当前位置:网站首页>[combinatorics] polynomial theorem (polynomial theorem | polynomial theorem proof | polynomial theorem inference 1 item number is the number of non negative integer solutions | polynomial theorem infe
[combinatorics] polynomial theorem (polynomial theorem | polynomial theorem proof | polynomial theorem inference 1 item number is the number of non negative integer solutions | polynomial theorem infe
2022-07-03 16:35:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 The polynomial theorem
- Two 、 The polynomial theorem prove
- 3、 ... and 、 The polynomial theorem inference 1
- Four 、 The polynomial theorem inference 2
One 、 The polynomial theorem
The polynomial theorem :
set up
n
n
n As a positive integer ,
x
i
x_i
xi It's a real number ,
i
=
1
,
2
,
⋯
,
t
i=1,2,\cdots,t
i=1,2,⋯,t
(
x
1
+
x
2
+
⋯
+
x
t
)
n
\ \ \ \ (x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_t)^n
(x1+x2+⋯+xt)n
=
∑
full
foot
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
Not
negative
whole
Count
Explain
individual
Count
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
x
1
n
1
x
2
n
2
⋯
x
t
n
t
= \sum\limits_{ Satisfy n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n Number of nonnegative integer solutions }\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}x_1^{n_1}x_2^{n_2}\cdots x_t^{n_t}
= full foot n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Not negative whole Count Explain individual Count ∑(n1n2⋯ntn)x1n1x2n2⋯xtnt
The above polynomials have
t
t
t The item , this
t
t
t Items added
n
n
n Power ;
Two 、 The polynomial theorem prove
In polynomials
(
x
1
+
x
2
+
⋯
+
x
t
)
n
(x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_t)^n
(x1+x2+⋯+xt)n :
Carry out the following processing step by step :
The first
1
1
1 Step : from
n
n
n In a factor , choose
n
1
n_1
n1 Personal factor , Each factor contributes
1
1
1 individual
x
1
x_1
x1 , Total contribution
n
1
n_1
n1 individual
x
1
x_1
x1 , The selection methods are
(
n
n
1
)
\dbinom{n}{n_1}
(n1n) Kind of ;
The first
2
2
2 Step : from
n
−
n
1
n-n_1
n−n1 In a factor , choose
n
2
n_2
n2 Personal factor , Each factor contributes
1
1
1 individual
x
2
x_2
x2 , Total contribution
n
2
n_2
n2 individual
x
2
x_2
x2 , The selection methods are
(
n
−
n
1
n
2
)
\dbinom{n-n_1}{n_2}
(n2n−n1) Kind of ;
⋮
\vdots
⋮
- The first
t
t
n
−
n
1
−
n
2
−
⋯
−
n
t
−
1
n-n_1-n_2 - \cdots -n_{t-1}
n−n1−n2−⋯−nt−1 In a factor , choose
n
t
n_t
nt Personal factor , Each factor contributes
1
1
1 individual
x
t
x_t
xt , Total contribution
n
t
n_t
nt individual
x
t
x_t
xt , The selection methods are
(
n
−
n
1
−
n
2
−
⋯
−
n
t
−
1
n
t
)
\dbinom{n-n_1-n_2 - \cdots -n_{t-1}}{n_t}
(ntn−n1−n2−⋯−nt−1) Kind of ;
t Step : from
According to the principle of step-by-step counting , product rule , Multiply the number of categories in each step above , Is the number of all kinds :
(
n
n
1
)
(
n
−
n
1
n
2
)
(
n
−
n
1
−
n
2
−
⋯
−
n
t
−
1
n
t
)
\ \ \ \ \dbinom{n}{n_1} \dbinom{n-n_1}{n_2} \dbinom{n-n_1-n_2 - \cdots -n_{t-1}}{n_t}
(n1n)(n2n−n1)(ntn−n1−n2−⋯−nt−1)
After deployment , Many can be asked out , The resulting :
=
n
!
n
1
!
n
2
!
