, YessliceThe elements are sorted .cmpIt has to happenFn(&T, &T) -> std::cmp::Ordering.Rust Support
.cmp()Method , It can be used as the sorting method specified above :students.sort_by(|a, b| a.last_name.cmp(&b.last_name));If you want to sort by a field , Then use another field as the final basis , Then we need to compare tuples :
students.sort_by( |a, b| { let a_key = (&a.last_name, &a.first_name); let b_key = (&b.last_name, &b.first_name); a_key.cmp(&b_key) } );slice.sort_by_key(key): According to the sorting keysliceIncremental sorting of elements , Sorting keys can use functions or closureskeygive .keyThe type of must implementFn(&T) -> K where K: OrdSpecial type . During sorting , The value of the sort key is not cached , thereforekeyMay be called more than once .If
TWhen one or more sortable fields are included , You can choose a variety of sorting methods :// grade_point_average() Implements a sort method : // Sort by grade average , In front of the lowest row students.sort_by_key(|s| s.grade_point_average())key(element)Cannot return a reference borrowed from an element . As the following call , But you can use.sort_by():students.sort_by_key(|s| &s.last_name); // error , Life span cannot be inferred
Reverse sort method :
- Use
.sort_by, And pass in two parameters to change the ordercmpClosure . such as|b, a|, instead of|a, b|, Then reverse sort will be performed . slice.reverse(): Reverse sort slice elements in place .
- Use
After sorting , Can perform efficient search methods : Two points search
slice.binary_search(&value)、slice.binary_search_by(&value, cmp)andslice.binary_search_by_key(&value, key): Search from the sorted slicesvaluevalue ,valueIt's a quote .- Their return type is
Result<usize, usize>. If in the specified sort ,slice[index] == value, Then they returnOk(index). If this index value is not found , So returnErr(insertion_point), At this time ininsertion_pointPosition insertvalueWill keep the order . f32andf64YesNaNvalue , So they have not been realizedOrd, Therefore, it cannot be directly used as a key for sorting and binary search . If you must operate on floating-point numbers , Then you can choose to useord_subsetpackage .
How to search for unordered vectors :
slice.contains(&value): staysliceAny element of is equal tovaluewhen , returntrue. This method will check the sliced elements one by one .If you want to find the position of the value in the slice , The implementation is similar to JavaScript Medium
array.indexOf(value)The effect of , You can use the following iterators :slice.iter().position(|x| *x == value); // This iterator returns `Option<usize>`
14.2.8 - Compare slices
If type
TSupport==and!=The operator , So array[T; N]、 section[T]、 vectorVec<T>Will also support .- If the length term of the slice is right , Each corresponding element is also equal , Then they will be equal .
- Arrays and vectors also follow the above rules .
If type
TSupport<、<=、>and>=The operator , So array[T; N]、 section[T]、 vectorVec<T>Will also support . Slices are compared in lexicographic order .Common slice comparison methods
slice.starts_with(other): staysliceThe first series of values equals another sliceoterhThe element is , This method returnstrue:assert_eq!([1, 2, 3, 4].start_with(&[1, 2]), true); assert_eq!([1, 2, 3, 4].start_with(&[2, 3]), false);slice.ends_with(other): in the light ofsliceCompare a series of values at the end .assert_eq!([1, 2, 3, 4].start_with(&[3, 4]), true);
14.2.9 - Random element
Random numbers are not built into the standard library .
randPackage provides the following methods , Used to extract data from an array 、 Get random output from slice or vector .rng.choose(slice): Return to rightsliceReferences to random elements in . The return value isOption<&T>, Only when the slice is empty will it returnNone.rng.shuffle(slice): YessliceElements are randomly sorted in place . Must pass insliceModifiable reference of .
The above method comes from
rand::RngSpecial type , Calling them requires aRng( Random number generator ).By calling
rand::thread_rng()Can getRng;To disrupt
my_vecThe order of , It can be executed :use rand::{ Rng, thread_rng}; thread_rng().shuffle(&mut my_vec);
14.2.10-Rust Principle of eliminating invalid errors
Don't modify the set while iterating .
stay Python Such invalid errors will be encountered in : Modifying data during iterations invalidates the iterator .
my_list = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] for index, val in enumerate(my_list): if val > 4: del my_list[index] # bug: Modify the list during the iteration print(my_list) # Output results :[1, 3, 7],7 Greater than 4.- stay Java in , The above implementation will generate exceptions ;
- stay C++ in , This is an undefined behavior ;
- stay Python in , Although this behavior is clearly defined , But it's not intuitive : Iterators skip an element .
