当前位置:网站首页>Eight super classic pointer interview questions (3000 words in detail)
Eight super classic pointer interview questions (3000 words in detail)
2022-07-06 03:02:00 【Eight days a week】
Catalog
The first question is :
int main()
{
int a[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int *ptr = (int *)(&a + 1);
printf( "%d,%d", *(a + 1), *(ptr - 1));
return 0;
}
Predict its output .
Solution to the problem : Pointer questions need to be drawn , You can't get around without drawing . The picture below is a The memory layout of the array .
 int * ptr =(int *)(&a + 1);ptr Refer to the figure :
int * ptr =(int *)(&a + 1);ptr Refer to the figure :
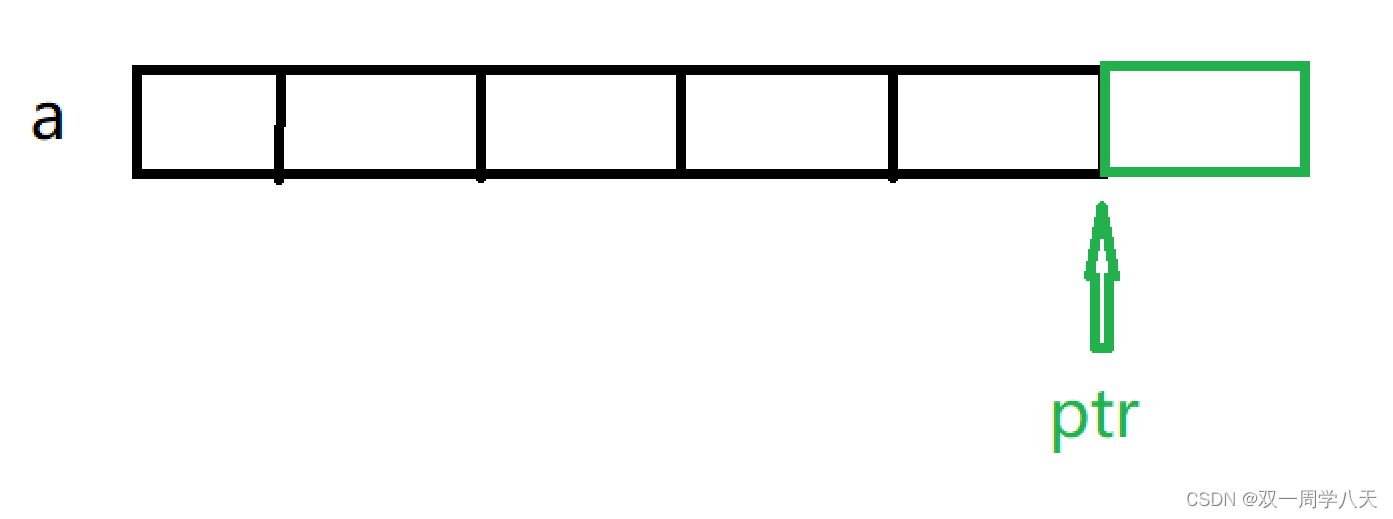
Many students may not understand : The array name is the address of the first element of an array , But except for two cases :
1.&+ Array name —————————————— Here is the address of the entire array .
2.sizeof( Array name )—————————— Here is the number of bytes occupied by the entire array .
Back to topic ,(&a+1) Medium 1 Step length is an array , Add a byte of the whole array to the address of the first element .
So let's see printf() Medium a+1、ptr-1:

Then the answer is clear at a glance : They are the second element ——2, With five elements ——5.
The second question is :
struct Test
{
int Num;
char *pcName;
short sDate;
char cha[2];
short sBa[4];
}*p;
// hypothesis p The value of is 0x100000. What are the values of the expressions in the following table ?
// It is known that , Structure Test The variable size of type is 20 Bytes
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", p + 0x1);
printf("%p\n", (unsigned long)p + 0x1);
printf("%p\n", (unsigned int*)p + 0x1);
return 0;
}
Ideas and solutions :
0x It starts with a hexadecimal number .
At the first printf() in p+0x1, One Test Structure proportion 20 Bytes , And p yes struct Test *p type ,p Add one at a time 1 Move the corresponding 20 byte ( For details, please see Primary pointer Pointer and pointer type ). And because it's hexadecimal ,20=0x14, therefore p+0x1=0x100014.
In the second printf() in (unsigned long)p+0x1, ad locum p The pointer variable is first cast to unsigned long type , therefore p+0x1 It's the ordinary addition of integers , obtain 0x100001. then %p Will be p The data of is printed out in the form of address .
