Xiao Bo mentioned many times in his previous blog post , Can be in VBA Write in SQL To operate Excel file , Realize various data processing and analysis requirements . that , You may have such a question :Excel Native VBA, PivotTable , Data analysis Is the function insufficient , Why do you have to use SQL To implement? ? stay Excel VBA Use in SQL Where are the advantages ? Today, I'll take you to have a good look at these problems .

First , stay VBA Write in SQL, This is basically VBA High level functions of , Not everyone knows , therefore , In addition to SQL, Indeed, there are other technical solutions . secondly , If we are more skilled in using other technologies , We can use our best technology stack to solve problems . In terms of consequence , As long as it can solve practical problems , All good plans .
however , What I want to discuss here is , If we are right VBA A native method , PivotTable ,SQL Under the premise of being familiar with knowledge , How can we choose a technology stack to solve practical problems , This is the time ,SQL What's the advantage of ? I think there are several points :
One 、 The highest efficiency of execution
Follow VBA Native methods and Excel The formula compares ,SQL The execution speed is much faster . When the number of tables exceeds 10000 rows , This advantage is more and more obvious . More data , The more suitable to use SQL To solve the problem , More efficient ;
Two 、 The code is extremely concise
①、 Data matching scenario : If we have multiple fields to match , In principle, more Vlookup perhaps VBA Create multiple dictionaries in , however , If we use SQL External connection of , Maybe one line of code is enough ;
②、 Data grouping and aggregation scenario : If we were VBA Record macros in to generate PivotTable code , To find the maximum by grouping and aggregating ,EXCEL A lot of code will be generated automatically in the background , These codes are extremely unreadable , But if we use SQL Group By, combination max,min,average Wait for the aggregate function , We only use one line SQL Sentence can be used .
3、 ... and 、 Easier to implement
There are some special scenes , Use native VBA The method will be extremely complex , But use SQL Maybe just one line of code . Take my previous blog post VBA How to realize the filtering conditions “ Some values are excluded ” give an example , This scene , That article used a lot of space to use pure VBA Skills to achieve such a seemingly simple need , Single one “ Screening —— Some values are not included ” Of VBA scene , We need to use Recording macro function , One dimensional array 、 Two dimensional array function 、 Transpose method of array 、 Dictionary remove Method 、 Dictionary key fast storage array method etc. . But in fact , If we use SQL, The knowledge points needed are much less .
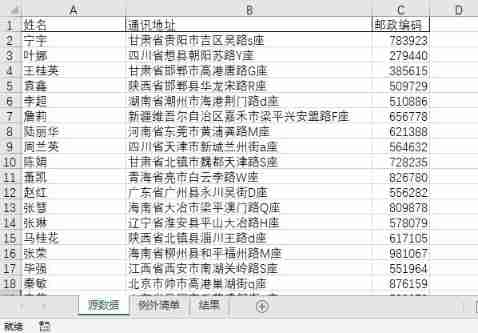
Let's review this scene again ,【 Source data 】 The table contains 【 full name 】【 postal address 】【 Postal Code 】 The three column ,【 Exception list 】 The table stores names to be excluded ,【 result 】 Table requires return 【 Source data 】 Table does not contain 【 Exception list 】 All data of the name . We use Python faker Library generation 20000 Row data , It is convenient to compare the efficiency of different methods when comparing large samples .
If you use SQL, In essence, we need to 【 Source data 】 Table left outer connection (Left Join)【 Exception list 】 surface , be based on 【 full name 】 Column , Plus where The conditions are good .
The specific code is as follows :
