当前位置:网站首页>Image segmentation in opencv
Image segmentation in opencv
2022-07-07 08:42:00 【Top of the program】
Original picture :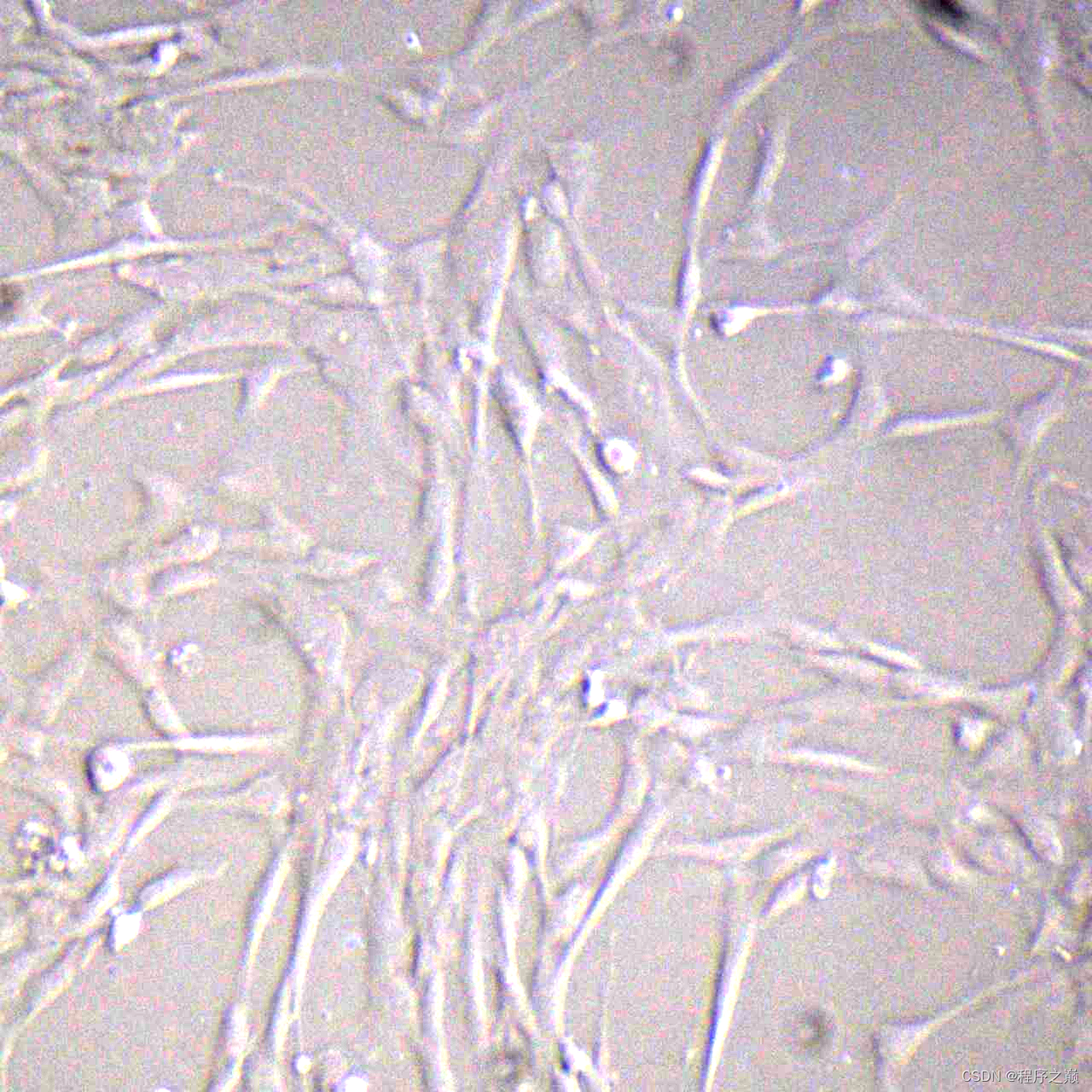
The graph obtained by final segmentation :
def OpenCVSegmentation():
cv2.namedWindow('origin', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('gray', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('closed', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('result', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('binary', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('DILATE', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.namedWindow('ERODE', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
img = cv2.imread("../data/imgs/20211126-Z2111001-4-1-1_0_1.png") # Load the image
h, w = img.shape[:2] # Get the height and width of the image
# Set the size of the display picture window
cv2.resizeWindow('origin', int(w / 3), int(h / 3))
cv2.resizeWindow('gray', int(w/3), int(h/3))
cv2.resizeWindow('closed', int(w/3), int(h/3))
cv2.resizeWindow('result', int(w/3), int(h/3))
cv2.resizeWindow('binary', int(w / 3), int(h / 3))
cv2.resizeWindow('DILATE', int(w / 3), int(h / 3))
cv2.resizeWindow('ERODE', int(w / 3), int(h / 3))
cv2.imshow("origin", img) # Show the original image
# Filtering and denoising
blured = cv2.blur(img,(3,3)) # Filter to remove noise
