当前位置:网站首页>Understanding of processes and threads
Understanding of processes and threads
2022-07-06 06:09:00 【Wandering mage 12】

One 、 The concept of process and thread ( A word summary )
process : The program we run usually corresponds to one or more processes , Process is the basic unit of memory allocated by the operating system .
Threads : A process usually contains one or more threads , Threads are operating system allocations CPU The basic unit of .
Single threaded program ---> There is only one execution clue in our program ( The main thread )---> Create multiple threads ( There are multiple concurrent parts )
Technology exchange group :830709780
notes : A program has at least one process , A process has at least one thread ( The main thread ), Processes have independent memory units during execution , Multiple threads share memory , Thus greatly improving the efficiency of the program .
Two 、 Difference between process and thread
1. The way of operating system resource management is different , The process has a separate address space , After a process crashes, there will be a protection mode so that it will not affect other processes . Threads are not , Threads have their own stack and local variables , But there is no separate address space between threads , So a thread hanging may affect the whole process hanging .
2. The concurrency of processes is not as high as that of threads .
3. Each independent thread has an entry for the program to run 、 Exit of sequential execution sequence and program . But threads can't execute independently , Must exist in the application . Multiple thread execution control provided by the application .
4. For applications , Multithreading means that multiple execution parts can be executed at the same time . But for the operating system, it does not regard multiple threads as multiple independent applications , To achieve process scheduling and management and resource allocation
notes : Multithreading is easy to schedule , Effectively achieve concurrency . The overhead of memory is relatively small . Creating a thread is faster than creating a process .
3、 ... and 、 The concept of thread pools
When writing multithreaded programs , It must be noted that the creation and release of threads have a large overhead , And if you create too many threads , Scheduling switching between threads also has overhead , So the more threads, the better , The best use is to create several threads , Then reuse them .
Thread pool : First use a container , Create several threads in advance , When using threads, borrow a thread from the thread pool , After use , Do not release threads , Instead, put the thread back in the pool , Let threads be reused .
notes : Pooling technology is basically space for time .

Four 、 Code demonstration ( Call the third-party interface to download ( Multithreading and thread pooling ) picture )
# coding=utf8
# @time:2022/5/19 17:02
import time
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import requests
def down_picture(picture_url):
resp = requests.get(picture_url)
if resp.status_code == 200:
filename = picture_url[picture_url.rfind('/'):]
with open(f'images/{filename}', 'wb') as f:
f.write(resp.content)
def read_picture():
futures = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as pool: # Thread pool , The biggest process 10
# threads = []
star = time.time()
format = 'png'
header = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; U; ABrowse 0.6; Syllable) AppleWebKit/420+ (KHTML, like Gecko)'}
data = {'key': '919928ff6d14cXXXXXXXXXXXXXX', 'url': 'https://www.hXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.com'} # Fill in the parameters according to the actual situation
for page in range(1, 6):
resp = requests.get('http://api.xxxxxxx.com', params=data, headers=header) # Fill in the parameters according to the actual situation
picture_list = resp.json()['newslist']
# print(picture_list)
for picture in picture_list:
picture_url = picture['picUrl']
# print(picture_url)
# down_picture(picture_url)
# Thread pool
f = pool.submit(down_picture, picture_url)
'''''''''
# Common multithreading methods
thd = threading.Thread(target=down_picture,args=(picture_url,))
threads.append(thd)
thd.start()
# print(threads)
# Wait for all the execution time of the child thread just started
for t in threads:
t.join()
'''''''''
for f in futures:
f.result()
end = time.time()
print(end - star) # 4.877447128295898
if __name__ == '__main__':
read_picture()Download situation :