Python Or other languages , have access to
filterCreate a new vector to fix the above problem .Use Rust Repeat the above error :
fn main() { let mut my_vec = vec![1, 3, 5, 6, 8]; for (index, &val) in my_vec.iter().enumerate() { if val > 4 { my_vec.remove(index); // bug: You can't borrow my_vec Modifiable reference of // my_vec.retain(|&val| val <= 4); // Fix the above bug Methods } } println!("{:?}", my_vec); }Rust The program will be rejected at compile time : Calling
my_vec.iter()when , The loop borrows the shared reference of the vector . The lifetime of this reference is as long as that of the iterator , UntilforThe end of the cycle still exists . When there is a shared reference , Out of commissionmy_vec.remove(index)Modify vector .
See 《Rust Programming 》( Jim - Brandy 、 Jason, - By orendov , Translated by lisongfeng ) Chapter 16
Original address
边栏推荐
- QQ电脑版取消转义符输入表情
- 【Rust 笔记】17-并发(上)
- 【云原生】微服务之Feign自定义配置的记录
- Daily question 1688 Number of matches in the competition
- RGB LED infinite mirror controlled by Arduino
- One question per day 1765 The highest point in the map
- PC寄存器
- 【Rust 笔记】16-输入与输出(上)
- 中职网络安全技能竞赛——广西区赛中间件渗透测试教程文章
- Smart construction site "hydropower energy consumption online monitoring system"
猜你喜欢

【实战技能】非技术背景经理的技术管理
Appium自动化测试基础 — Appium测试环境搭建总结
Graduation project of game mall
Sword finger offer 35 Replication of complex linked list
Overview of variable resistors - structure, operation and different applications
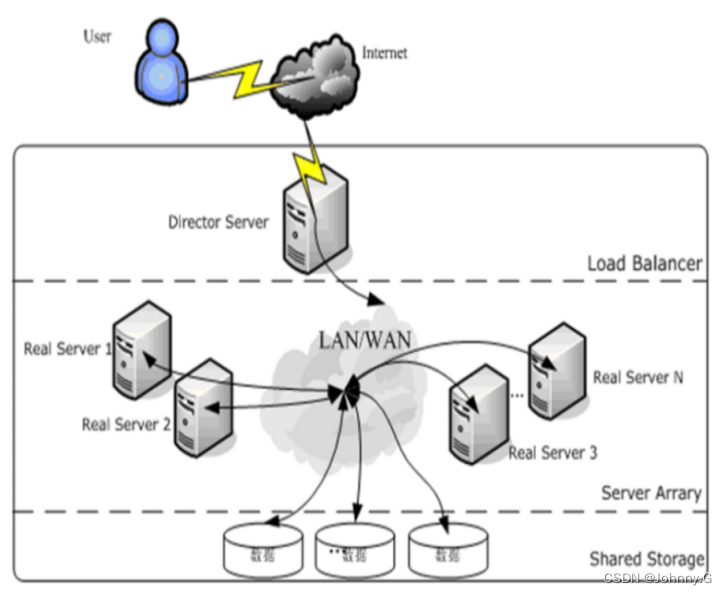
LVS简介【暂未完成(半成品)】
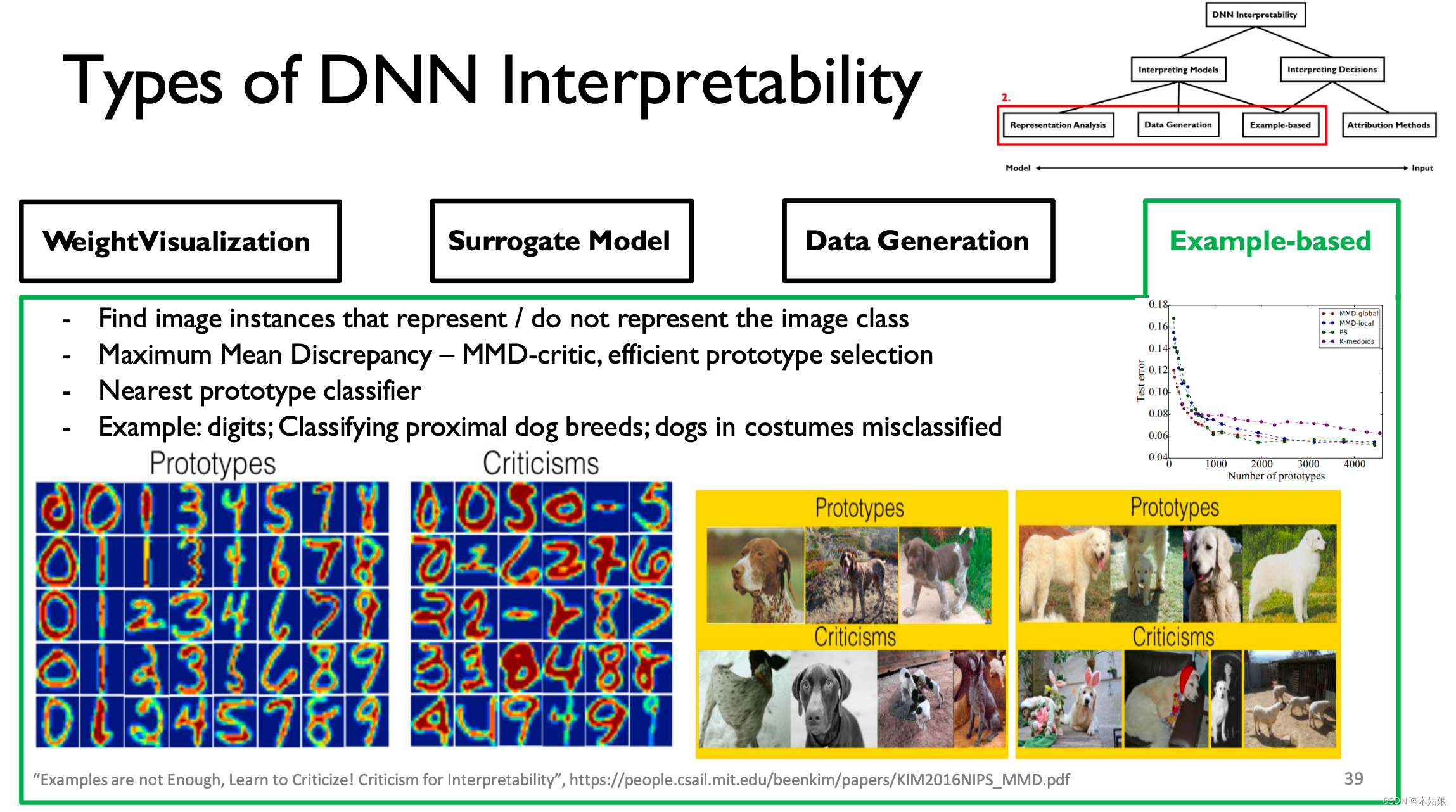
MIT-6874-Deep Learning in the Life Sciences Week 7
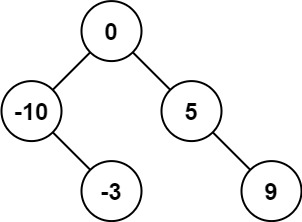
LeetCode 0108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 数组中值为根,中值左右分别为左右子树
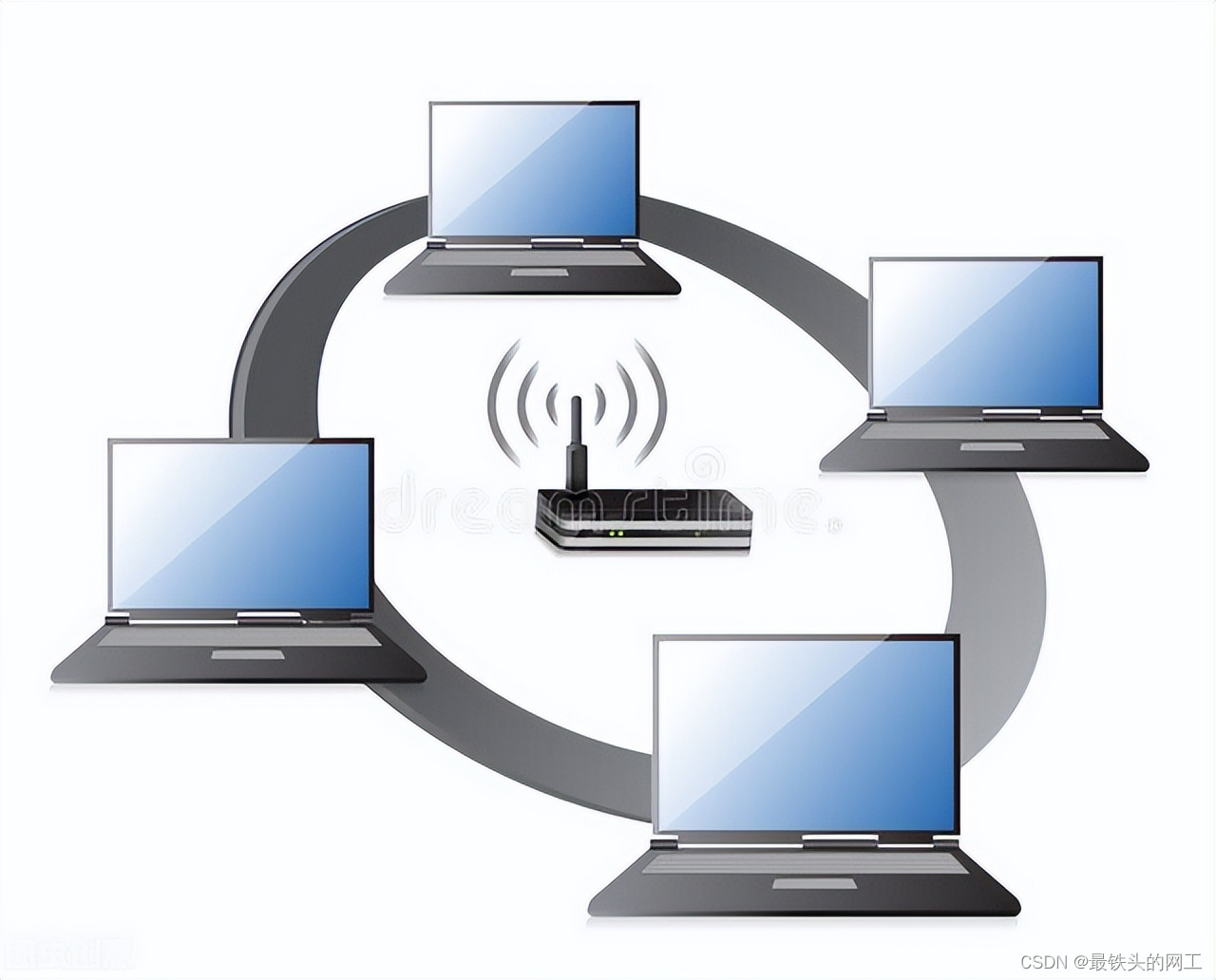
网络工程师考核的一些常见的问题:WLAN、BGP、交换机

【实战技能】如何做好技术培训?
随机推荐
One question per day 1447 Simplest fraction
