当前位置:网站首页>One article to get UDP and TCP high-frequency interview questions!
One article to get UDP and TCP high-frequency interview questions!
2022-07-06 13:03:00 【Java misty rain】
Job interview , I'm often asked UDP and TCP, Today, I'd like to summarize the core high-frequency interview questions , Then the interviewer asked you about your knowledge , Just read this one !
PS: It's a little long , Please read... Patiently .
Catalog :
1、UDP and TCP Characteristics and differences of
2、UDP 、TCP Format of the first part
3、TCP Three and four waves of
4、TCP Three handshakes of ( Why three times ?)
5、TCP Four waves ( Why four times ?)
6、TCP The difference between long connection and short connection
7、TCP Sticky package 、 Unpacking and solutions
8、TCP Reliable transmission
9、TCP The sliding window
10、TCP flow control
11、TCP Congestion control
12、 Provide network utilization
Preface
The network layer only sends packets to the destination host , But the real communication is not the host but the process in the host . The transport layer provides logical communication between processes , The transport layer shields the core details of the lower network layer from the high-level users , Make the application look like an end-to-end logical communication channel between two transport layer entities .
1、UDP and TCP Characteristics and differences of
User datagram protocol UDP(User Datagram Protocol)
It's disconnected , Deliver... As much as possible , no congestion control , Message oriented ( Do not merge or split the messages sent by the application program , Just add UDP The first one ), Support one-to-one 、 One to many 、 Many to one and many to many interactive communication .
Transmission control protocol TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
It's connection-oriented , Provide reliable delivery , With flow control , Congestion control , Provide full duplex communication , Byte stream oriented ( Consider the message passed down from the application layer as a byte stream , Organize byte streams into blocks of different sizes ), Every one of them TCP Connections can only be point-to-point ( one-on-one ).
2、UDP 、TCP Format of the first part
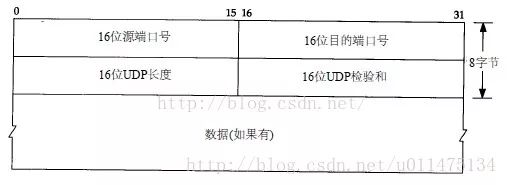
UDP The first field only has 8 Bytes , Include source port 、 Destination port 、 length 、 Inspection and .12 The pseudo header of a byte is for computation verification and temporary addition .

