当前位置:网站首页>Stack Title: nesting depth of valid parentheses
Stack Title: nesting depth of valid parentheses
2022-07-07 07:05:00 【Great Cherny】
List of articles
subject
Title and provenance
title : Nesting depth of valid parentheses
Source :1111. Nesting depth of valid parentheses
difficulty
6 level
Title Description
requirement
A string is a valid bracket string , If and only if the string contains only "(" \texttt{"("} "(" and ")" \texttt{")"} ")", And meet one of the following conditions :
- The string is an empty string ;
- The string can be written as AB \texttt{AB} AB( A \texttt{A} A And B \texttt{B} B String connection ), among A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B Are valid bracket strings ;
- The string can be written as (A) \texttt{(A)} (A), among A \texttt{A} A Is a valid parenthesis string .
For valid bracket strings S \texttt{S} S, Its nesting depth depth(S) \texttt{depth(S)} depth(S) The definition is as follows :
- depth("") = 0 \texttt{depth("")} = 0 depth("")=0;
- depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B)) \texttt{depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B))} depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B)), among A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B Are valid bracket strings ;
- depth("(" + A + ")") = 1 + depth(A) \texttt{depth("(" + A + ")") = 1 + depth(A)} depth("(" + A + ")") = 1 + depth(A), among A \texttt{A} A Is a valid parenthesis string .
for example , "" \texttt{""} ""、 "()()" \texttt{"()()"} "()()" and "()(()())" \texttt{"()(()())"} "()(()())" Is a valid bracket string ( The nesting depth is 0 \texttt{0} 0、 1 \texttt{1} 1 and 2 \texttt{2} 2), ")(" \texttt{")("} ")(" and "(()" \texttt{"(()"} "(()" Is not a valid parenthesis string .
Given a valid bracket string seq \texttt{seq} seq, Divide it into two disjoint subsequences A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B, bring A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B Is a valid bracket string , And A.length + B.length = seq.length \texttt{A.length + B.length = seq.length} A.length + B.length = seq.length.
Choose any A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B bring max(depth(A), depth(B)) \texttt{max(depth(A), depth(B))} max(depth(A), depth(B)) The minimum value of .
Returns an array of answer \texttt{answer} answer( The length is seq.length \texttt{seq.length} seq.length), Express choice A \texttt{A} A and B \texttt{B} B The coding : If seq[i] \texttt{seq[i]} seq[i] among A \texttt{A} A be answer[i] = 0 \texttt{answer[i] = 0} answer[i] = 0, otherwise answer[i] = 1 \texttt{answer[i] = 1} answer[i] = 1. If there are multiple answers that meet the requirements , Just return any one of them .
Example
Example 1:
Input : seq = "(()())" \texttt{seq = "(()())"} seq = "(()())"
Output : [0,1,1,1,1,0] \texttt{[0,1,1,1,1,0]} [0,1,1,1,1,0]
Example 2:
Input : seq = "()(())()" \texttt{seq = "()(())()"} seq = "()(())()"
Output : [0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1] \texttt{[0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1]} [0,0,0,1,1,0,1,1]
Data range
- 1 ≤ seq.size ≤ 10000 \texttt{1} \le \texttt{seq.size} \le \texttt{10000} 1≤seq.size≤10000
solution
Ideas and algorithms
Before considering dividing the valid bracket string into two disjoint subsequences , First, we need to consider the nesting depth of each bracket . Valid parenthesis string , Each left parenthesis has a matching right parenthesis , The nesting depth of a pair of matching left and right parentheses is the same .
To calculate the nesting depth of each bracket , You can use the stack to store the left parenthesis , Get the nesting depth according to the number of elements in the stack . Traverse valid bracket strings from left to right seq \textit{seq} seq, If the left bracket is encountered, the left bracket is put on the stack , If the right bracket is encountered, the left bracket at the top of the stack will be out of the stack , Indicates that the current right bracket matches the left bracket at the top of the stack . According to the definition of nesting depth , The nesting depth of the left bracket and the right bracket are calculated as follows :
For the left bracket , The number of elements in the stack after the stack operation is the nesting depth of the left bracket ;
For the right bracket , The number of elements in the stack before the stack operation is the nesting depth of the right bracket .
