当前位置:网站首页>[user defined type] structure, union, enumeration
[user defined type] structure, union, enumeration
2022-07-07 00:49:00 【RookieStriver】
Before we learn C When it comes to language , There are several custom types that we need to master , Then I also share my understanding based on my own learning . Hope to learn from each other , Common progress !
List of articles
One : Structure
1.1: The basics of structure
A structure is a collection of values , These values are called member variables . Each member of a structure can be a variable of a different type .
1.2: Statement of structure
struct tag
{
member-list;
}variable-list;// Global variables
For example, describe a student :
struct Stu
{
char name[20];//mingzi
int age;//nianlin
char sex[2];//xingbie
char id[20];//xuehao
1.3: Special statement
When declaring a structure . It can be stated incompletely .
For example, anonymous structure type .
struct
{
int a;
char b;
float c;
}x;
struct
{
int a;
char b;
float c;
}a[20], *p;
The above two structures omit the structure label when declaring (tag).
So here comes the question ?
p = &x; Is it legal ?
Warning : The compiler will treat the above two declarations as two completely different types , So it's illegal .
1.4: Self reference of structure
Can you include a member whose type is the structure itself ?
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node next;
};
This kind of self quotation is not feasible !
The following is the correct way of self reference :
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node * next;// Pointer type of structure
};
1.5: Structure variable definition and initialization
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
}p1;// Define global variables while declaring types p1;
struct Point p2;// Define structure variables p2;
// initialization : Define variables and assign initial values at the same time 、
struct Point p3 = {
x, y};
1.6: Structure memory alignment
We have mastered the basic use of structures , Now let's discuss the size of the structure
int main()
{
struct s1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s1));//12
struct s2
{
char c1;
char c2;
int i;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s2));//8
struct s3
{
double d;
char c;
int i;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s3));//16
struct s4
{
char c1;
struct s3 S3;
int i;
};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s4));//32
system("pause");
return 0;
}
How to calculate the structure size ?
First, you have to master the alignment rules of the structure :
1: The first member is associated with the structure variable The offset for the 0 The address of .
2: Other member variables should be aligned to Align numbers An integral multiple of the address of .
Align numbers = The compiler defaults to an alignment number and the smaller value of the member size .(VS The default value in is 8)
3: The total size of the structure is An integer multiple of the maximum number of alignments .
4: If the structure is nested , The nested structure is aligned to an integral multiple of its maximum alignment , The overall size of the structure is All maximum alignments ( Includes the number of alignments for nested structures ) Integer multiple .
Why memory alignment exists ?
On the whole, it's : Memory alignment of structures is a way of trading space for time !
So when designing structures , We have to satisfy the alignment , And save space **, Then let the members who occupy less space gather together as much as possible .**
1.7: Change the default alignment number
We met before #pragma This preprocessing instruction , We use... Again , We can change our default alignment number .
#pragma pack(8)
struct s1
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default !
#pragma pack(1)// Set the default alignment number to 1
struct s2
{
char c1;
int i;
char c2;
};
#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default !
int main()
{
// What is the result of the output
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s1));//12
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct s2));//6
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Conclusion : When the structure is not aligned properly , We can change the default alignment number ourselves .
1.8: Structural parameters
struct S
{
int data[1000];
int num;
};
struct S s = {
{
1, 2, 3, 4 }, 1000 };
// Structural parameters
void print1(struct S s)
{
printf("%d\n", s.num);
}
// Structure address transfer parameter
void print2(struct S * ps)
{
printf("%d\n", ps->num);
}
int main()
{
print1(s);// Transmissive structure
print2(&s);// Pass structure address
system("pause");
return 0;
}
above print1 and print 2 Which function is better ?
The answer is : The preferred print2 function
reason : When a function passes parameters , Parameters need to be stacked , There will be time and space overhead . If you pass a structure object , The structure is too large , The system overhead of parameter stack pressing is large , Leading to performance degradation .
Conclusion : When structures transmit parameters , To transfer the address of the structure .
Two : Bit segment
2.1: What is a bit segment
The declaration and structure of a bit segment are similar , There are two differences :
- The member of the segment must be int,unsigned int , or signed int, short.
