当前位置:网站首页>Deep parsing pointer and array written test questions
Deep parsing pointer and array written test questions
2022-07-06 03:10:00 【iYYu】
Catalog
Preface
The previous article delved into the knowledge of pointers and pointer types , and The purpose of this paper is to analyze various written test questions of pointers and arrays To consolidate the understanding of pointer and deepen the mastery of pointer .
First, let's review the meaning of array names :
In most cases, the array name represents the address of the first element of the array , But there are Two exception :
- sizeof( Array name ), The array name here represents the whole array ,sizeof It calculates the space occupied by the entire array .
notes : Must be sizeof Inside A separate Put an array name to represent the whole array , Otherwise, the address of the first element of the array .- & Array name , The address taken here is the address of the entire array .
Only the above two exceptions , The rest of the array names represent the address of the first element of the array .
32 The space occupied by the pointer under the bit machine is 4 Bytes ,64 Next is 8.
1. Pointer and array written test question analysis
1.1 One dimensional array
int a[] = {
1,2,3,4};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16
// Here is the sizeof( Array name ), Represents the entire array
// The size of the entire array is calculated in bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8
// At first glance a+0 It's equal to not adding , It still represents the whole array
// however sizeof There is not a single array name inside , No address
// So it doesn't represent the whole array
// So here's a It stands for
// Address of the first element of the array ,+0 It's equal to not adding , It's the address , Namely 4/8 Bytes .
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4
// It's not alone here sizeof Inside , Therefore, it represents the address of the first element
// That is, dereference the address of the first element , Get the first element of the array , Size is 4 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8
// Again a Not alone in sizeof Inside , Represents the address of the first element
// First element address +1 Is the address of the second element , The size of the address is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4
// Here we calculate the memory space occupied by the second element of the array , yes 4 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));
// Here take the address of the array , Is the address is also 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));///16
// Take the address of the array &a--> int (*)[4] It is the type of
// Then dereference the array pointer , We get the array again
// Therefore, the calculation is the size of the space occupied by the array
// You can understand that * and & Offset , There is only one array name left
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8
// The address taken here is the address of the entire array &a--> int (*)[4]
// Array pointer +1 Skip the entire array backwards , Point to the starting position of the next array
// So it's the address , Namely 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8
// Take the address of the first element
// It calculates the size of the address
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8
// Take the address of the first element ,+1 Is the address of the second element
// It calculates the size of the address
1.2 A character array
char arr[] = {
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));//6
// Here is sizeof Put a separate array name inside , Then the calculation is
// The size of the space occupied by the whole array , Unit is byte
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr+0));//4/8
//arr+0 Represents the address of the first element of the array
// Address size 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));//1
// Not alone in sizeof The interior is so arr It's the first element address
// The first element address dereference results in the first element of the array , The size is one byte
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));//1
// Calculate the size of the second element
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));//4/8
// Address fetch arr It takes out the address of the entire array
// Yes, the address size is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr+1));//4/8
// Fetch the address of the entire array +1, Represents skipping the entire array
// Point to the starting position of the next array .
// Then it's also the address , Size is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
//&arr[0]+1 Is the address of the second element
// Address size 4/8
Be careful : The same array , But it's not sizeof 了 .
char arr[] = {
'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));// Random value
//strlen Is to find the length of the string , Find out \0 The length before
// The initialization of the above character array does not \0
// And the data in memory is continuously stored
// therefore strlen Will always look back , Until I find \0
// So the final result is random
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr+0));// Random value
//arr+0 Or the first element address , So the principle is the same as above
printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));// Report errors
//strlen The parameter of is the starting address of the array
//*arr Is a character a Pass as parameter to strlen
// character a Of ASCII Code value is 97
//strlen(97),97 Your address obviously doesn't belong to us
// This leads to the problem of wild pointer , So the program will report an error
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));// Report errors
// Alphabet character b Pass to strlen, The principle of same
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));// Random value
// It also starts from the starting address of the array and looks backwards \0
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr+1));// Random value -6
// Take out arr The address of +1 Skip the entire character array
// Point to the starting address of the following array
// A from &arr Start looking for , A from &arr+1 Start looking for
// So the final result is a random value -6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0]+1));// Random value -1
// Start from the second element address and look backwards
What is the difference between string initialization and the above ?