In the third printf() in ,p Is converted into a pointer again , But this time in the form of unsigned integers .unsigned int * It limits the space of each pointer access to four bytes . therefore p+1 As the result of the 0x100004
Third question :
int main()
{
int a[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int *ptr1 = (int *)(&a + 1);
int *ptr2 = (int *)((int)a + 1);
printf( "%x,%x", ptr1[-1], *ptr2);
return 0;
}Same as question 1 :
ptr1: from int * ptr1=(int *)(&a+1); Draw the picture below :
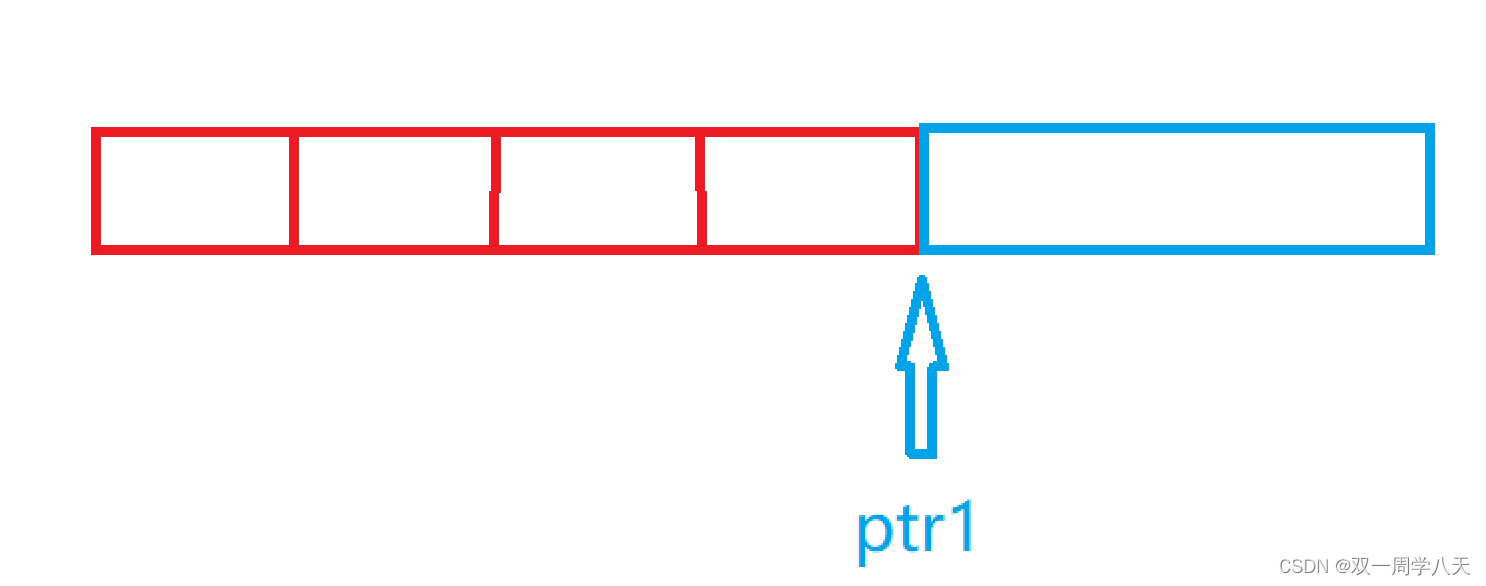
ptr1[-1] It's the same thing as *(ptr1-1). Because in fact ‘[]’ And ’*‘ The function of is the same .( For details, see Seven thousand word explanation operator )
ptr2:
But let's take a closer look int *ptr2 = (int *)((int)a + 1); Array name in a Be coerced into int The type of . therefore a+1 Only one byte can be moved forward . In order to better observe, I turn this part of the diagram into this form .( because vs Compiler is small end storage , Move left, the data here is 01000000 instead of 00000001)