⋯
n
t
!
=\cfrac{n!}{n_1! n_2! \cdots n_t!}
=n1!n2!⋯nt!n!
Note that the above formula is the total permutation number of multiple sets
=
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
=\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}
=(n1n2⋯ntn)
3、 ... and 、 The polynomial theorem inference 1
The polynomial theorem inference 1 :
In the above polynomial theorem , Different number of items It's the equation
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n
n1+n2+⋯+nt=n
Number of nonnegative integer solutions
C
(
n
+
t
−
1
,
n
)
C(n + t -1 , n)
C(n+t−1,n)
Proof process :
1 . The coefficient before each term
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}
(n1n2⋯ntn) meaning :
n
1
n_1
n1 representative
x
1
x_1
x1 The index of ,
n
1
n_1
n1 Equivalent to how many formulas , When multiplying , Take it
x
1
x_1
x1
n
2
n_2
n2 representative
x
2
x_2
x2 The index of ,
n
2
n_2
n2 Equivalent to how many formulas , When multiplying , Take it
x
2
x_2
x2
⋮
\vdots
⋮
n
t
n_t
nt representative
x
t
x_t
xt The index of ,
n
t
n_t
nt Equivalent to how many formulas , When multiplying , Take it
x
t
x_t
xt
2 . One-to-one correspondence :
n
1
,
n
2
,
⋯
,
n
t
n_1, n_2, \cdots , n_t
n1,n2,⋯,nt A different set of choices , amount to
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n
n1+n2+⋯+nt=n
A solution to , Corresponding to different
x
1
,
x
2
,
⋯
,
x
n
x_1 , x_2, \cdots, x_n
x1,x2,⋯,xn The previous item ;
Three corresponding relationships :
Different solutions ,
n
1
,
n
2
,
⋯
,
n
t
n_1, n_2, \cdots , n_t
n1,n2,⋯,nt Different configuration , These items Number of different configurations ,
amount to
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n
n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Number of nonnegative integer solutions of ,
It is also equivalent to polynomial Expanded Number of items ;
So find
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n
n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Number of nonnegative integer solutions of ,
It corresponds to
n
1
,
n
2
,
⋯
,
n
t
n_1, n_2, \cdots , n_t
n1,n2,⋯,nt Number of different configurations ,
Corresponding Number of terms after polynomial expansion ,
The result is
C
(
n
+
t
−
1
,
n
)
C(n + t -1 , n)
C(n+t−1,n)
This number is also the combinatorial number of multiple sets
Derivation process Refer to the multiple set combination problem :
Multiple sets :S
=
{
n
1
⋅
a
1
,
n
2
⋅
a
2
,
⋯
,
n
k
⋅
a
k
}
,
0
≤
n
i
≤
+
∞
S = \{ n_1 \cdot a_1 , n_2 \cdot a_2 , \cdots , n_k \cdot a_k \} , \ \ \ 0 \leq n_i \leq +\infty
S={ n1⋅a1,n2⋅a2,⋯,nk⋅ak}, 0≤ni≤+∞
taker
r
r A combination of elements ,
r
≤
n
i
r \leq n_i
r≤ni , The derivation process is as follows :
stayk
k