TCP Format ratio of the first part UDP complex .
Serial number : Used to number byte streams , For example, the serial number is 301, Indicates that the number of the first byte is 301, If the length of the data carried is 100 byte , Then the sequence number of the next message segment should be 401.
Confirmation no. : Sequence number of the next message segment expected to be received . for example B Correctly received A A message segment sent , Serial number is 501, The length of the data carried is 200 byte , therefore B The expected sequence number of the next message segment is 701,B Send to A The confirmation number in the confirmation message segment of is 701.
Data migration : It refers to the offset of the data part from the beginning of the message segment , Actually, it means the length of the head .
Control bits : The eight digits are from left to right CWR,ECE,URG,ACK,PSH,RST,SYN,FIN.
CWR:CWR The logo with the ECE Signs are used for IP The first ECN Field ,ECE Mark is 1 when , Notify the other party that the congestion window has been reduced ;
ECE: If it's worth 1 Will inform the other party , The network from the other side to this side is blocked . After receiving the packet IP In the head ECN by 1 When will TCP In the first part ECE Set to 1;
URG: This bit is set to 1, Indicates that there is urgent data in the package , For data that needs to be processed urgently , Related to the emergency pointer at the back ;
ACK: This bit is set to 1, Confirm that the field of the answer is valid ,TCP Except when the connection is initially established SYN The bit outside the package must be set to 1;
PSH: This bit is set to 1, Indicates that the received data needs to be transferred to the upper application protocol immediately , Set up as 0, First, cache the data ;
RST: This bit is set to 1, Express TCP Connection exception must force disconnection ;
SYN: Used to establish a connection , This bit is set to 1, Indicates that you want to establish a connection , And set the initial value of serial number in the field of serial number ;
FIN: This bit is set to 1, No more data will be sent in the future , Want to disconnect . When communication ends and you want to disconnect , The hosts of both sides can exchange with each other FIN The position is 1 Of TCP paragraph .
Each host is to the other's FIN The packet can be disconnected after confirming the response . however , Host received FIN Set to 1 Of TCP You don't have to reply to a FIN package , Instead, you can wait until all the data in the buffer is automatically deleted because it has been successfully sent FIN package ;
window : The window value is the basis for the receiver to let the sender set its sending window . The reason for this limitation is , Because the receiver's data cache space is limited .
3、 What is? TCP Three and four waves of ?
TCP Is a connection - oriented unicast protocol , Before sending the data , The communicating parties must establish a connection with each other . So-called “ Connect ”, It is a piece of information about each other that is stored in the memory of the client and the server , Such as IP Address 、 Port number, etc .
TCP You can view it as a byte stream , It will deal with IP Lost packets of layers or layers below 、 Repetition and error problems . In the process of establishing the connection , The two sides need to exchange some connection parameters . These parameters can be placed in TCP Head .
TCP It provides a kind of reliability 、 Connection oriented 、 Byte stream 、 Transport layer services , Use three handshakes to establish a connection ; Use four waves to close a connection .
One TCP The connection consists of a 4 Tuples make up , Two IP Address and two port Numbers . One TCP Connections are usually divided into three phases : start-up 、 The data transfer 、 sign out ( close ).
When TCP When the data on the other end is received , It will send a confirmation , But this confirmation will not be sent immediately , It's usually delayed for a while ( The section on providing network utilization has talked about ).
ACK It's cumulative , A confirmation byte number N Of ACK Means all until N Bytes of ( barring N) It has been accepted successfully . The advantage of this is that if one ACK The loss of , Probably later ACK That's enough to confirm the previous segment .
A complete TCP The connection is bidirectional and symmetrical , Data can flow equally in both directions . Provide a duplex service for upper application . Once a connection has been established , Each of these connections in one direction TCP Each segment contains one segment in the opposite direction ACK.
The function of the serial number is to make one TCP The receiver can discard duplicate segments , Record segments that arrive in a random order . because TCP Use IP To transmit message segments , and IP It does not provide the ability to eliminate duplicates or ensure correct ordering .
On the other hand ,TCP Is a byte stream protocol , Never send data in a random order to the upper program . therefore TCP The receiver will be forced to hold the data with a large sequence number before handing it over to the application , Until the missing small serial number segment is filled .
4、TCP Three handshakes of ( Why three times ?)
Three handshakes :