(int)a+1 Move one byte back, as shown in the following figure :
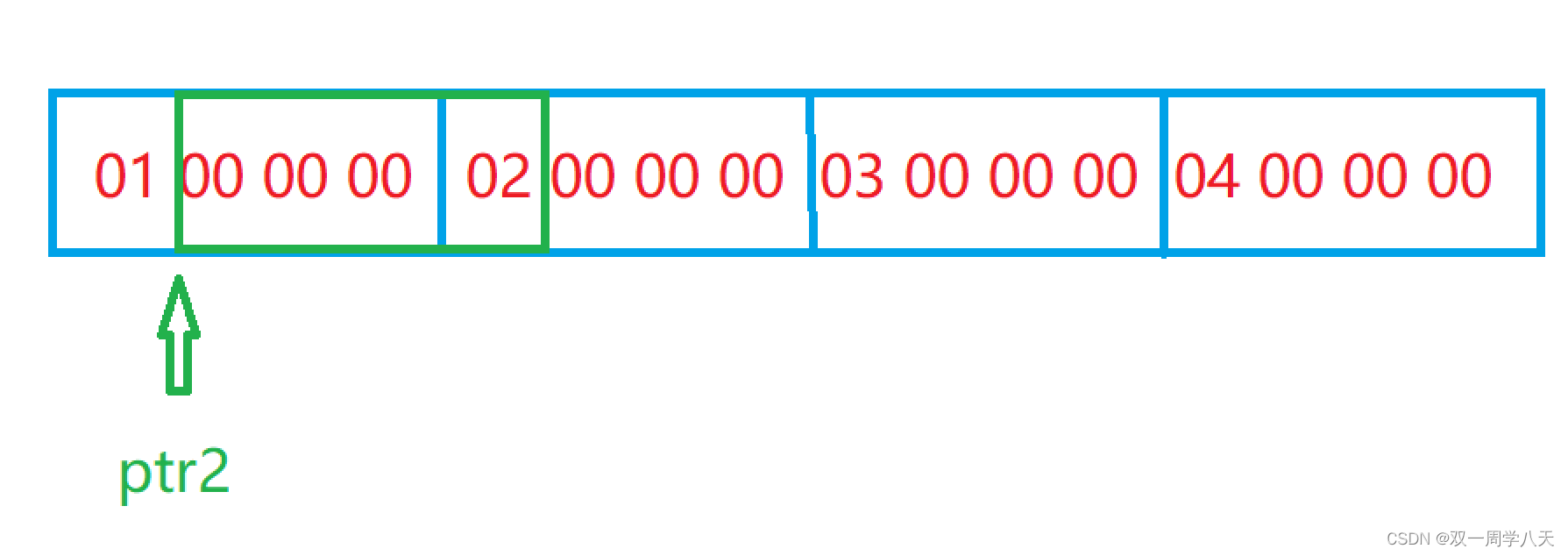
This is it. ptr2 The data pointed to .
in summary , The answer for :0x02 00 00 00,00 00 00 04.
Fourth question :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[3][2] = { (0, 1), (2, 3), (4, 5) };
int *p;
p = a[0];
printf( "%d", p[0]);
return 0;
}
Ideas and answers :
Here it is applied to comma expression ( For details, see Seven thousand word explanation operator ) And the secondary array .
Actually in a[3][2] The data in is :
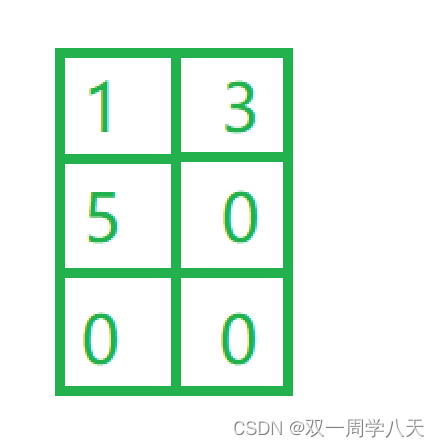
a Point to 
p=a[0] Point to 
So the answer is 1.
Fifth question :
int main()
{
int a[5][5];
int(*p)[4];
p = a;
printf( "%p,%d\n", &p[4][2] - &a[4][2], &p[4][2] - &a[4][2]);
return 0;
}
Ideas and answers :

This is a[5][5] Layout , The number represents the element of emperor ascendancy .