After clarifying the calculation method of the nesting depth of brackets , Go back to the original question , Put valid parenthesis strings seq \textit{seq} seq Divided into two disjoint subsequences A A A and B B B, Minimize the nesting depth of two subsequences . As long as the half bracket in the stack belongs to the subsequence A A A, The other half of the parentheses belong to the subsequence B B B, It can satisfy the minimum nesting depth of two subsequences . In terms of implementation , Divide the brackets of odd layers to A A A, Assign brackets of even layers to B B B that will do .
Because the nesting depth of a pair of matching left and right parentheses is the same , Therefore, a pair of matching left and right parentheses must be in the same subsequence . Thus we can see that , The number of left and right parentheses in any subsequence must be equal , And the left bracket must appear before the matching right bracket , Therefore, both subsequences are valid parenthesis strings .
Because only the left parenthesis is stored in the stack , Therefore, there is no need to really maintain a stack , Just record the nesting depth in the traversal process .
Code
class Solution {
public int[] maxDepthAfterSplit(String seq) {
int length = seq.length();
int[] answer = new int[length];
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (seq.charAt(i) == '(') {
depth++;
answer[i] = depth % 2 == 1 ? 0 : 1;
} else {
answer[i] = depth % 2 == 1 ? 0 : 1;
depth--;
}
}
return answer;
}
}
Complexity analysis
Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n), among n n n Is string seq \textit{seq} seq The length of . Need to traverse the string seq \textit{seq} seq once , Each time the nesting depth is updated O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1).
Spatial complexity : O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1). In addition to the return value , The space complexity used is constant .
边栏推荐
- 【JDBC以及内部类的讲解】
- [noi simulation] regional division (conclusion, structure)
- Config distributed configuration center
- FPGA课程:JESD204B的应用场景(干货分享)