hypothesis A For the client ,B For the server side .
First B be in LISTEN( monitor ) state , Waiting for customer's connection request .
A towards B Send connection request message ,SYN=1,ACK=0, Choose an initial sequence number x.
B Receive connection request message , If you agree to establish a connection , to A Send connection confirmation message ,SYN=1,ACK=1, The confirmation number is x+1, Also choose an initial sequence number y.
A received B After the connection confirmation message of , And to B Send a confirmation , The confirmation number is y+1, Serial number is x+1.
B received A After the confirmation of , Connection is established .
Why three times ?
1、 The third handshake is to prevent invalid connection requests from reaching the server , Let the server open the connection by mistake .
2、 To put it in a more understandable perspective why 3 The second handshake .
Connect before the client and server communicate ,“3 The second handshake ” The role of both sides is to be clear about their own and the other side's income 、 Hair power is normal .
The first handshake : The client sends network packets , The server received it . Then the server can draw a conclusion : Client sending capability 、 The reception capability on the server side is normal .
The second handshake : Server sends packets , The client received it . This way the client can draw a conclusion : Server side reception 、 Sending capability , Client reception 、 The ability to send is normal . From the client's perspective , I received a response packet from the server , Indicates that the server received the network packet I sent during the first handshake , And the response packet was successfully sent , This means that , Server side reception 、 Normal sending capacity . And on the other hand , I received the server response packet , Indicates that the network packet I sent for the first time reached the server successfully , such , My own sending and receiving abilities are normal .
The third handshake : Client sends packets , The server received it . Then the server can draw a conclusion : Client reception 、 Sending capability , Sending from the server 、 Reception is normal . First of all 、 After the second handshake , The server does not know whether the client's receiving ability and its sending ability are normal or not .
And on the third handshake , The server receives the client's response to the second handshake . From the server side , The response data from my second handshake was sent , The client receives it . therefore , My ability to send is normal . The reception capacity of the client is normal .
Experienced the above three handshakes , Both the client and the server confirm their reception 、 The ability to send is normal . Then you can communicate normally .
The party that receives the packet each time can draw some conclusions , The sender didn't have a clue . Although I have the hair bag movement , But how do I know if I sent it , And the other side has not received it ?
And you can see that from the top , At least three handshakes are required . Two failed to get both sides to their own 、 Reception by the other party 、 Send ability all normal conclusion .
Actually every time the party that receives network packet is to be able to get at least : Sending by the other party 、 Our acceptance is normal . And each step is related , Next time “ Respond to ” It's the first time “ request ” Trigger , So you can actually draw additional conclusions from each handshake .
Like the third handshake , The server receives the packet , Indicates that the server side can only get the client side send ability 、 The reception capability on the server side is normal , But combine it the second time , Specifies the response package that the server sent the second time , The client receives it , And responded , And that leads to additional conclusions : Client reception 、 Server side sending is normal .
5、TCP Four waves ( Why four times ?)
Four waves :