char arr[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr));//7
//[a b c d e f \0]
// The end of the string comes with \0, And here sizeof An internal single array name
// It calculates the memory space occupied by the entire array ,7 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr+0));//4/8
// Not alone in sizeof Inside , there arr Represents the address of the first element
//arr+0 It hasn't changed , So it's the address , Size is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*arr));//1
// Not alone in sizeof Inside ,arr It's the first element address
// Dereference to get the first element , Size is 1 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[1]));//1
// Calculate the size of the second element ,1 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr));//4/8
// Fetch the address of the entire array , Yes, the address is 4 or 8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr+1));//4/8
// Fetch the address of the entire array +1 Skip the entire array backwards
// Point to the starting address of the next array , The address is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8
// Take out the first element address +1 Is the address of the second element
// Yes, the address size is 4/8 Bytes
Be careful : The same array , But it's not sizeof 了 .
char arr[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr));//6
// here arr It's the first element address , Calculation \0 Previous string length
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr+0));//6
//arr+0 Or the first element address
printf("%d\n", strlen(*arr));// Report errors
//strlen The function parameter of is address
// And here is a character variable
printf("%d\n", strlen(arr[1]));// Report errors
// The principle of same
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr));//6
//&arr Take the address of the array , The address of the array also starts from the address of the first element of the array
// The length is still 6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr+1));// Random value
// Skip the whole arr Array , Start from the back of the array \0
// I don't know when I will meet \0
printf("%d\n", strlen(&arr[0]+1));//5
// First element address +1, Count backwards from the second element address
char *p = "abcdef";
//p Is a pointer , Put the constant string abcdef The first element address of is stored in p in
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p));//4/8
//p It's a pointer variable , The pointer size is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p+1));//4/8
//p yes char Type a pointer , that p+1 The address to the next element
// Yes, the address is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*p));//1
//p Address of the first element stored , Dereference access character a
//a Take up a byte
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p[0]));//1
// ditto
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p));//4/8
// Pointer to the variable p It will also open up its own memory space in memory
// Take out p The address of , It's the address 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p+1));//4/8
//&p It's an address ,+1 It's also an address
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p[0]+1));//4/8
// Take the address of the first character ,+1 Is the address of the second element
char *p = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", strlen(p));//6
//p What's in it is a The address of , So from a Count back
printf("%d\n", strlen(p+1));//5
//p+1 Is the address of the second element , Count backwards from the second element
printf("%d\n", strlen(*p));// Report errors
//strlen The parameter of the function is the address , And here is 'a'
printf("%d\n", strlen(p[0]));// Report errors
// ditto
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p));// Random value
// Different from the array name , Take out p The address of the space opened in memory and
// The address of the first element of the string doesn't matter , from p Count back
// When did you meet \0 Is random
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p+1));// Random value
// ditto
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p[0]+1));//5
// Count backwards from the address of the second element
1.3 Two dimensional array
int a[3][4] = {
0};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//48
// A two-dimensional array of three rows and four columns