k Of the elements , take
r
r
r Elements , Each element takes
0
∼
r
0 \sim r
0∼r Different elements ,
Usek
−
1
k-1
k−1 Split by lines
k
k
k The position of the elements ,
k
−
1
k - 1
k−1 A dividing line is equivalent to
k
k
k Boxes , Put... In each box
0
∼
r
0 \sim r
0∼r Different elements ,
The total number of elements placed isr
r
r individual , The number of dividing lines is
k
−
1
k-1
k−1 individual , Here comes a combinatorial problem , stay
k
−
1
k-1
k−1 A split line and
r
r
r Between elements , selection
r
r
r Elements , Namely Of multiple sets
r
≤
n
i
r \leq n_i
r≤ni Cases of Number of combinations ;
The result is :N
=
C
(
k
+
r
−
1
,
r
)
N= C(k + r - 1, r)
N=C(k+r−1,r)
Reference resources : 【 Combinatorial mathematics 】 Permutation and combination ( The combinatorial number of multiple sets | The repetition of all elements is greater than the number of combinations | The combinatorial number of multiple sets deduction 1 Division line derivation | The combinatorial number of multiple sets deduction 2 Derivation of the number of nonnegative integer solutions of indefinite equations )
Four 、 The polynomial theorem inference 2
The polynomial theorem inference 3 :
∑
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
=
t
n
\sum\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t} = t^n
∑(n1n2⋯ntn)=tn
Proof process :
Polynomial theorem
(
x
1
+
x
2
+
⋯
+
x
t
)
n
\ \ \ \ (x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_t)^n
(x1+x2+⋯+xt)n
=
∑
full
foot
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
Not
negative
whole
Count
Explain
individual
Count
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
x
1
n
1
x
2
n
2
⋯
x
t
n
t
= \sum\limits_{ Satisfy n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n Number of nonnegative integer solutions }\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}x_1^{n_1}x_2^{n_2}\cdots x_t^{n_t}
= full foot n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Not negative whole Count Explain individual Count ∑(n1n2⋯ntn)x1n1x2n2⋯xtnt
If you will
x
1
=
x
2
=
⋯
=
x
t
=
1
x_1 = x_2 = \cdots = x_t = 1
x1=x2=⋯=xt=1 ,
You can get
(
1
+
1
+
⋯
+
1
)
n
\ \ \ \ (1 + 1 + \cdots + 1)^n
(1+1+⋯+1)n
=
∑
full
foot
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
Not
negative
whole
Count
Explain
individual
Count
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
1
n
1
1
n
2
⋯
1
n
t
= \sum\limits_{ Satisfy n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n Number of nonnegative integer solutions }\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}1^{n_1}1^{n_2}\cdots 1^{n_t}
= full foot n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Not negative whole Count Explain individual Count ∑(n1n2⋯ntn)1n11n2⋯1nt