The client sends one FIN paragraph , Contains a current sequence number that you want the recipient to see K. It also contains one ACK Confirm the latest data sent by the other party .
The server will K It's worth adding 1 As ACK Serial number value , Indicates receipt of the last package . At this point, the upper application is informed that the other side has initiated a shutdown operation , Usually this causes the application to initiate its own shutdown .
The server initiates its own FIN paragraph ,ACK=K+1, Seq=L.
Client confirmation . Get into TIME-WAIT state , wait for 2 MSL( Maximum message lifetime ) Release the connection after .ACK=L+1.
Why three handshakes to establish a connection , Closing the connection is four waves ?
1、TCP A connection is a two-way peer-to-peer mode of transmission , This means that both parties can send or receive data to each other at the same time . When a party closes the connection , It sends instructions to the other party , I'm going to close the connection .
2、 The other person will respond with one ACK, At this point the connection in one direction closes . But the data can still be transmitted in the other direction , in other words , The server receives... From the client FIN sign , Know that the client wants to disconnect this time , however , I serve , I also want to send data ? I wait until all the data is sent , Will send a FIN Segment to close the connection in this direction . Receiver send ACK Make sure to close the connection .
Be careful , Received FIN One party to a message can reply only one ACK, It is unable to return the other one immediately FIN Of the message segment , Because the end of the data transmission “ Instructions ” It's given by the upper application layer , I'm just a “ hamal ”, I don't understand “ The will of the upper class ”.
3、 The client sends it FIN After connection release message , The server received this message , It's in CLOSE-WAIT state . This state is for the server to send data that has not been transmitted yet , After transmission , The server will send FIN Connection release message .
4、 Because the server is LISTEN State, , Received a request to establish a connection SYN After the message , hold ACK and SYN Put it in a message and send it to the client . And when you close the connection , When receiving from the other party FIN When the message , It simply means that the other party is no longer sending data but can still receive data , Does the party now close the send data channel , You need the top application to decide , therefore , Own side ACK and FIN Generally, it will be developed separately .
TIME_WAIT
The client receives... From the server FIN Enter this state after the message , This is not a direct entry into CLOSED state , Also need to wait for a time timer to set the time 2MSL. There are two reasons to do this :
Make sure that the last acknowledgment message reaches . If B received A The confirmation message sent , Then the connection release request message will be sent again ,A Waiting for a while is to deal with this situation .
Waiting for a period of time is to make all messages generated during the duration of this connection disappear from the network , So that the old connection request message will not appear in the next new connection .
6、TCP The difference between short connection and long connection
Short connection :Client towards Server Send a message ,Server Respond Client, Then one reading and writing is done , At this time, either party can initiate close operation , But it's usually Client First initiate close operation . The short connection is usually only in Client/Server Pass a read-write operation between .
Advantages of short connection : It's easier to manage , Establishing existing connections is a useful connection , There is no need for additional controls .
A long connection :Client And Server After one read and write , The connection between them is not actively closed , Subsequent read and write operations will continue to use this connection .
In a long connected application scenario ,Client End will not actively close the connection between them ,Client And Server If the connection is not closed all the time , As clients connect more and more ,Server The pressure is also increasing , Now Server The end needs to take some strategies , For example, close some connections that have not read or write events for a long time , This can avoid some malicious connections Server End service damage ; If the condition allows, the client can be used as granularity , Limit the maximum number of long connections per client , So as to avoid a client implicating the back-end services .
Long connection and short connection are produced by Client and Server Closure strategy adopted , Specific application scenarios adopt specific strategies .
7、TCP Sticky package 、 Unpacking and solutions
Why do you often say TCP There are problems of sticking and unpacking without saying UDP ?
It can be seen from the first two sections that ,UDP It's based on the message sent ,UDP The first one 16bit To instruct UDP Length of data message , Therefore, in the application layer, different data packets can be distinguished well , So as to avoid the problems of sticking and unpacking .
and TCP It's based on a byte stream , Although the application layer and TCP The data interaction between transport layers is data blocks of different sizes , however TCP There is no boundary between these data blocks , Just a stream of unstructured bytes ; From the other TCP We can also see the frame structure of , stay TCP There is no field for data length in the first part of , Based on the above two points , In the use of TCP Data transfer , There is only the possibility of sticking or unpacking .
What is a sticky bag 、 unpacking ?
hypothesis Client towards Server Two consecutive packets were sent , use packet1 and packet2 To express , Then the data received by the server can be divided into three situations , Here are some examples :
Case one , The receiver normally receives two packets , That is to say, there is no phenomenon of unpacking and sticking .

The second case , The receiver receives only one packet , But this packet contains the information of two packets sent by the sender , This phenomenon is called "sticking package" . In this case, the receiver does not know the boundary between the two packets , So it's hard for the receiver to handle .

The third case , There are two forms of this situation , Here's the picture . The receiver received two packets , But these two packets are either incomplete , Or one more piece , In this case, unpacking and sticking happen . If these two cases are not treated specially , It is also not easy to deal with the receiver .

Why does it happen TCP Sticky package 、 unpacking ?
The data to be sent is greater than TCP The amount of space left in the send buffer , Unpacking will occur .
Data to be sent is greater than MSS( Maximum message length ),TCP Unpack before transmission .
The data to be sent is less than TCP Size of send buffer ,TCP Send the data written to the buffer several times at a time , Sticking will occur .
The application layer of the receiving data side does not read the data in the receiving buffer in time , Sticking will occur .
Sticky package 、 Unpacking solutions
because TCP It's byte stream oriented , Inability to understand the business data at the top , So there is no guarantee at the bottom that packets will not be split and recombined , This problem can only be solved by the upper layer of the application stack design , Solutions according to the industry's mainstream protocols , It can be summed up as follows :
Message fixed-length : The sender encapsulates each packet as a fixed length ( If it's not enough, we can make up for it 0 fill ), In this way, each time the receiving end reads the fixed length data in the receiving buffer, it will naturally split each packet .
Set message boundaries : The server separates the message content from the network flow according to the message boundary . Add a carriage return line break at the end of the packet to split , for example FTP agreement .
Divides messages into headers and bodies : The message header contains the total message length ( Or message body length ) Field of .
More complex application layer protocols like Netty Some of the protocols implemented in are for package sticking 、 Unpacking has done a good job .
8、TCP Reliable transmission
TCP Use timeout retransmission to achieve reliable transmission : If a sent message segment does not receive an acknowledgement within the timeout period , Then retransmit this message segment .
The time that a message segment passes from sending to receiving confirmation is called round trip time RTT, Weighted average round trip time RTTs The calculation is as follows :