Light a light with stm32
Educational Codeforces Round 107 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Colorings and Dominoes
中职网络安全技能竞赛——广西区赛中间件渗透测试教程文章
Sword finger offer 53 - I. find the number I in the sorted array
The difference between CPU core and logical processor
Transform optimization problems into decision-making problems
【Jailhouse 文章】Performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors
Wazuh开源主机安全解决方案的简介与使用体验
Educational codeforces round 109 (rated for Div. 2) C. robot collisions D. armchairs
Cluster script of data warehouse project
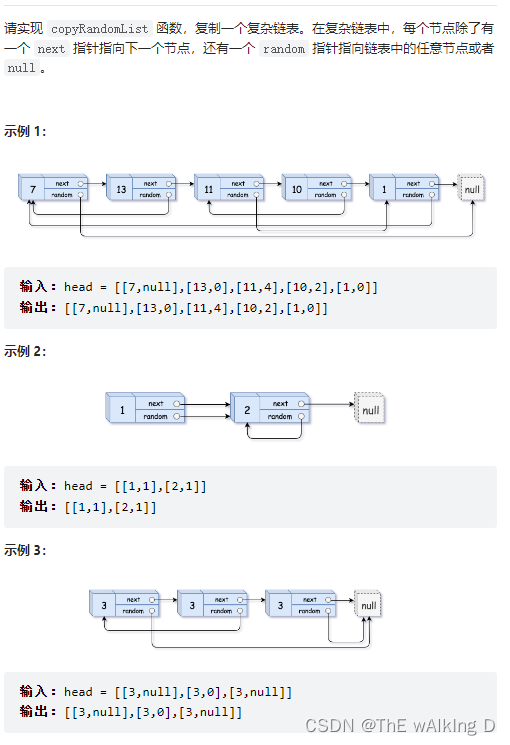
Sword finger offer 35 Replication of complex linked list
[article de jailhouse] jailhouse hypervisor
Sword finger offer 09 Implementing queues with two stacks
【Rust 笔记】17-并发(上)
leetcode-3:无重复字符的最长子串
redis发布订阅命令行实现
实时时钟 (RTC)
2020ccpc Qinhuangdao J - Kingdom's power
shared_ Repeated release heap object of PTR hidden danger