# cv2.imshow("Blur", blured) # Display the image after low-pass filtering
# Get the grayscale image
gray = cv2.cvtColor(blured,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("gray", gray)
# Define structural elements
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(9, 9))
# Open close operation , First open the operation to remove the background noise , Then continue the closed operation to fill the holes in the target
opened = cv2.morphologyEx(gray, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
closed = cv2.morphologyEx(opened, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
cv2.imshow("closed", closed)
# Find binary graph
# ret, binary = cv2.threshold(closed,150,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# cv2.imshow("binary", binary)
# binary = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(closed, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 5)
binary = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(closed, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY,31, 5)
cv2.imshow("binary", binary)
# inflation
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))
binary = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_DILATE, kernel)
cv2.imshow("DILATE", binary)
# corrosion
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (25, 25))
binary = cv2.morphologyEx(binary, cv2.MORPH_ERODE, kernel)
cv2.imshow("ERODE", binary)
# Find the outline
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# Draw the outline
cv2.drawContours(img,contours,-1,(0,0,255),3)
# Draw the result
cv2.imshow("result", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
OpenCVSegmentation()
Reference article :
OpenCV-Python Overview of image morphological transformation and morphologyEx Function introduction
Python OpenCV morphologyEx() function
opencv The problem of image binarization (cv2.adaptiveThreshold function )
opencv-python Adaptive threshold binarization function cv2.adaptiveThreshold Use and effect
边栏推荐
- 路由信息协议——RIP
- Compilation and linking of programs
- Greenplum6.x-版本变化记录-常用手册
- grpc、oauth2、openssl、双向认证、单向认证等专栏文章目录
- POJ - 3784 running medium
- GFS distributed file system
- Novice entry SCM must understand those things
- Interface as a parameter (interface callback)
- Redis summary
- oracle一次性说清楚,多种分隔符的一个字段拆分多行,再多行多列多种分隔符拆多行,最终处理超亿亿。。亿级别数据量
猜你喜欢
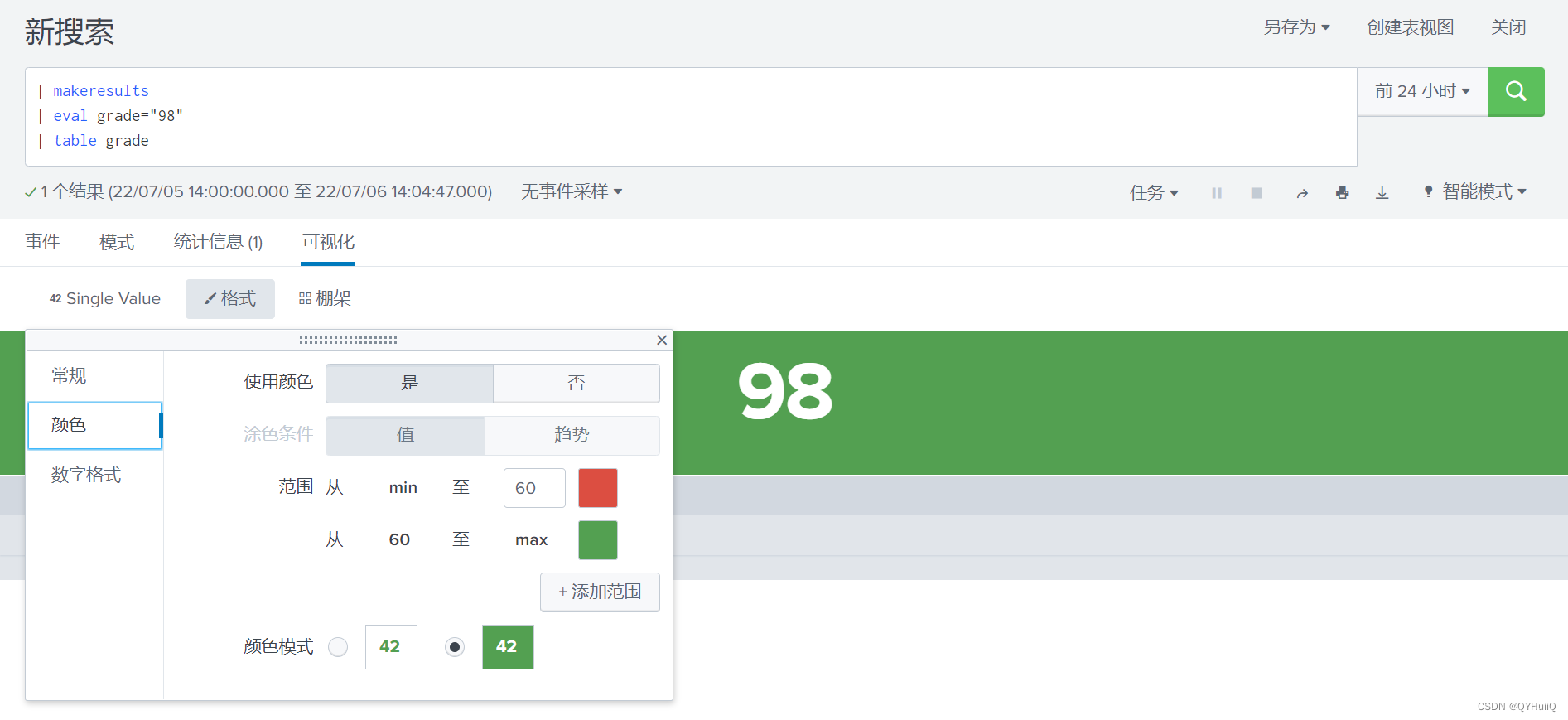
The single value view in Splunk uses to replace numeric values with text
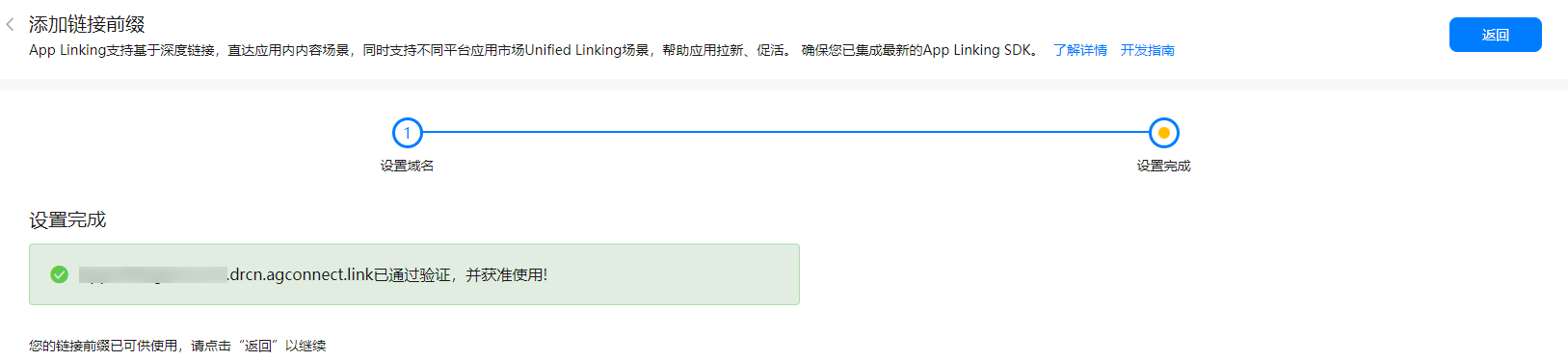
How to integrate app linking services in harmonyos applications
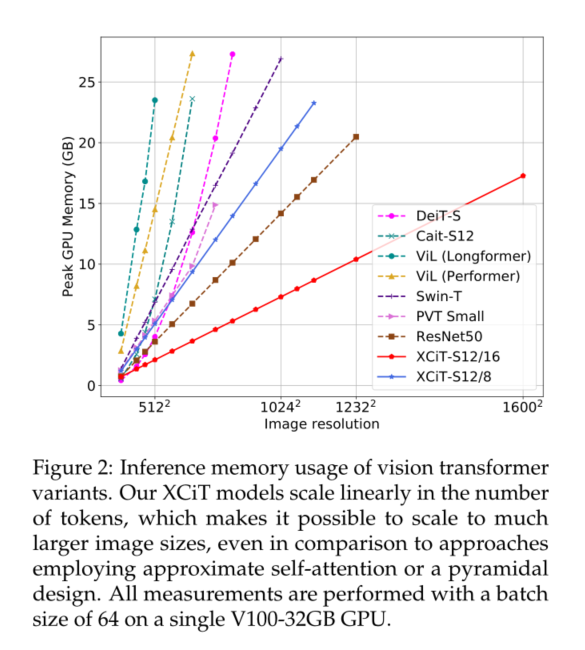
Xcit learning notes
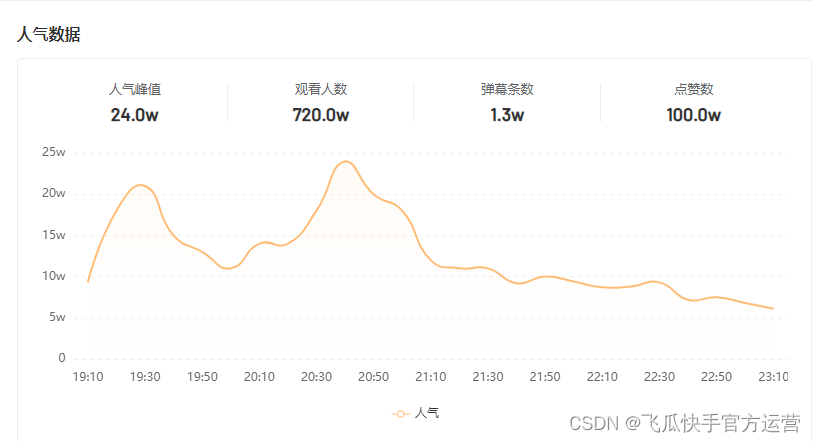
单场带货涨粉10万,农村主播竟将男装卖爆单?