1 Sub myQuery() 2 Dim conn As Object, rs As Object, sht1 As Worksheet, sht2 As Worksheet, sht3 As Worksheet, sql As String, startTime As Date, endTime As Date 3 startTime = Timer 4 Set conn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection") 5 Set rs = CreateObject("ADODB.recordset") 6 Set sht1 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" Source data ") 7 Set sht2 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" Exception list ") 8 Set sht3 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" result ") 9 conn.Open "provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;extended properties=excel 12.0;data source=" & ThisWorkbook.FullName 10 sql = "SELECT a.* FROM [ Source data $]a LEFT JOIN [ Exception list $]b ON a. full name =b. full name WHERE b. full name IS NULL" 11 Set rs = conn.Execute(sql) 12 For i = 0 To rs.Fields.Count - 1 ' Output recordset Field names to 【 result 】 surface 13 sht3.Cells(1, i + 1) = rs.Fields(i).Name 14 Next 15 sht3.Cells(2, 1).CopyFromRecordset rs ' Output recordset Results to 【 result 】 surface 16 conn.Close 17 Set conn = Nothing 18 endTime = Timer 19 sht3.Activate 20 MsgBox " Cumulative operation " & (endTime - startTime) & " second " 21 22 End Sub
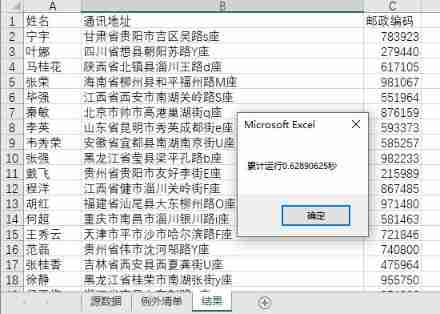
The running results are as follows , It takes about 0.63 second :
Let's review the use of VBA Dictionary to achieve this requirement , The code is as follows :
1 Sub dictWay() 2 Dim conn As Object, rs As Object, sht1 As Worksheet, sht2 As Worksheet, sht3 As Worksheet, sql As String, startTime As Date, endTime As Date, maxRow1 As Integer, myDic As Object, maxRow2 As Integer 3 startTime = Timer 4 Application.ScreenUpdating = False 5 Set sht1 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" Source data ") 6 Set sht2 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" Exception list ") 7 Set sht3 = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(" result ") 8 Set myDic = CreateObject("scripting.dictionary") 9 maxRow1 = sht1.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row 10 maxRow2 = sht2.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row 11 Dim i As Integer, j As Integer, k As Integer 12 For i = 2 To maxRow2 13 myDic.Add sht2.Cells(i, 1).Value, "" 14 Next 15 16 k = 1 17 For i = 1 To maxRow1 18 If myDic.exists(sht1.Cells(i, 1).Value) = False Then 19 For j = 1 To 3 20 sht3.Cells(k, j).Value = sht1.Cells(i, j).Value 21 Next 22 k = k + 1 23 End If 24 25 Next 26 27 endTime = Timer 28 sht3.Activate 29 Application.ScreenUpdating = True 30 MsgBox " Cumulative operation " & (endTime - startTime) & " second " 31 32 End Sub
In order to make this method as fast as possible , We used a dictionary , At the same time, it turns off Excel Screen refresh . Final 20000 Line data , It takes about 4 second :
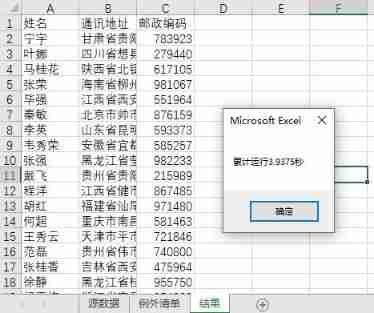
You can see , Prior to VBA Compared with , Just one line SQL sentence , The logic is clear and easy to understand , The code is simple and clear , The running time of the program is traditional 1/6 Less than , This is the small climbing force pushing in VBA Use in SQL The main reason is ~~
Welcome to scan code to pay attention to my official account Get more crawlers 、 Knowledge of data analysis !

![[算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题5:单词长度的最大乘积](/img/e0/cea31070d6365eb57013cdead4a175.png)

![[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 12: the sum of the left and right sub arrays is equal](/img/11/ee0628a68542236fc641966579a31a.png)
![[algorithme] swordfinger offer2 golang question d'entrevue 2: addition binaire](/img/c2/6f6c3bd4d70252ba73addad6a3a9c1.png)

![[算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题3:前n个数字二进制形式中1的个数](/img/64/0f352232359c7d44f12b20a64c7bb4.png)
![[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 4: numbers that appear only once](/img/f7/23ffc81ec8e9161c15d863c1a67916.png)