- Big coffee gathering | nextarch foundation cloud development meetup is coming
- leetcode 509. Fibonacci Number(斐波那契数字)
- This article introduces you to the characteristics, purposes and basic function examples of static routing
- MySQL binlog related commands
- Answer to the second stage of the assignment of "information security management and evaluation" of the higher vocational group of the 2018 Jiangsu Vocational College skills competition
- JDBC database connection pool usage problem
猜你喜欢

Big coffee gathering | nextarch foundation cloud development meetup is coming
ip地址那点事
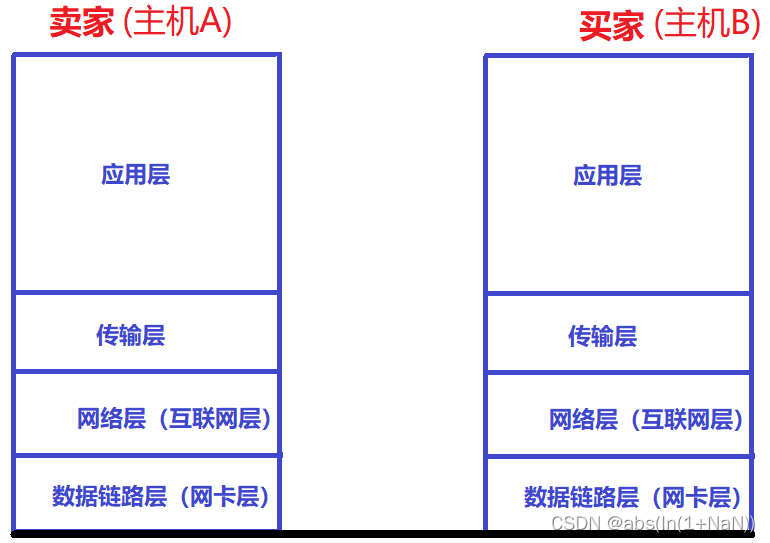
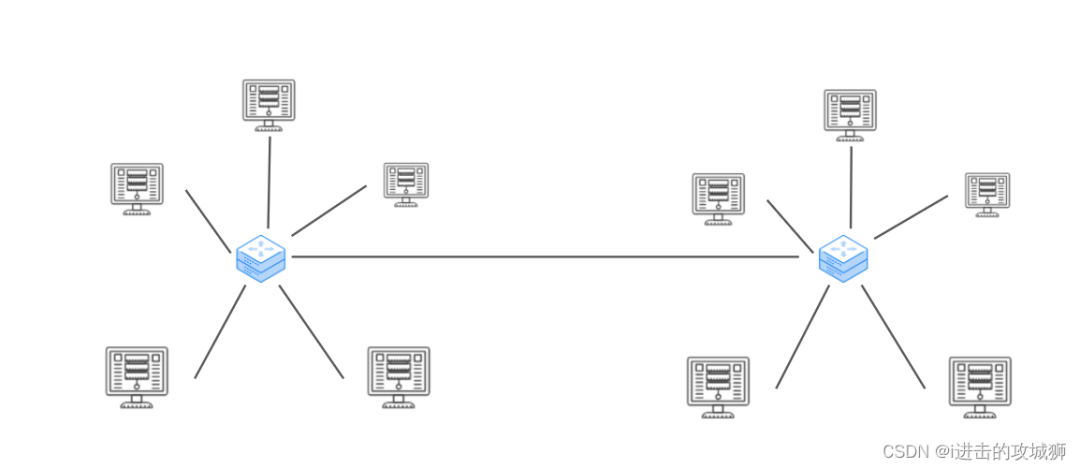
Basic process of network transmission using tcp/ip four layer model
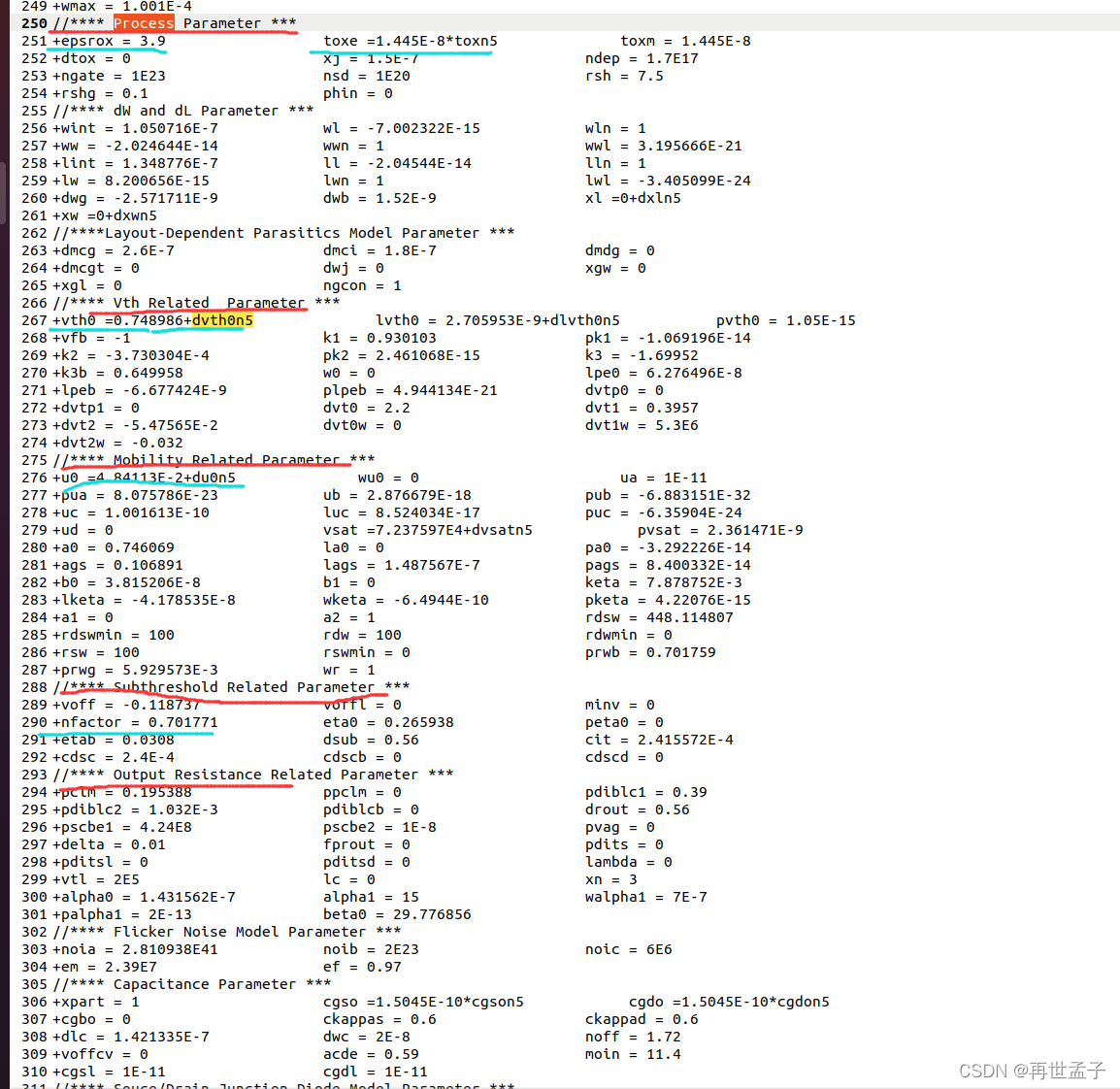
MOS tube parameters μ A method of Cox
![Stack and queue-p79-10 [2014 unified examination real question]](/img/7f/e5bba2f64bb77e1781076361c32f01.jpg)
Stack and queue-p79-10 [2014 unified examination real question]
场馆怎么做体育培训?
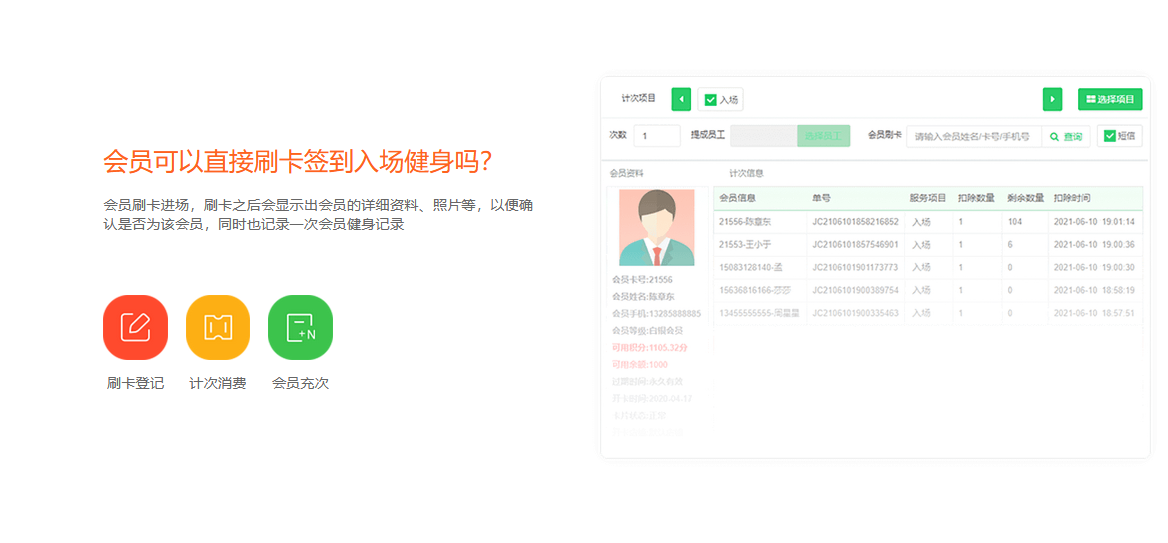
健身房如何提高竞争力?