among ,0 ≤ a < 1,RTTs With a The increase is more susceptible to RTT Influence . Timeout time RTO It should be slightly greater than RTTs,TCP The timeout used is calculated as follows :

among RTTd Is the weighted average of the deviation .
9、TCP The sliding window
Windows are part of the cache , Used to temporarily store byte streams . The sender and the receiver each have a window , The receiver passes TCP The window field in the message segment tells the sender its own window size , The sender sets its own window size based on this value and other information .
Bytes in the send window are allowed to be sent , Bytes in the receive window are allowed to be received . If the byte on the left of the send window has been sent and received an acknowledgement , Then slide the sending window a certain distance to the right , Until the first byte on the left is not sent and acknowledged ; The receiving window slides like , The left byte of the receiving window has sent a confirmation and delivered to the host , Just slide the receiving window right .
The receiving window will only confirm the last byte arriving in order in the window , For example, the bytes received by the receiving window are {31, 34, 35}, among {31} Arrive in order , and {34, 35} It's not , So only for bytes 31 Confirm . After the sender gets a byte of confirmation , You know that all the bytes before this byte have been received .

10、TCP flow control
Flow control is to control the sending rate of the sender , To ensure that the receiving party can receive .
The window field in the acknowledgement message sent by the receiver can be used to control the size of the sender window , Thus, the transmission rate of the sender is affected . Set the window field to 0, Then the sender cannot send data .
actually , To avoid this problem , From time to time, the main transmitter sends a data segment called window detection , This data segment contains only one byte to get the latest window size information .
11、TCP Congestion control
If the network is congested , Groups will be lost , At this time, the sender will continue to retransmit , This leads to higher network congestion . So when there's congestion , The sender's rate should be controlled . This is very similar to flow control , But the starting point is different . Flow control is to allow the receiver to receive in time , And congestion control is to reduce the congestion of the whole network .

TCP Four algorithms are used to control congestion :
Slow start 、 Congestion avoidance 、 Fast retransmission 、 Fast recovery .
The sender needs to maintain a called congestion window (cwnd) State variable of , Note the difference between the congestion window and the sender window : Congestion window is just a state variable , It is the sender window that actually determines how much data the sender can send .
For discussion , Make the following assumptions :
The receiver has a large enough receive cache , So there's no flow control ;
although TCP Based on bytes , But here, the size of the window is set as message segment .

Slow start and congestion avoidance
The initial execution of the transmission starts slowly , Make cwnd = 1, The sender can only send 1 Message segments ; When confirmation is received , take cwnd double , Therefore, the number of message segments that the sender can send later is :2、4、8 ...
Notice that the slow start of each round will cwnd double , This will make cwnd It's growing very fast , Thus, the transmission speed of the sender increases too fast , Network congestion is more likely . Set a slow start threshold ssthresh, When cwnd >= ssthresh when , Enter congestion avoidance , Each round will only cwnd Add 1.
If there is a timeout , Then order ssthresh = cwnd / 2, Then re execute slow start .
Fast retransmission and fast recovery
At the receiver , It is required that each received message segment should confirm the last received ordered message segment . For example, it has received M1 and M2, Received at this time M4, Should be sent to M2 The confirmation of .
At the sender , If three Reconfirmations are received , Then we can know that the next message segment is lost , Perform fast retransmission at this time , Immediately retransmit the next message segment . For example, receive three M2, be M3 The loss of , Retransmission immediately M3.
under these circumstances , Just missing individual segments , Not network congestion . So perform a quick recovery , Make ssthresh = cwnd / 2 ,cwnd = ssthresh, Note that direct access to congestion avoidance at this time .
Slow start and fast recovery refers to cwnd Set value of , instead of cwnd The rate of growth . Slow start cwnd Set to 1, And recover cwnd Set to ssthresh.