a[5][5]:
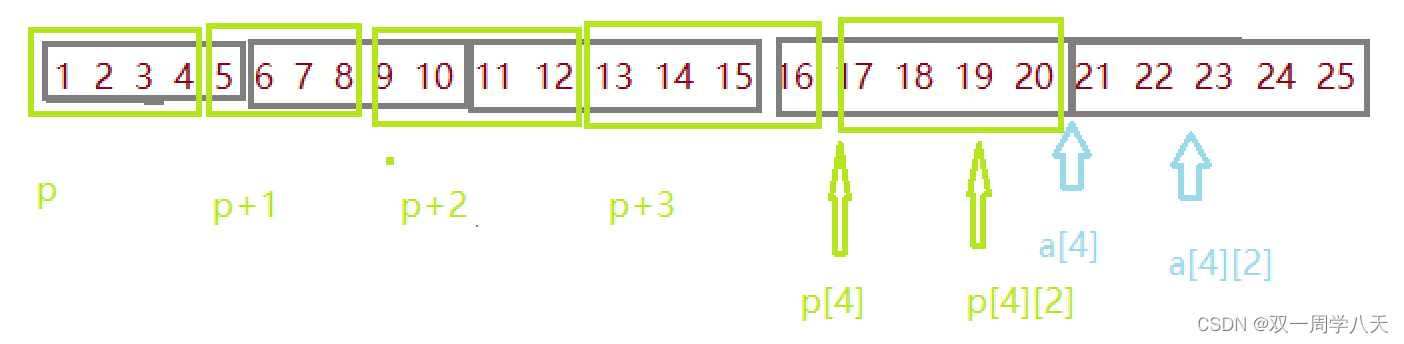
First analysis a[4][2],a[4][2] Also equivalent to *(*(a+4)+2), Which one do you think is easy to understand . Here's the picture :
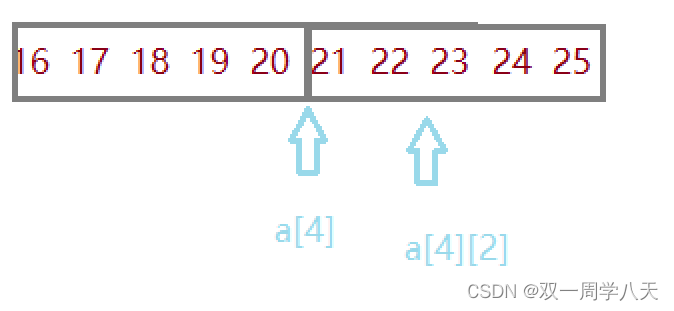
p[4][2]:
from int (*p)[4] obtain :p by int [4] Pointer to type , that p Just point to an array with four elements . It can be obtained. p+1 It moves four elements at a time :
&p[4][2] - &a[4][2] The value of is the number of elements with difference , therefore &p[4][2] - &a[4][2]=-4
But here we need to talk about :
&p[4][2] - &a[4][2] The integer result is -4,-4 What is stored in memory is a binary complement , The principle is as follows

So in our memory -16 That's true
Original code :1000 0000 0000 0100