Pvtv2--pyramid vision transformer V2 learning notes

Coquette data completes the cloud native transformation through rainbow to realize offline continuous delivery to customers

Laravel8 uses passport login and JWT (generate token)
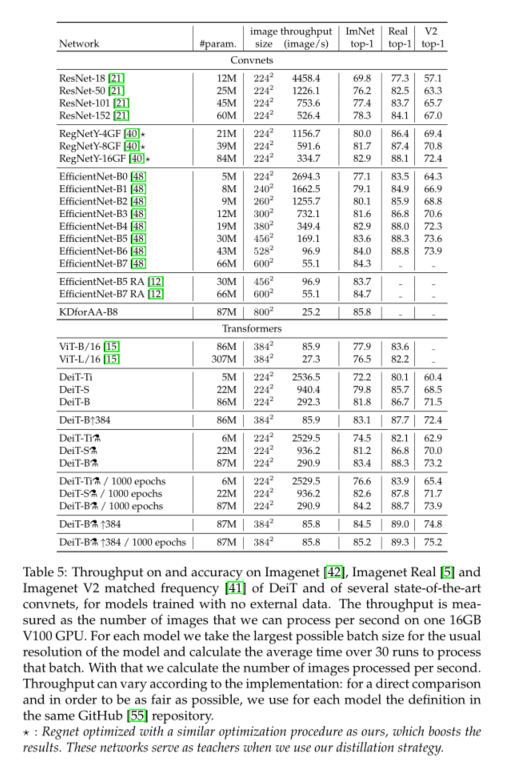
Deit learning notes
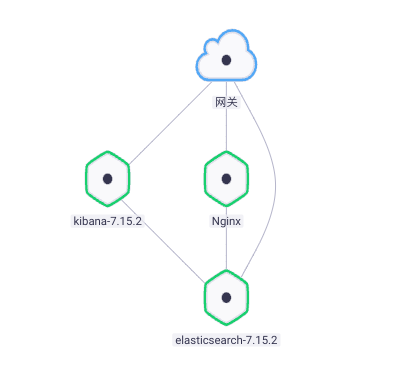
Fluentd is easy to use. Combined with the rainbow plug-in market, log collection is faster
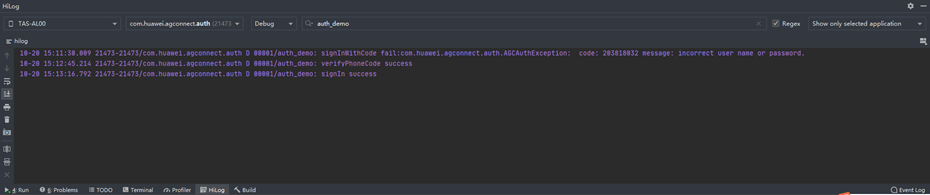
Rapid integration of authentication services - harmonyos platform
随机推荐
[南京大学]-[软件分析]课程学习笔记(一)-introduction
IP guard helps energy enterprises improve terminal anti disclosure measures to protect the security of confidential information
关于基于kangle和EP面板使用CDN
Virtual address space
Coquette data completes the cloud native transformation through rainbow to realize offline continuous delivery to customers
说一个软件创业项目,有谁愿意投资的吗?
GFS distributed file system
Laravel8 uses passport login and JWT (generate token)
Deit learning notes
23 Chengdu instrument customization undertaking_ Discussion on automatic wiring method of PCB in Protel DXP
oracle一次性说清楚,多种分隔符的一个字段拆分多行,再多行多列多种分隔符拆多行,最终处理超亿亿。。亿级别数据量
Golang compilation constraint / conditional compilation (/ / +build < tags>)
Golan idea IntelliJ cannot input Chinese characters
Upload an e-office V9 arbitrary file [vulnerability recurrence practice]
Open3d ISS key points
Implementation of navigation bar at the bottom of applet
Iptables' state module (FTP service exercise)
使用AGC重签名服务前后渠道号信息异常分析
Arm GIC (IV) GIC V3 register class analysis notes.
Pvtv2--pyramid vision transformer V2 learning notes