12、 Provide network utilization
1、Nagle Algorithm
Even if the sender still has the data that should be sent , But if there is little data , A processing mechanism for delayed transmission . say concretely , That is, data can only be sent under any of the following conditions . If both conditions are not met , Then wait for a while before sending data .
All the sent data have received the acknowledgement .
When the maximum segment length data can be sent .
2、 Delay acknowledge response
After receiving the data, the receiver can not immediately return the confirmation response , It's a mechanism to delay for a period of time .
In the absence of receiving 2* The data with the maximum segment length will not be acknowledged until .
In other cases , Maximum delay 0.5 second Send a confirmation response .
TCP File transfer in progress , Most of them return a confirmation response every two data segments .
3、 Take a reply
In a TCP A mechanism in which both data and acknowledgment are sent , thus , Network utilization will increase , The load on the computer will also be reduced , But this kind of response must wait until the application finishes processing the data and returns the data as the receipt .
If this article helps you , Don't forget to give me a 3 even , give the thumbs-up , forward , Comment on ,
I'll see you next time ! How to get answers : Liked Commented Closed ~
Learn more knowledge and skills , Follow up with private bloggers (03)

边栏推荐
- Wechat applet development experience
- Affichage du changement de valeur du Buff de gain de l'interface graphique de défaillance
- NovAtel 板卡OEM617D配置步骤记录
- What are the advantages of using SQL in Excel VBA
- 系统设计学习(二)Design a key-value cache to save the results of the most recent web server queries
- How to ensure data consistency between MySQL and redis?
- Itext 7 生成PDF总结
- WSL common commands
- Fairygui loop list
- How to reduce the shutdown time of InnoDB database?
猜你喜欢
Fairygui gain buff value change display

Mixed use of fairygui button dynamics
![[算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题3:前n个数字二进制形式中1的个数](/img/64/0f352232359c7d44f12b20a64c7bb4.png)
[算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题3:前n个数字二进制形式中1的个数

Affichage du changement de valeur du Buff de gain de l'interface graphique de défaillance
几道高频的JVM面试题

FairyGUI增益BUFF數值改變的顯示
10 minutes pour maîtriser complètement la rupture du cache, la pénétration du cache, l'avalanche du cache
Chromatic judgement bipartite graph
The service robots that have been hyped by capital and the Winter Olympics are not just a flash in the pan

121 distributed interview questions and answers
随机推荐
【干货】提升RTK模糊度固定率的建议之周跳探测
Combination of fairygui check box and progress bar
[GNSS] robust estimation (robust estimation) principle and program implementation
十分鐘徹底掌握緩存擊穿、緩存穿透、緩存雪崩
[algorithm] sword finger offer2 golang interview question 10: subarray with sum K
FairyGUI增益BUFF数值改变的显示
Rt-ppp test using rtknavi
记录:动态Web项目servlet访问数据库404错误之解决
Music playback (toggle & playerprefs)
[算法] 剑指offer2 golang 面试题10:和为k的子数组
Employment of cashier [differential constraint]
KF UD decomposition pseudo code implementation advanced [2]
[rtklib 2.4.3 B34] version update introduction I
阿里云微服务(三)Sentinel开源流控熔断降级组件
Sharing ideas of on-chip transplantation based on rtklib source code
错误:排序与角标越界
Answer to "software testing" exercise: Chapter 1
架构师怎样绘制系统架构蓝图?
《软件测试》习题答案:第一章
Record: newinstance() obsolete replacement method