- The member name of the bit field is followed by A colon and a number .
such as :
struct A
{
int a : 2;
int b : 5;
int c : 10;
int d : 30;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct A));//8
system("pause");
return 0;
}
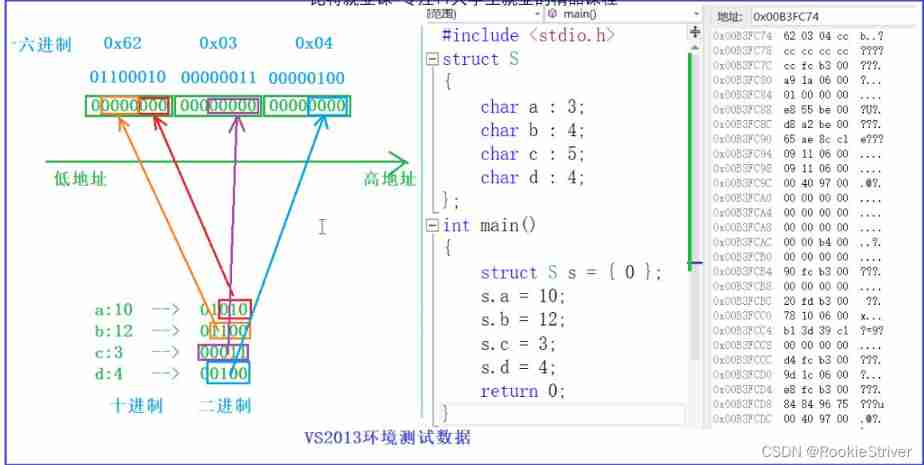
A It's a bit segment type , What is the size of that segment ?
understand : The space of the bit segment is based on 4 Bytes (int) perhaps 1 Bytes (char) To open up , The number after the member represents Needed bit Bit size .
2.2: Bit segment memory allocation
- The members of a segment can be int,unsigned int,signed int, perhaps char( It belongs to the integer family ) type .
- The space of the bit segment is based on 4 Bytes (int) perhaps 1 Bytes (char) To open up .
- Bit segments involve many uncertainties , Bit segments are not cross platform , Pay attention to portable program should avoid using bit segment .
// An example
struct S
{
char a:3;
char b:4;
char c:5;
char d:4;
};
struct S s = {
0};
s.a = 10;
s.b = 12;
s.c = 3;
s.d = 4;
How space is opened up ?
2.3: The cross platform problem of bit segment
- int It's uncertain whether a bit segment is treated as a signed number or an unsigned number .
- The number of the largest bits in the bit segment cannot be determined .(16 The machine is the largest 16,32 The machine is the largest 32).
- The members in the bit segment are allocated from left to right in memory , Or right to left allocation criteria have not yet been defined .
- When a structure contains two bit segments , The second segment is relatively large , Cannot hold the remaining bits of the first bit segment , Whether to discard the remaining bits or to use , This is uncertain .
summary : Compared to the structure , Bit segments can achieve the same effect , But it can. Good space saving , But there are cross platform problems .
3、 ... and : enumeration
Enumeration, as the name suggests, is an example , List the possible values .
3.1: Definition of enumeration type
enum Day
{
Mon,
Tues,
Wed,
Thur,
Fri,
Sat,
Sun
};
enum Sex
{
MALE,
FEMALE,
SECRET
};
As defined above enum Day,enum Sex, All enumeration types .{} The contents in are possible values of enumeration types , Also known as enumeration constants . These default values have values . The default from the 0 Start , In turn, increasing 1, Of course, initial values can also be assigned when defining .
for example :
enum Color
{
red = 1,
Green = 2,
Blue = 4
};
3.2: Advantages of enumeration
We can use #define Define constants , Why do I have to use enumeration ?
Advantages of enumeration :
- Increase the readability and maintainability of the code .
- and #define Defined identifier comparison , Enumeration has type checking , More rigorous .
- Prevent named pollution ( encapsulation ).
- Easy to debug .
- Easy to use , You can define more than one constant at a time .
3.3: Use of enumeration
enum Color
{
Red = 1,
Green = 2,
Blue = 4
};
int main()
{
enum Color clr = Green;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Be careful : Enumeration variables can only be assigned with enumeration constants , There will be no type difference .
Four : union ( Shared body )
4.1 Definition of joint type
Federation is also a special custom type , Variables defined by this type also contain a series of members , The characteristic is that these members Share the same space .
union Un
{
char c;
int i;
};
int main()
{
union Un un;// The definition of joint variables
printf("%d\n", sizeof(un));// Calculate the size of the joint variable
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.2 Characteristics of Union
The members of a union are spaces that share the same memory , The size of such a joint variable , At least the size of the largest member ( Because the Union has to be able to keep at least the largest member ).
union Un
{
char c;
int i;
};
int main()
{
union Un un;
printf("%d\n", &(un.i));
printf("%d\n", &(un.c));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.3: Calculation of joint size
- The size of the union is at least the size of the largest member .