More secure sharing , Please pay attention to 【 Security info】 WeChat official account !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
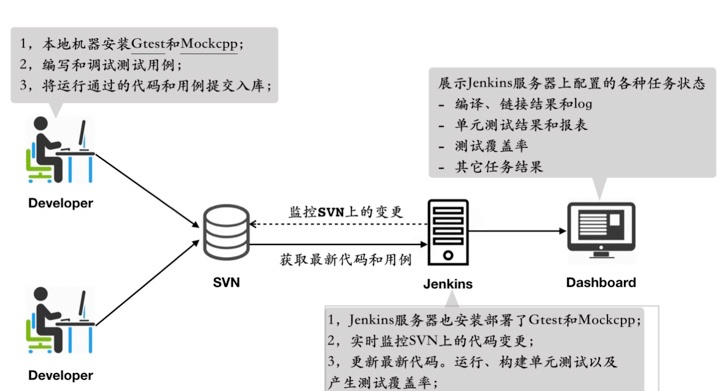
单元测试的意义
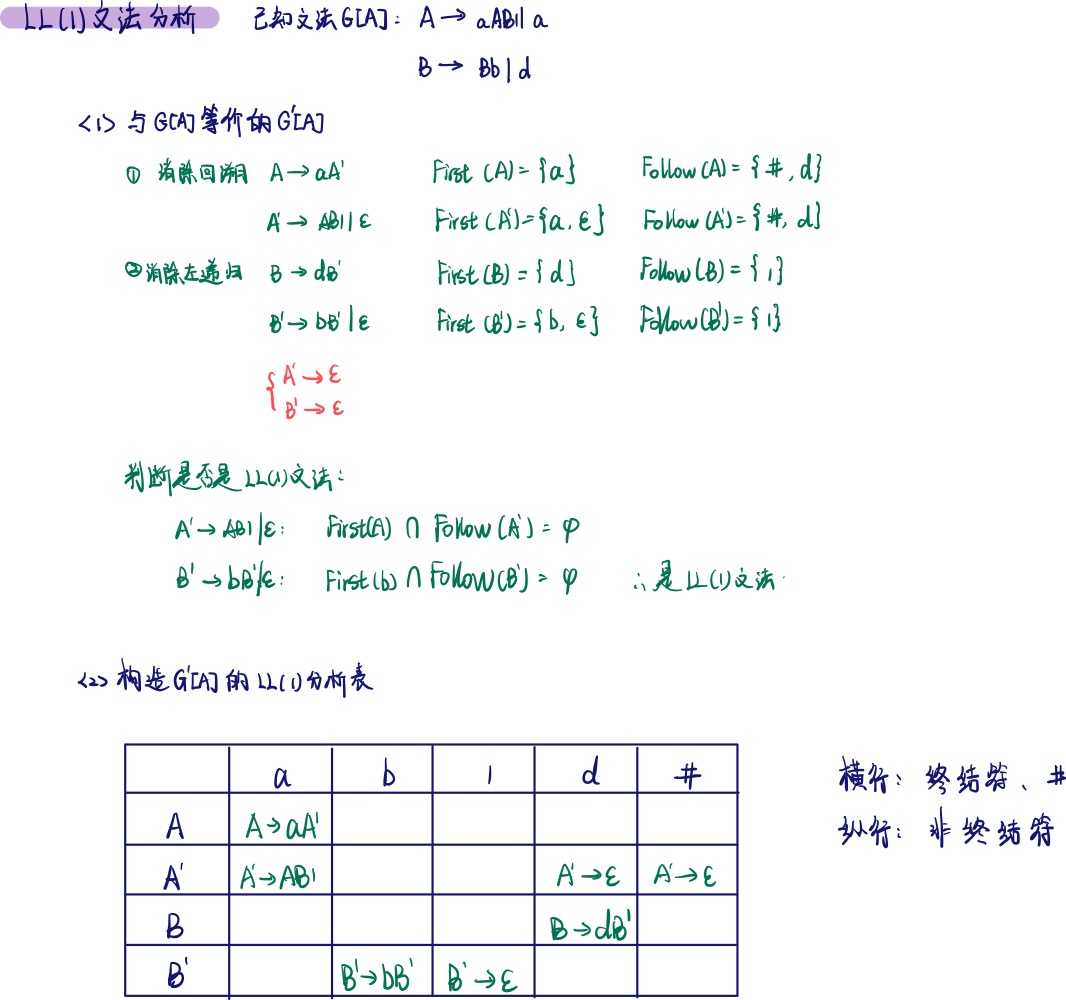
【课程笔记】编译原理
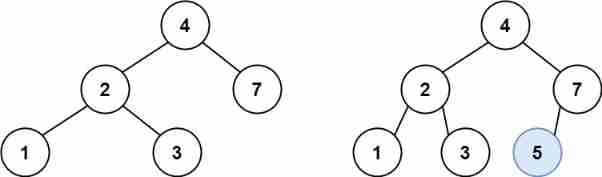
Leetcode 701 insertion operation in binary search tree -- recursive method and iterative method
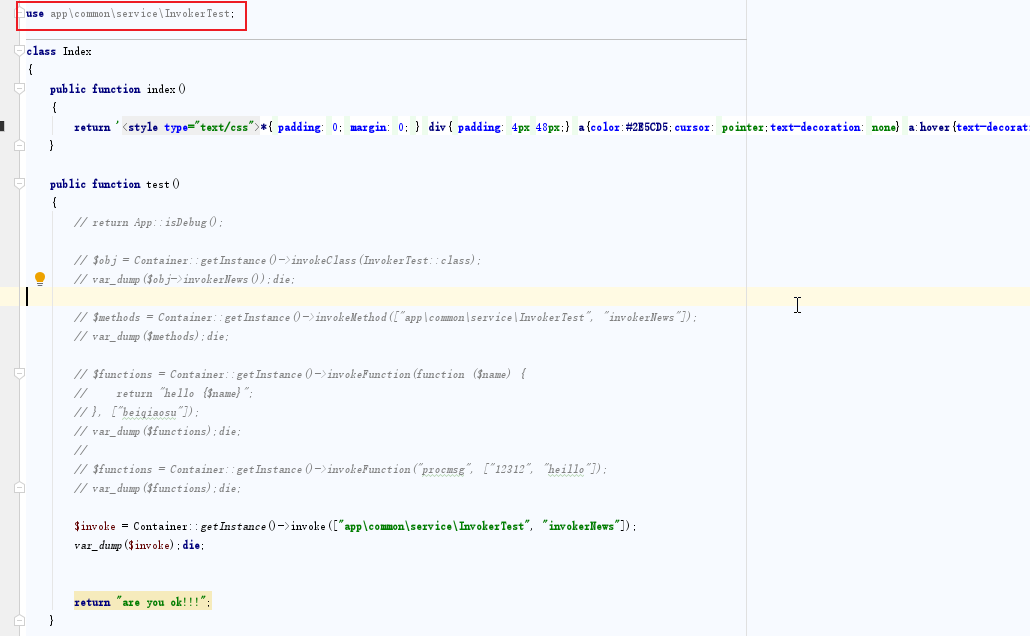
How to use the container reflection method encapsulated by thinkphp5.1 in business code
How Huawei routers configure static routes
![[web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis](/img/c5/256ab30e796f0859387585873cee8b.jpg)
[web security] nodejs prototype chain pollution analysis
![[Baiwen smart home] first day of the course_ Learn Embedded and understand the development mode of bare metal and RTOS](/img/ed/8d112054f31bd7e593050d1278b9f1.jpg)
[Baiwen smart home] first day of the course_ Learn Embedded and understand the development mode of bare metal and RTOS

网络协议模型

The usage and difference between strlen and sizeof
【Postman】Collections-运行配置之导入数据文件
随机推荐
Web service connector: Servlet
(5) Explanation of yolo-v3 core source code (3)
LAN communication process in the same network segment
Winter 2021 pat class B problem solution (C language)
isam2运行流程
Database: ODBC remote access SQL Server2008 in oracel
Fault, error, failure of functional safety
Testing and debugging of multithreaded applications
10M25DCF484C8G(FPGA) AMY-6M-0002 BGA GPS模块
Gtest之TEST宏的用法
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
如何在业务代码中使用 ThinkPHP5.1 封装的容器内反射方法
[Thesis code] SML part code reading
The difference and usage between continue and break
局域网同一个网段通信过程
【Postman】Monitors 监测API可定时周期运行
Application of Lie group in gtsam
数学三大核心领域概述:几何
Redistemplate common collection instructions opsforvalue (II)
【无标题】