Inverse code :1111 1111 1111 1011
Complement code :1111 1111 1111 1100
because %p It's an unsigned number , therefore %p Directly extract the complement in memory :0xfffffffc
because %d Is the output signed integer , Therefore, it is necessary to re convert the complement code into the original code before outputting :-4.
Sixth question :
int main()
{
int aa[2][5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int *ptr1 = (int *)(&aa + 1);
int *ptr2 = (int *)(*(aa + 1));
printf( "%d,%d", *(ptr1 - 1), *(ptr2 - 1));
return 0;
}Ideas and solutions :
aa The memory step of the array is as follows :

aa Address pointing to the first line :
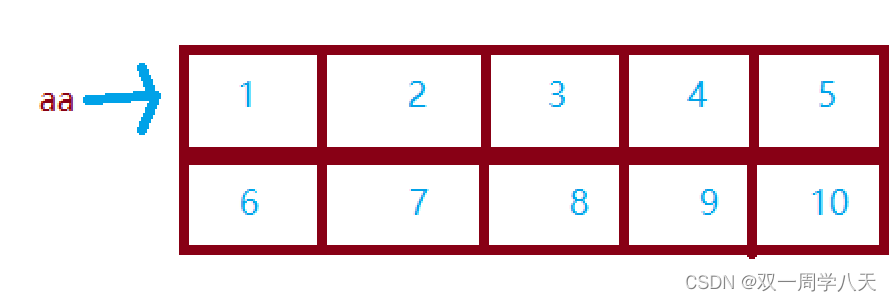