- When the maximum member size is not an integral multiple of the maximum number of alignments , It's about aligning to an integer multiple of the maximum number of alignments .
union Un1
{
char c[5];
int i;
};
union Un2
{
char c[7];
int i;
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un1));// Size is 8
printf("%d\n", sizeof(union Un2));// Size is 16
system("pause");
return 0;
}
We have the above pairs of structures , Bit segment , union , Enumerating these user-defined types makes a basic interpretation , If you have gained something, I hope to give a wave of support to the third company , Please also point out any comments or suggestions in the comment area , Thank you. !
边栏推荐
- Liuyongxin report | microbiome data analysis and science communication (7:30 p.m.)
- Policy Gradient Methods
- Data analysis course notes (V) common statistical methods, data and spelling, index and composite index
- mongodb客户端操作(MongoRepository)
- Leecode brushes questions and records interview questions 01.02 Determine whether it is character rearrangement for each other
- Data processing of deep learning
- Command line kills window process
- 学习使用代码生成美观的接口文档!!!
- Deep understanding of distributed cache design
- Lombok makes ⽤ @data and @builder's pit at the same time. Are you hit?
猜你喜欢
JS+SVG爱心扩散动画js特效

The programmer resigned and was sentenced to 10 months for deleting the code. Jingdong came home and said that it took 30000 to restore the database. Netizen: This is really a revenge

Data sharing of the 835 postgraduate entrance examination of software engineering in Hainan University in 23
【vulnhub】presidential1
uniapp实现从本地上传头像并显示,同时将头像转化为base64格式存储在mysql数据库中