// The total size of the array is 3*4*4 = 48
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0][0]));//4
// The first element in the first line , The size is 4
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0]));//16
// It's understandable :
//a[0] Is the array name in the first row
//a[1] Is the array name in the second line
//a[2] Is the array name in the third line
// The array list is placed alone in sizeof The internal calculation is the size of the entire first row array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[0]+1));//4/8
//a[0]+1 == &a[0][0]+1
// Not alone in sizeof Inside
// Here a[0] It represents the address of the first element in the first row of the array
//+1 Is the array of the second element in the first row
// Yes, the address is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(a[0]+1)));//4
// It says a[0]+1 Is the address of the second element in the first line
// Then the second element is obtained by dereferencing it
// Size is 4 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8
//a Not alone in sizeof There is no internal address
// there a Represents the address of the first row of the two-dimensional array
//+1 Is the address on the second line
// Yes, the address size is 4 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(a+1)));//16
//a+1 Is the address on the second line , Dereference to get the array of the second row
// Here we calculate the size of the second row array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8
// Get the address of the first row of the array
//+1 Get the address on the second line , The address is 4/8 Bytes
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*(&a[0]+1)));//16
// Take out one line of address +1 Is the address on the second line
// Then dereference to get the array of the second row
// Here we calculate the size of the second row array
printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//16
//a Represents the address of the first element , It's the address on the first line
// If you dereference the first line, you will get the first line
// The size of this row of arrays is calculated
printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[3]));//16
// There is no fourth line ,sizeof Will not visit the bank
//sizeof Just focus on its type , So it's equivalent to a[0]
// The array list is placed alone in sizeof Inside
// Calculate the size of the row array
// Be careful :sizeof Just know its type , You can analyze
// The space occupied by this type
summary
The meaning of array names :
- sizeof( Array name ), The array name here represents the entire array , It calculates the size of the entire array .
- & Array name , The array name here represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array .
- In addition, all array names represent the address of the first element .
边栏推荐
- BUUCTF刷题笔记——[极客大挑战 2019]EasySQL 1
- 【paddle】加载模型权重后预测报错AttributeError: ‘Model‘ object has no attribute ‘_place‘
- 3857墨卡托坐标系转换为4326 (WGS84)经纬度坐标
- Buuctf question brushing notes - [geek challenge 2019] easysql 1
- 八道超经典指针面试题(三千字详解)
- jsscript
- 手写数据库客户端
- Linear programming matlab
- [ruoyi] enable Mini navigation bar
- SD卡报错“error -110 whilst initialising SD card
猜你喜欢
Tomb. Weekly update of Finance (February 7 - February 13)
【Kubernetes 系列】一文学会Kubernetes Service安全的暴露应用

I sorted out a classic interview question for my job hopping friends

My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- on the pointer
不赚钱的科大讯飞,投资价值该怎么看?
Solution: attributeerror: 'STR' object has no attribute 'decode‘
银行核心业务系统性能测试方法
Apt installation ZABBIX

Performance test method of bank core business system
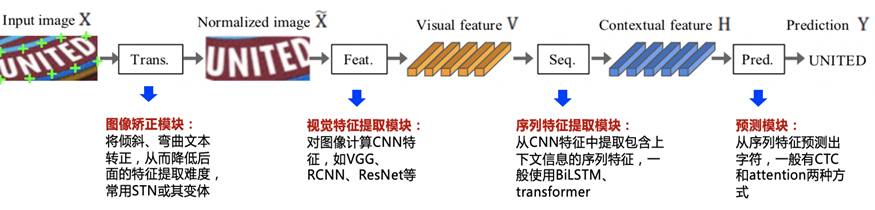
Overview of OCR character recognition methods
随机推荐
适合程序员学习的国外网站推荐
Rust language -- iterators and closures
CSP numeric sort
Game theory matlab
How to read excel, PDF and JSON files in R language?
Overview of OCR character recognition methods
Summary of Bible story reading
[ruoyi] enable Mini navigation bar
【若依(ruoyi)】设置主题样式
XSS challenges bypass the protection strategy for XSS injection
2.13 simulation summary
2022工作中遇到的问题四
Résumé des méthodes de reconnaissance des caractères ocr
八道超经典指针面试题(三千字详解)
Introduction to robotframework (I) brief introduction and use
[matlab] access of variables and files
OCR文字識別方法綜述
手写数据库客户端
【paddle】加载模型权重后预测报错AttributeError: ‘Model‘ object has no attribute ‘_place‘
Redis cache breakdown, cache penetration, cache avalanche