&aa What is removed is the address of the whole array , therefore &aa+1 Here's the picture :
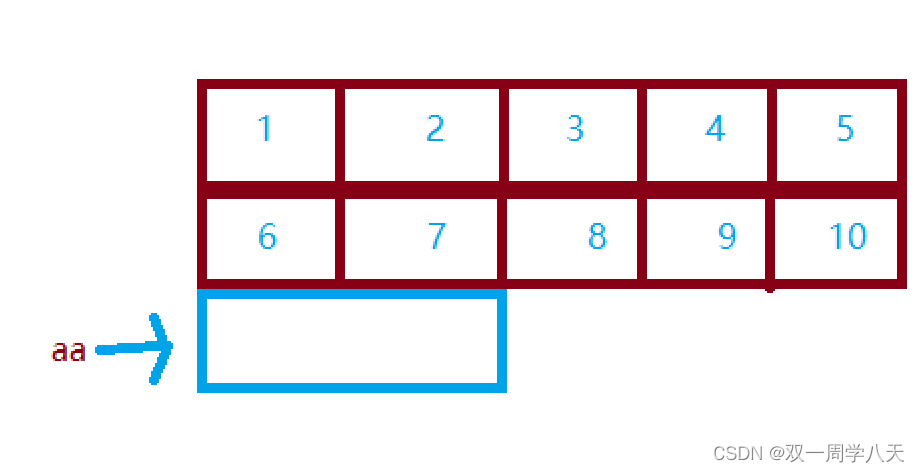
aa+1 Will point to the data in the second row :
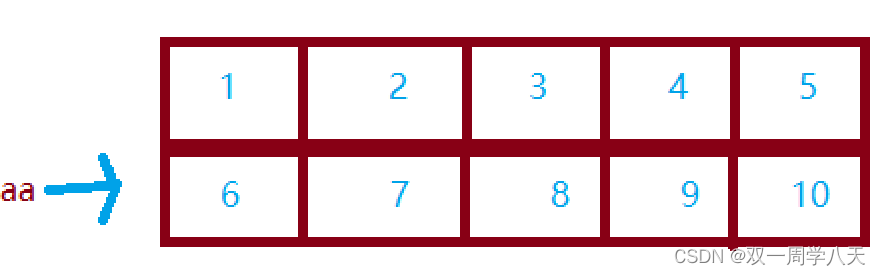
therefore :
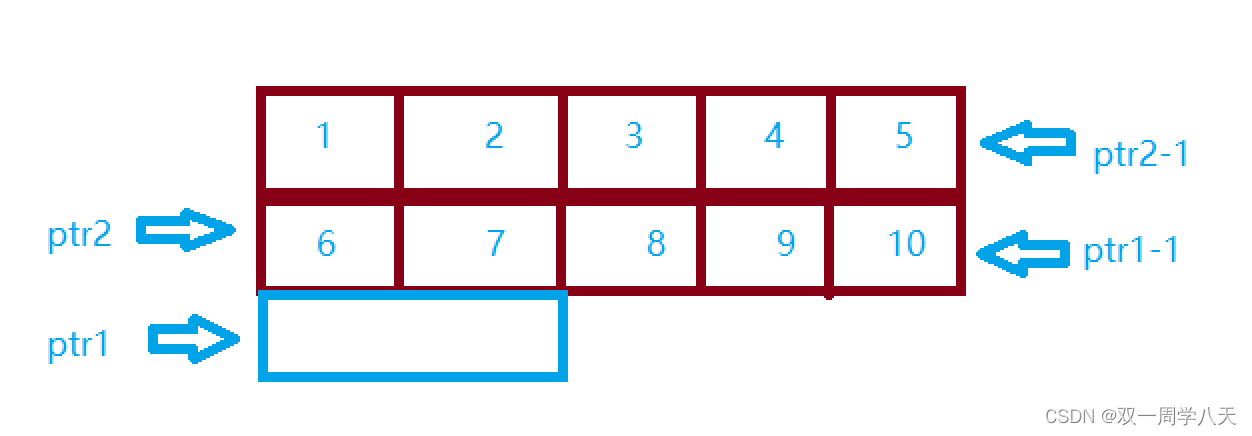 The answer is coming :10,5
The answer is coming :10,5
Question seven :
This is a written test of Alibaba :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *a[] = {"work","at","alibaba"};
char**pa = a;
pa++;
printf("%s\n", *pa);
return 0;
}Ideas and solutions :
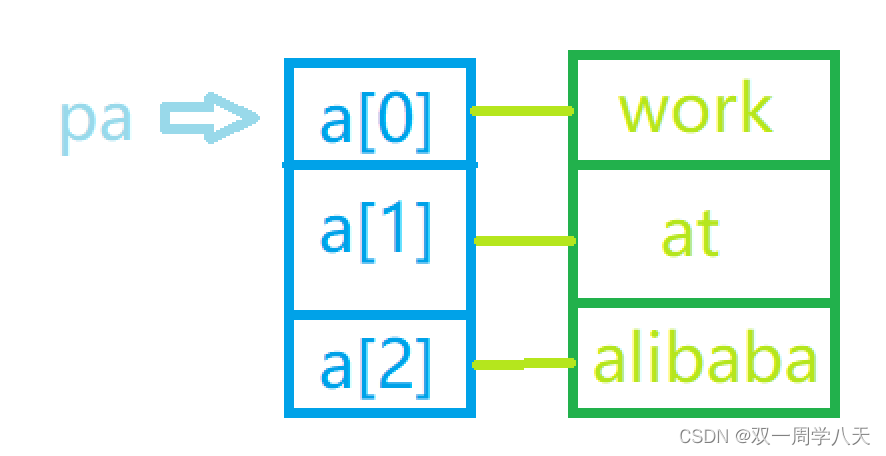
pa++ Here's the picture :
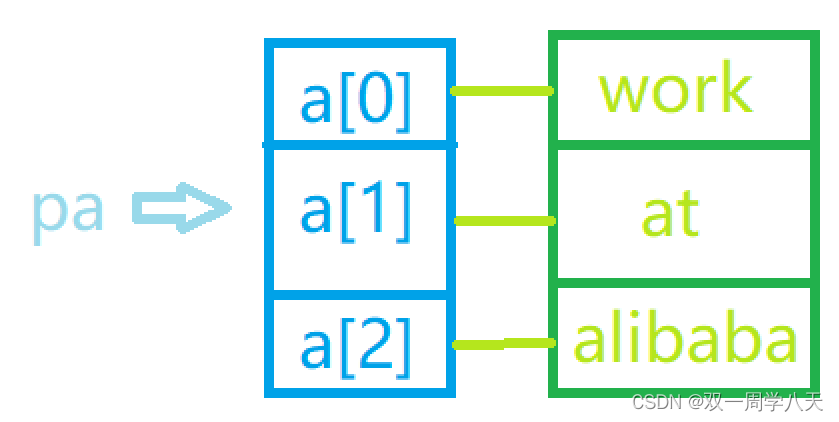
So the answer is :“at”
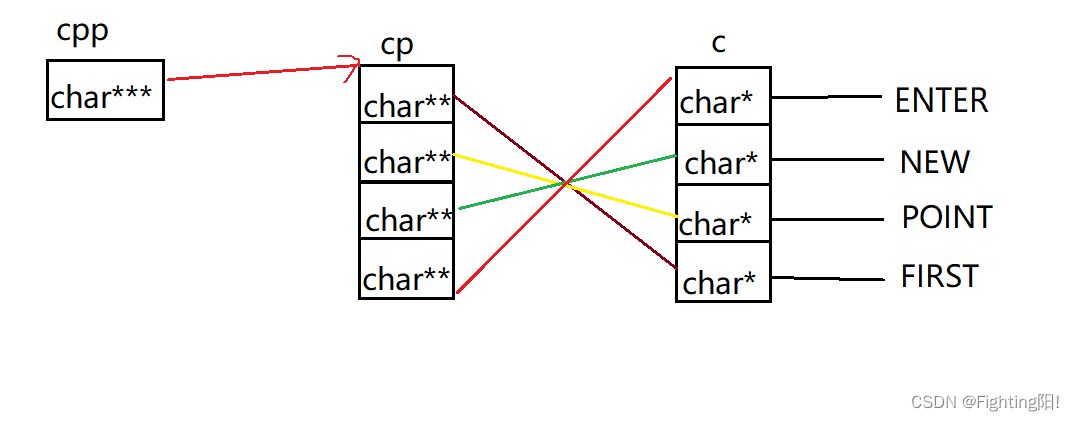
The eighth question :
int main()
{