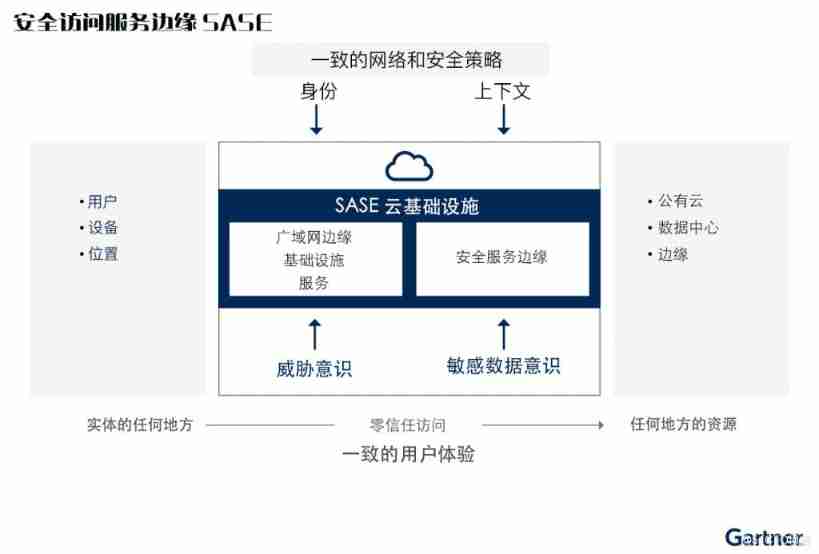
2021 SASE integration strategic roadmap (I)
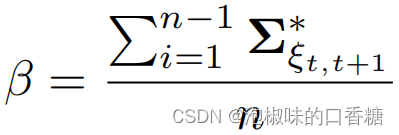
Attention SLAM:一种从人类注意中学习的视觉单目SLAM
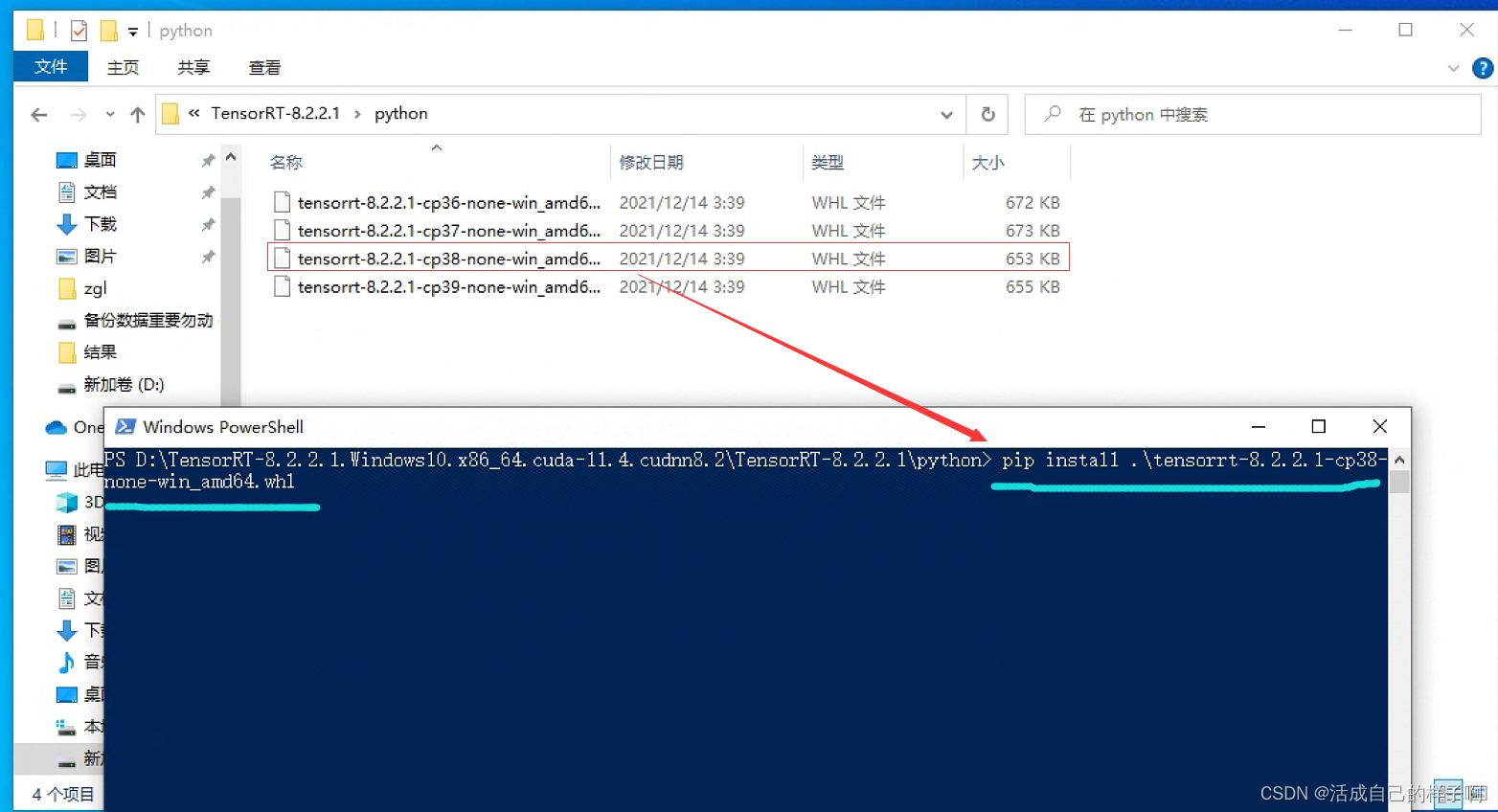
【YoloV5 6.0|6.1 部署 TensorRT到torchserve】环境搭建|模型转换|engine模型部署(详细的packet文件编写方法)
Interface master v3.9, API low code development tool, build your interface service platform immediately
Are you ready to automate continuous deployment in ci/cd?
随机推荐
集合(泛型 & List & Set & 自定义排序)
[yolov5 6.0 | 6.1 deploy tensorrt to torch serve] environment construction | model transformation | engine model deployment (detailed packet file writing method)
Geo data mining (III) enrichment analysis of go and KEGG using David database
基于SSM框架的文章管理系统
Threejs image deformation enlarge full screen animation JS special effect
Leecode brush questions record interview questions 32 - I. print binary tree from top to bottom
什么是时间
[software reverse automation] complete collection of reverse tools
Leecode brush question record sword finger offer 58 - ii Rotate string left
stm32F407-------SPI通信
@TableId can‘t more than one in Class: “com.example.CloseContactSearcher.entity.Activity“.
Advanced learning of MySQL -- basics -- multi table query -- subquery
ZYNQ移植uCOSIII
5种不同的代码相似性检测,以及代码相似性检测的发展趋势
Notes of training courses selected by Massey school
The programmer resigned and was sentenced to 10 months for deleting the code. Jingdong came home and said that it took 30000 to restore the database. Netizen: This is really a revenge
Mujoco finite state machine and trajectory tracking
Liuyongxin report | microbiome data analysis and science communication (7:30 p.m.)
【JokerのZYNQ7020】AXI_ EMC。
Personal digestion of DDD