=
∑
full
foot
n
1
+
n
2
+
⋯
+
n
t
=
n
Not
negative
whole
Count
Explain
individual
Count
(
n
n
1
n
2
⋯
n
t
)
= \sum\limits_{ Satisfy n_1 + n_2 + \cdots + n_t = n Number of nonnegative integer solutions }\dbinom{n}{n_1 n_2 \cdots n_t}
= full foot n1+n2+⋯+nt=n Not negative whole Count Explain individual Count ∑(n1n2⋯ntn)
边栏推荐
- [sword finger offer] 58 - I. flip the word order
- MySQL single table field duplicate data takes the latest SQL statement
- [combinatorics] combinatorial identity (sum of combinatorial identity products 1 | sum of products 1 proof | sum of combinatorial identity products 2 | sum of products 2 proof)
- Caching mechanism of Hibernate / session level caching mechanism
- PHP中register_globals参数设置
- AcWing 第58 场周赛
- QT串口ui设计和解决显示中文乱码
- 高等数学(第七版)同济大学 习题2-1 个人解答
- How programming apes grow rapidly
- PyTorch 1.12发布,正式支持苹果M1芯片GPU加速,修复众多Bug
猜你喜欢
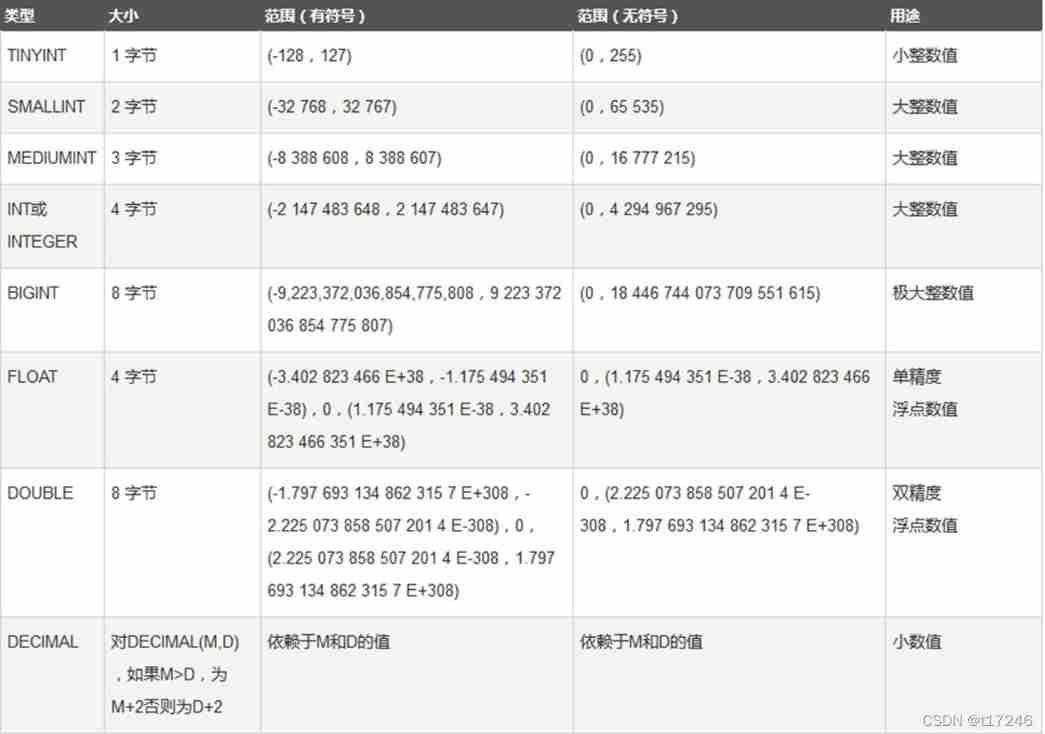
First knowledge of database
Pytorch 1.12 was released, officially supporting Apple M1 chip GPU acceleration and repairing many bugs

Data driving of appium framework for mobile terminal automated testing

2022 love analysis · panoramic report of digital manufacturers of state-owned enterprises

Visual SLAM algorithms: a survey from 2010 to 2016

Unreal_ Datatable implements ID self increment and sets rowname
Record a jar package conflict resolution process
8 cool visual charts to quickly write the visual analysis report that the boss likes to see

Thread pool executes scheduled tasks

NSQ source code installation and operation process
随机推荐
QT serial port UI design and solution to display Chinese garbled code
[combinatorics] non descending path problem (number of non descending paths with constraints)
What is the maximum number of concurrent TCP connections for a server? 65535?
Golang 匿名函数使用
There are several APIs of airtest and poco that are easy to use wrong in "super". See if you have encountered them
如何在本机搭建SVN服务器
消息队列消息丢失和消息重复发送的处理策略
Svn usage specification
疫情常态化大背景下,关于远程办公的思考|社区征文
Slam learning notes - build a complete gazebo multi machine simulation slam from scratch (II)
Explore Cassandra's decentralized distributed architecture
"Everyday Mathematics" serial 56: February 25
8 cool visual charts to quickly write the visual analysis report that the boss likes to see
"The NTP socket is in use, exiting" appears when ntpdate synchronizes the time
Hibernate的缓存机制/会话级缓存机制
Le zèbre a été identifié comme un chien, et la cause de l'erreur d'AI a été trouvée par Stanford
Unreal_ Datatable implements ID self increment and sets rowname
Custom plug-in construction and use of QT plug-in
相同切入点的抽取
Expression of request header in different countries and languages