char *c[] = {"ENTER","NEW","POINT","FIRST"};
char**cp[] = {c+3,c+2,c+1,c};
char***cpp = cp;
printf("%s\n", **++cpp);
printf("%s\n", *--*++cpp+3);
printf("%s\n", *cpp[-2]+3);
printf("%s\n", cpp[-1][-1]+1);
return 0;
}Ideas and solutions :
The relationship between pointers is as follows :
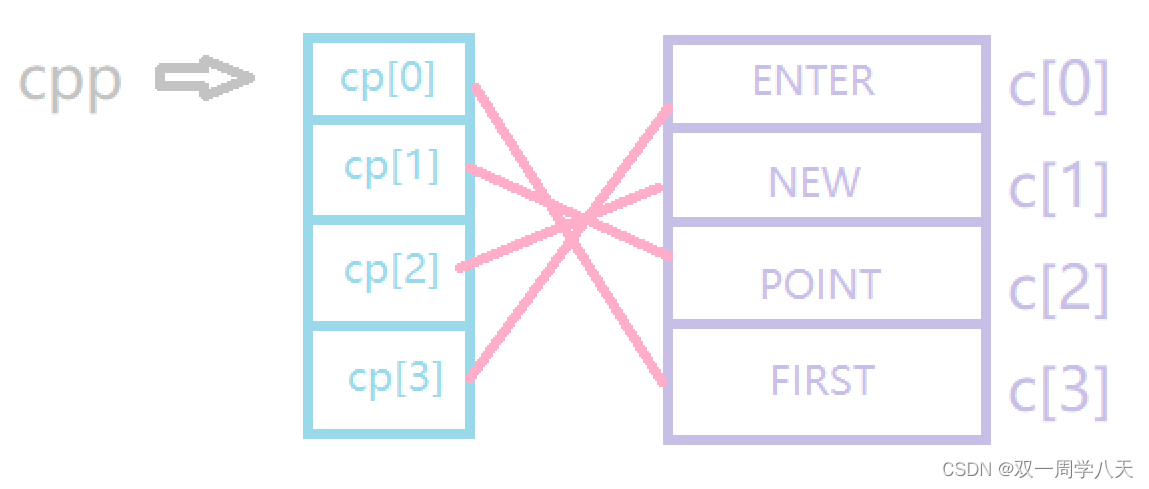
**++cpp It's equivalent to *(*(cpp+1)) Get as shown :
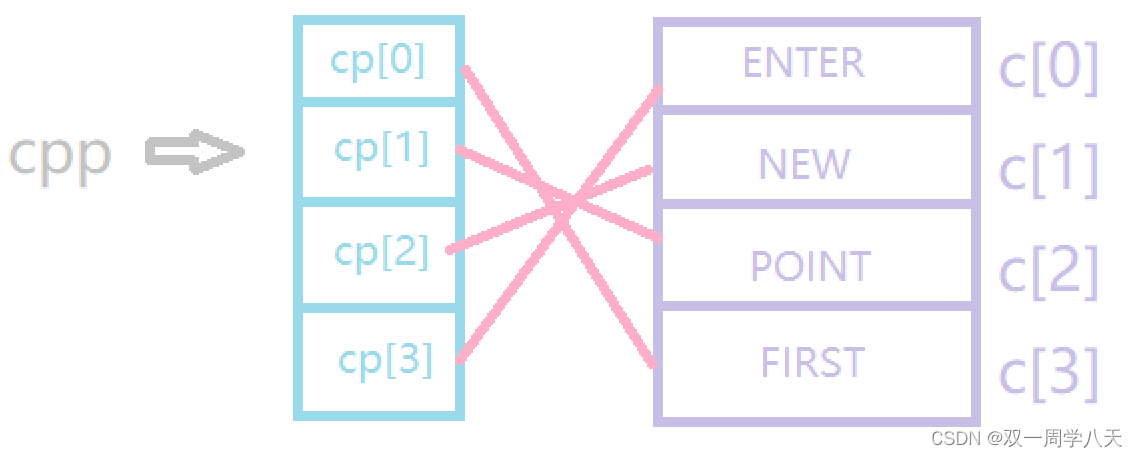
Follow the pointer to get :POINT
*--*++cpp+3 Equivalent to *(*(cpp+1)+1)+3, We analyze from the inside out ,
from cpp+1 Get as shown :
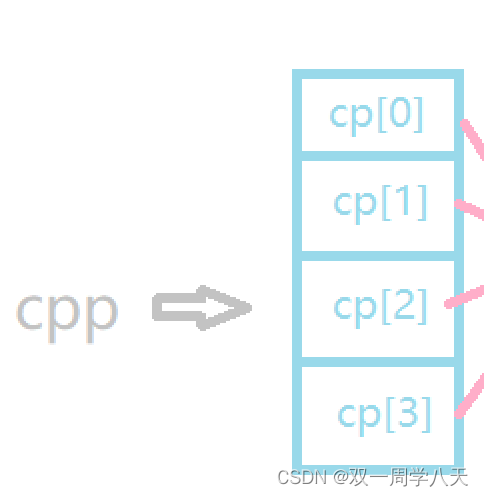
also *(cpp+1)+1 obtain :
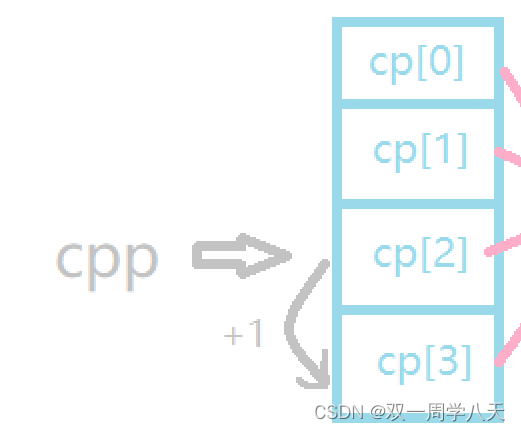
*(*(cpp+1)+1) The solution is c[0] The address of ,*(*(cpp+1)+1)+3 That's it .