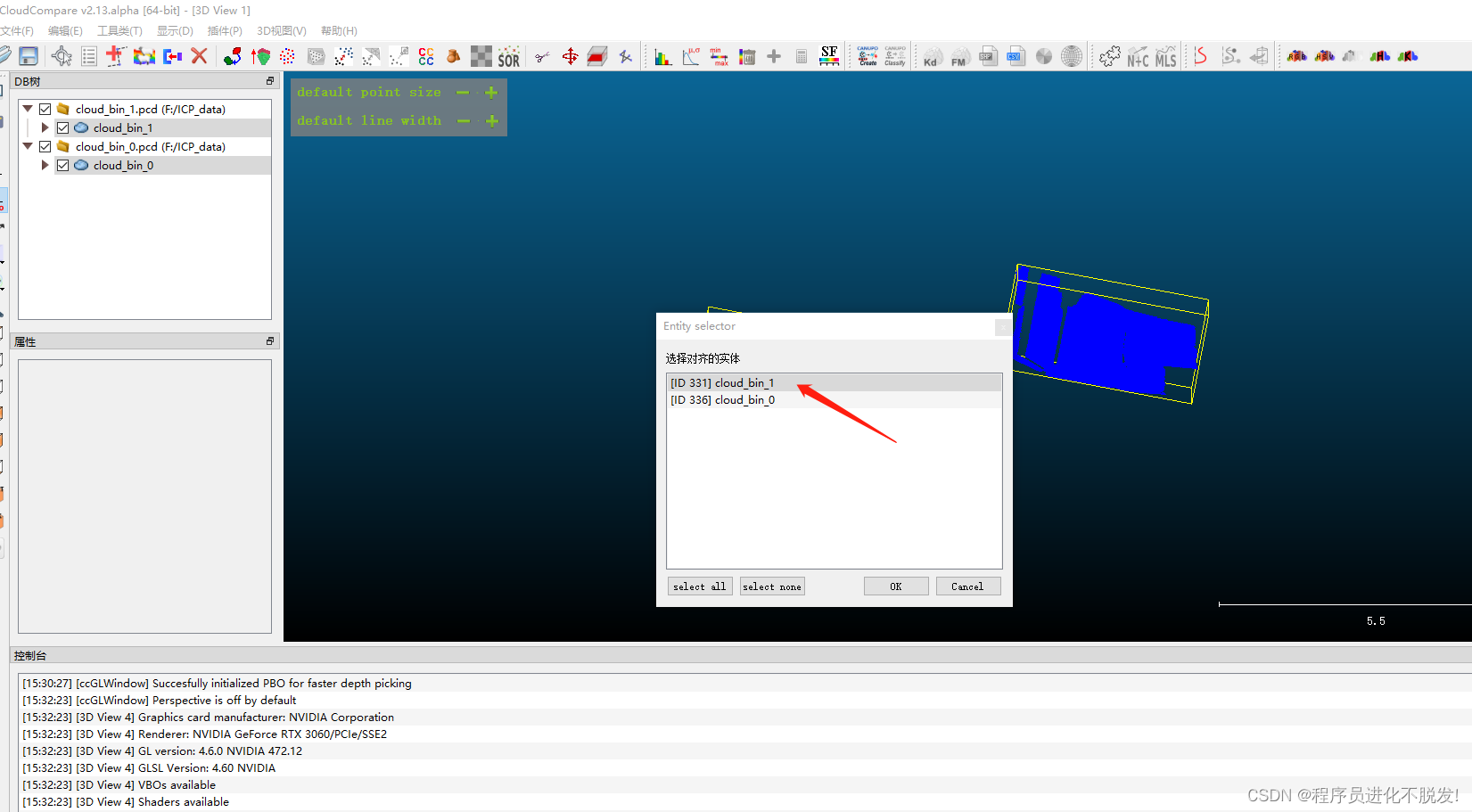
Cloudcompare point pair selection

Brand · consultation standardization
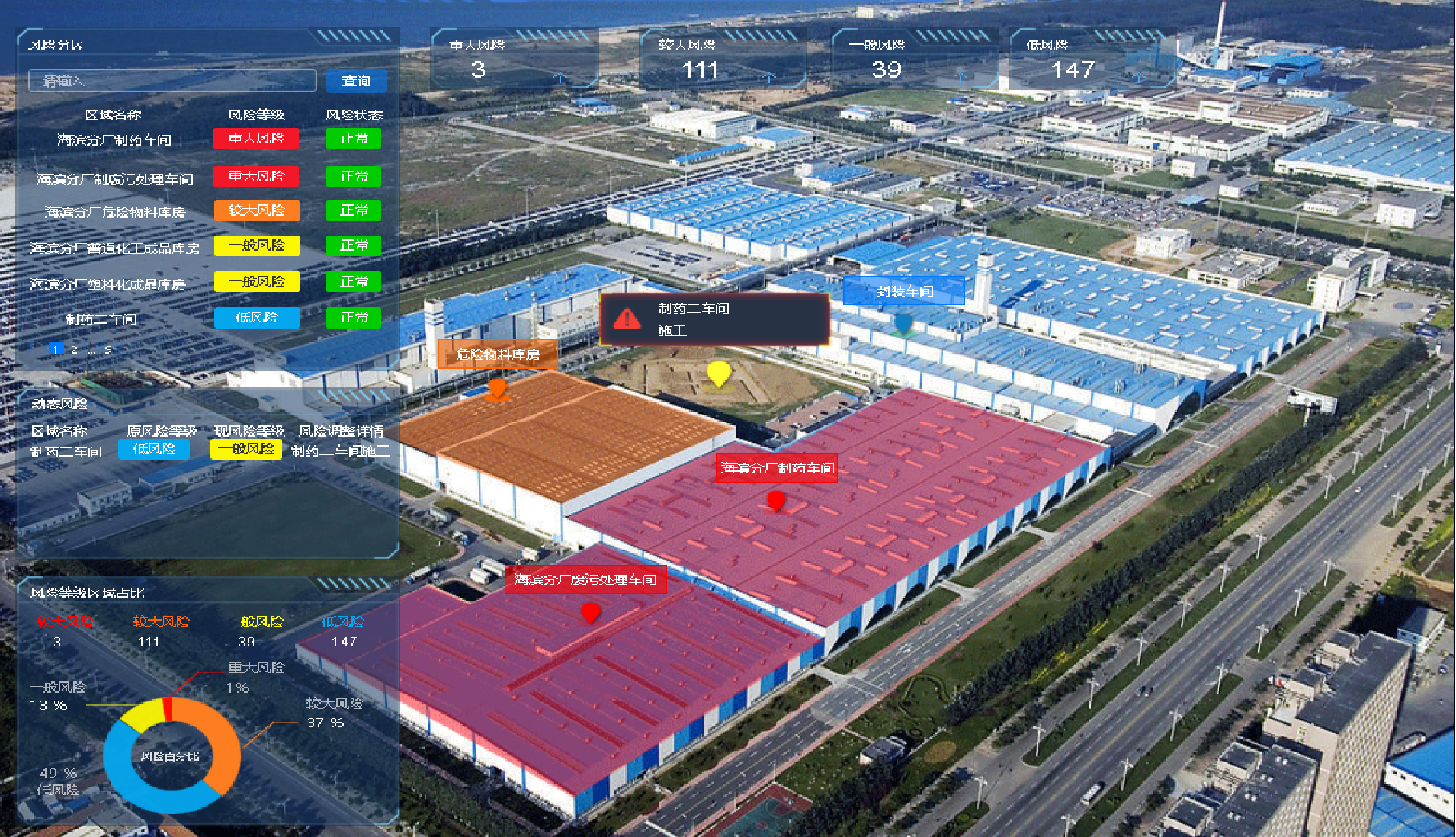
Four goals for the construction of intelligent safety risk management and control platform for hazardous chemical enterprises in Chemical Industry Park
随机推荐
带你刷(牛客网)C语言百题(第一天)
Redhat5 installing vmware tools under virtual machine
2018 Jiangsu Vocational College skills competition vocational group "information security management and evaluation" competition assignment
How can gyms improve their competitiveness?
Stack and queue-p79-9
AVL树的实现
多学科融合
Graduation design game mall
Unable to debug screen program with serial port
华为机试题素数伴侣
Jmeter 5.5版本发布说明
leetcode 509. Fibonacci Number(斐波那契数字)
Networkx绘图和常用库函数坐标绘图
一文带你了解静态路由的特点、目的及配置基本功能示例
oracle如何备份索引
.net 5 FluentFTP连接FTP失败问题:This operation is only allowed using a successfully authenticated context
How can brand e-commerce grow against the trend? See the future here!
unity3d学习笔记
Bus消息总线
MYSQL----导入导出&视图&索引&执行计划