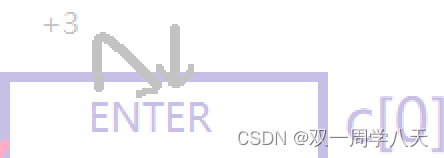
therefore *(*(cpp+1)+1)+3 Print it out ER.
*cpp[-2]+3:
*cpp[-2]+3 amount to :**(cpp-2)+3 Get the picture below :
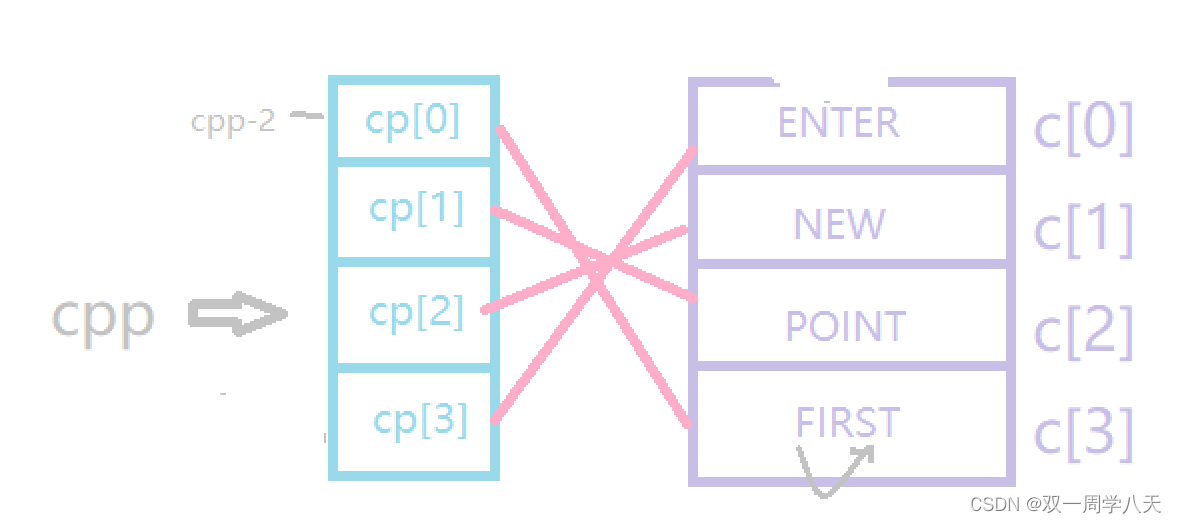
It can be seen that the answer is :ST
边栏推荐
- Self made CA certificate and SSL certificate using OpenSSL
- 2.12 simulation
- How to read excel, PDF and JSON files in R language?
- Introduction to robotframework (I) brief introduction and use
- Zhang Lijun: penetrating uncertainty depends on four "invariants"
- What are the principles of software design (OCP)
- ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
- 07 单件(Singleton)模式
- [Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 23
- My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- on the pointer
猜你喜欢
2345 file shredding, powerful file deletion tool, unbound pure extract version
Solve 9 with C language × 9 Sudoku (personal test available) (thinking analysis)
微服务间通信
主数据管理理论与实践

Deeply analyze the chain 2+1 mode, and subvert the traditional thinking of selling goods?
【 kubernets series】 a Literature Study on the Safe exposure Applications of kubernets Service
【指针训练——八道题】
Universal crud interface
淘宝焦点图布局实战

【Kubernetes 系列】一文学会Kubernetes Service安全的暴露应用
随机推荐
Atcoder beginer contest 233 (a~d) solution
Solution: attributeerror: 'STR' object has no attribute 'decode‘
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16
微服务注册与发现
一个复制也能玩出花来
Qt发布exe软件及修改exe应用程序图标
My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- under the pointer
My C language learning record (blue bridge) -- on the pointer
解决:AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘decode‘
DDoS attacks - are we really at war?
Day 50 - install vsftpd on ceontos6.8
Sign SSL certificate as Ca
Redis skip table
Daily question brushing plan-2-13 fingertip life
I sorted out a classic interview question for my job hopping friends
淘宝焦点图布局实战
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 24
[network security interview question] - how to penetrate the test file directory through
How to read excel, PDF and JSON files in R language?
MySQL advanced notes